Bottom tuyere configuration optimization in 120 t combination blown converter
-
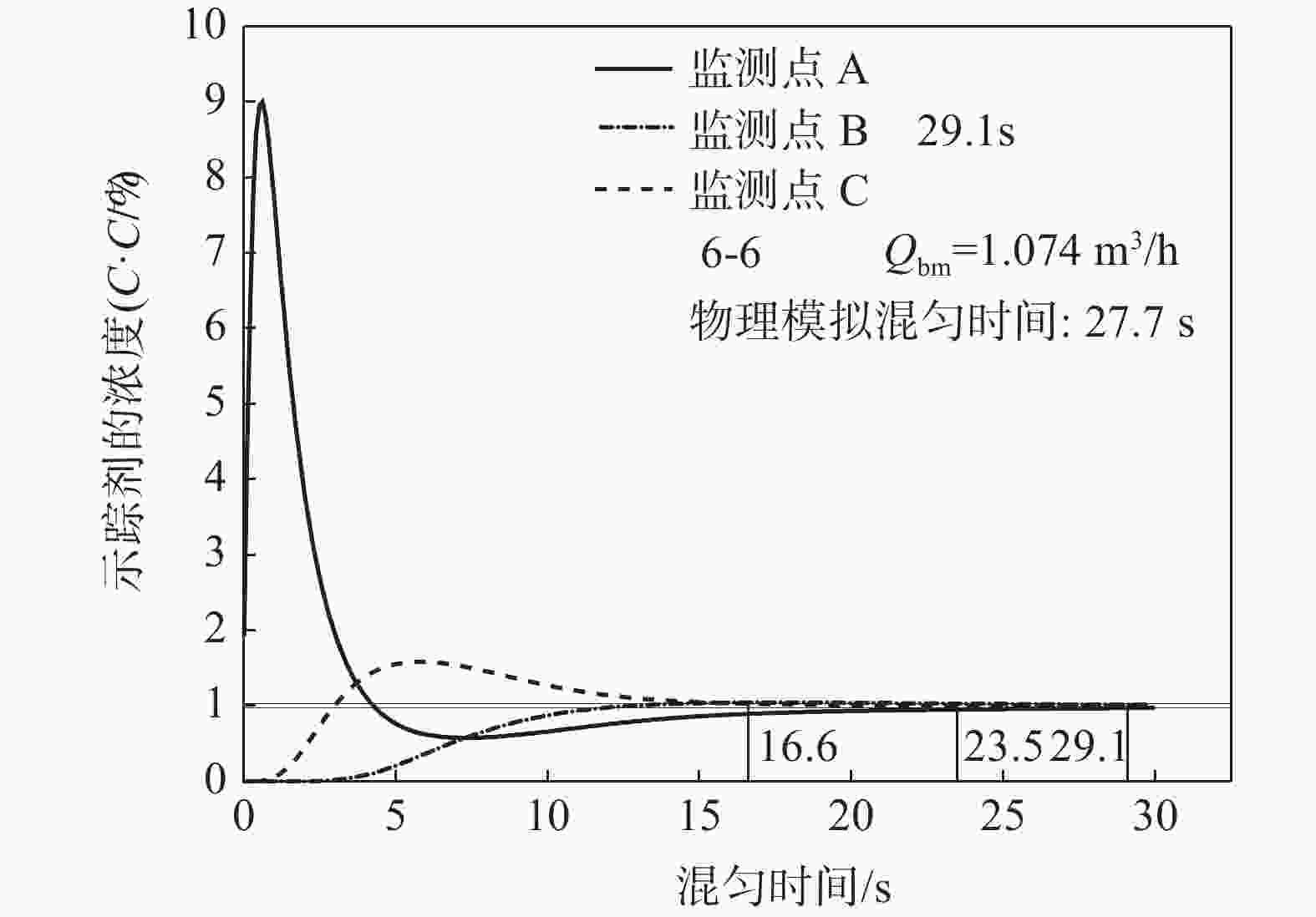
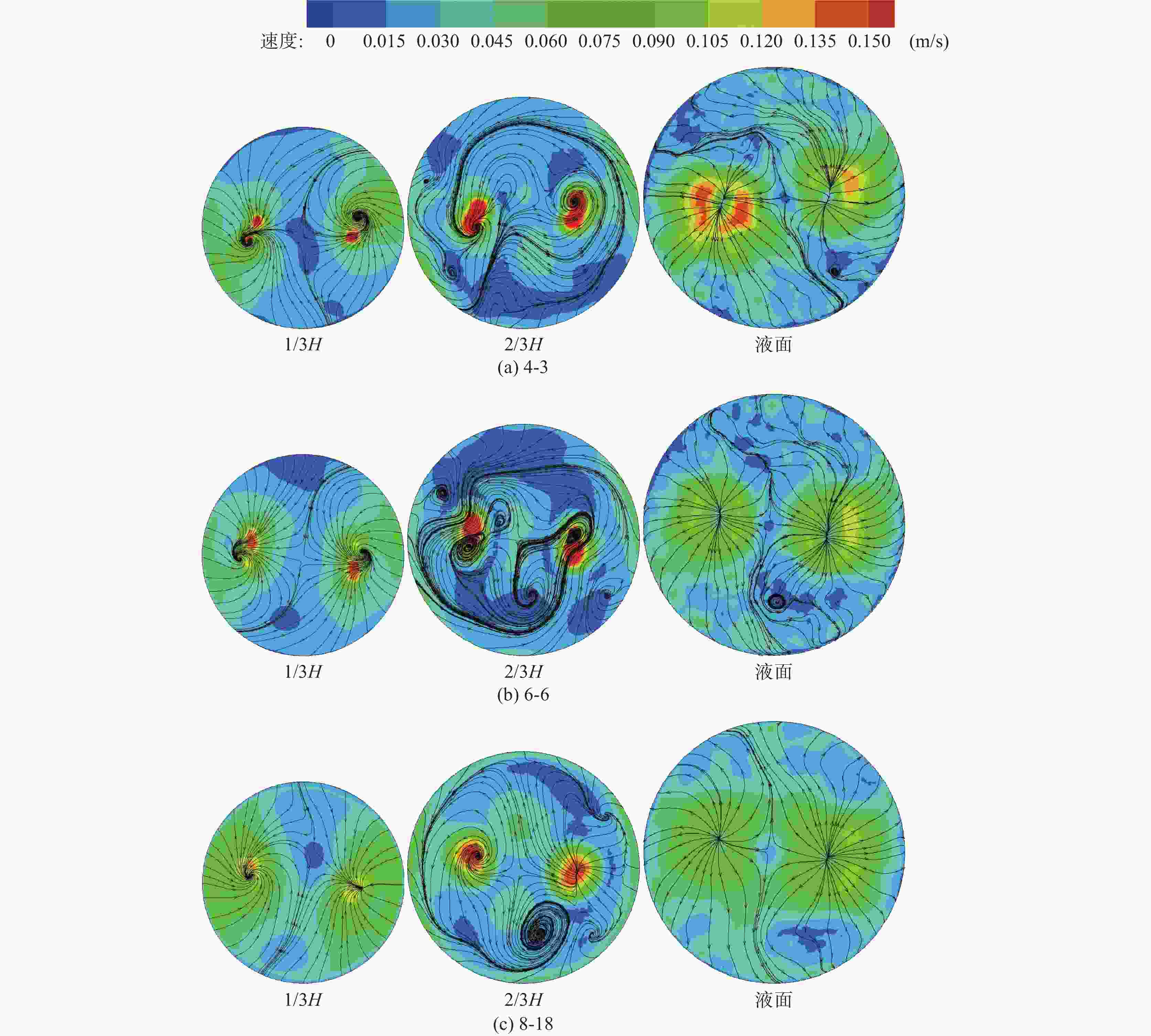
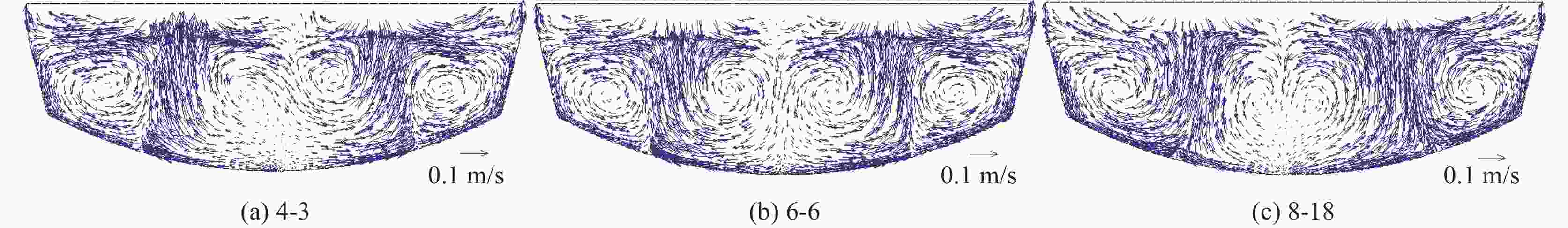
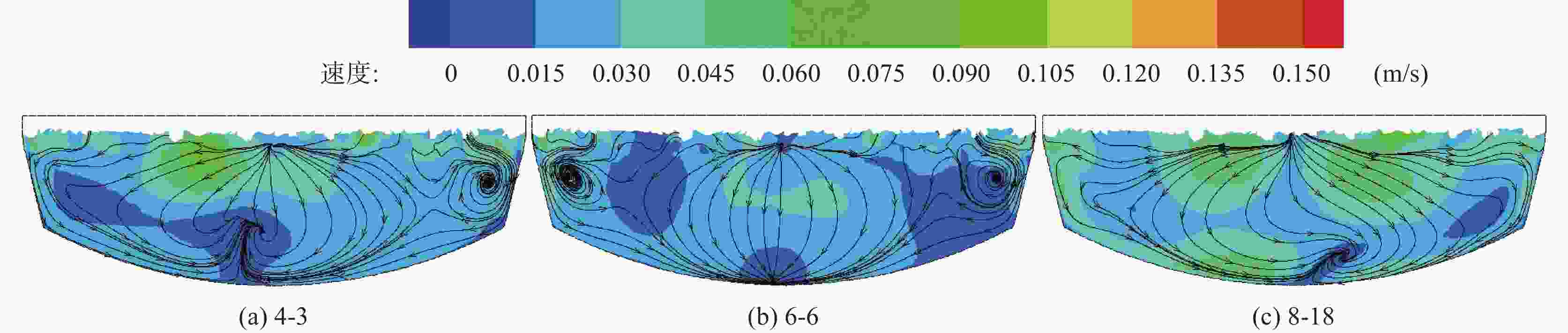
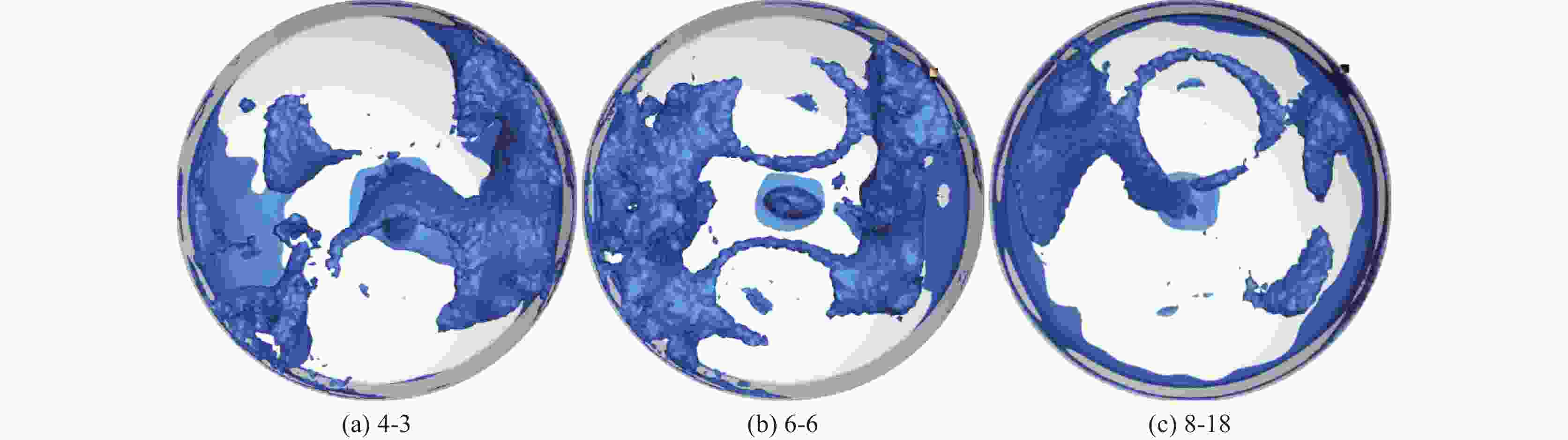
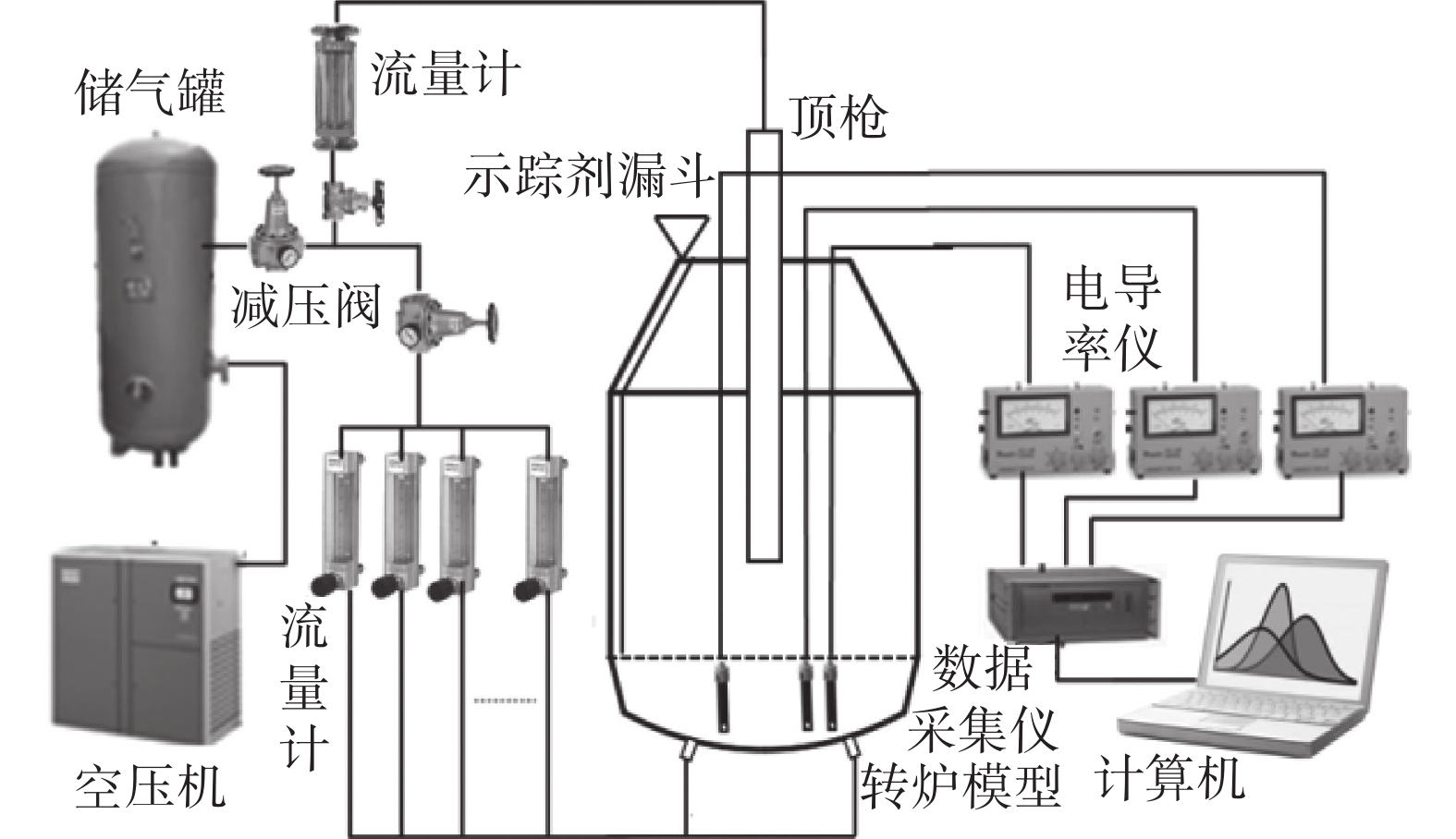
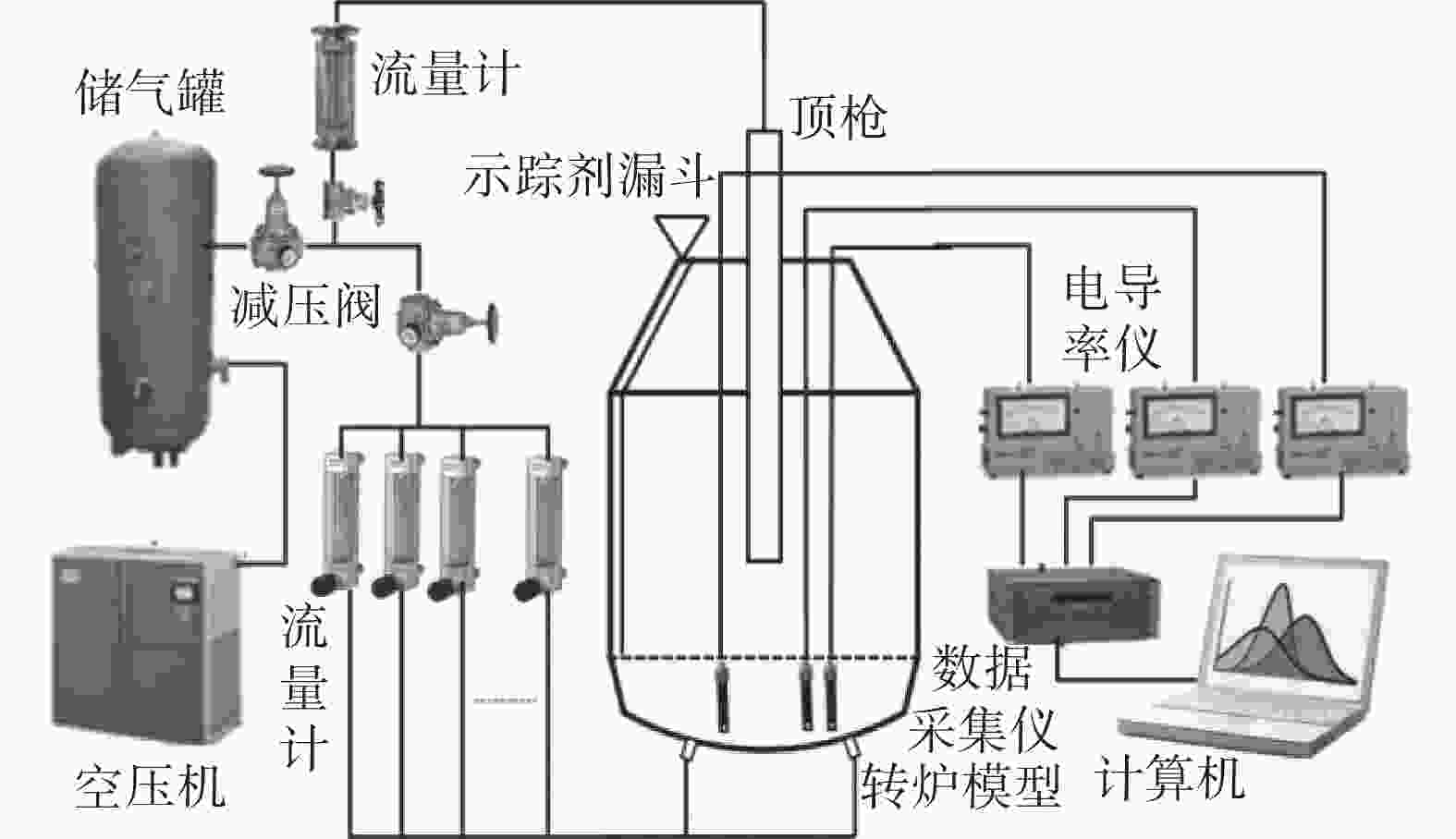
摘要: 以120 t顶底复吹转炉为原型,依据相似原理在实验室利用几何相似比为1:10的模型开展了物理模拟试验,研究了氧枪枪位、底枪支数和布置、供气流量等因素对转炉熔池搅拌混匀的影响;建立了转炉纯底吹气液两相流模型,研究了不同底枪方案对熔池速度场的影响。结果表明:底吹流量为0.534 m3/h和1.074 m3/h的纯底吹时,4~8支底枪的最佳布置方案的混匀时间平均值分别为28.50、28.25 s和27.50 s;复吹时,对于8支底枪的最佳布置方案,顶吹流量为122 m3/h,不同氧枪枪位下熔池混匀时间随底吹流量的增大而降低,最佳枪位在200~230 mm。通过数学模拟研究了物理模拟试验得到的最佳4、6、8支底枪布置方案的速度场,发现底吹时水平截面流场的涡心个数少,垂直截面流场涡心不对称程度大时,可降低“死区”体积,从而提高底吹气体的搅拌能力,使熔池的混匀时间降低。底吹流量为1.074 m3/h时,研究的4、6、8支最佳底枪布置方案的死区体积比分别为15.44%、23.56%和10.30%。Abstract: Physical experiment in a model with a geometric similarity ratio of 1:10 for a 120 t top-bottom combined blown converter based on the similarity theory was conducted in laboratory. The effect of bottom gas flowrate, number and arrangement of bottom tuyeres on the bath mixing was studied. A mathematical model of gas-liquid two-phase flow in the converter at single bottom blowing was established in the simulation. The effect of bottom tuyere configurations on velocity field in molten bath was studied. The results showed that the average mixing time with the optimized configurations of 4, 6 and 8 bottom tuyeres at bottom gas flow rate of 0.534 m3/h and 1.074 m3/h is 28.50, 28.25 s and 27.50 s in the case of single bottom blowing. In the case of combined blowing, the mixing time in the molten bath decreases with increase in bottom gas flow rates with the optimized configuration of 8 bottom tuyeres at top gas flow rate of 122 m3/h under different top lance heights. The velocity fields in the bath with the optimized configurations of 4, 6 and 8 bottom tuyeres were investigated in the mathematical simulation. It is found that less vortex centers of flow fields on horizontal sections and large asymmetry of vortex centers of flow fields on vertical sections can decrease “dead zone” volumes, which can improve the stirring ability of bottom gas and reduce mixing time in molten bath. The “dead zone” volumes in molten bath from the optimized configurations of 4, 6 and 8 bottom tuyeres studied here are 15.44%, 23.56% and 10.30%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- converter /
- top and bottom blow /
- bath /
- stirring and mixing /
- fluid flow /
- physical modeling /
- mathematical simulation
-
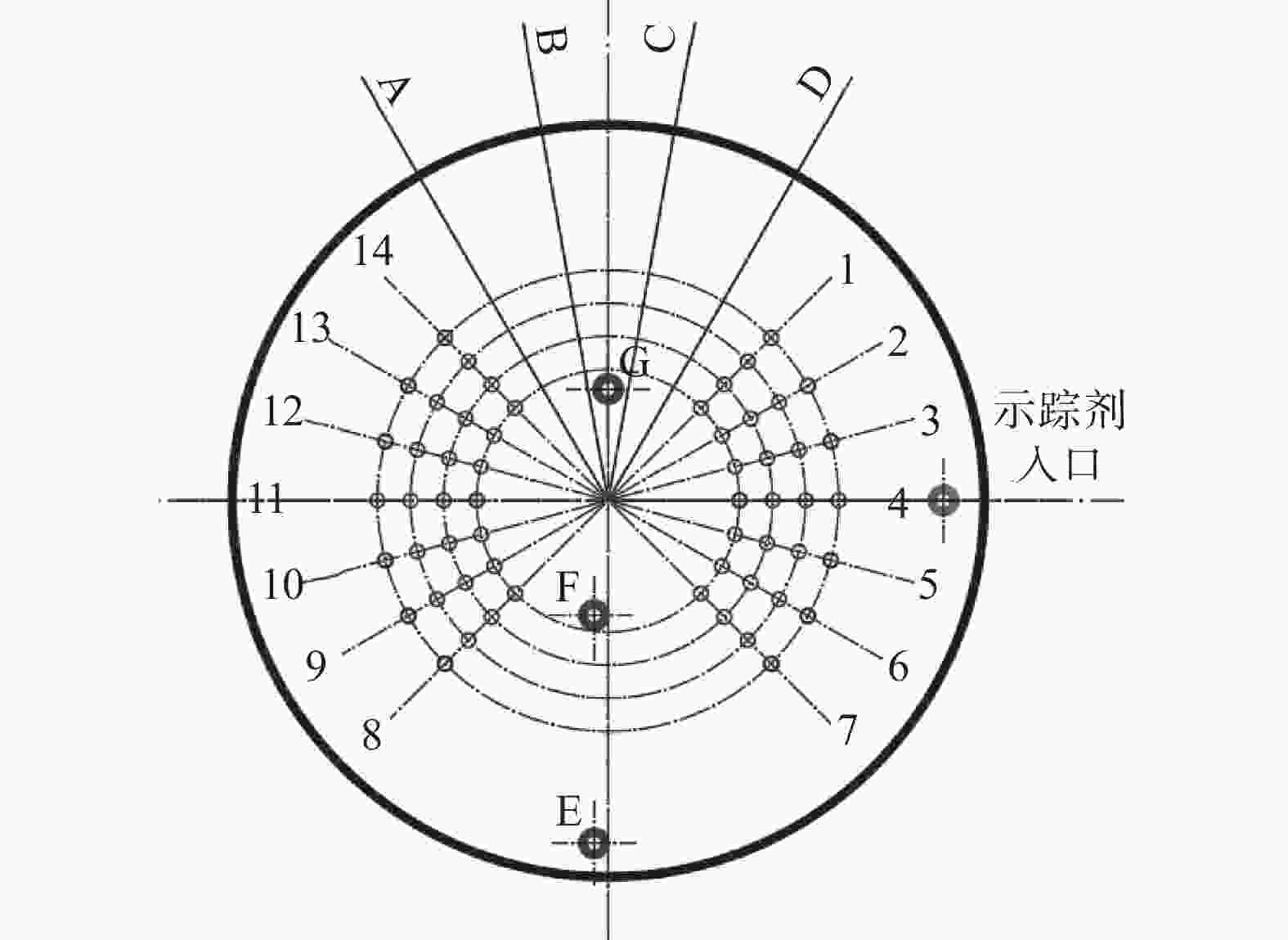
表 1 原型转炉与模型转炉的主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of prototype converter and model converter
熔池直径/mm 熔池深度/mm 氧枪喷头孔数/孔 氧枪喷头喷孔夹角/(°) 顶吹气体流量/(m3·h−1) 底吹气体流量/(m3·h−1) 原型 5380 1410 5 15 37200 465/930/1395/1860 模型 538 141 5 15 122 0.216/0.534/1.074/1.608/2.142 表 2 4支底枪布置方案
Table 2. Arrangements of 4 bottom tuyeres
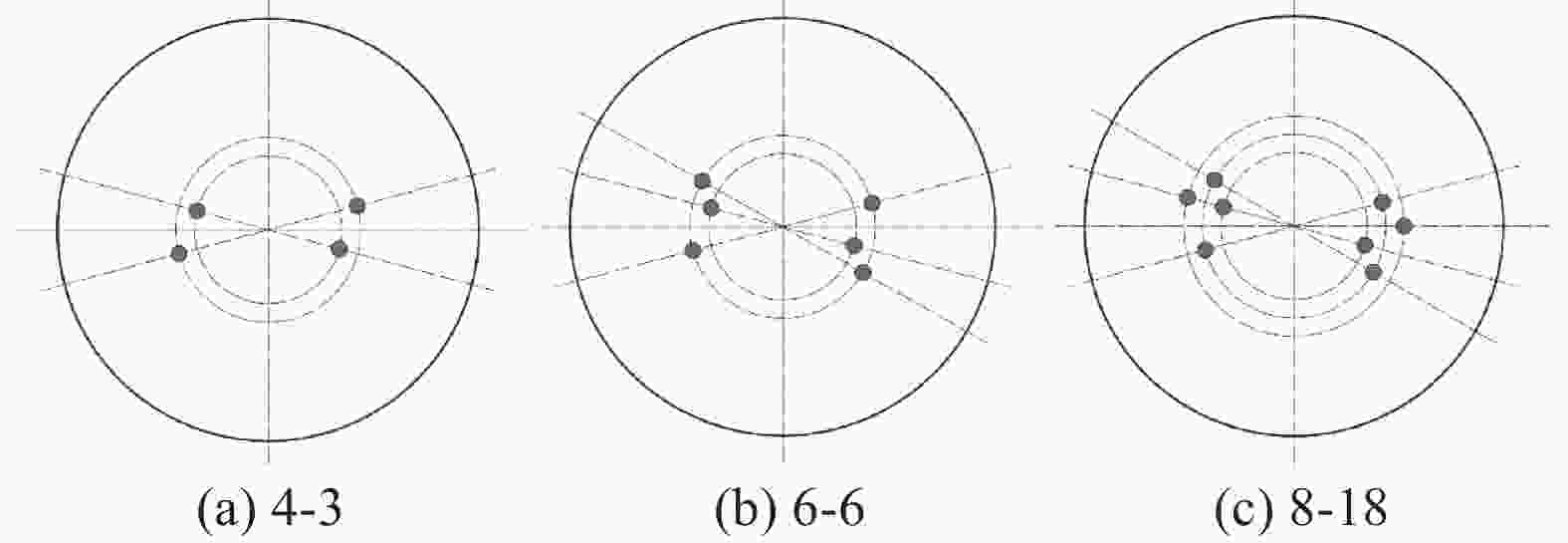
布置方案 底枪编号 布置方案 底枪编号 4-1 B(2-5-10-13) 4-9 B(5-12)-C(3-10) 4-2 B(3-6-9-12) 4-10 C(5-12)-D(3-10) 4-3 A(5-12)-B(3-10) 4-11 A(6-13)-B(4-11) 4-4 A(5-13)-B(2-10) 4-12 B(6-13)-C(4-11) 4-5 A(6-14)-B(4-10) 4-13 A(4-11)-B(2-9) 4-6 A(5-13)-B(3-9) 4-14 B(4-11)-C(2-9) 4-7 B(3-6-10-13) 4-15 B(3-5-10-12) 4-8 B(2-6-10-12) 表 3 6支底枪布置方案
Table 3. Arrangements of 6 bottom tuyeres
布置方案 底枪编号 布置方案 底枪编号 6-1 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-C(4-11) 6-9 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-C(1-8) 6-2 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-D(4-11) 6-10 A(5-12)-B(2-9)-C(4-11) 6-3 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-C(6-13) 6-11 A(5-12)-B(3-9)-C(4-11) 6-4 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-D(6-13) 6-12 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-11) 6-5 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-C(7-14) 6-13 A(5-13)-B(3-10)-C(4-11) 6-6 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13) 6-14 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(4-11) 6-7 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-C(2-9) 6-15 A(5-12)-B(2-6-9-13) 6-8 A(5-12)-B(3-10)-D(2-9) 6-16 A(6-13)-B(3-10)-C(4-11) 表 4 8支底枪布置方案
Table 4. Arrangements of 8 bottom tuyeres
布置
方案底枪编号 布置
方案底枪编号 8-1 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(4-6-11-13) 8-15 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-6-8-11) 8-2 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(4-7-11-13) 8-16 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(1-4-8-11) 8-3 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(4-6-11-14) 8-17 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(4-11) 8-4 A(6-12)-B(3-10-14)-C(4-6-11) 8-18 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(4-12) 8-5 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(2-4-9-11) 8-19 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(5-11) 8-6 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(1-4-9-11) 8-20 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(5-12) 8-7 A(6-12)-B(3-10)-C(2-4-8-11) 8-21 A(5-12)-B(1-3-6-8-10-13) 8-8 A(6-12)-B(3-8-10)-C(2-4-11) 8-22 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(2-9) 8-9 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-6-11-13) 8-23 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(1-9) 8-10 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-7-11-13) 8-24 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(2-8) 8-11 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-6-11-14) 8-25 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(1-8) 8-12 A(5-12)-B(2-10-13)-C(4-6-11) 8-26 A(1-5-8-12)-B(3-6-10-13) 8-13 A(5-12)-B(2-6-10)-C(4-11-13) 8-27 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-D(4-11) 8-14 A(5-12)-B(2-10)-C(4-6-9-11) 8-28 A(5-12)-B(3-6-10-13)-C(7-14) -
[1] Yan Guangting, Tang Ping, Zhang Shuyun. Influence of bottom blowing oxygen and bottom tuyeres configuration on mixing characteristics of converter bath[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 1990,(1):45−61. (颜广庭, 唐萍, 张淑筠. 底吹氧量及底枪配置对复吹转炉熔池混合特性的影响[J]. 四川冶金, 1990,(1):45−61. [2] Yang Wenyuan, Ding Yongliang, Wang Minglin, et al. Water modeling of interaction between jets from multi-nozzle lance and bath in large converter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2004,39(3):16−19. (杨文远, 丁永良, 王明林, 等. 大型转炉多孔喷头射流与熔池作用的水模研究[J]. 钢铁, 2004,39(3):16−19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2004.03.004 [3] Ni Hongwei, Yu Shuren, Qiu Linghui, et al. Cold model study on 90 t top-bottom combined blown converter[J]. Steelmaking, 2002,18(3):39−43. (倪红卫, 喻淑仁, 邱玲慧, 等. 90 t复吹转炉水模实验研究[J]. 炼钢, 2002,18(3):39−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2002.03.010 [4] Abdul Quiyoom, Ravi Golani, Vikas Singh, et al. Effect of differential flow schemes on gas-liquid flow and liquid phase mixing in a basic oxygen furnace[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017,170(10):777−789. [5] Ajmani, Chatterjee. Cold model studies of mixing and mass transfer in steelmaking vessels[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2005,32(6):515−527. [6] Stišovic T, Koch K. Bottom blowing investigations on a cold model reactor to optimise mixing behaviour in metallurgical processes[J]. Steel Research, 2002,73(9):373−377. doi: 10.1002/srin.200200002 [7] Lai Z Y, Xie Z, Zhong L C. Influence of bottom tuyere configuration on bath stirring in a top and bottom combined blown converter[J]. ISIJ International, 2008,48(6):793−798. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.48.793 [8] Zhong Lingcai, Zhou Xiaobin, Zhu Yingxiong, et al. Bath mixing behavior in a 100 t top-bottom-side blown converter[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2011,10(4):241−243. (钟良才, 周小宾, 朱英雄, 等. 100 t顶底侧吹转炉熔池混匀行为[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2011,10(4):241−243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.04.002 [9] 杨晨. 120 t顶底复吹转炉水力学模型优化研究[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学, 2016.Yang Chen. Optimization of hydraulic model for 120 t on top bottom conbined blown converter [D]. Anshang: University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2016. [10] 陈敏. 210 t顶底复吹转炉水模型实验研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2011.Chen Min. Cold model study 210 t top-bottom combined blown converter [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2011. -




 下载:
下载: