Hydrothermal synthesis and phase transformation properties of W-doped VO2(M) nanoparticles
-
摘要: 以偏钒酸铵为钒源,水合肼为还原剂,偏钨酸铵为掺杂剂,采用一步水热法在280 ℃制备了掺W量(原子分数表示)从0到2.0%的VO2粉体,并将其加入到聚氨酯中,制备VO2/PU复合薄膜。通过XRD、TEM、XPS、DSC对合成的样品进行了物相组成、形貌、元素价态和相变性能分析,利用紫外-可见-近红外光谱仪测定了薄膜的透射率。结果表明:随着W掺杂量从0增加到2.0%,二氧化钒升温时的相变温度从61.8 ℃降低至15 ℃。基于掺杂1.0%的二氧化钒粉体制备的VO2/PU复合薄膜,ΔTsol可达11.7%,基本满足智能窗的实际应用要求。Abstract: In this paper, using ammonium metavanadate as the vanadium source, hydrazine monohydrate as the reducing agent and ammonium metatungstate as the dopant, the VO2 powder doped with W from 0.0 to 2.0 at% was prepared by one-step hydrothermal method at 280 ℃, and was added to polyurethane to prepare VO2/PU composite films. XRD, TEM, XPS and DSC were used to analyze the phase composition, morphology, element valence state and phase transformation performance of the synthesized samples. The transmittance of the films was measured by UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer. The results show that with W doping increasing from 0.0 to 2.0 at%, the phase transition temperature of vanadium dioxide decreases from 61.8 ℃ to 15 ℃. The composite film based on 1 at% W-doped vanadium dioxide powder shows a good solar modulating ability (ΔTsol = 11.7%), which meets the practical application requirements of intelligent windows.
-
Key words:
- vanadium dioxide /
- one-step hydrothermal treatment /
- W-doped /
- phase transformation properties /
- films
-
表 1 具有不同掺钨量的样品的金属-绝缘体相变温度汇总
Table 1. Summary of metal insulator transition temperatures for samples with different W-doping concentrations
掺钨量/% Tc-heating /℃ Tc-cooling /℃ Tc/℃ 热滞宽度/℃ ΔH−heating/
(J·g−1)ΔH−cooling/
(J·g−1)ΔH/(J·g−1) 0 61.8 33.1 47.5 28.7 30.19 −32.31 31.25 0.5 49.5 27.7 38.6 21.8 25.66 −26.22 25.94 1.0 40.3 19.4 29.9 20.9 23.36 −22.14 22.75 1.5 30.4 9.1 19.8 21.3 17.82 −16.39 17.11 2.0 25.3 4.7 15 20.6 13.96 −15.13 14.55 注:ΔH=(ΔH−heating+|ΔH−cooling|)/2 ; Tc= (Tc-heating + Tc-cooling)/2。 表 2 不同掺钨量VO2薄膜的热致变色性能
Table 2. Thermochromic properties of VO2 films with different W-doping concentrations
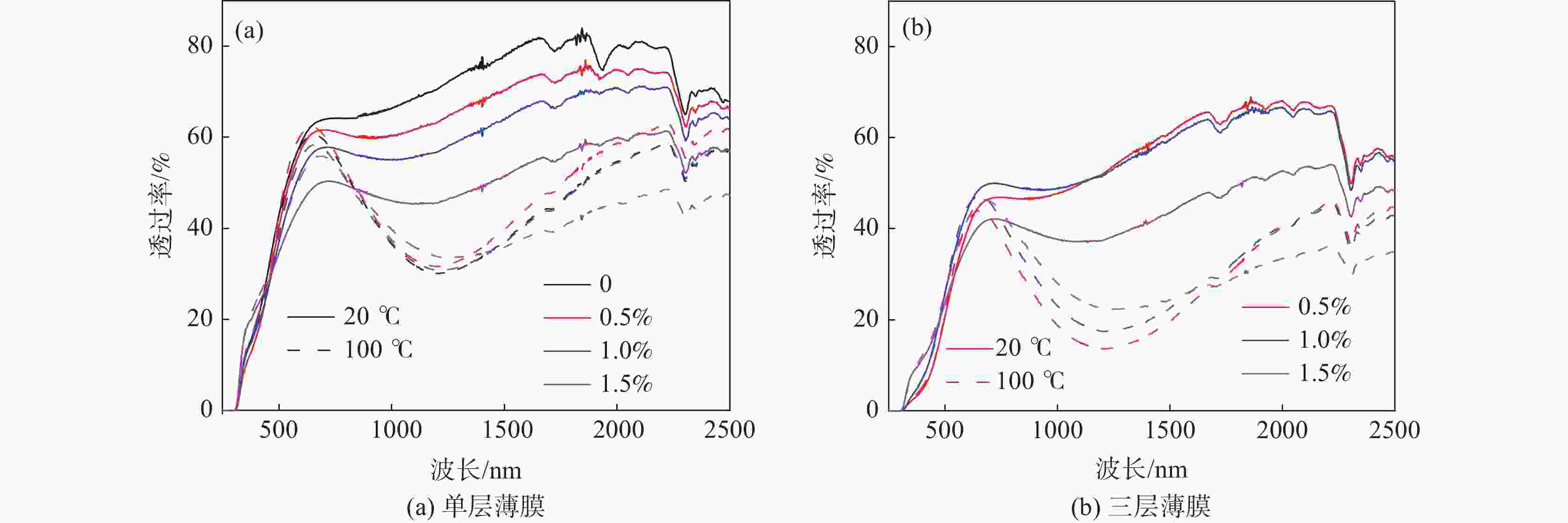
掺钨量/% 涂膜浆料体积/mL Tsol /% Tlum /% ΔTsol /% 20 ℃ 100 ℃ 20 ℃ 100 ℃ 0 0.8 57.5 43.7 53.0 52.3 13.8 0.5 0.8 53.6 45.3 51.2 54.6 8.3 0.4+0.4+0.4 39.4 26.7 32.4 34.1 12.7 1.0 0.8 49.8 42.7 46.8 49.5 7.1 0.4+0.4+0.4 41.8 30.1 37.1 37.9 11.7 1.5 0.8 43.5 42.4 41.4 46.3 1.1 0.4+0.4+0.4 34.5 31.4 31.6 35.9 3.1 -
[1] Xu Fang, Cao Xun, Luo Hongjie, et al. Recent advances in VO2-based thermochromic composites for smart windows[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018,6(8):1913−1919. [2] Zheng Jianyun, Bao Shanhu, Jin Ping. TiO2(R)/VO2(M)/TiO2(A) multilayer film as smart window: Combination of energy-saving, antifogging and self-cleaning functions[J]. Nano Energy, 2015:11136−11145. [3] Liang Zihui, Zhao Li, Meng Wanfan, et al. Tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide thin films as smart windows with self-cleaning and energy-saving functions[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017:694124−694131. [4] Ji Haining, Liu Dongqing, Cheng Haifeng, et al. Large area infrared thermochromic VO2 nanoparticle films prepared by inkjet printing technology[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019:194235−194243. [5] Liang Shan, Shi Qiwu, Zhu Hongfu, et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of W-doped VO2 (M) nanorods with a tunable phase-transition temperature for infrared smart windows[J]. ACS Omega, 2016,1(6):1139−1148. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00221 [6] Warwick Michael-E-A, Binions Russell. Chemical vapour deposition of thermochromic vanadium dioxide thin films for energy efficient glazing[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2014:21453−21466. [7] Dang Yuanyuan, Wang Danping, Zhang Xin, et al. Structure and thermochromic properties of Mo-doped VO2 thin films deposited by sol-gel method[J]. Inorganic and Nano-metal Chemistry, 2019,49(4):120−125. doi: 10.1080/24701556.2019.1611852 [8] Guo H, Khan M-I, Cheng C, et al. Vanadium dioxide nanowire-based microthermometer for quantitative evaluation of electron beam heating[J]. Nature Communications, 2014,5(1):4986. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5986 [9] Yin Xianglu, Zeng Zehua, Gao Rongrong, et al. Thermolysis preparation of monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide with ultrafine particles under an inert gas atmosphere[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(1):1−6. (尹翔鹭, 曾泽华, 高荣荣, 等. 惰性气氛下热分解法制备M相二氧化钒超细颗粒[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(1):1−6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.01.001 [10] Barra Hamdi-Muhyuddin, Chen Soo-Kien, Tamchek Nizam, et al. Nanostructured VO2 (A) and VO2 (M) derived from VO2 (B): Facile preparations and analyses of structural, thermal, optical and thermophysical properties[J]. Medžiagotyra, 2021,27(3):269−275. [11] Zhang Liangmiao, Yao Jianning, Guo Yunfeng, et al. VO2(A) nanorods: One-pot synthesis, formation mechanism and thermal transformation to VO2(M)[J]. Ceramics International, 2018,44(16):19301−19306. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.157 [12] Chen Ru, Miao Lei, Liu Chengyan, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis and influence of W doping and oxygen nonstoichiometry on the phase transition of VO2[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015,5(1):14087. doi: 10.1038/srep14087 [13] Sirvent P, Pérez G, Guerrero A. Efficient VO2(M) synthesis to develop thermochromic cement-based materials for smart building envelopes[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2021:269124765. [14] Chang Tianci, Cao Xun, Long Yi, et al. How to properly evaluate and compare the thermochromic performance of VO2-based smart coatings[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(42):24164−24172. doi: 10.1039/C9TA06681K [15] Wu Jialiang, Tong Liping, Wang Huifen, et al. Regulation of phase transition temperature and preparation for doping-VO2 smart thermal control films[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2022,131(8):85101. doi: 10.1063/5.0054066 [16] Wu Shaowen, Tian Shouqin, Liu Baoshun, et al. Facile synthesis of mesoporous VO2 nanocrystals by a cotton-template method and their enhanced thermochromic properties[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018:176427−176434. [17] Morin F J. Oxides which show a metal-to-insulator transition at the neel temperature[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1959,3(1):34−36. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.3.34 [18] Whittaker Luisa, Patridge Christopher J, Banerjee Sarbajit. Microscopic and nanoscale perspective of the metal−insulator phase transitions of VO2: Some new twists to an old tale[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011,2(7):745−758. doi: 10.1021/jz101640n [19] Li Dengbing, Li Ming, Pan Jing, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of Mo-doped VO2 /TiO2 composite nanocrystals with enhanced thermochromic performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014,6(9):6555−6561. [20] Li Bin, Yao Jiajun, Tian Shouqin, et al. A facile one-step annealing route to prepare thermochromic W doped VO2 (M) particles for smart windows[J]. Ceramics International, 2020,46(11):18274−18280. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.042 [21] He Xinfeng, Zeng Yijie, Xu Xiaofeng, et al. Orbital change manipulation metal-insulator transition temperature in W-doped VO2[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015,17(17):11638−11646. doi: 10.1039/C4CP04889J -




 下载:
下载: