Study on the effect of calcined seed crystal addition on the quality of TiO2
-
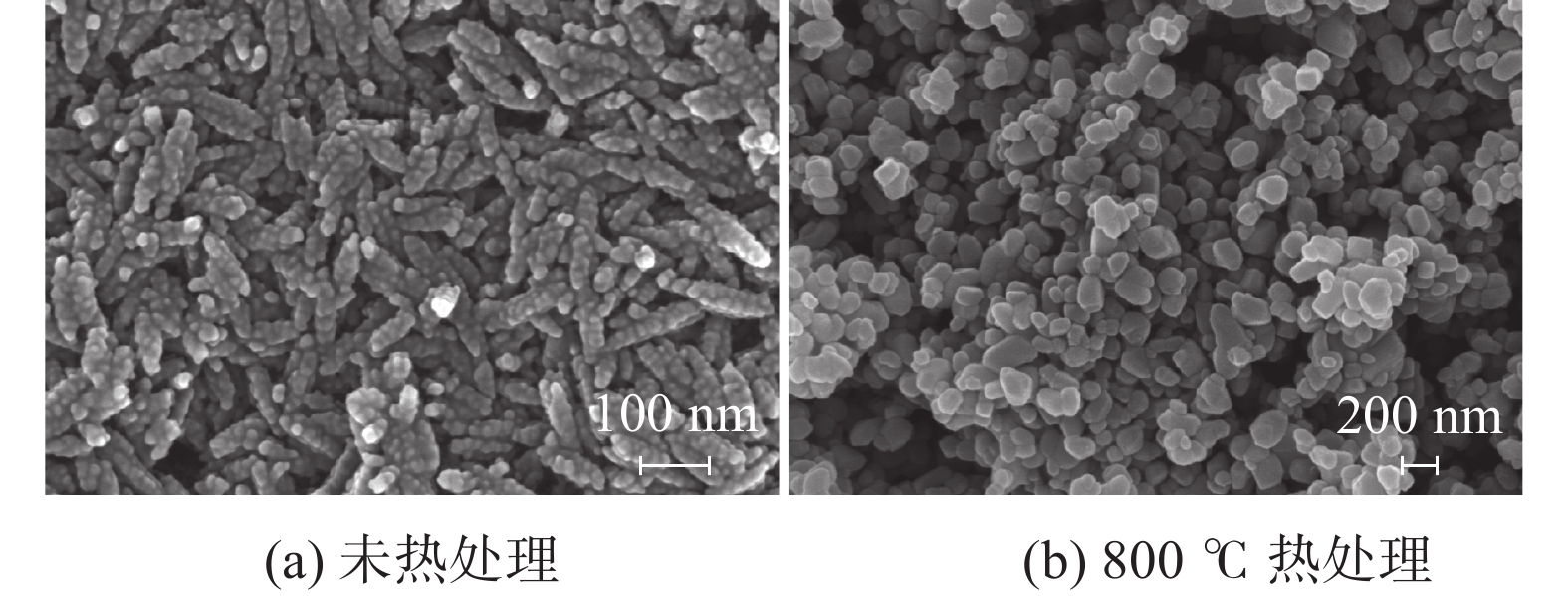
摘要: 以水解偏钛酸和煅烧晶种为原料,在偏钛酸中加入不同比例的煅烧晶种,通过调整煅烧温度制备金红石含量98%~99%的钛白初品,考察煅烧晶种加量对煅烧温度的影响。然后通过XRD、SEM等手段对钛白粉的晶体结构、形貌、粒度分布和颜料性能进行分析。结果表明:随着煅烧晶种加量增加,金红石合格所需煅烧温度呈现下降趋势,煅烧晶种加量在4%~6%时对金红石合格所需煅烧温度影响不大。随着晶种加量的增加,初品平均粒径呈现下降趋势,离散系数呈现先下降后增加的趋势,当晶种加量达到6%,离散系数最小。随煅烧晶种加量的增加,铝系和锌系盐处理样品的蓝相(SCX)均随晶种加量的增加呈现增加趋势,消色力(TCS)均呈现先增加后降低的趋势,煅烧晶种加量在5%左右时,样品消色力达到最佳值。Abstract: Using hydrolyzed metatitanic acid and calcined seed crystals as raw materials, different proportions of calcined seed crystals were added to metatitanic acid, and the calcination temperature was adjusted to prepare the TiO2 product with a rutile content of 98% to 99%. The influence of the amount of calcined seed crystals on the calcining temperature was investigated. Then the crystal structure, morphology, particle size distribution and pigment properties of the TiO2 were analyzed by XRD, SEM and other means. The results show that as the content of calcined seed crystals increases, the calcination temperature required for qualified rutile shows a downward trend. When the amount of calcined seed crystals increases from 4% to 6%, the required calcination temperature has little effect. As the amount of seed crystals increases, the average particle size of the TiO2 product shows a downward trend, and the dispersion coefficient shows a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. When the amount of seed crystals increases to 6%, the dispersion coefficient is the smallest. With the increase in the amount of calcined seed crystals, the SCX value of the aluminum-based and zinc-based salt treated samples showed an increasing trend with the increase in the amount of seed crystals, and the TCS value showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the amount of calcined seed crystals is about 5%, the TCS value of the sample reaches the best value.
-
Key words:
- titanium dioxide /
- calcined seed crystal /
- particle size /
- dispersion coefficient /
- pigment performance
-
表 1 煅烧晶种加量对晶胞参数的影响
Table 1. The effect of calcined seed crystal addition on unit cell parameters
类别 晶种加量/% 锐钛相 金红石相 a/nm c/nm 晶胞体积/nm3 a/nm c/nm 晶胞体积/nm3 铝系 2 0.378 387 2 0.951 015 3 0.136 16 0.459 279 4 0.295 787 7 0.062 39 4 0.378 405 1 0.950 974 4 0.136 17 0.459 280 8 0.295 779 2 0.062 39 6 0.378 414 5 0.951 006 9 0.136 18 0.459 302 3 0.295 802 1 0.062 40 8 0.378 427 6 0.951 021 2 0.136 19 0.459 308 0 0.295 807 8 0.062 40 锌系 2 0.378 429 5 0.951 082 2 0.136 20 0.459 310 5 0.295 826 0 0.062 41 4 0.378 432 3 0.951 098 5 0.136 21 0.459 309 7 0.295 824 1 0.062 41 6 0.378 446 2 0.951 068 0 0.136 21 0.459 330 2 0.295 833 6 0.062 42 8 0.378 452 3 0.950 995 6 0.136 21 0.459 311 3 0.295 824 2 0.062 41 -
[1] Zhao Yan, Wang Lina, Qi Tao, et al. Preparation and application of calcining seed in the production process of rutile titanium pigment[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009,9(4):750−753. (赵岩, 王丽娜, 齐涛, 等. 金红石型钛白粉生产过程中煅烧晶种的制备与应用[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009,9(4):750−753. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.04.020 [2] Wang Zinan, Chen Kui, Zhu Jiawen, et al. Effects of crystal seeds and salt dopants on phase transformation of TiO2 in calcination process[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020,52(3):45−50. (王子楠, 陈葵, 朱家文, 等. 晶种和盐处理剂对煅烧过程中二氧化钛晶型转变的影响[J]. 无机盐工业, 2020,52(3):45−50. doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2019-0210 [3] Wu Jianchun, Lu Ruifang, Liu Chan, et al. Analysis of factors affecting the whiteness of titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(1):13−17. (吴健春, 路瑞芳, 刘婵, 等. 钛白粉白度影响因素分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(1):13−17. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.01.003 [4] Li Jianjun, Yang Zhen, Li Tianda, et al. Study on the influence of the particle size of titanium dioxide on powder coatings[J]. China Coatings, 2017,32(9):60−63. (李建军, 杨振, 李添达, 等. 钛白粉粒径分布对粉末涂料性能的影响研究[J]. 中国涂料, 2017,32(9):60−63. doi: 10.13531/j.cnki.china.coatings.2017.09.012 [5] Rong Eryi, Zhu Jiawen, Chen Kui, et al. Effects of calcining seed, phosphate and magnesium on titanium dioxide crystal[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2016,48(7):21−24. (容尔益, 朱家文, 陈葵, 等. 煅烧晶种和磷、镁对二氧化钛晶体的影响[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016,48(7):21−24. [6] Su Yanfang, Li Zhenqiu, Cao Chengyun. Preparation of rutile type high quality titanium dioxide[J]. Paper Science & Technology, 2012,31(1):47−49. (苏彦方, 黎振球, 曹承赟. 金红石型高品质二氧化钛的制备[J]. 造纸科学与技术, 2012,31(1):47−49. [7] Ma Weiping, Sun Ke, Cheng Chaoyan, et al. Effect of salt treating agent on conversion rate of rutile for titanium dioxide hydrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(5):45−50. (马维平, 孙科, 成朝艳, 等. 水合二氧化钛掺加盐处理剂对金红石含量的影响研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(5):45−50. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.05.008 [8] Xu Zhen, Deng Lin, Wang Bin. Effect of salt treatment on preparation of rutile type titanium dioxide[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2021,49(7):49−51,84. (徐振, 邓林, 王彬. 盐处理剂对金红石型钛白粉制备的影响研究[J]. 广州化工, 2021,49(7):49−51,84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2021.07.017 -





 下载:
下载: