Reduction kinetics of iron oxide in metatitanic acid by organic reductant
-
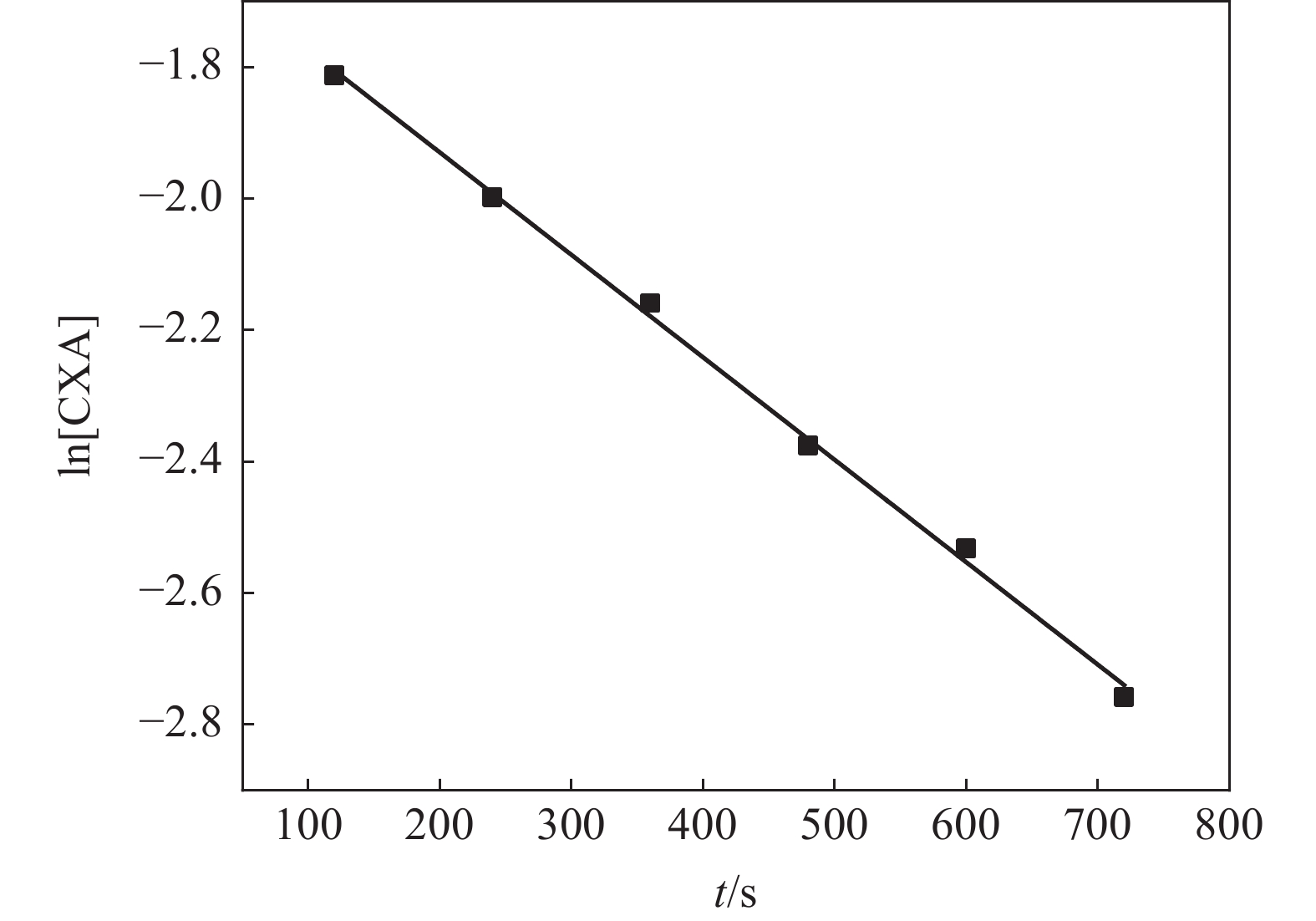
摘要: 研究了一种有机还原剂对偏钛酸中氧化铁的还原过程动力学,以探讨过程机理,指导实际生产。结果表明,该还原反应有机还原剂的反应分级数为1,氧化铁的反应分级数为2。在有机还原剂过量的情况下,氧化铁的还原过程速率大小与反应温度、搅拌强度和体系酸度有关。还原速率随温度的增加而增加,表观反应活化能为51.73 kJ/mol。还原速率随搅拌强度的增加先增加而后变化不大,表明在一定的搅拌强度下,扩散步骤不是过程的控制环节。还原速率随酸度的增加先增加后减小,这与偏钛酸中氧化铁的溶解和有机还原剂的分解有关。推断在有机还原剂过量及一定的搅拌强度下,还原反应步骤是有机还原剂对偏钛酸中氧化铁的还原过程的控制环节。Abstract: The reduction kinetics of iron oxide in metatitanic acid by organic reductant was investigated in the paper to explore the process mechanism and guide the actual production. The results show that the step reaction order is one for the organic reductant and two for iron oxide. Under the condition of excessive reductant, the reduction rate of iron oxide is affected by reaction temperature, stirring strength and acidity of metatitanic acid. The reduction rate increases with increasing temperature, and the apparent activation energy in the reaction is 51.73 kJ/mol. The reduction rate first increases and then changes slowly with increasing stirring strength, which shows that the reduction rate is not controlled by diffusion step under higher stirring strength. The reduction rate first increases and then decreases with increasing acidity of metatitanic acid, which was relevant to the dissolution of iron oxide and the resolution of organic reductant. Therefore, it can be inferred that the reduction rate of iron oxide in metatinic acid by organic reductant is controlled by reduction reaction step under the conditions of excessive organic reductant dosage and certain stirring intensity.
-
Key words:
- metatitanic acid /
- iron oxide /
- reduction /
- organic reductant /
- kinetics
-
表 1 不同温度下的反应速率常数
Table 1. The reaction rate constants under different temperatures
T/℃ k /(m3·mol−1·s−1) 40 9.01×10−4 45 15.0×10−4 50 18.9×10−4 55 25.6×10−4 60 30.5×10−4 表 2 不同搅拌强度下的反应速率常数
Table 2. The reaction rate constants under different stirring strength
搅拌强度/(r·min−1) k /(m3·mol−1·s−1) 100 8.71×10−4 200 8.92×10−4 300 8.97×10−4 400 9.01×10−4 表 3 不同酸度下的反应速率常数
Table 3. The reaction rate constants under different acidity
cH2 SO4/(g.dm−3) k /(m3·mol−1·s−1) 0.5 9.01×10−4 1 9.65×10−4 2 9.81×10−4 5 9.41×10−4 -
[1] 唐振宁. 钛白粉的生产与环境治理[M]. 北京: 化工工业出版社, 2000.Tang Zhenning. The production of titanium dioxide and environmental treatment[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000. [2] Zeng Rui. Contrast of two kinds of bleaching technologies for metatitanic acid[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2004,21(3):44−46. (曾瑞. 两种偏钛酸漂白工艺的对比[J]. 钛工业进展, 2004,21(3):44−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.03.014 [3] Huang Lili. A new reducing agent in bleaching technology for titanium dioxide production by sulfuric acid method[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2021,(4):174−175. (黄丽丽. 一种新型的硫酸法钛白生产漂白还原剂[J]. 科学技术创新, 2021,(4):174−175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2021.04.078 [4] Christine Poggenburg, Robert Mikutta, Axel Schippers, et al. Impact of natural organic matter coatings on the microbial reduction of iron oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018,224:223−248. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.01.004 [5] Hu Jinglong, Zeng Qiang, Chen Hongyu, et al. Effect of bacterial cell addition on Fe(III) reduction and soil organic matter transformation in a farmland soil[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022,325:25−38. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.03.018 [6] Steven A Banwart. Reduction of iron (III) minerals by natural organic matter in groundwater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999,63(19-20):2919−2928. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00267-7 [7] Chen Jie, Gu Baohua, Richard A Royer, et al. The roles of natural organic matter in chemical and microbial reduction of ferric iron[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2003,307(1-3):167−178. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00538-7 [8] Su Chang, Zhang Meiling, Lin Luoying, et al. Reduction of iron oxides and microbial community composition in iron-rich soils with different organic carbon as electron donors[J]. International Biodeterioration, 2020,148(3):104881−104889. [9] Zhang Ruichang, Tu Chen, Zhang Haibo, et al. Enhancing effects of dissolved and media surface-bound organic matter on titanium dioxide nanoparticles transport in iron oxide-coated porous media under acidic conditions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022,438:129421−129432. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129421 [10] Abdubaki Mohamed Hussen Shadi, Mohammad Anuar Kamaruddin, Noorzalila Muhammad Niza, et al. Facile isotherms of iron oxide nanoparticles for the effectively removing organic and inorganic pollutants from landfill leachate: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics modelling[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022,10(3):107753−107764. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107753 [11] Xu Renkou. Kinetics of reduction and dissolution of iron oxides in soils by organic compounds[J]. Tropical and Subtropical Soil Science, 1994,3(2):71−76. (徐仁扣. 土壤中氧化铁的有机还原溶解动力学[J]. 热带亚热带土壤科学, 1994,3(2):71−76. -





 下载:
下载: