Study on transformation behavior of ultra-high strength steel for construction machinery
-
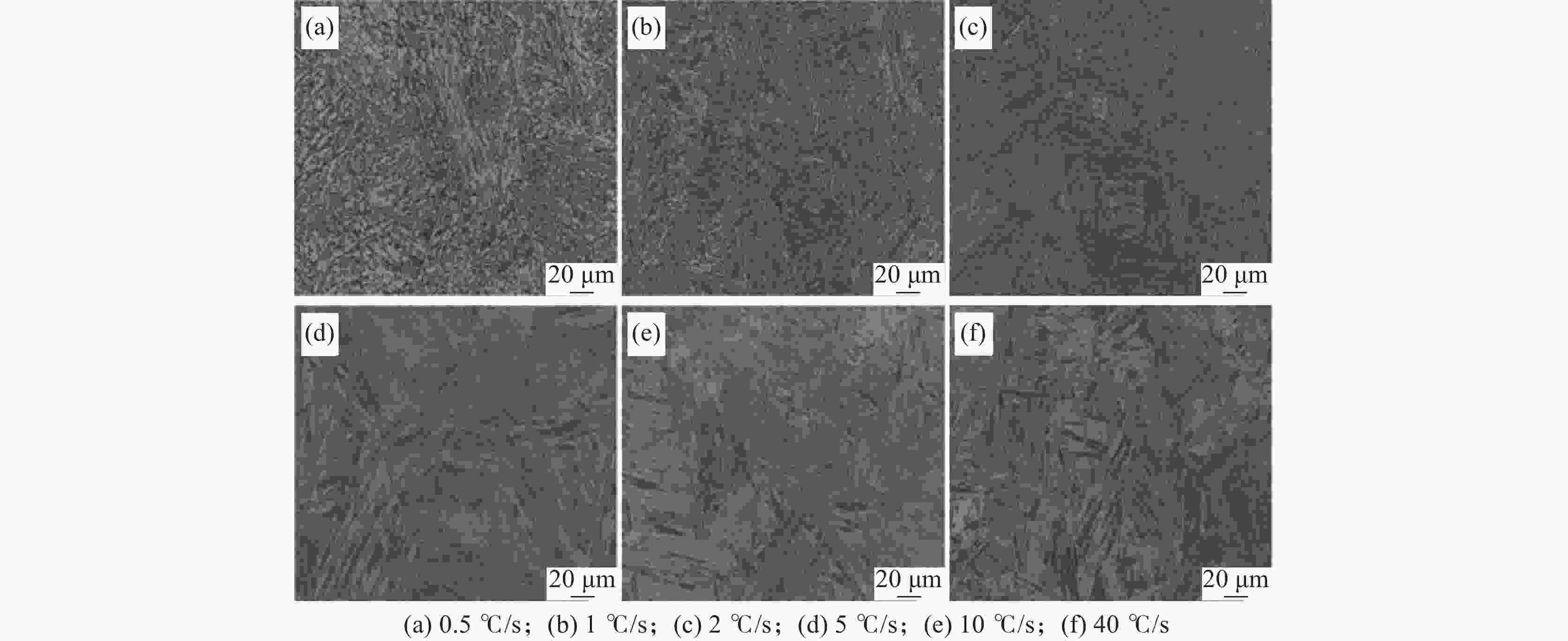
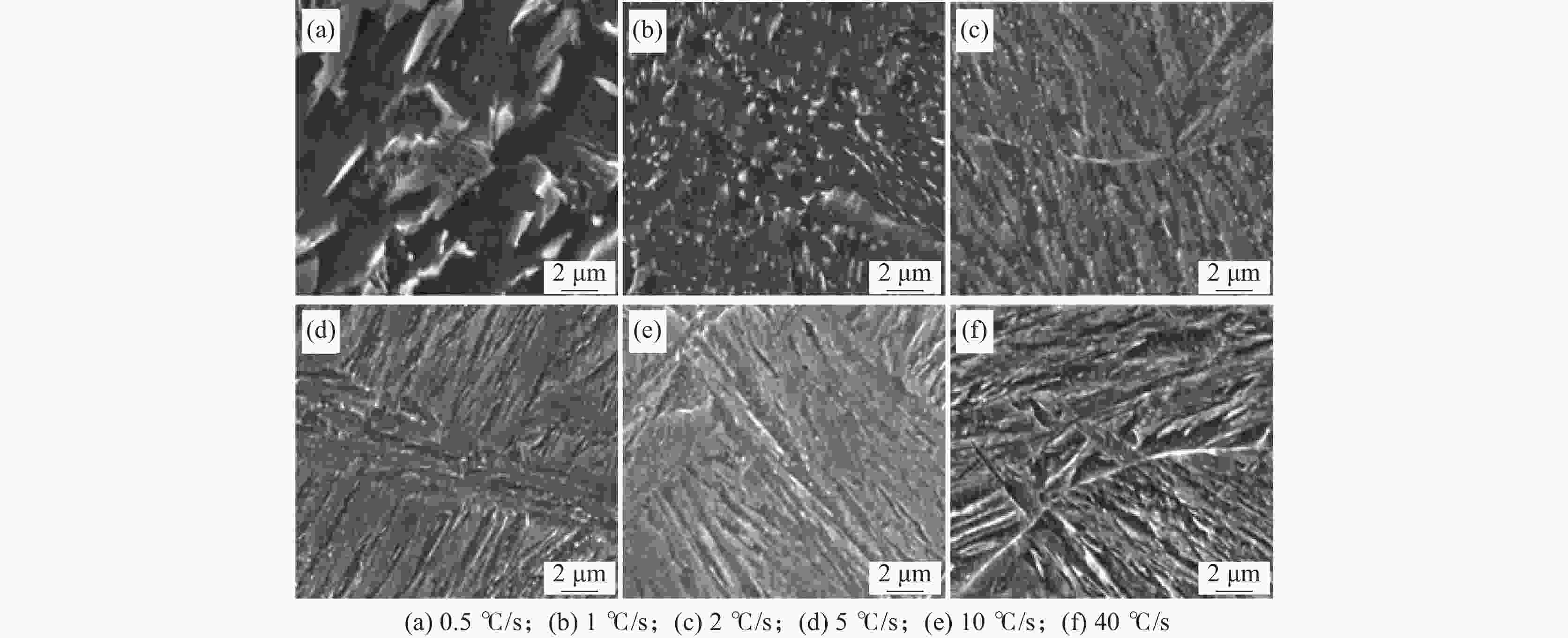
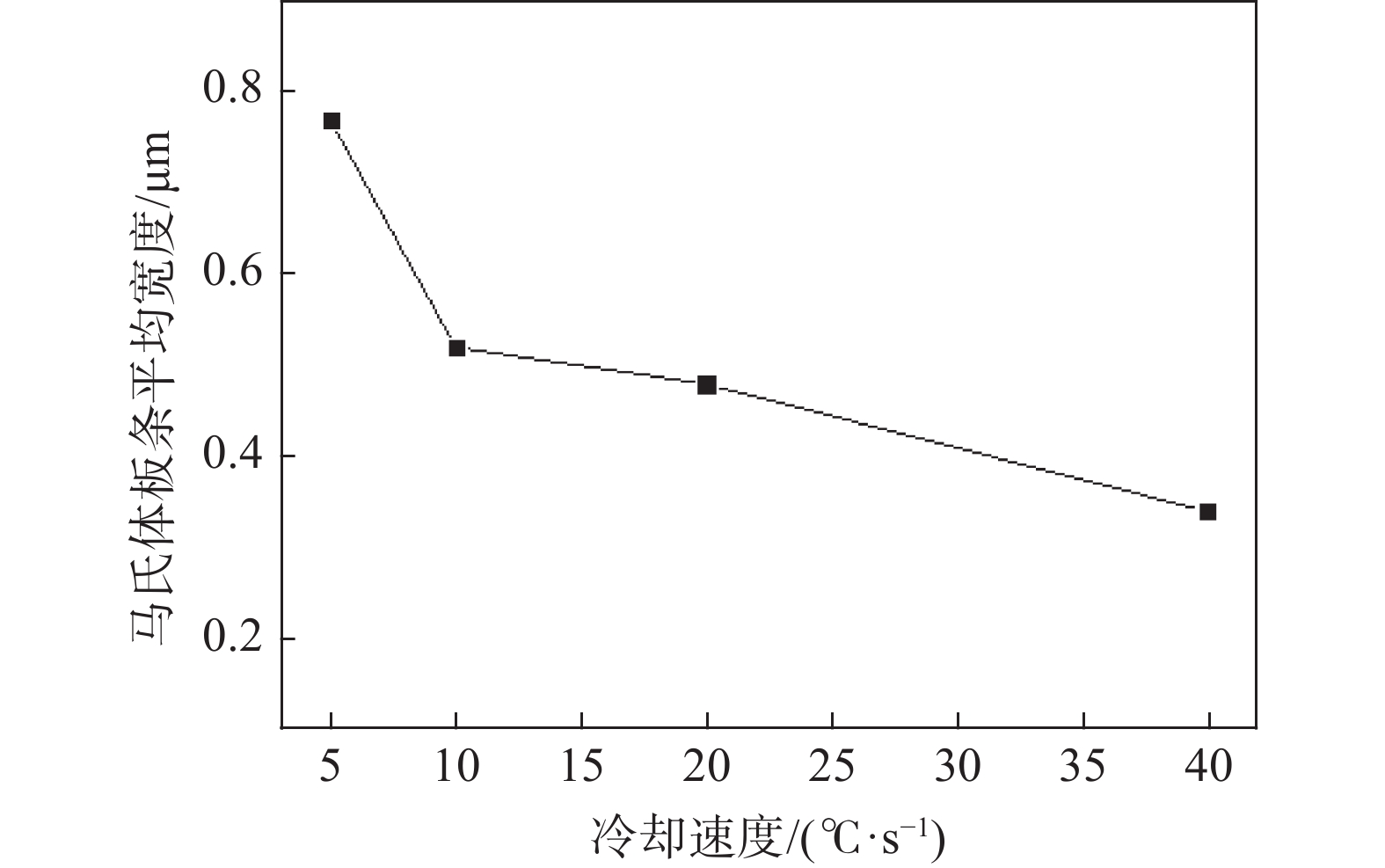
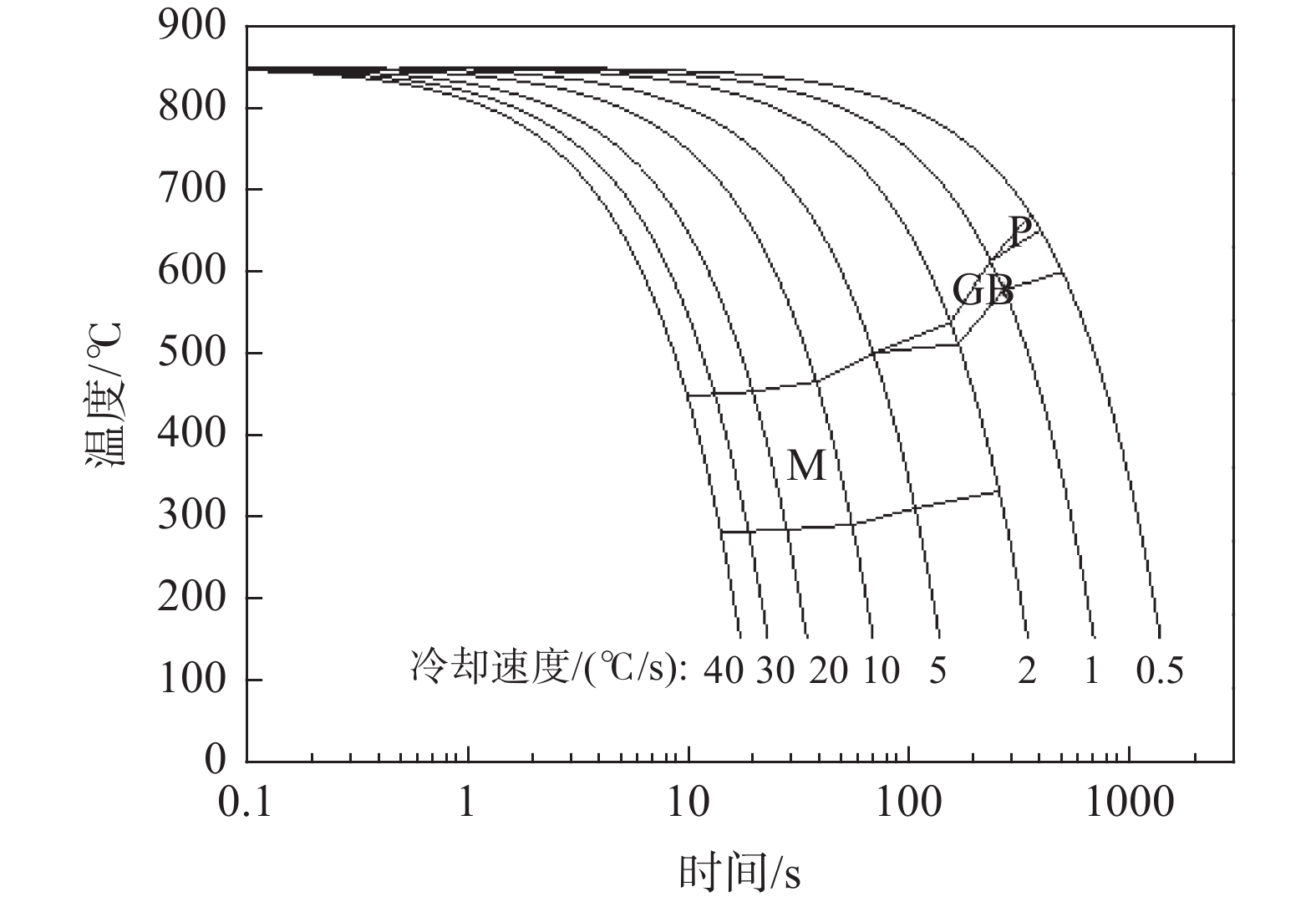
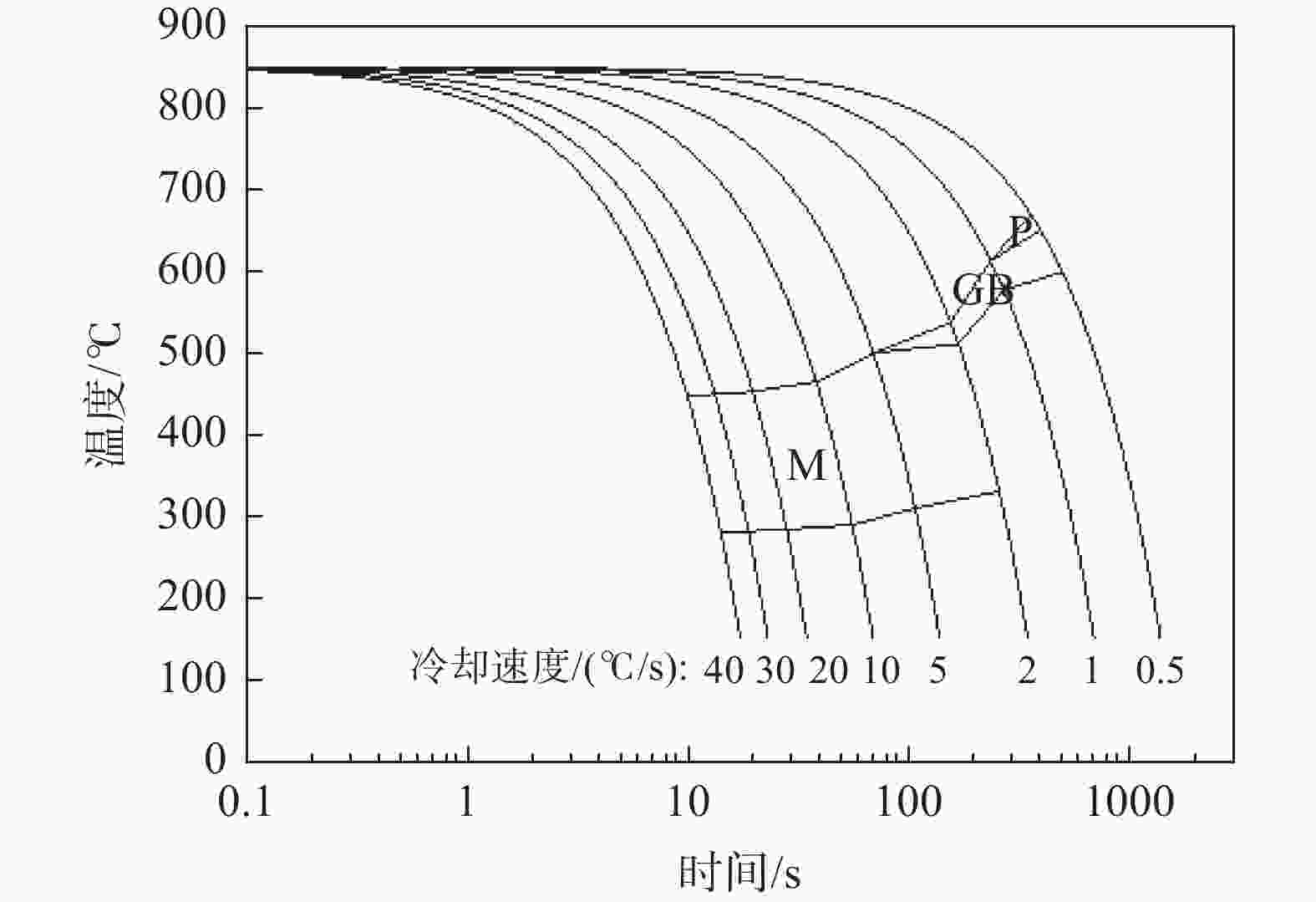
摘要: 借助MMS-200热模拟试验机研究了Cr-Mo-Ni-B系工程机械用超高强钢连续冷却条件下的相变行为,通过热膨胀曲线、光学显微镜(OM)和扫描电镜(SEM)分析了冷却速度(0.5~40 ℃/s)对其相变温度和微观组织的影响。结果表明,随着冷却速度增大,钢相变温度Bs、Bf、Ms、Mf均降低,中低温相变加强。冷却速度在2 ℃/s以下时,发生珠光体相变和贝氏体相变;冷却速度在2~5 ℃/s时,出现粒状贝氏体和板条马氏体的混合组织;冷却速度在5 ℃/s以上时,粒状贝氏体消失,微观组织为单一的板条马氏体。在中低温相变组织形成温度范围内,冷却速度对M-A岛的形貌、尺寸、数量以及马氏体板条宽度有显著的影响。随着冷速的增大,M-A岛的形貌由块状向颗粒状变化,其尺寸减小,数量增多;马氏体板条的平均宽度减小。Abstract: Transformation behavior of Cr-Mo-Ni-B ultra-high strength steel for construction machinery under continuous cooling condition was studied by means of MMS-200 thermomechanical simulator. The effect of cooling rate (0.5~40 ℃/s) on its transformation temperature and microstructure was analyzed by thermal dilatometry curves, optical microscopy (OM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results show that transformation temperatures of Bs, Bf, Ms and Mf decrease and phase transformation at medium and low temperature is promoted with the increase of cooling rate. As the cooling rate is below 2 ℃/s, pearlite and bainite transformations occur. Mixture microstructure of granular bainite and lath martensite is observed when cooling rate is in range of 2 ℃/s and 5 ℃/s. As the cooling rate is above 5 ℃/s, granular bainite disappears and fully martensitic microstructure is obtained. In the formation temperature range of medium and low temperature transformation microstructure, the morphology, size and quantity of M/A islands as well as width of martensite lath are influenced significantly by cooling rate. With the increase of cooling rate, the morphology of M/A islands is modified from blocky shape into granular shape, their size decreases and the volume amount increases. The average width of the martensite lath decreases as a result of increasing the cooling rate.
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of the experimental steel
% C Si Mn P S Nb+V+Ti Cr Mo+Ni B 0.18 0.24 0.8~1.0 0.006 <0.0011 ≤0.07 <0.45 ≤1.9 0.0019 -
[1] Akihide N, Takayuki I, Tadashi O. Development of YP 960 and 1100 MPa class ultra high strength steel plates with excellent toughness and high resistance to delayed fracture with excellent toughness and high resistance to delayed fracture for construction and industrial machinery[J]. JFE Technical Report, 2008,(11):13−18. [2] Kah P, Pirinen M, Suoranta R, et al. Welding of ultra high strength steels[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014,849:357−365. [3] Salminen A, Farrokhi F, Unt A, et al. Effect of optical parameters on fiber laser welding of ultrahigh strength steels and weld mechanical properties at subzero temperatures[J]. Journal of Laser Applications, 2016,28(2):1−7. [4] Klein M, Rauch R, Spindler H, et al. Ultra high strength steels produced by thermomechanical hot rolling – advanced properties and applications[J]. BHM Berg- und Hüttenmännische Monatshefte, 2012,157(3):108−112. [5] Wen Changfei, Deng Xiangtao, Wang Zhaodong, et al. Influence of rolling and cooling process on microstructure and properties of ultra-high strength low alloy steel Q1300[J]. Steel Rolling, 2018,35(5):6−11. (温长飞, 邓想涛, 王昭东, 等. 轧制冷却工艺对低合金超高强钢Q1300组织性能的影响[J]. 轧钢, 2018,35(5):6−11. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1003-9996.20170043 [6] Zheng Dongsheng, Liu Dan, Luo Deng, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-high strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2020,41(12):90−96. (郑东升, 刘丹, 罗登, 等. 回火温度对超高强钢微观组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2020,41(12):90−96. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2020-0175 [7] Qiang X H, Jiang X, Bijlaard F S K, et al. Mechanical properties and design recommendations of very high strength steel S960 in fire[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016,112:60−70. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.01.008 [8] Ali M, Porter D, Kömi J, et al. Effect of cooling rate and composition on microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-strength steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2019,26(12):1350−1365. doi: 10.1007/s42243-019-00276-0 [9] Mandal G, Dey I, Mukherjee S, et al. Phase transformation and mechanical properties of ultrahigh strength steels under continuous cooling conditions[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022,19:628−642. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.033 [10] Bandyopadhyay P S, Ghosh S K, Kundu S, et al. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of thermomechanically processed ultrahigh-strength steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011,42(9):2742−2752. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0711-2 [11] Esterl R, Sonnleitner M, Schnitzer R. Influences of thermomechanical treatment and Nb micro-alloying on the hardenability of ultra-high strength steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2019,50(7):3238−3245. doi: 10.1007/s11661-019-05235-8 [12] Wang Huiling, Sun Dianqiang, Cheng Huimei, et al. Research on production technology of 900 MPa light gauge quenched and tempered high strength plate[J]. Wide and Heavy Plate, 2021,27(3):34−36. (王会岭, 孙电强, 成慧梅, 等. 900 MPa级薄规格调质高强钢生产技术研究[J]. 宽厚板, 2021,27(3):34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7864.2021.03.009 [13] 高志玉. 特厚板用HSLA钢的热变形行为与组织演变研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2016.Gao Zhiyu. Study on hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of HSLA steel for extra thick plate[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2016. [14] Zhang Shouqing, Hu Xiaofeng, Du Yubin, et al. Cross section effect of Ni-Cr-Mo-B ultra-heavy steel plate for offshore platform[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinaca, 2020,56(9):1227−1238. (张守清, 胡小峰, 杜瑜宾, 等. 海洋平台用Ni-Cr-Mo-B超厚钢板的截面效应[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(9):1227−1238. [15] 王顺兴. 金属热处理原理与工艺(第二版)[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2009: 131.Wang Shunxing. Metal heat treatment principles and process (Second Edition)[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2009: 131. [16] Mousavi Anijdan S H, Yue S. The effect of cooling rate, and cool deformation through strain-induced transformation, on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of microalloyed steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012,43(4):1140−1162. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0958-7 [17] Porter D A, Easterling K E, Sherif M Y. Phase transformations in metals and alloys (Third Edition)[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009: 401−404. [18] Dhua S K, Mukerjee D, Sarma D S. Effect of cooling rate on the as-quenched microstructure and mechanical properties of HSLA-100 steel plates[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003,34(11):2493−2504. doi: 10.1007/s11661-003-0009-0 -




 下载:
下载: