Mathematical simulation and industrial experiment study on bottom blowing process of 40 t eccentric arc furnace
-
摘要: 通过对某钢厂40 t偏心电弧炉底吹工艺建立数学模型,利用流体计算软件Fluent数值模拟了不同底吹条件下电弧炉熔池内的流体流动特征,分析了不同底吹流量对流体流动的作用规律。结果表明:随吹气量的增大, 熔池表面平均速度不断增大,得出最优的吹气量为30~40 m3/h。同时结合工业生产数据发现,采用底吹搅拌技术后能加速电弧炉熔池的传热和传质速度,缩短冶炼时间,降低生产成本。Abstract: This paper establishes a mathematical model of bottom gas blowing for a 40 t eccentric electric arc furnace in a steel plant. The fluid flow characteristics in the bath of an electric arc furnace under different bottom blowing conditions were numerically simulated using Fluent software. The effect of different bottom blowing rates on fluid flow is analyzed. The results show that the blowing gas increases the average velocity of the molten pool surface. The optimum blowing rate is 30 ~ 40 m3/h. At the same time, combined with the industrial production data, it is found that the bottom-blown stirring technology can speed up the heat and mass transfer of the melting pool, shorten the smelting time, and reduce the production cost.
-
Key words:
- eccentric arc furnace /
- bottom blowing /
- mathematical simulation /
- flow characteristics
-
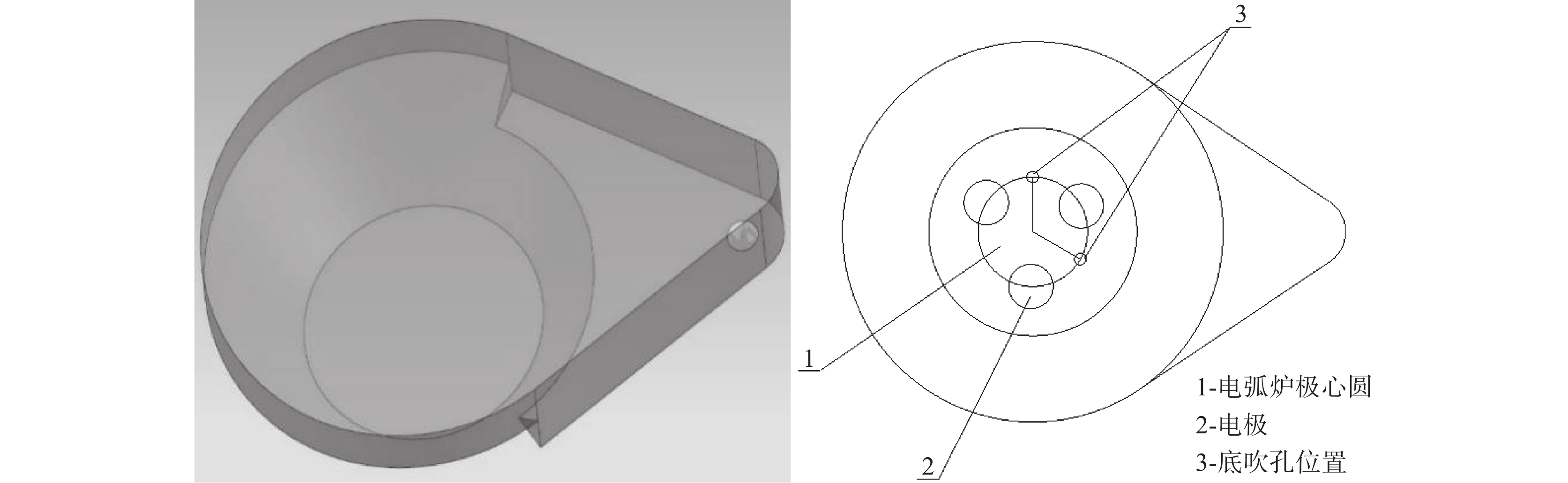
表 1 40 t偏心电弧炉参数
Table 1. 40 t Eccentric arc furnace parameters
熔池高度/mm 熔池底部直径/mm 熔池上部直径/mm 极心圆直径/mm 底吹孔布置直径/mm 底吹孔直径/mm 900 2000 3560 1050 1400 125 表 2 有无底吹降耗指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of the indexes of bottom-blowing and loss-reducing
指标 炉龄/次 冶炼周期
/min电极消耗/(kg·t−1) 电耗/(kWh·t−1) 耐材消耗/(kg·t−1) 无底吹 118 114 4.82 381 14.4 有底吹 152 106 4.65 360 12.6 表 3 终渣渣样对比
Table 3. Comparison of final slag samples
% 项目 CaO FeO MgO MnO SiO2 Al2O3 Cr2O3 TFe 无底吹 42,52 5.86 9.64 3.68 33.52 5.28 17.98 5.27 有底吹 35.85 4.67 7.13 2.74 29.26 4.13 12.79 3.95 -
[1] Zhang Bo. Development trend of steelmaking technology[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993,14(3):62−68. (张波. 炼钢技术发展动向[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993,14(3):62−68. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1993.03.012 [2] Zeng Xianguang. Electric arc furnace bottom argon stirring process[J]. Special Steel, 2000,21(3):1−5. (曾先光. 电弧炉底吹氩气搅拌工艺[J]. 特殊钢, 2000,21(3):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2000.03.001 [3] Cheng Zhiwang, Xu Yong. Process technology of stainless steel smelting[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2011,17(1):1−5. (程志旺, 许勇. 不锈钢冶炼工艺技术[J]. 特钢技术, 2011,17(1):1−5. doi: 10.16683/j.cnki.issn1674-0971.2011.01.015 [4] Dong Kai, Li Jinwei, Zhu Changfu, et al. The application of bottom blowing stirring to Consteel furnace[J]. Industrial Heating, 2011,(1):60−62. (董凯, 李金伟, 朱长富, 等. 底吹搅拌在Consteel电炉中的应用[J]. 工业加热, 2011,(1):60−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2011.01.018 [5] Liu Jinkun, Rui Shusen, Wu Zhenting, et al. Flow state analysis in bath of bottom-blown arc furnace[J]. Journal of Northeastern University, 1995,16(3):298−301. (刘金琨, 芮树森, 武振廷, 等. 底吹电弧炉熔池流动状态的解析[J]. 东北大学学报, 1995,16(3):298−301. [6] 李宝宽, 赫冀成. 炼钢中的计算流体力学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998.Li Baokuan, He Jicheng. Computational fluid dynamics in steelmaking processes[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998. [7] Yang Yadi, Zhao Jing, Cui Jianzheng, et al. Numerical simulation on interfacial behavior and mixing phenomena in three-phase argon-stirred ladles[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(5):138−148. (杨亚迪, 赵晶, 崔剑征, 等. 三相氩气搅拌钢包内界面行为及混合现象的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(5):138−148. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.05.022 [8] Jiang Xingliang, Ni Hongwei, Wang Shejiao, et al. A mathematical simulation for optimization of 70 t ladle bottom argon blowing process[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2013,12(2):103−109. (蒋兴亮, 倪红卫, 王社教, 等. 70 t钢包底吹氩工艺优化的数理模拟研究[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2013,12(2):103−109. -





 下载:
下载: