Effect of heat treatment on mechanical and corrosion resistance properties of Fe-25Mn-18Cr-3.5Ni-2Al stainless steel
-
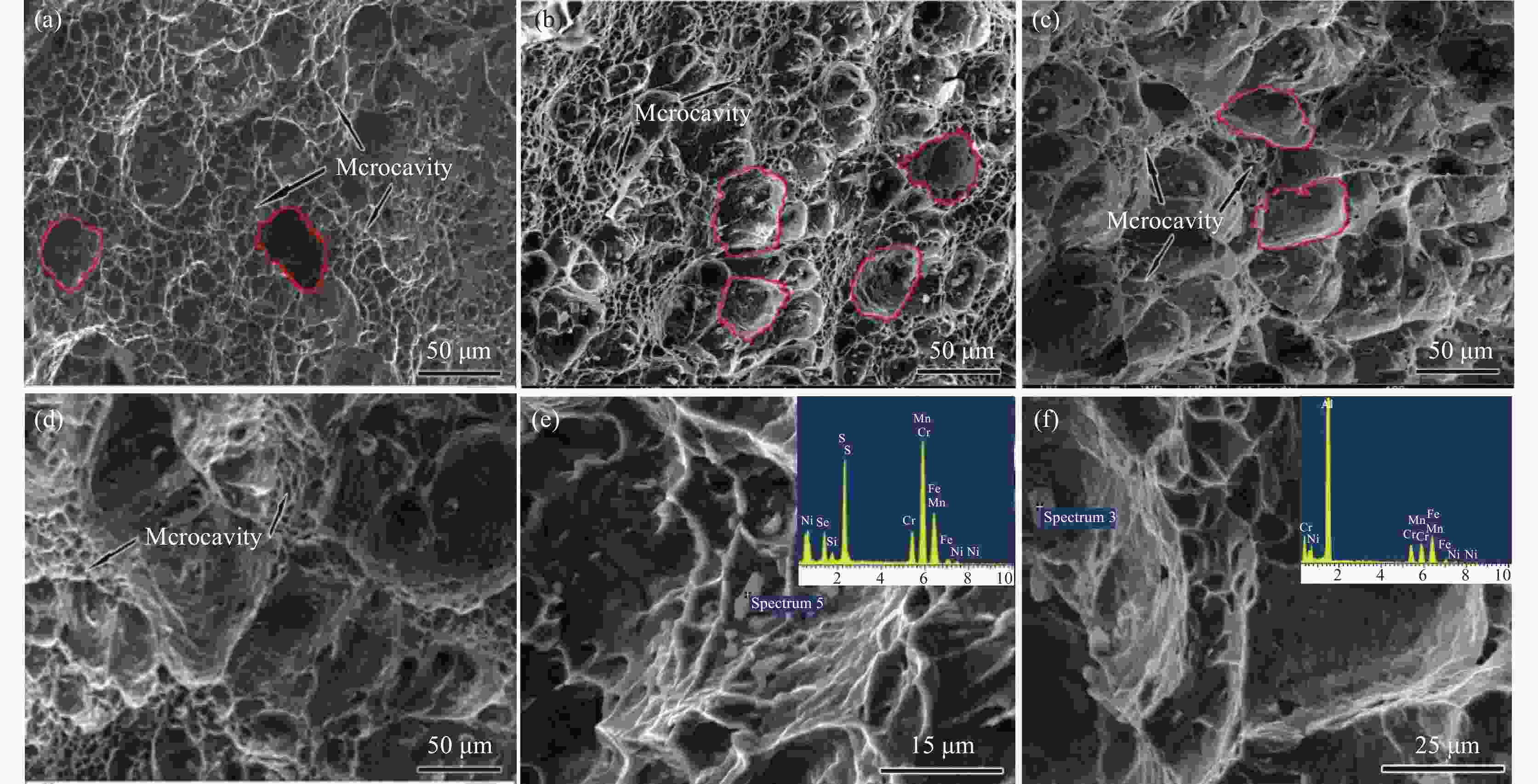
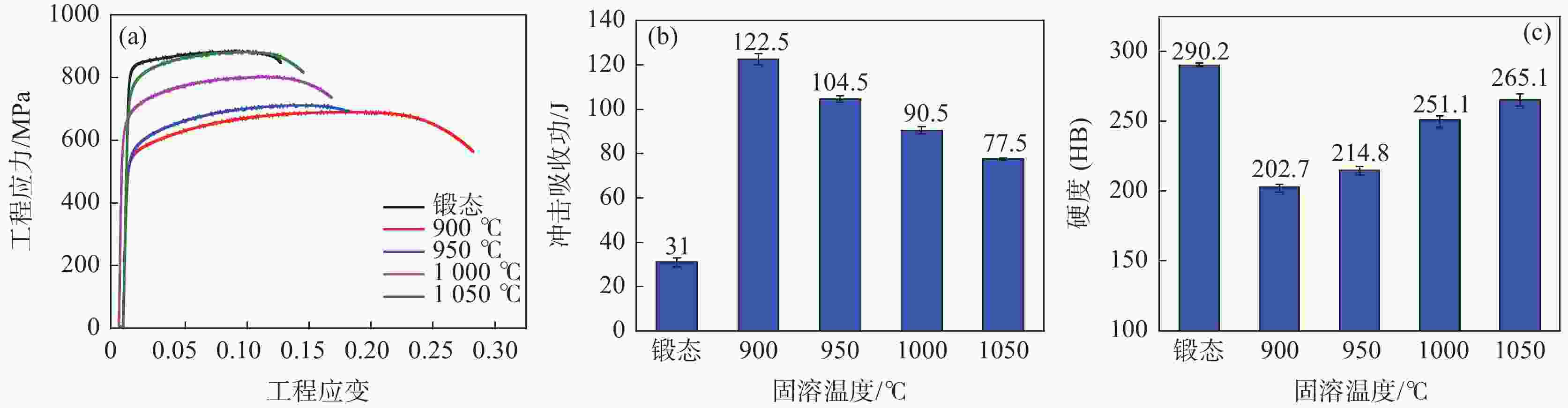
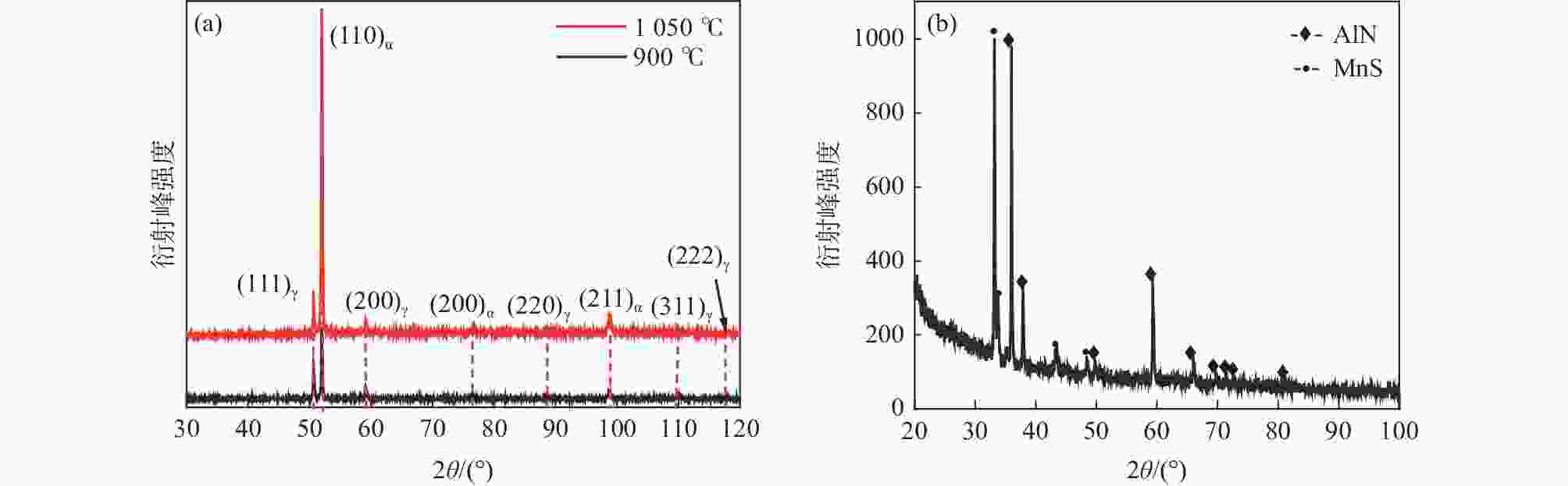
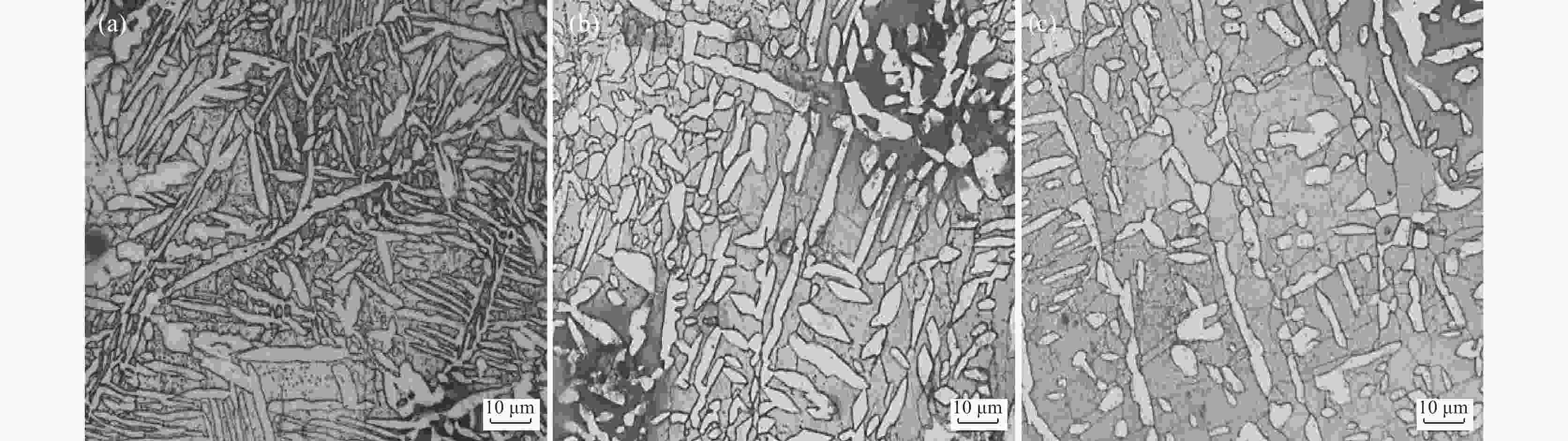
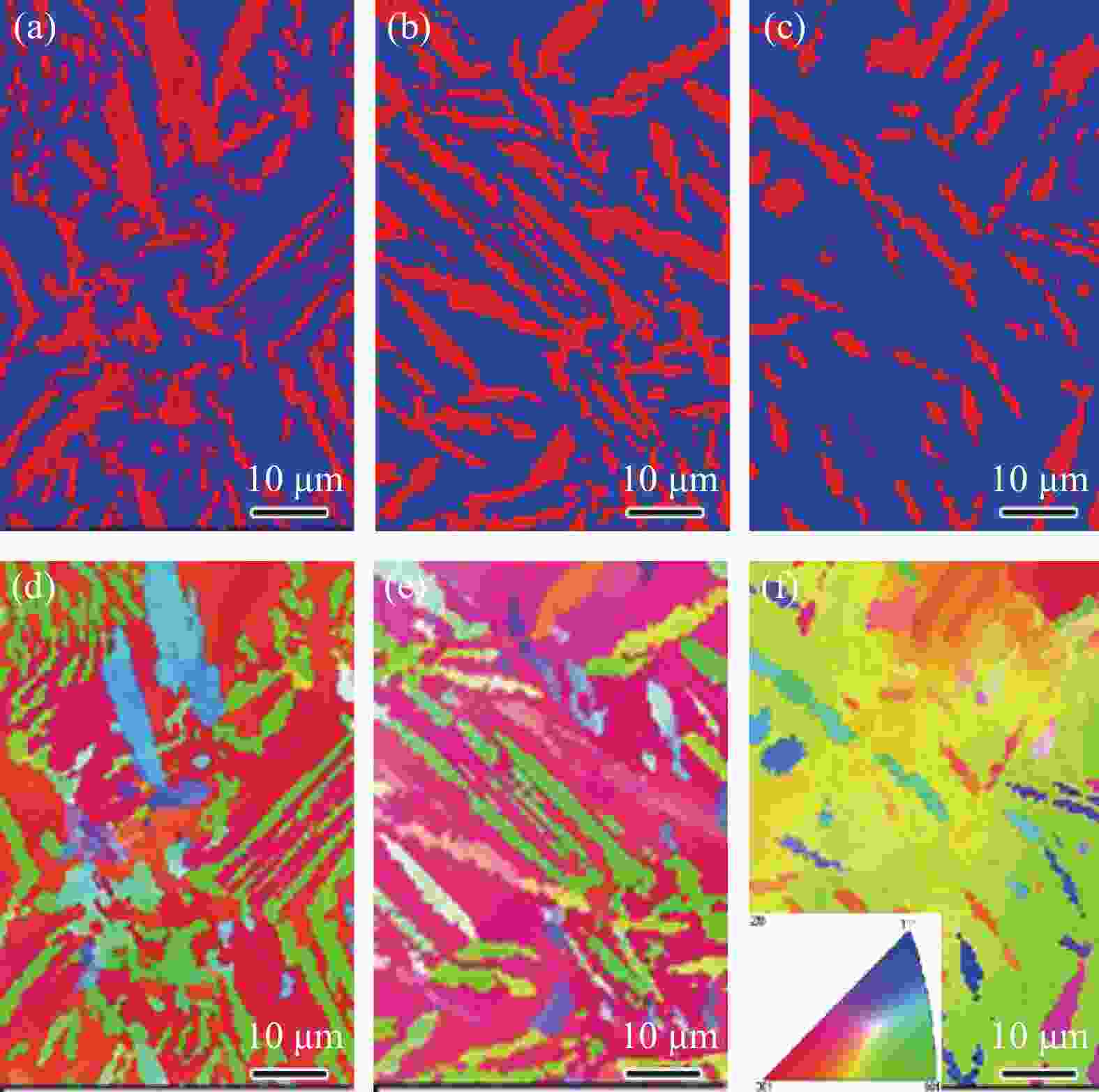
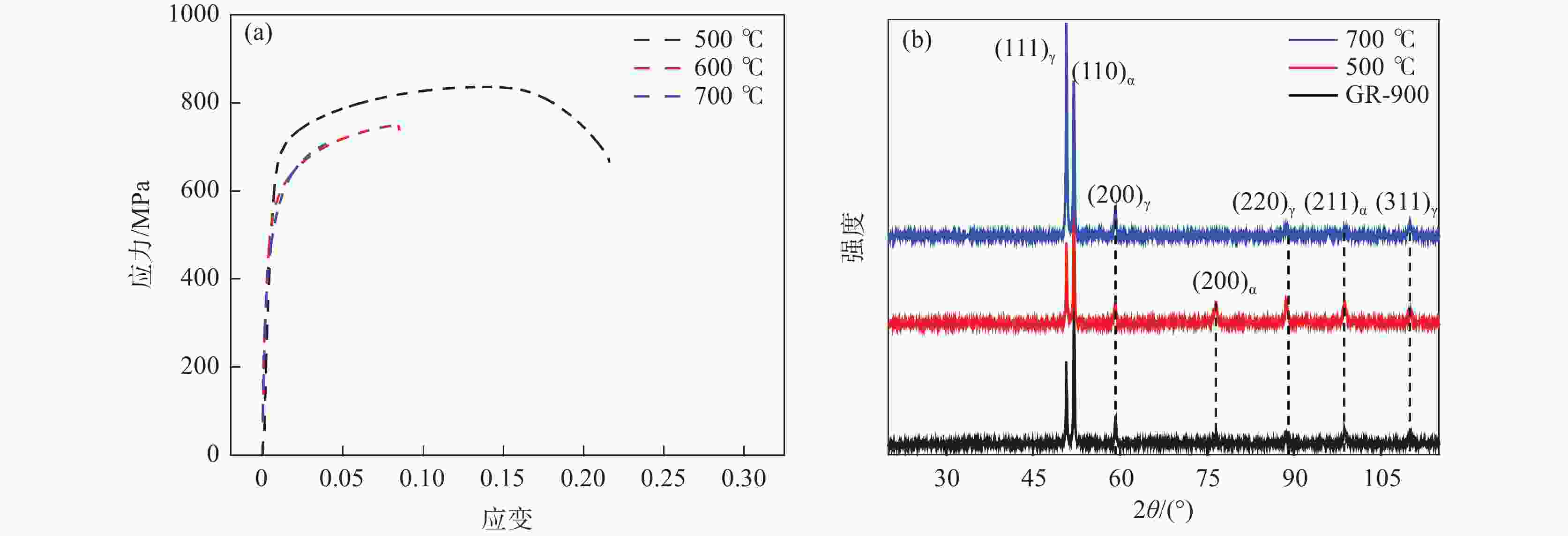
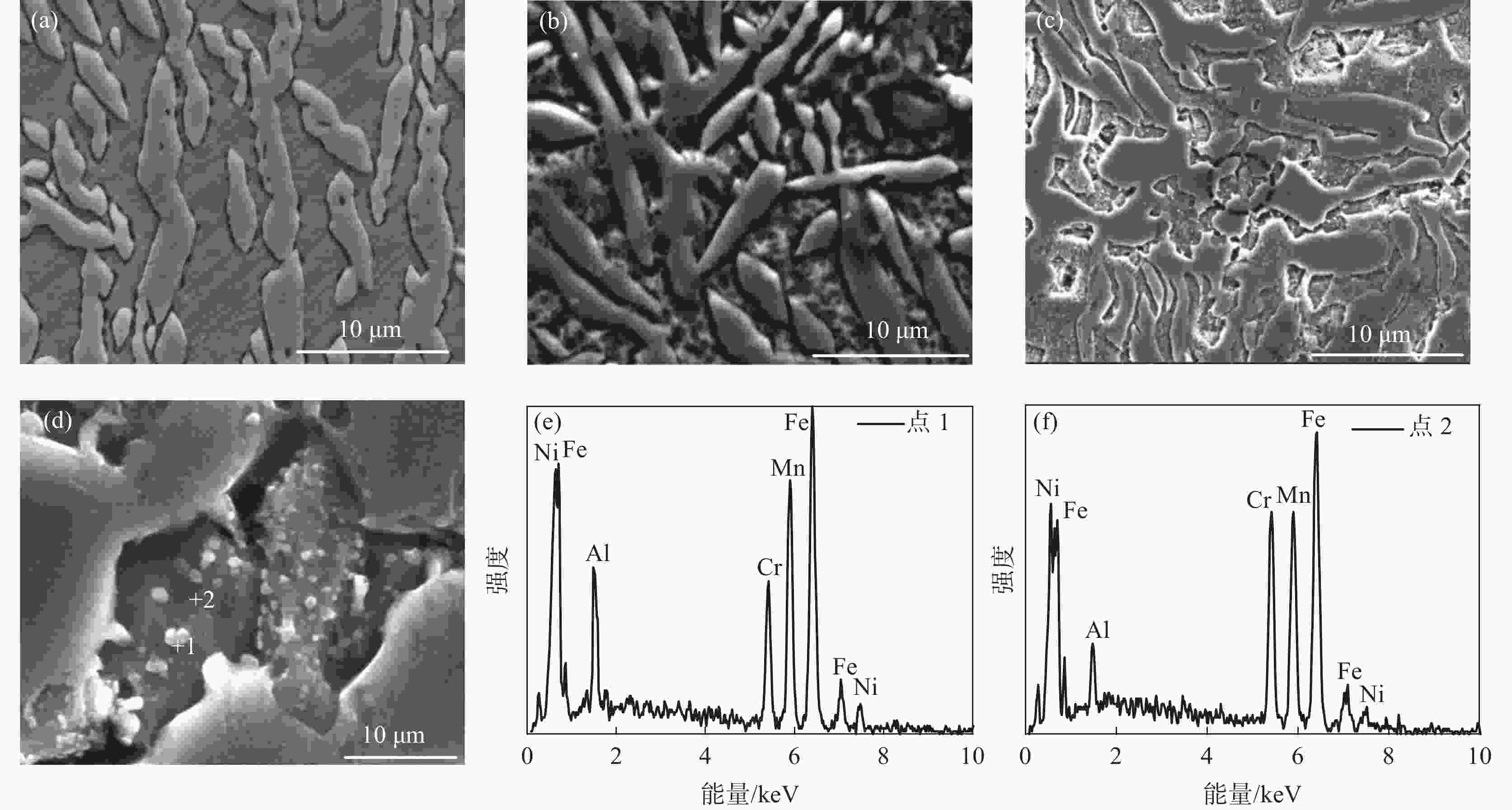
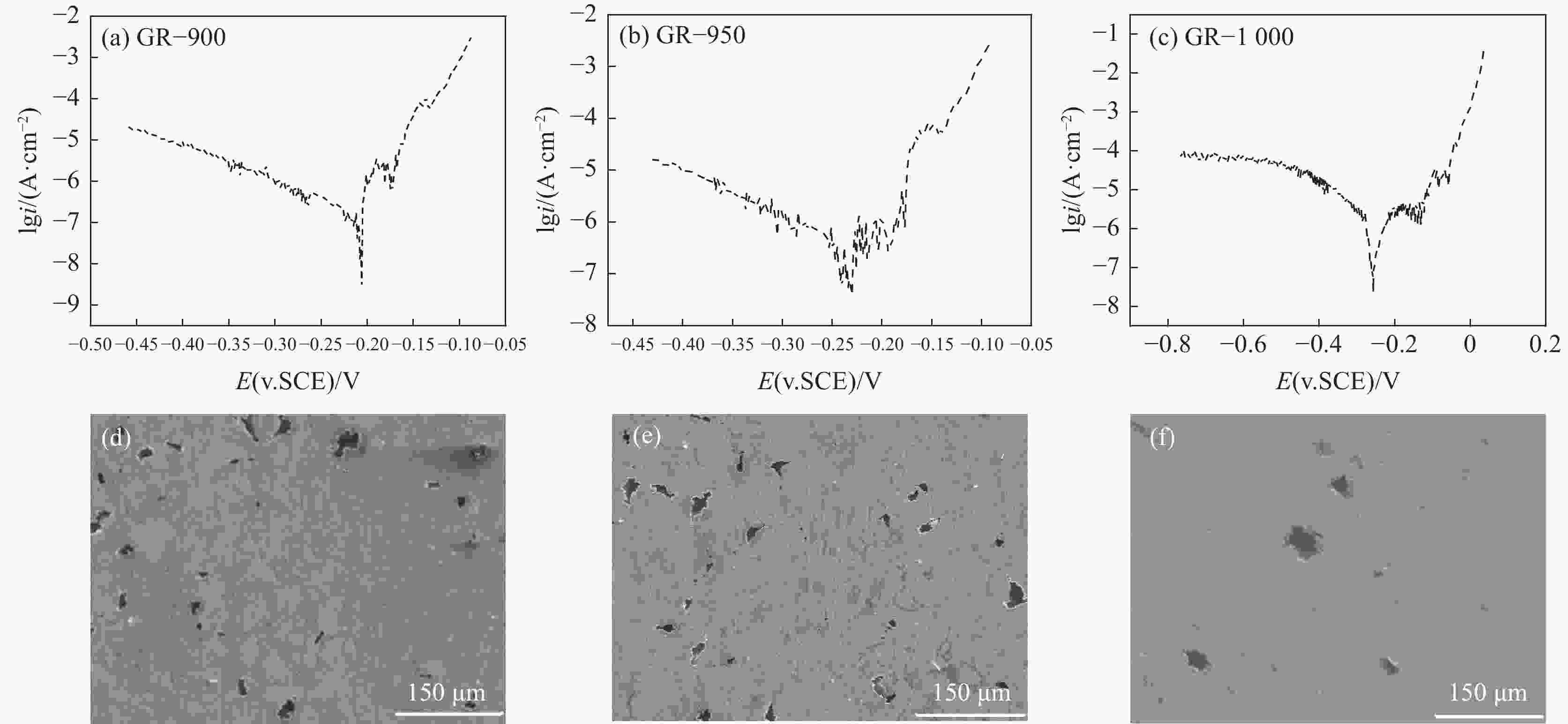
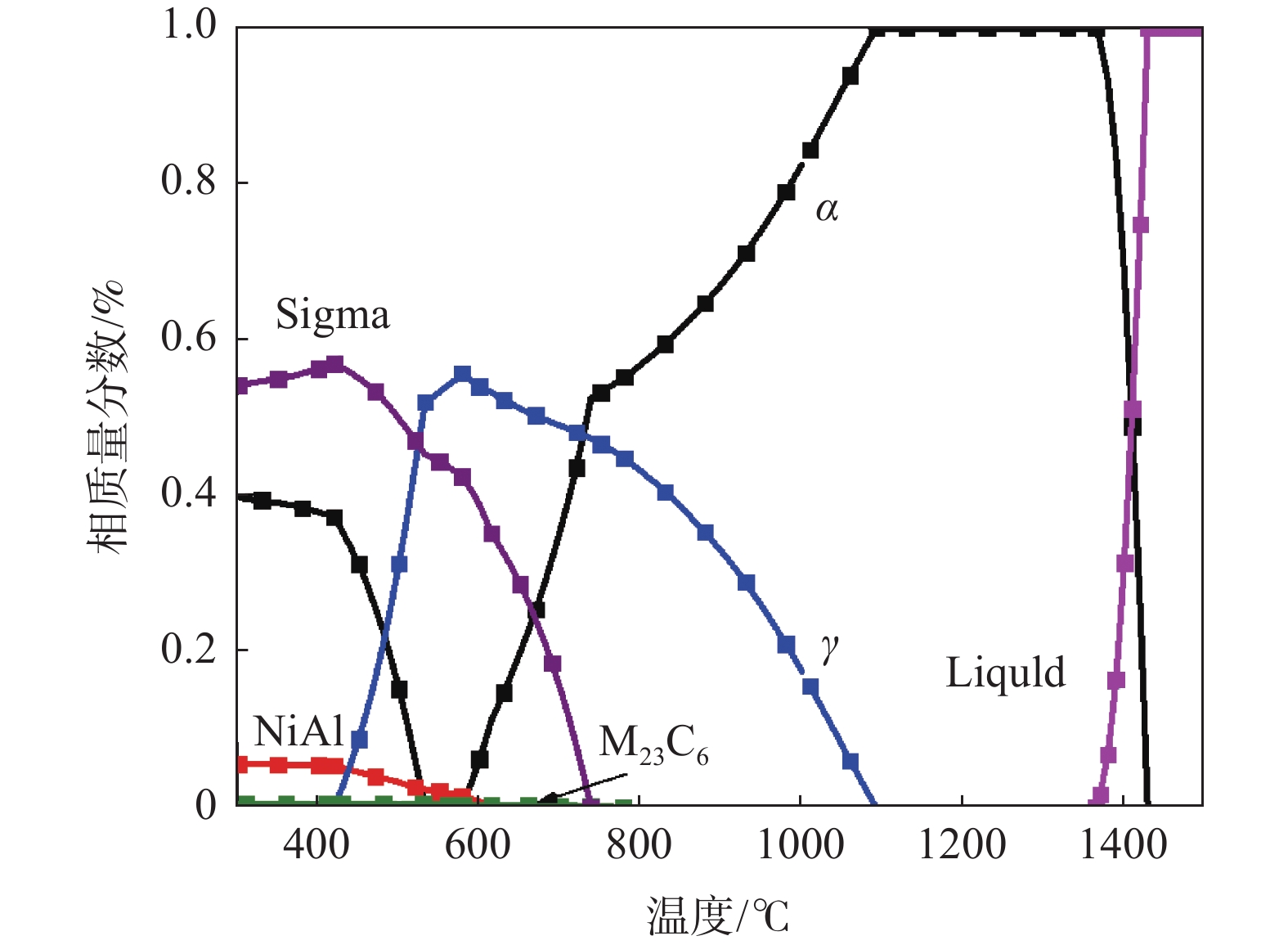
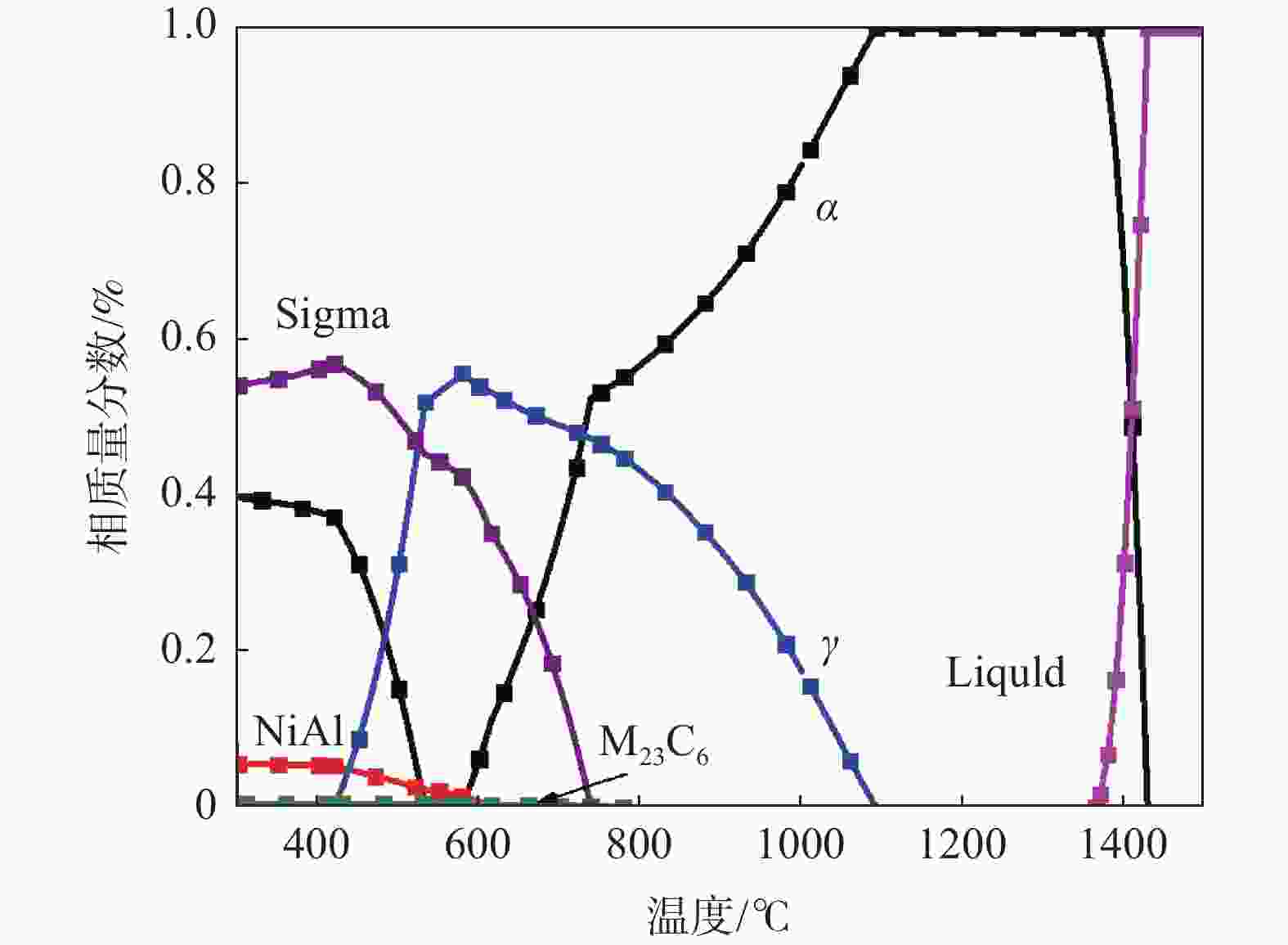
摘要: 采用拉伸、冲击和电化学测试方法研究了Fe-25Mn-18Cr-3.5Ni-2Al试验钢不同热处理工艺下的性能,通过SEM,EBSD和XRD等分析表明:奥氏体相体积分数随着固溶温度升高逐渐下降,900、950、1000 ℃固溶后,EBSD分析奥氏体相体积分数依次降低至60.2%,48.7%和20.0%,奥氏体由尖锐的鱼骨状转变为孤立的长针状分布在铁素体晶界上,铁素体相含量上升,试验钢的强度、硬度增加,冲击韧性下降,在900~1000 ℃固溶处理后铁素体相含量依次增大,(001)bcc取向逐渐减弱。经过700 ℃回火后易于在α相内出现弥散分布的NiAl纳米颗粒,导致脆性断裂。极化测试得到点蚀电位随固溶温度升高逐渐正移,1000 ℃固溶处理试样在3.5%NaCl极化测试中出现较长的钝化区和二次钝化,Ecorr=−257 mV,Eb=−46.5 mV,兼具较好耐蚀性能与力学性能,推荐作为实际生产热处理温度。Abstract: The properties of Fe-25Mn-18Cr-3.5Ni-2Al test steel under different heat treatment processes were tested by tensile, impact, and electrochemical methods. The SEM, EBSD, and XRD analysis showed that the volume fraction of the austenite phase decreased gradually with the increase of solid solution temperature. After solid solution at 900, 950 ℃, and 1000 ℃, the volume fraction of the austenite phase separated by EBSD decreased to 60.2%, 48.7%, and 20.0%, respectively. Austenite changes from a sharp fishbone shape to an isolated long needle shape distributed on the ferrite grain boundary. With the increase of ferrite phase content, the strength and hardness of the test steel increase, and the impact toughness decreases. After solution treatment at 900−1000 ℃, the ferrite phase content increases, and the orientation of (001)bcc decreases gradually. After tempering at 700 ℃, only α NiAl nanoparticles with dispersed distribution appear in the phase and show a brittle fracture. The polarization test shows that the pitting potential gradually moves forward with the increase of solution temperature. The sample treated at 1000 ℃ has a long passivation zone and secondary passivation in the 3.5% NaCl polarization test. Ecorr=−257 mV, Eb=−46.5 mV, has good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties and is recommended as the actual production heat treatment temperature.
-
Key words:
- stainless steels /
- secondary austenite phase /
- brittle fracture /
- pitting corrosion
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of tested steel
% C Cr Mn Si Ni Al P S Fe 0.022 17.89 25.83 0.23 3.5 2.06 0.006 0.003 余量 -
[1] Li Hao, Gao Dongqiang, Yang Zhen, et al. Effect of temperature on cracking of Cr2O3 oxide scale of super 304H alloy[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2017,(6):621−627. (李浩, 高东强, 杨珍, 等. 温度对Super304H合金Cr2O3. 氧化膜开裂影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2017,(6):621−627. doi: 10.11903/1002.6495.2017.039 [2] La Peiqing, Li Yufeng, Liu Shanguang. Corrosion resistance of aluminum-doped 316L stainless steel[J]. Material Protection, 2010,43(12):62−64. (喇培清, 李玉峰, 刘闪光. 316L不锈钢中添加Al后的抗腐蚀性能[J]. 材料保护, 2010,43(12):62−64. [3] Michler T, Naumann J, Weber S, et al. S-N fatigue properties of a stable high aluminum austenitic stainless steel for hydrogen applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013,38(23):9935−9941. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.05.145 [4] Jin J E, Lee Y K. Effects of Al on microstructure and tensile properties of C-bearing high Mn TWIP steel[J]. Acta Material, 2012,60(4):1680−1688. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.12.004 [5] Dudziak T, Ukaszewicz M, Simms N. Steam oxidation of TP347HFG, super 304H and HR3C-Analysis of significance of steam flowrate and specimen surface finish[J]. Corrosion Engineering and Technology, 2014,50(4):272−282. doi: 10.1179/1743278214y.0000000222 [6] Yamamoto Y, Brady M P, Lu Z P, et al. Alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels strengthened by Laves phase and MC carbide precipitates[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2007,38(27):37−46. doi: 10.1007/s11661-007-9319-y [7] Fang Yiliu, Liu Zhenyu, Song Hongmei. Prediction of surface cracks in lean duplex stainless steel 2101 by using processing map[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010,22(11):34. (方轶琉, 刘振宇, 宋红梅. 热加工图对节约型双相不锈钢2101表面裂纹的预测[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2010,22(11):34. [8] Ke R, Alkire R. ChemInform abstract: Surface analysis of corrosion pits initiated at MnS inclusions in 304 stainless steel[J]. Chem. Inform., 1992,23(35):21. doi: 10.1002/chin.199235021 [9] Li Guoping, Wang Jianjun, Wu Tianhai, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2205 DSS metal inert-gas welding joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2016,30(12):897−902. (李国平, 王建军, 吴天海, 等. 2205双相不锈钢TIG焊接头组织及力学性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2016,30(12):897−902. doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2016.252 [10] Kang D H, Lee H W. Effect of different chromium additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of multipass weld joint of duplex stainless steel[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2012,43(12):4678−4687. doi: 10.1007/s11661-012-1310-6 [11] Pan Jixiang, Chen Xingrun, Wang Jianxin. Microstructure evolution in 2205 duplex stainless steel slab during heat treatment processes[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2013,25(6):49−52. (潘吉祥, 陈兴润, 王建新. 2205双相不锈钢连铸坯加热过程组织转变[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2013,25(6):49−52. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.2013.06.009 [12] Liang H E, Guo Y J, Wu Xiayu, et al. Effect of solution annealing temperature on pitting behavior of duplex stainless steel 2204 in chloride solutions[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2016,23(4):357−363. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30057-7 [13] Ramirez A J, Lippold J C, Brandi S D. The relationship between chromium nitride and secondary austenite precipitation in duplex stainless steels[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2003,34(8):1575−1597. doi: 10.1007/s11661-003-0304-9 [14] 史金涛. 铝合金与亚稳奥氏体不锈钢低温变形组织优化与性能调控[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2018.Shi Jintao. Tailoring the microstructures and mechanical properties of cryogenic rolling aluminum alloy and metastable austenitic stainless steel[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology of Beijing, 2018. [15] Xiang Hongliang, Liu Chunyu, Deng Liping, et al. Effect of solution temperature on microstructure and properties of economical duplex stainless steel[J]. Materials Report, 2019,3(16):132−143. (向红亮, 刘春育, 邓丽萍, 等. 固溶温度对节约型双相不锈钢组织及性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2019,3(16):132−143. [16] Li Jun. Effect of solid solution treatment on structure and properties of super duplex stainless steel S32750[J]. Special Steel, 2012,33(4):64−66. (李俊. 固溶处理对超级双相不锈钢S32750组织和性能的影响[J]. 特殊钢, 2012,33(4):64−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2012.04.019 [17] Mcguire M F. Stainless steels for design engineers[M]. ASM International, 2008. DOI: 10.31399/asm.tb.ssde.9781627082860. [18] 孙胜英. 合金成分设计对含铝奥氏体耐热钢组织和性能的影响[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.Sun Shengying. Effect of alloy composition design on microstructure and properties of alumina-forming austenitic steels[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology of Beijing, 2019. -




 下载:
下载: