Effect of manganese on vanadium extraction by calcification from vanadium slag
-
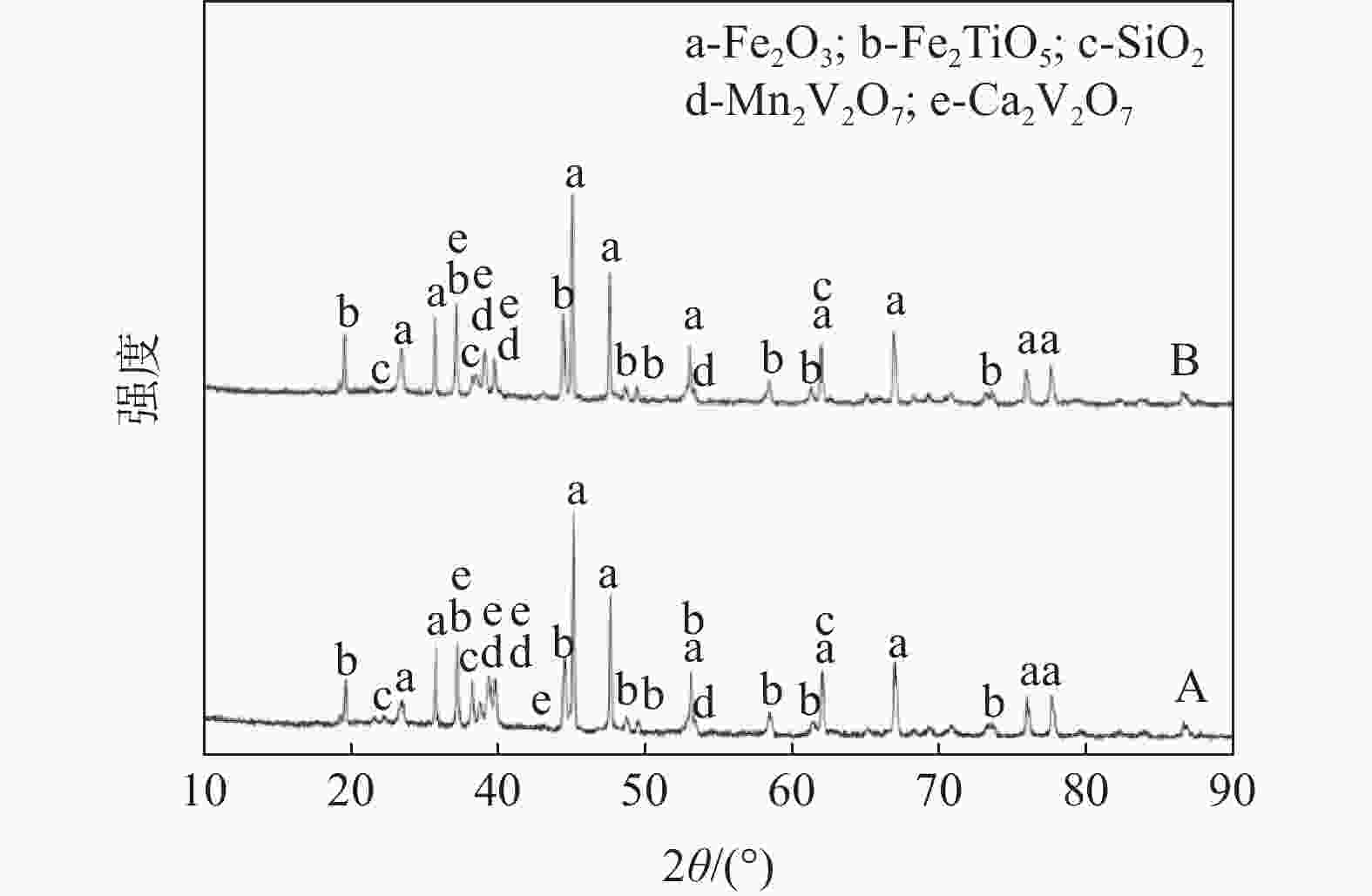
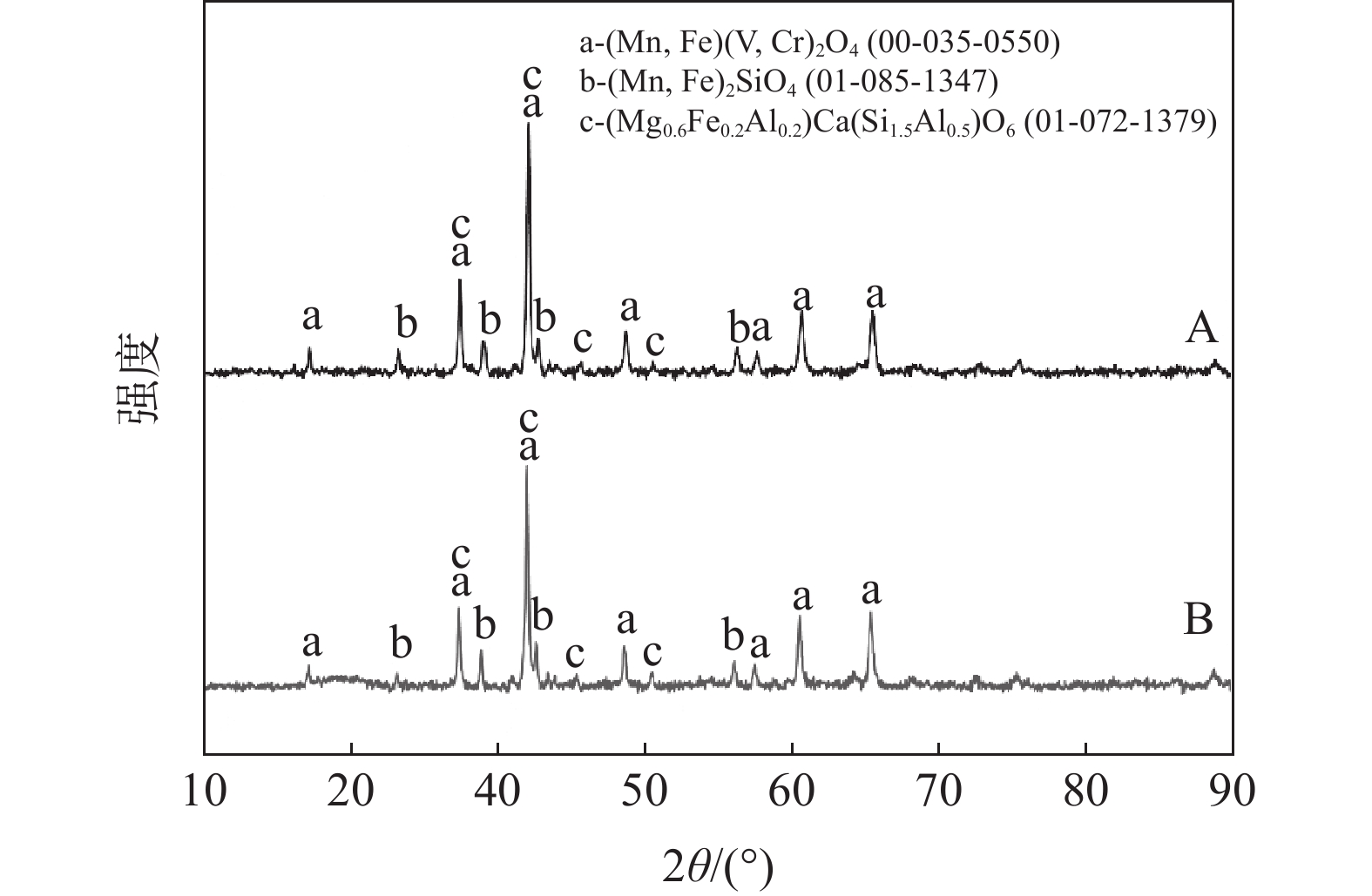
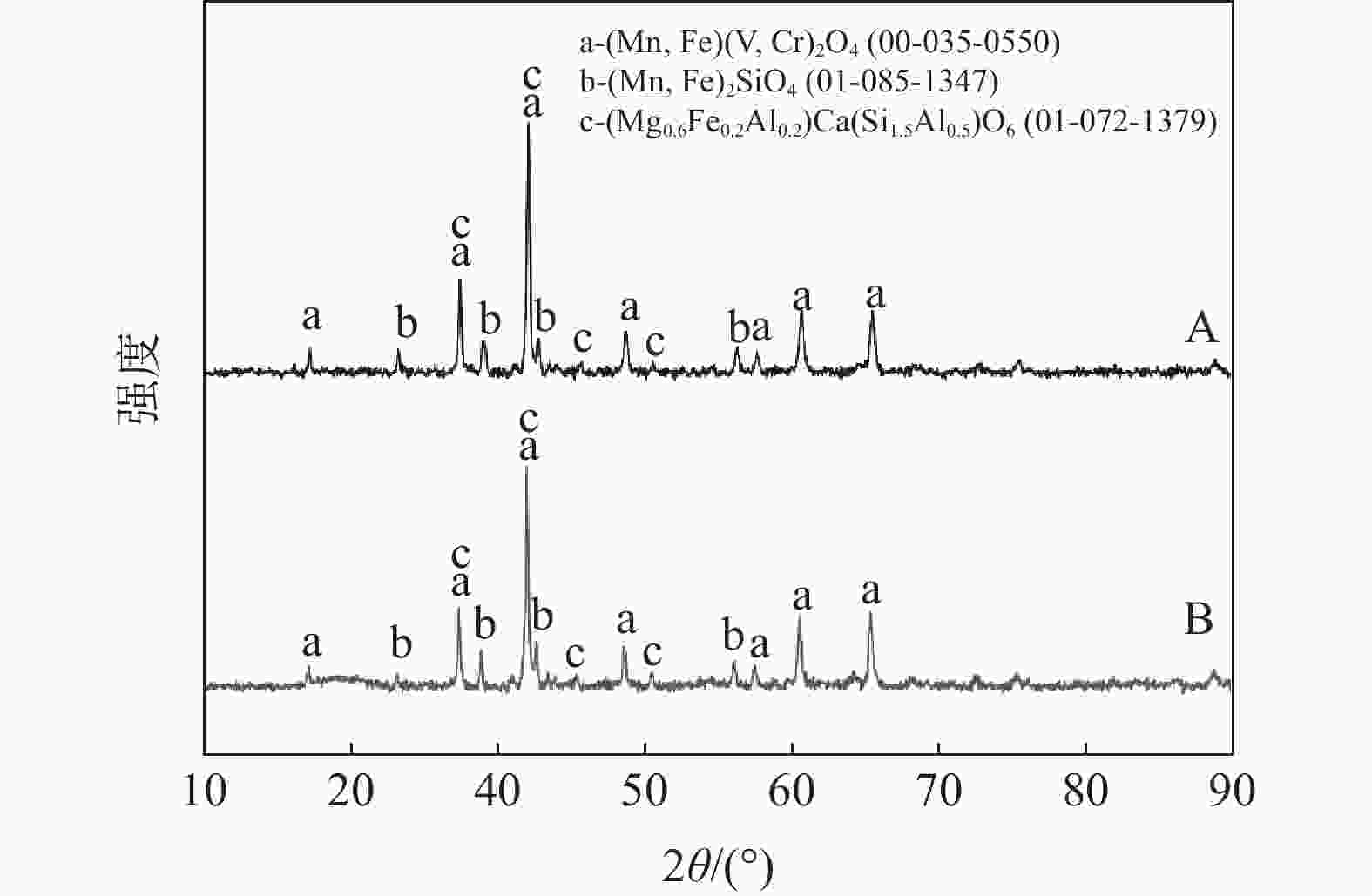
摘要: 以Mn含量不同的两批钒渣为研究对象,利用XRD和SEM-EDS分析方法探究钒渣物相组成和微观结构,查明不同Mn含量钒渣钙化焙烧熟料的物相变化及对钒浸出率的影响。结果表明:钒渣主要由钒铁尖晶石、铁橄榄石及透辉石物相构成,在一定范围内,渣中V、Mn、Fe等主要成分的小幅波动不影响钒渣的主要物相组成;钒渣焙烧熟料均由赤铁矿Fe2O3、铁板钛矿Fe2TiO5、硅酸盐SiO2及钒酸盐相组成,其中,钒酸盐成分主要为Mn2V2O7与Ca2V2O7复盐,钒主要赋存于钒酸盐复盐中,钒渣中Mn含量变化对熟料物相组成未产生明显影响;在较低钙钒比以及相同焙烧-浸出条件下,Mn对钙化提钒的焙烧-浸出效果有一定的促进作用,MnO含量分别为6.98%和8.26%的钒渣焙烧熟料钒的浸出率分别为93.66%和94.51%。Abstract: In this paper, two batches of vanadium slag with different Mn content were taken as the research object. XRD and SEM-EDS were used to explore the phase composition and microstructure of vanadium slag, and to find out the phase change of calcified roasted clinker with different Mn content and its effect on vanadium leaching rate. The results show that the vanadium slag is mainly composed of vanadium iron spinel, iron olivine and diopside. In a certain range, the small fluctuation of main components such as V, Mn and Fe in the slag does not affect the composition of the main phase of vanadium slag. Both roasting clinkers consist of Fe2O3, Fe2TiO5, silicate and vanadate. Of these phases, vanadate mainly refers to the double salt of Mn2V2O7 and Ca2V2O7, vanadium mainly occurs in this salt. The change of Mn content in vanadium slag has no obvious effect on the clinker phase composition. Mn can promote the roasting-leaching effect of calcified vanadium extraction under the same roasting-leaching conditions and low calcium-vanadium ratio. The leaching rates of vanadium from roasted clinkers with MnO content of 6.98% and 8.26% are 93.66% and 94.51%, respectively.
-
表 1 原料的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of raw materials
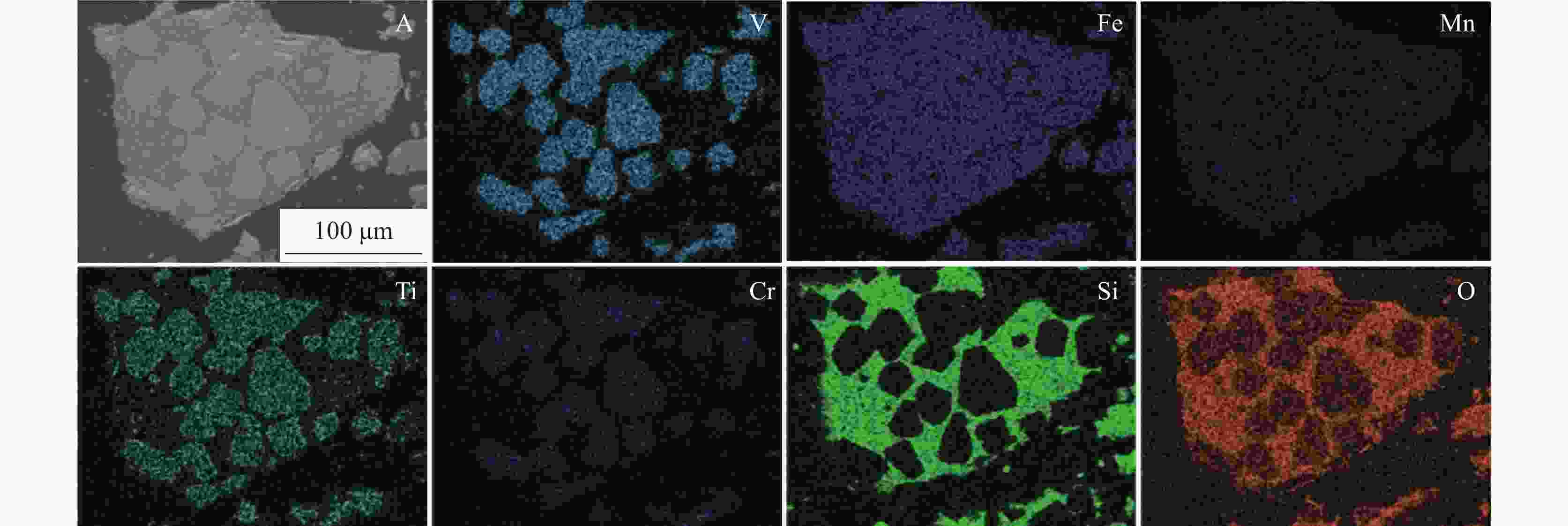
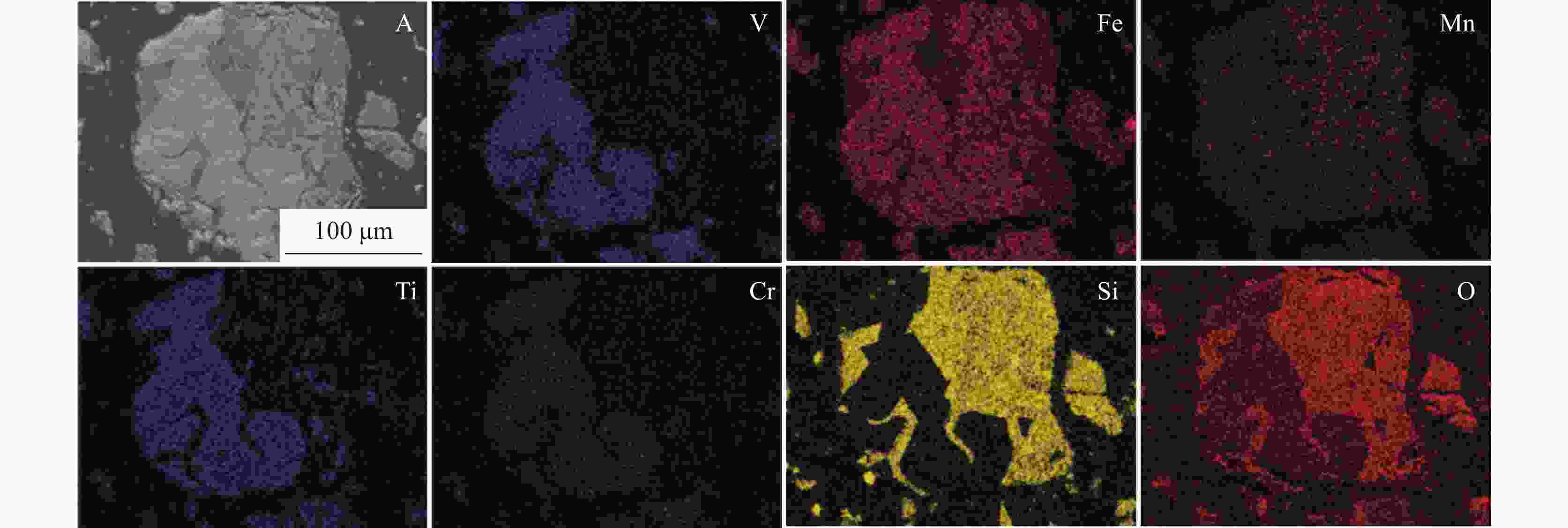
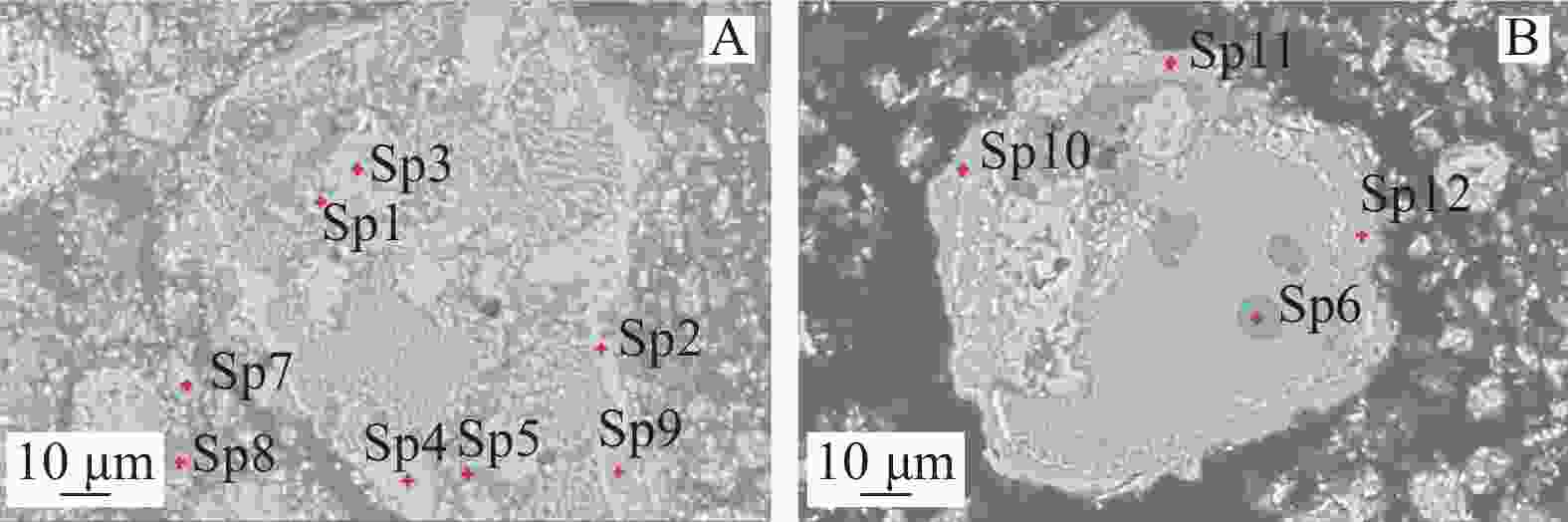
% 编号 V MnO TFe TiO2 SiO2 CaO MgO P 钒渣A 7.87 6.98 33.38 11.39 16.69 2.05 3.23 0.061 钒渣B 8.37 8.26 37.38 10.98 14.39 2.01 0.823 0.054 石灰石 0.451 52.00 0.645 位置 Fe Mn Cr V Ti Ca Mg Si Al Sp1 32.45 5.38 4.33 20.84 9.85 0.09 1.34 0.06 1.84 Sp2 32.96 9.10 0.14 0.56 0.75 0.51 3.50 13.44 0.02 Sp3 9.71 3.41 0.19 0.24 2.27 8.34 0.27 20.67 5.66 位置 Fe Mn Cr V Ti Ca Mg Si Al Sp1 35.67 6.19 3.03 19.85 12.60 0.26 0.03 0.58 Sp2 16.16 10.81 0.24 0.35 8.62 0.74 21.51 0.24 Sp3 2.17 0.96 0.06 0.30 2.92 31.28 6.69 表 4 图7中选定点EDS分析结果
Table 4. The EDS compositions of selected points in Fig.7
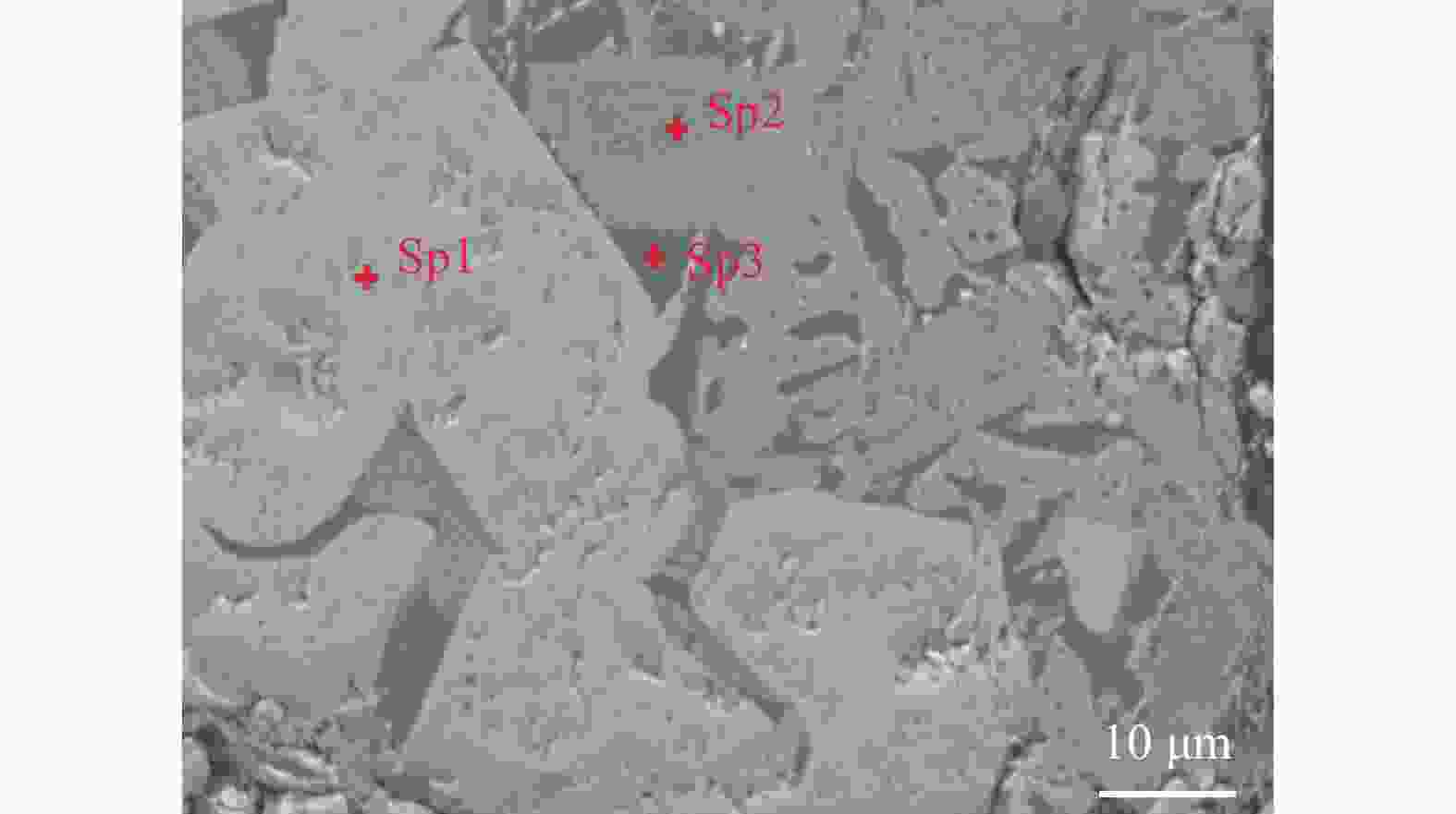
% 元素 C O Mg Al Si Ca Ti V Cr Mn Fe Sp1 4.65 24.27 1.19 0.43 1.66 3.53 0.73 7.53 56.01 Sp2 5.13 23.91 1.27 0.56 0.29 3.93 0.63 0.61 7.64 56.04 Sp3 3.94 24.34 0.80 0.50 0.21 19.92 2.37 4.53 43.38 Sp4 4.76 26.58 1.17 0.50 1.24 19.89 4.54 5.71 35.61 Sp5 7.88 40.81 0.25 1.24 32.26 3.28 0.59 4.97 2.82 5.91 Sp6 8.37 38.28 0.85 5.91 26.49 6.41 2.10 0.20 3.10 7.76 Sp7 7.33 27.52 2.28 3.03 5.31 10.58 0.93 26.50 0.38 11.91 3.65 Sp8 4.57 26.82 6.52 0.38 6.53 10.88 0.72 28.81 12.40 2.37 Sp9 3.38 17.62 2.01 0.77 13.59 0.47 39.29 20.10 2.76 Sp10 3.24 19.55 2.40 0.35 13.27 0.88 38.83 18.82 2.66 Sp11 3.68 12.88 1.94 0.91 13.43 0.31 38.68 18.05 1.72 Sp12 4.67 19.88 2.47 0.41 13.02 38.61 18.60 2.34 表 5 图8中选定点EDS分析结果
Table 5. The EDS compositions of selected points in Fig.8
% 元素 C O Mg Al Si Ca Ti V Cr Mn Fe Sp1 5.60 25.67 0.15 1.16 0.84 0.25 1.46 64.86 Sp2 4.62 27.52 0.46 0.85 0.17 20.31 2.17 2.95 3.71 37.24 Sp3 3.88 28.24 0.50 1.00 0.23 20.45 1.73 2.91 3.68 37.37 Sp4 8.16 40.37 4.67 29.12 4.30 0.58 3.76 2.04 5.97 Sp5 5.19 16.91 0.76 0.45 15.36 0.48 38.95 18.61 3.28 Sp6 4.21 15.08 0.67 0.51 14.11 0.34 36.31 17.78 1.55 Sp7 4.18 20.58 0.82 0.33 14.76 0.91 37.33 18.35 2.74 Sp8 4.28 20.67 0.85 0.66 15.13 0.94 37.20 17.82 2.46 Sp9 3.29 19.52 0.73 0.17 15.64 1.04 38.40 18.59 2.62 Sp10 4.41 20.62 0.87 0.21 15.58 0.40 37.92 17.87 2.11 Sp11 5.00 21.07 0.78 0.22 15.09 0.45 37.56 18.04 1.77 -
[1] Zhang Yimin, Bao Shenxu, Liu Tao, et al. The technology of extracting vanadium from stone coal in China: History, current status and future prospects[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011,109(1-2):116−124. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.06.002 [2] Dhal B, Thatoi H N, Das N N, et al. Chemical and microbial remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and mining/metallurgical solid waste: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013,250-251(30):272−291. [3] A P M , B A F C . Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 180( 1–3): 1-19. [4] Jiang Tao, Wen Jing, Zhou Mi, et al. Phase evolutions, microstructure and reaction mechanism during calcification roasting of high chromium vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds:An Interdisciplinary Journal of Materials Science and Solid-state Chemistry and Physics, 2018,742:402−412. [5] Fu Zibi. Development history and trend of vanadium extraction process from vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Chinese Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2011,40(6):29−33. (付自碧. 钒钛磁铁矿提钒工艺发展历程及趋势[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2011,40(6):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2011.06.008 [6] Chen Donghui. Annual evaluation for vanadium industry in 2018[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2019,(8):5−15. (陈东辉. 钒产业2018年年度评价[J]. 河北冶金, 2019,(8):5−15. [7] Li Xinsheng, Xie Bing. Extraction of vanadium from high calcium vanadium slag using direct roasting and soda leaching[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2012,19(7):595−601. doi: 10.1007/s12613-012-0600-8 [8] Chen Housheng. Research on the process of extracting V2O5 from vanadium slag by lime roasting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1992,(6):3−11. (陈厚生. 钒渣石灰焙烧法提取V2O5工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1992,(6):3−11. [9] Liu Zuohua, Li Yan, Chen Manli, et al. Enhanced leaching of vanadium slag in acidic solution by electro-oxidation[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016,159:1−5. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.09.019 [10] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Zheng Xiaole, et al. Efficient separation of chromium and vanadium by calcification roasting–sodium carbonate leaching from high chromium vanadium slag and V2O5 preparation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019,230:115881. [11] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Liu Yajing, et al. Extraction behavior of vanadium and chromium by calcification roasting-acid leaching from high chromium vanadium slag: Optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2018:1−11. [12] Pan Ziwei, Zheng Shili, Wang Zhonghang, et al. Research on simultaneous extraction of vanadium and chromium from high chromium vanadium slag by sub-molten salt method[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(2):1−8. (潘自维, 郑诗礼, 王中行, 等. 亚熔盐法高铬钒渣钒铬高效同步提取工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(2):1−8. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.02.001 [13] Zheng Shili, Du Hao, Wang Shaona, et al. Efficient and cleaner technology of vanadium extraction from vanadium slag by sub-molten salt method[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(1):15−19. (郑诗礼, 杜浩, 王少娜, 等. 亚熔盐法钒渣高效清洁提钒技术[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(1):15−19. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.01.003 [14] Cao Peng. Research on vanadium slag roasted with calcium salt[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(1):30−34. (曹鹏. 钒渣钙化焙烧试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(1):30−34. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.01.006 [15] Guo Shuanghua. Extraction of vanadium from ferro vanadium slag by process of roasting calcification-acidic leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2018,37(2):111−113. (郭双华. 用钙化焙烧-酸浸法从钒铁渣中提取钒试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2018,37(2):111−113. [16] Shi Zhixin, Yuan Tianyu, Liu Jinyan, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of vanadium spinel in the process of calcified roasting vanadium slag[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2014,23(5):95−98. (史志新, 苑天宇, 刘锦燕, 等. 钙化焙烧钒渣过程中钒尖晶石的矿物学特征[J]. 矿冶, 2014,23(5):95−98. [17] Shi Zhixin, Liu Jinyan. Discussion on the mineralogical characteristics of phase in the process of vanadium slag roasting[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2014,34(7):12−17. (史志新, 刘锦燕. 钒渣焙烧过程中物相的矿物学特征探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2014,34(7):12−17. doi: 10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2014.07.003 [18] Wang Chunmei, Liu Jinyan, Shi Zhixin, et al. Discussion on the influence factor of vanadium slag phase structure and calcification roasting phase transition on vanadium conversion rate[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2015,35(6):26−30. (王春梅, 刘锦燕, 史志新, 等. 钒渣物相结构及钙化焙烧相变对钒转化率的影响因素探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2015,35(6):26−30. [19] Fu Nianxin, Zhang Lin, Liu Wuhan, et al. Mechanism analysis of phase transformation process in calcified roasting of vanadium slags[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018,28(2):377−386. (付念新, 张林, 刘武汉, 等. 钒渣钙化焙烧相变过程的机理分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018,28(2):377−386. -




 下载:
下载: