Study on the microstructure evolution during hot deformation of GH5188 superalloy
-
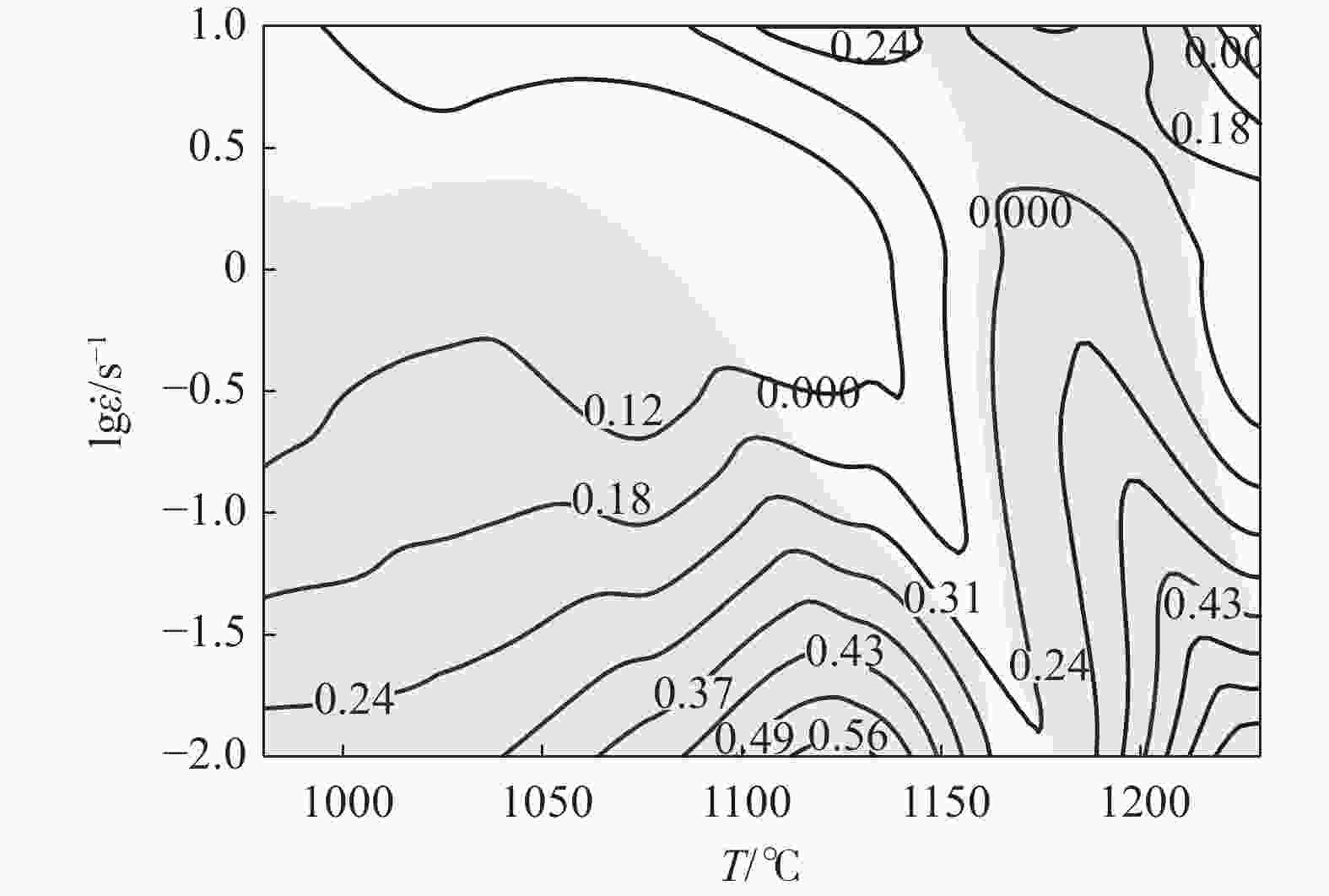
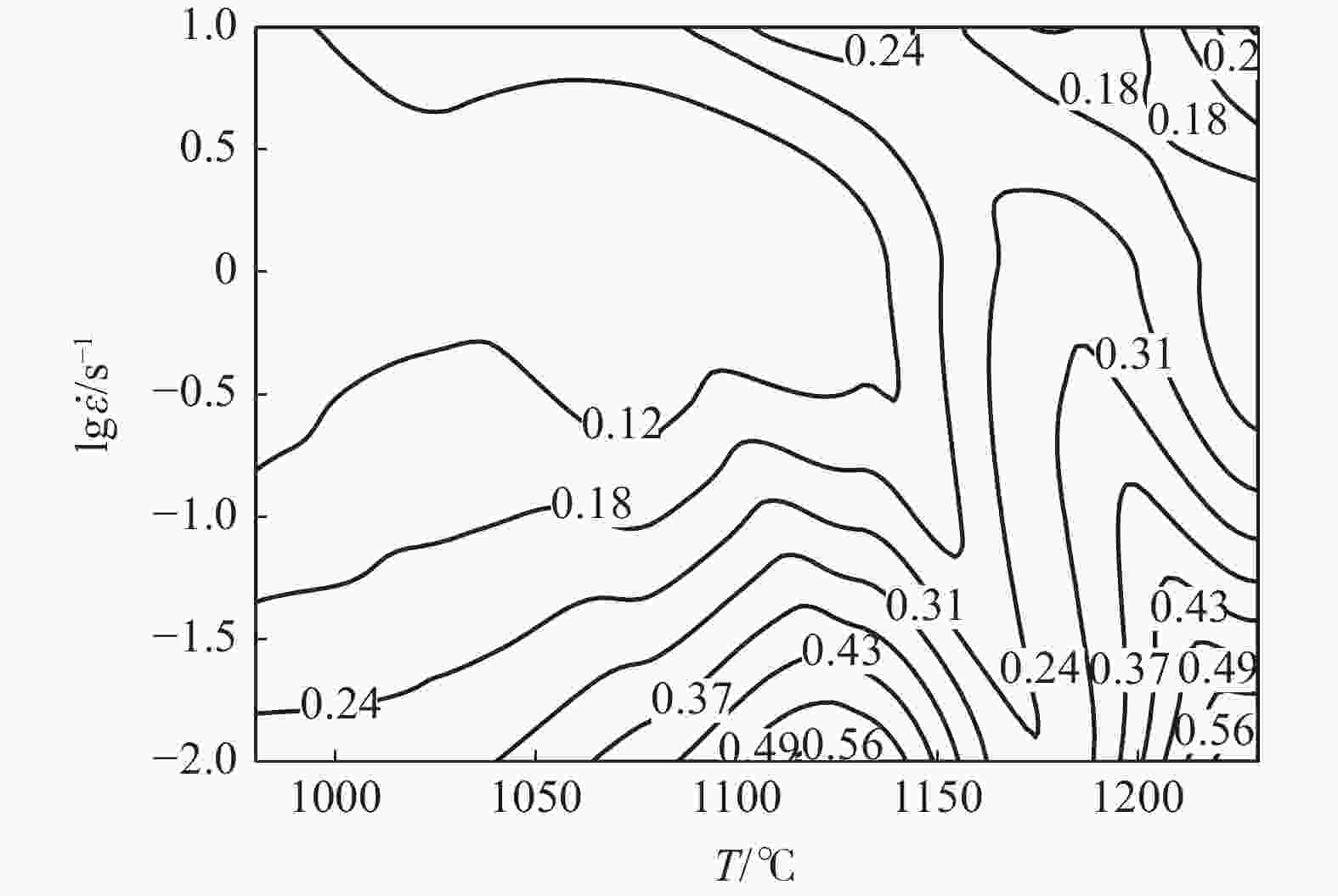
摘要: 采用Gleeble-3800热模拟试验机研究了GH5188高温合金多道次变形和保温过程中的组织传递规律,建立了变形速率0.01~10 s−1,变形量50%,变形温度980~1230 ℃下的热加工图,探讨了单道次变形后保温时间对双道次变形组织、双道次变形后保温时间和保温温度对组织遗传性以及双道次降温变形和保温时间对显微组织的影响。结果表明:热加工图中高功率耗散率区的边界条件分别为1050~1175 ℃、0.01~0.1 s−1和1200~1225 ℃、0.01~1 s−1,低功率耗散率区的边界条件分别为975~1150 ℃、0.01~10 s−1和1150~1225 ℃、0.1~10 s−1;第一道次变形后保温时间过长不利于第二道次动态再结晶的发生;双道次变形后保温时,发生了明显的再结晶现象,随着保温时间的增加,晶粒未发生明显的长大;随着第二道次变形温度的降低,试样再结晶比例降低,保温温度越低,越不容易发生静态再结晶。
-
关键词:
- GH5188高温合金 /
- 多道次变形 /
- 热加工图 /
- 再结晶 /
- 保温过程
Abstract: In this paper, the transformation law of microstructure evolution during multi-pass deformation and heat preservation was investigated by a Gleeble-3800 thermal simulation testing machine. A hot working diagram was established at deformation rate 0.01−10 s−1, deformation amount 50%, and deformation temperature 980−1230 ℃. The effects of holding time after single-pass deformation on the microstructure of double-pass deformation, holding time after double-pass deformation and holding temperature on the microstructure evolution, and deformation and holding time after double-pass cooling on the microstructure were discussed. The results show that the boundary conditions of the high power dissipation zone in the hot working diagram are 1050−1175 ℃, 0.01−0.1 s−1, and 1200−1225 ℃, 0.01−1 s−1, respectively. The boundary conditions of the low power dissipation zone are 975−1150 ℃, 0.01−10 s−1, and 1150−1225 ℃, 0.1−10 s−1, respectively. Too long holding time after the first deformation is not conducive to the second dynamic recrystallization. The recrystallization phenomenon occurred after the double-pass deformation, and the grain size did not grow obviously with the increasing holding time. In addition, with the second deformation temperature decrease, the proportion of recrystallization in the specimen decreases, and the lower the holding temperature, the less likely static recrystallization occurs. -
表 1 GH5188棒材化学成分
Table 1. Chemical conposition of GH5188 superalloy bar
% C Cr Ni Co W Fe B La 0.078 21.023 21.447 余量 13~16 0.497 0.0029 <0.4 Mn Si P S Al Bi Pb Ti 0.837 0.430 0.0070 <0.001 0.054 <0.001 <0.005 0.012 表 2 GH5188合金在不同变形条件下应变速率敏感指数m
Table 2. The strain rate sensitivity index m of GH5188 alloy under different deformation conditions
$ \dot{\mathrm{\epsilon }} $/s-1 m 980 ℃ 1030 ℃ 1080 ℃ 1130 ℃ 1180 ℃ 1230 ℃ 0.01 0.15777 0.17063 0.26144 0.398 0.14436 0.51328 1 0.03578 0.05818 0.03382 0.04866 0.16238 0.06807 5 0.04356 0.06479 0.06049 0.11201 0.09937 0.16033 10 0.05495 0.07496 0.08893 0.16888 0.06117 0.23961 表 3 GH5188合金在不同变形条件下功率耗散效率因子η值
Table 3. The power dissipation efficiency factor η value of GH5188 alloy under different deformation conditions
$ \dot{\mathrm{\epsilon }} $/s-1 η 980 ℃ 1030 ℃ 1080 ℃ 1130 ℃ 1180 ℃ 1230 ℃ 0.01 0.27254 0.29152 0.41451 0.56938 0.2523 0.67837 1 0.06909 0.10996 0.06543 0.0928 0.27939 0.12746 5 0.08348 0.1217 0.11408 0.20146 0.18078 0.27635 10 0.10418 0.13947 0.16333 0.28896 0.11529 0.38659 表 4 GH5188合金在不同变形条件下流变失稳判据ζ值
Table 4. Rheological instability criterion ζ value of GH5188 alloy under different deformation conditions
$ \dot{\mathrm{\epsilon }} $/s−1 ζ 980 ℃ 1030 ℃ 1080 ℃ 1130 ℃ 1180 ℃ 1230 ℃ 0.01 −0.05577 −0.04705 −0.05663 −0.05045 −0.00074 −0.04567 1 −0.03844 −0.02314 −0.00647 0.08102 −0.06442 0.10418 5 0.03598 0.01975 0.09698 0.12356 −0.14983 0.12158 10 0.05094 0.0318 0.09292 0.10252 −0.28007 0.09796 -
[1] Gao Yawei, Dong Jianxin, Yao Zhihao, et al. Microstructure characteristics and microstructure evolution of GH5188 superalloy during hot and cold working[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017,46(10):7. (高亚伟, 董建新, 姚志浩, 等. GH5188高温合金组织特征及冷热加工过程组织演变[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017,46(10):7. [2] Li Juntao, Yan Ping, Wu Jiantao, et al. New high-strength hot-corrosion-resistant directional solidification superalloy DZ409[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016,28(2):7. (李俊涛, 燕平, 吴剑涛, 等. 新型高强抗热腐蚀定向凝固高温合金DZ409[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2016,28(2):7. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20150242 [3] Wang Haitao, Zhang Guoling, Yu Huashun, et al. Effects of chromium, aluminum and silicon on the oxidation resistance of iron-based superalloys[J]. Materials Engineering, 2008,(12):5. (王海涛, 张国玲, 于化顺, 等. 铬、铝、硅对铁基高温合金抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2008,(12):5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2008.12.018 [4] Jia Chonglin. Development and demand application of superalloys[J]. Metal Materials Research, 2011,37(4):6. (贾崇林. 高温合金的发展与需求应用[J]. 金属材料研究, 2011,37(4):6. [5] Qin Qin, Mao Zijian, Liu Zhaofan. Application status and development of superalloys in aeroengine field[J]. Tool Technology, 2017,51(9):4. (秦琴, 毛子荐, 刘昭凡. 高温合金在航空发动机领域的应用现状与发展[J]. 工具技术, 2017,51(9):4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2017.09.001 [6] Zhang Xin, Li Hongwei, Mei Zhan, et al. Role of the inter-pass cooling rate in recrystallization behaviors of Ni-based superalloy during interrupted hot compression[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019,32(5):17. [7] Semiatin S L , Weaver D S , Goetz R L , et al. Deformation and recrystallization during thermomechanical processing of a nickel-base superalloy ingot material[C]// Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publications, 2007: 129-140. [8] Zhang Yun, Cao Furong, Lin Kaizhen, et al. Dynamic recrystallization behavior of GH4742 superalloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013,23(11):9. (张云, 曹富荣, 林开珍, 等. GH4742高温合金的动态再结晶行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013,23(11):9. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.11.010 [9] Ouyang Lingxiao, Luo Rui, Gui Yunwei, et al. Hot deformation characteristics and dynamic recrystallization mechanisms of a Co–Ni-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020,788:139638. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139638 [10] Wu Hong, Liu Minxue, Wang Yan, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation of dynamic recrystallization for a FGH96 superalloy during isothermal compression[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020,9(3):23. [11] Guan Bo, Wang Yitao, Li Jianbo, et al. Comprehensive study of strain hardening behavior of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021,882:160623. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160623 [12] Kong Yonghua, Chang Pengpeng, Li Qian, et al. Hot deformation characteristics and processing map of nickel-based C276 superalloy[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,622:738−744. [13] Zhang Jianbo, Wu Chongji, Peng Yuanyi, et al. Hot compression deformation behavior and processing maps of ATI 718Plus superalloy - Science direct[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020,835:1263. [14] Li Sha, Zeng Li, Miao Huajun, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of Ni-based superalloy GH4700[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013,34(9):51−56. [15] Pan Qinglin, Li Bo, Wang Ying, et al. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of Ni-base superalloy Rene'41 using processing map[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A Structural Materials Properties Microstructure & Processing, 2013,585(15):371−378. [16] Wang Ying, Pan Qingling, Zhang Yuwei, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014,45(11):3752−3761. [17] Cai Dayong, Xiong Liangyin, Liu Wenchang, et al. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of a Ni-base superalloy using processing map[J]. Materials & Design, 2009,30(3):921−925. [18] Zhang Hongbin, Zhang Kaifeng, Zhen Lu, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of a γ′-hardened nickel-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014,604(16):1−8. [19] Zhao Lihua, Zhang Yanshu, Wu Guifang. Static recrystallization kinetics of GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Materials Heat Treatment, 2015,(5):6. (赵立华, 张艳姝, 吴桂芳. GH4169高温合金的静态再结晶动力学[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,(5):6. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2015.05.039 [20] Wu Zhigang, Li Defu, Guo Shengli, et al. Study on dynamic recrystallization model of GH625 nickel-based superalloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012,41(2):6. (吾志岗, 李德富, 郭胜利, 等. GH625镍基高温合金动态再结晶模型研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012,41(2):6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-185X.2012.02.011 -




 下载:
下载: