Constitutive relationship analysis and microstructural evolution of biomedical Ni-Ti alloy during warm deformation
-
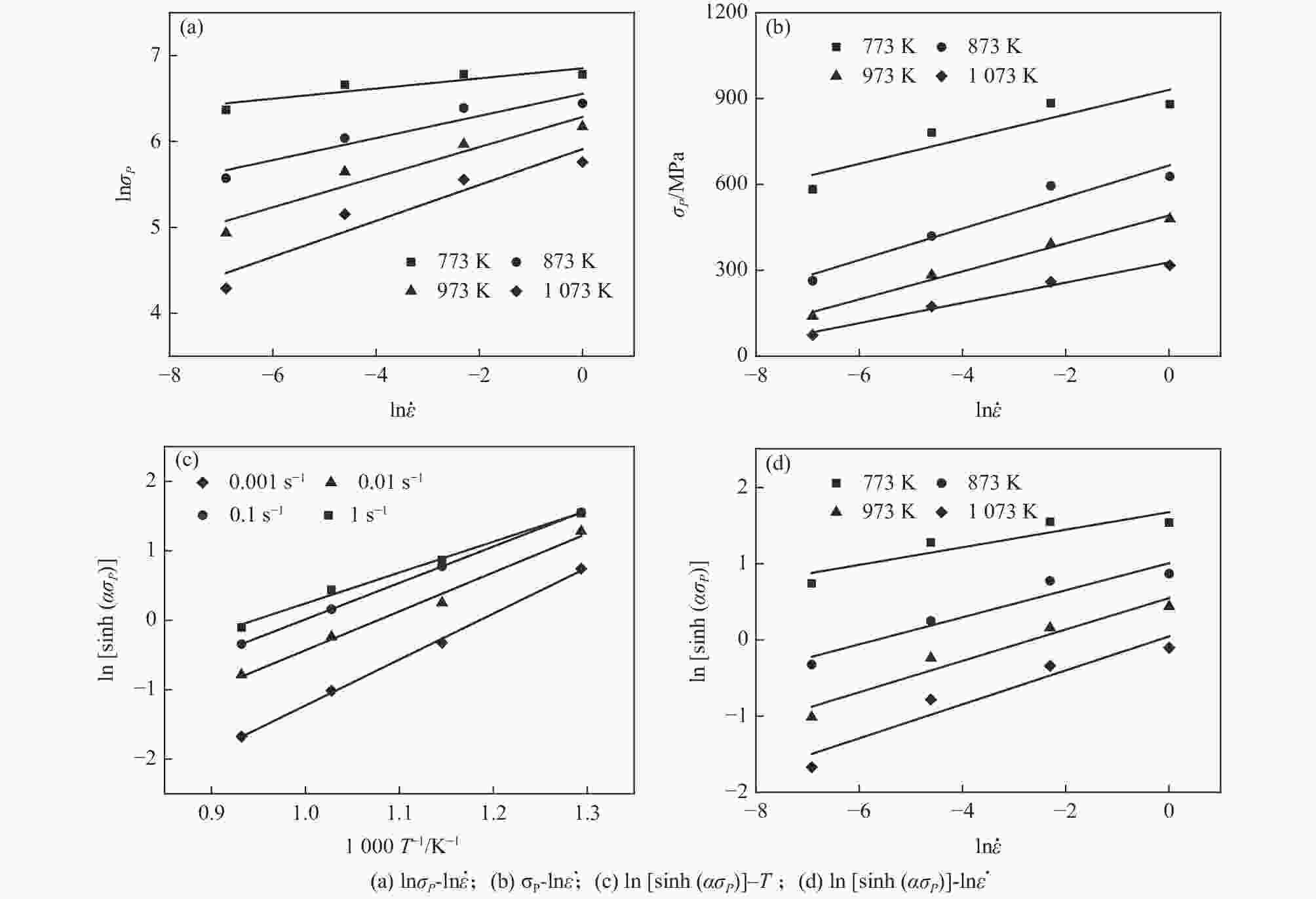
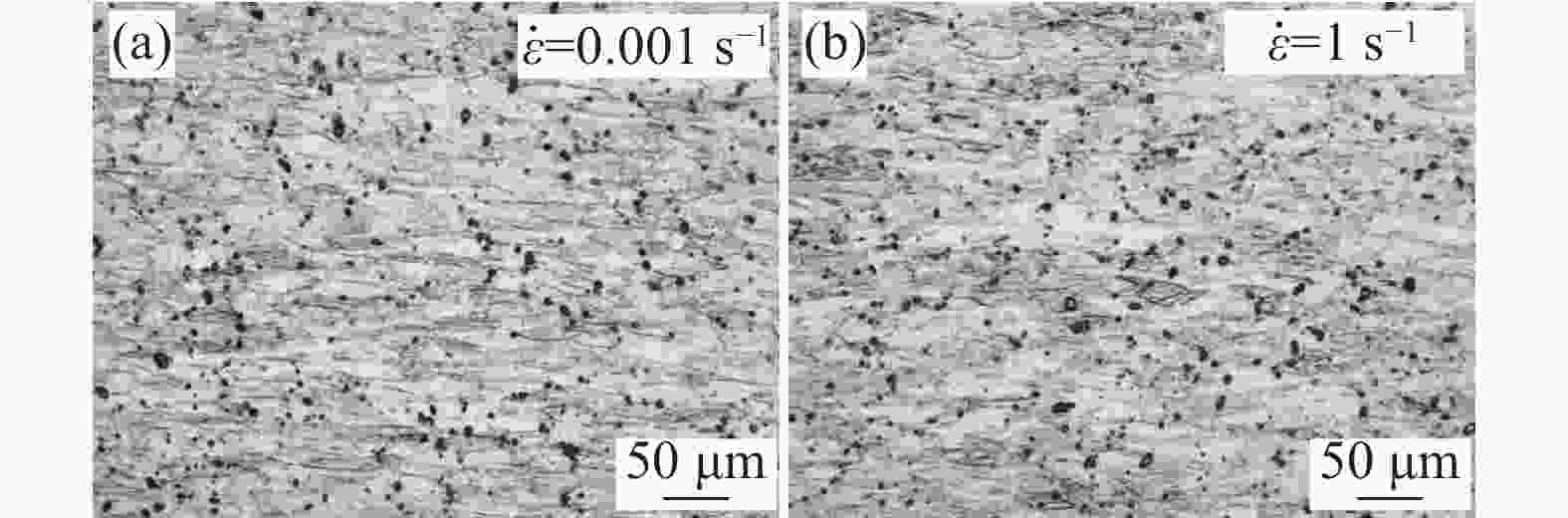
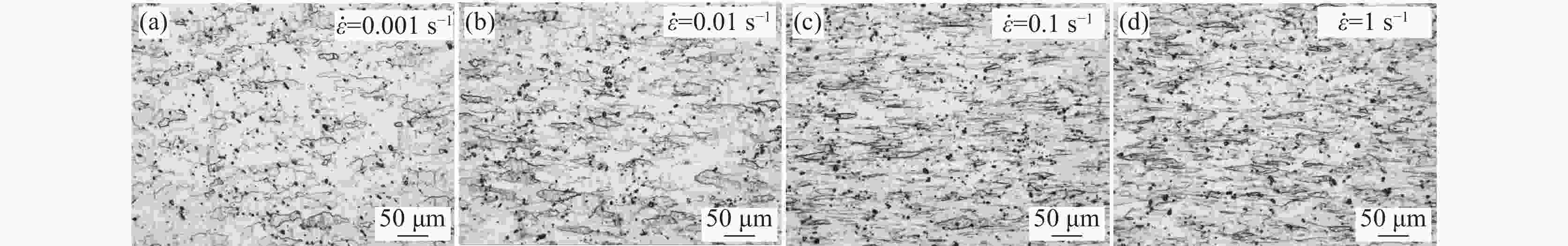
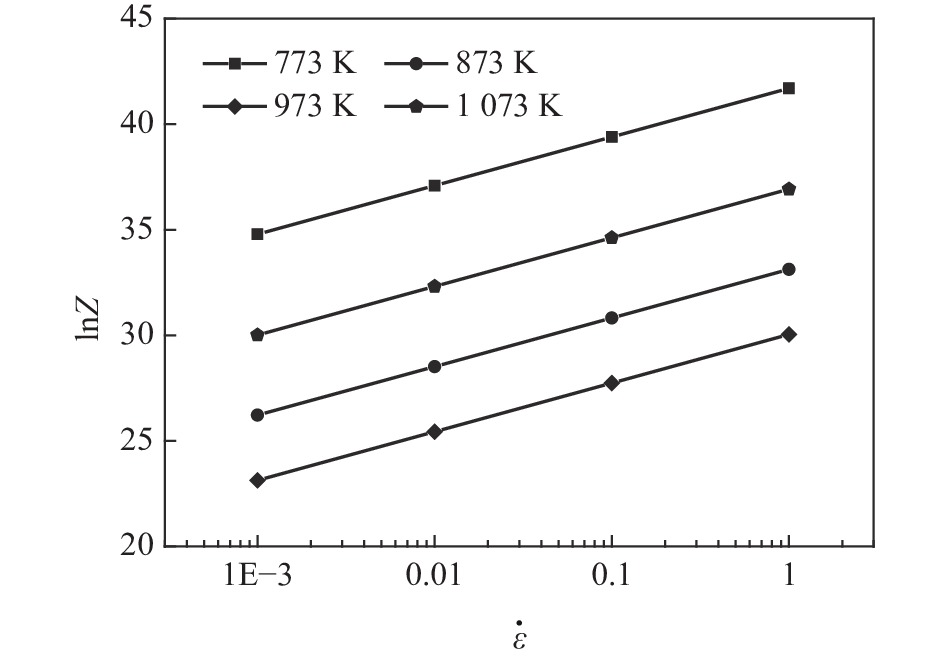
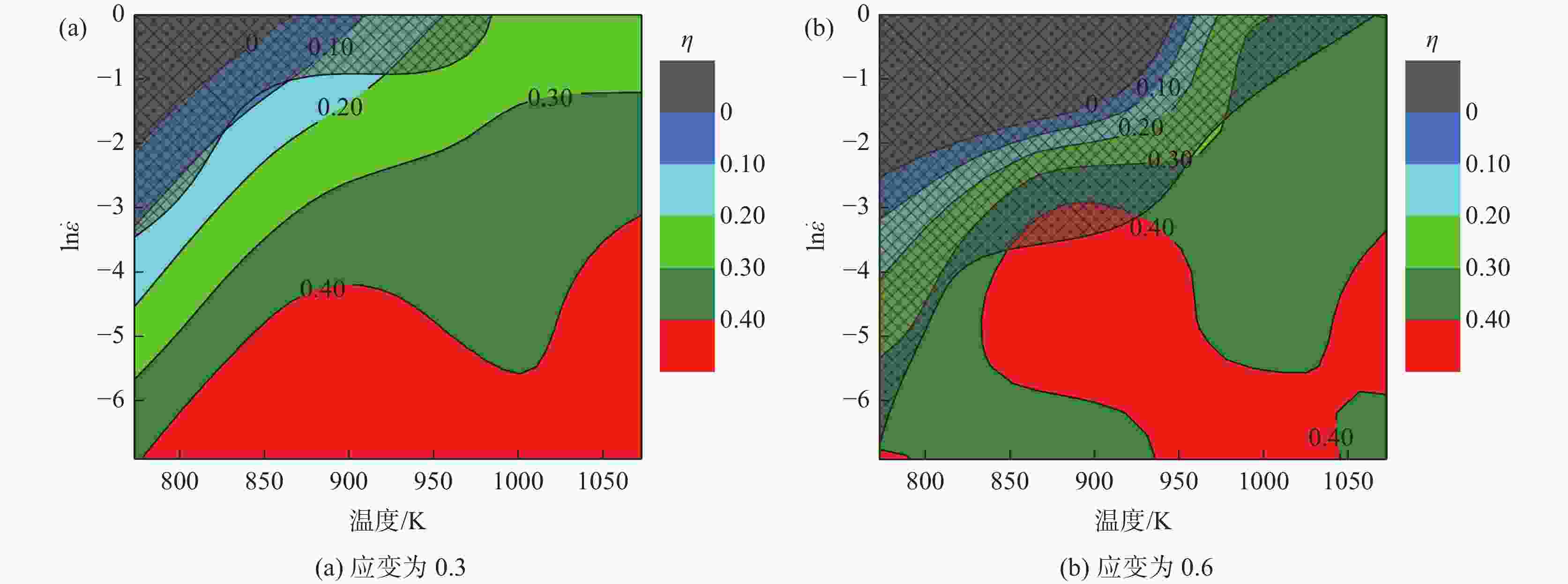
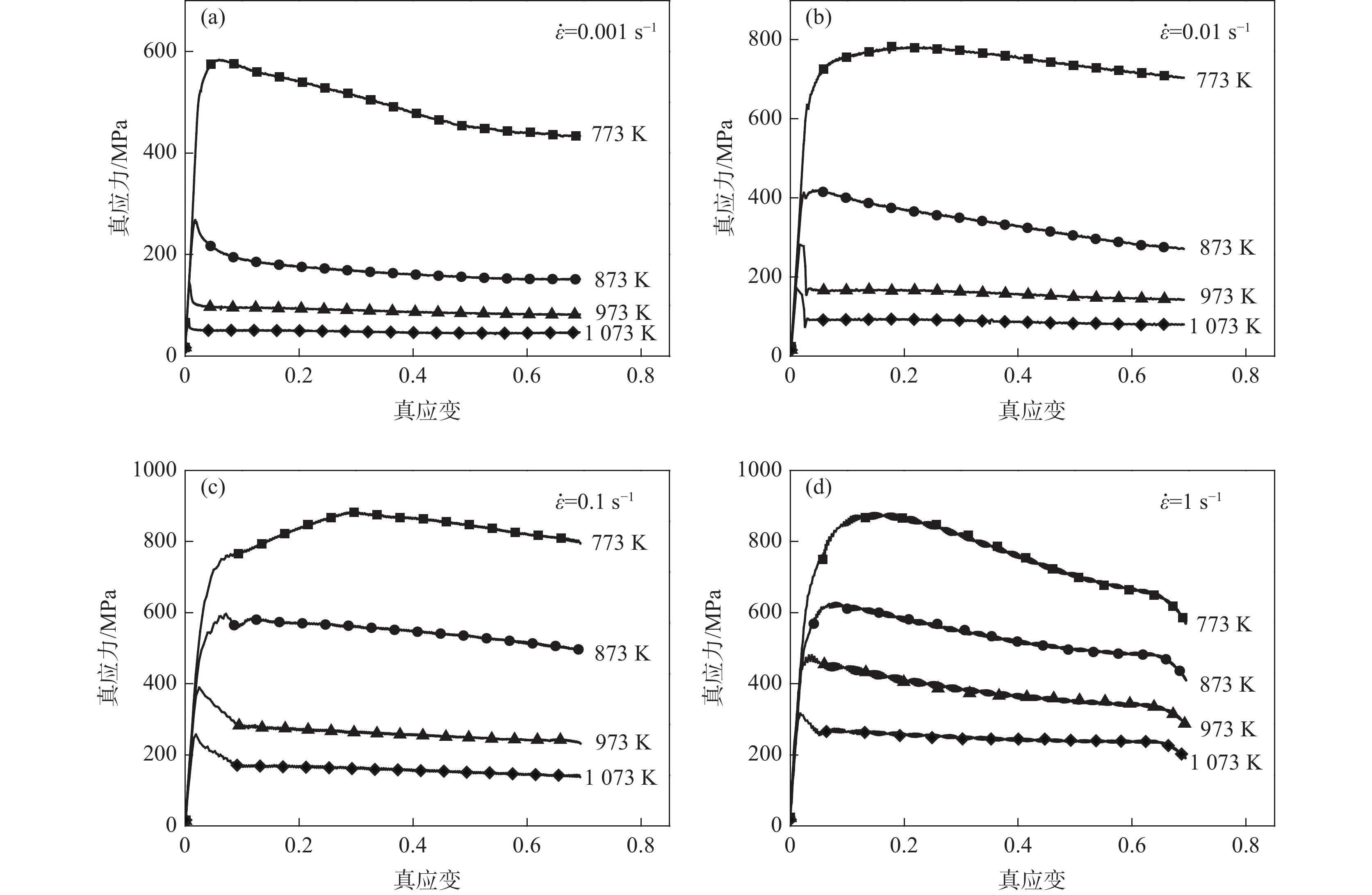
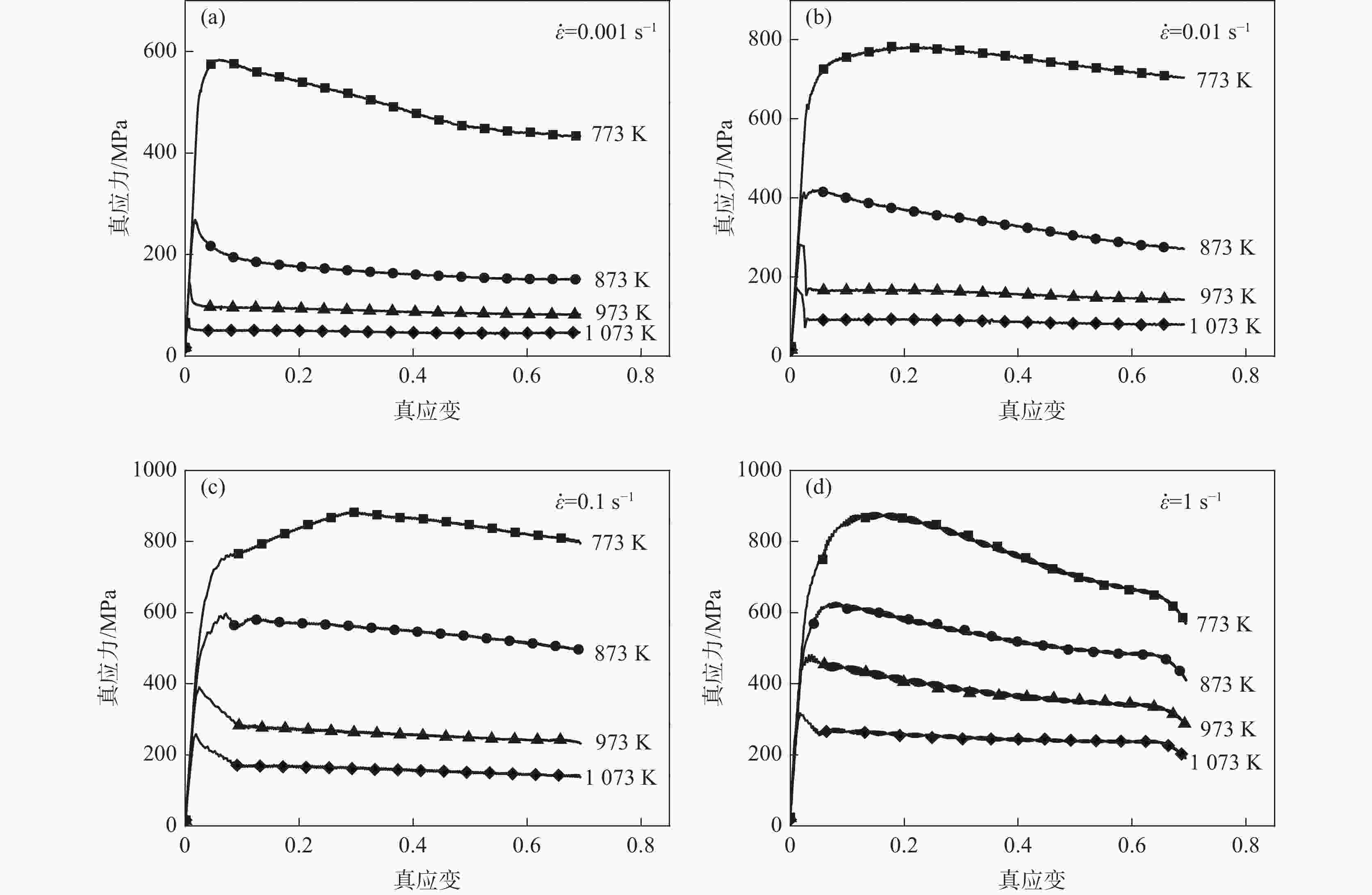
摘要: 为研究医用镍钛合金的温变形行为,利用Gleeble-3800 热模拟试验机对其进行压缩试验,获得了合金压缩过程的真应力-真应变曲线,分析了合金在变形过程中的本构关系和微观组织演变过程,并建立了加工图,确定出较好的加工参数。结果表明,动态回复和再结晶是压缩变形过程中主要的软化机制,当30≤lnZ≤42时,合金发生动态回复,当23≤lnZ≤26时,合金发生动态再结晶。根据合金微观组织分析结果及热加工图,合金在较低应变速率和较高温度下变形时具有良好的塑性变形能力和细小的再结晶组织,合金较好的两个变形工艺参数区域为:区域1为变形温度935~1045 K,应变速率0.001~0.004 s−1;区域2为变形温度1045~1073 K,应变速率0.003~0.03 s−1。Abstract: In order to study warm deformation behavior of the biomedical Ni-Ti alloy, compression tests were performed on a Gleeble-3800 thermal simulator. The true stress-true strain curves were obtained. The constitutive relationship and microstructures evolution during the deformation were analyzed. The processing map was established and optimum parameters for warm deformation were determined. The results show that dynamic recovery and recrystallization are the main softening mechanism during compression. Dynamic recovery occurs when 30≤lnZ≤42 and recrystallization occurs when 23≤lnZ≤26. According to the microstructural analysis and processing map, the alloy shows better workability and fine recrystallized microstructures at low strain rates and high deformation temperatures. And the optimum deformation parameters of the alloy were determined as follows: domain 1 occurs in the temperature range of 935-1 045 K and the strain rate range of 0.001-0.004 s−1, and domain 2 occurs in the deformation temperature range of 1 045-1 073 K and strain rate range of 0.003-0.03 s−1.
-
表 1 镍钛合金的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the Ni-Ti alloy
% Ni C N O Ti 55.99 0.009 <0.003 0.032 余量 -
[1] Patel S K, Behera B, Swain B, et al. A review on NiTi alloys for biomedical applications and their biocompatibility[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2020,33:5548−5551. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.538 [2] Jani J M, Leary M, Subic A, et al. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities[J]. Materials & Design, 2014,56:1078−1113. [3] Yin Yuxia, Wang Luning, Hao Shubin, et al. Biomedical application of Ni-Ti alloy in minimally invasive intervention[J]. China Medical Devices, 2019,34(6):153−156. (尹玉霞, 王鲁宁, 郝树斌, 等. 医用镍钛记忆合金在微创介入领域的应用[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2019,34(6):153−156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2019.06.042 [4] Lu Peng, Zhao Yanan, Zhang Yanqiu, et al. Recent research of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy tube[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2013,40(3):67−74. (陆鹏, 赵亚楠, 张艳秋, 等. 镍钛形状记忆合金管材的研究进展[J]. 应用科技, 2013,40(3):67−74. [5] Hu Jie, Liu Li. Study of process techniques of Ti-Ni shape memory alloy capillarity[J]. New Technology & New Process, 2006,(6):51−52. (胡捷, 刘力. 钛镍形状记忆合金毛细管加工工艺研究[J]. 新技术新工艺, 2006,(6):51−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5311.2006.06.021 [6] 易文林. 镍钛形状记忆合金薄壁管滚珠旋压成形研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2012.Yi Wenlin. Study on ball spinning of thin-walled tube of NiTi shape memory alloy[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2012. [7] Yang Yulan, Tong Xuewen, Li Changjiang, et al. A study of the rolling process of TC2 titanium alloy tube[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2003,20(4-5):66−69. (羊玉兰, 佟学文, 李长江, 等. TC2钛合金管材工艺研究[J]. 金属学报, 2003,20(4-5):66−69. [8] Morakabati M, Aboutalebi M, Kheirandish S, et al. High temperature deformation and processing map of a NiTi intermetallic alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2011,19(10):1399−1404. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2011.05.005 [9] Shamsolhodaei A, Zarei-Hanzaki A, Ghambari M, et al. The high temperature flow behavior modeling of NiTi shape memory alloy employing phenomenological and physical based constitutive models: A comparative study[J]. Intermetallics, 2014,53:140−149. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2014.04.015 [10] Mirzadeh H, Parsa M H. Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization of NiTi intermetallic compound[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,614:56−59. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.06.063 [11] Liu Hanyuan, Yu Zhentao, Yu Sen, et al. Research on hot compressive deformation behavior of Ni-Ti shape memory alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2018,47(24):59−63. (刘汉源, 于振涛, 余森, 等. Ni-Ti形状记忆合金热压缩变形行为的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2018,47(24):59−63. doi: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.2018.24.014 [12] Zhang Honggang, He Yong, Liu Xuefeng, et al. Hot deformation behavior and constitutive relationship of Ni-Ti shape memory alloy during compression at elevated temperatures[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007,43(9):930−936. (张红钢, 何勇, 刘雪峰, 等. Ni-Ti形状记忆合金热压缩变形行为及本构关系[J]. 金属学报, 2007,43(9):930−936. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2007.09.007 [13] Wang Tianxiang, Lu Shiqiang, Wang Kelu, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing parameter optimization of Ti60 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(10):3552−3561. (王天祥, 鲁世强, 王克鲁, 等. Ti60合金的热变形行为及加工工艺参数优化[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(10):3552−3561. [14] Kim S I, Ko B C, Lee C M, et al. Evolution of dynamic recrystallisation in AISI 304 stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2003,19:1648−1652. doi: 10.1179/026708303225008284 [15] Wang C, Liu Y T, Lin T, et al. Hot compression deformation behavior of Mg-5Zn-3.5Sn-1Mn-0.5Ca-0.5Cu alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019,157:109896. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109896 [16] Zeng Weidong, Zhou Yigang, Zhou Jun, et al. Recent development of processing map theory[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006,(5):673−677. (曾卫东, 周义刚, 周军, 等. 加工图理论研究进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006,(5):673−677. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2006.05.001 [17] Prasad Y. Processing maps: A status report[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2003,12(6):638−645. doi: 10.1361/105994903322692420 [18] Prasad Y, Seshacharyulu T. Modeling of hot deformation for microstructural control[J]. International Materials Reviews, 1998,43(6):243−258. doi: 10.1179/imr.1998.43.6.243 -




 下载:
下载: