Synthesis and properties of the diatomite/BiVO4 composite photocatalysts
-
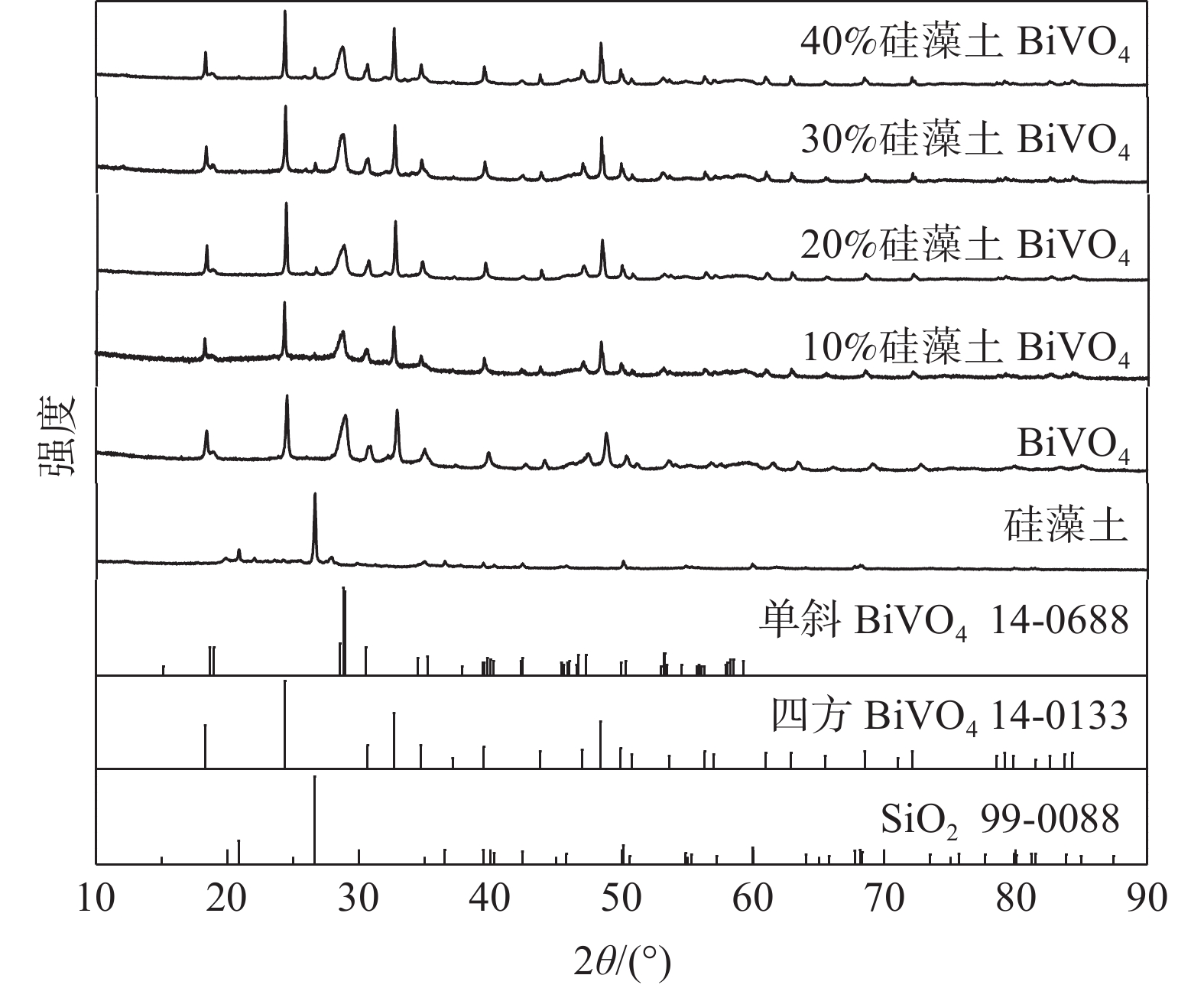
摘要: 采用液相沉淀法制备了不同硅藻土含量(5%~80%)的硅藻土/BiVO4复合材料,利用XRD和UV-Vis对样品进行了表征。结果表明,复合材料为单斜BiVO4、四方BiVO4和SiO2混合相。升高煅烧温度可使BiVO4向单斜相转化,且在较高煅烧温度时,增大硅藻土的含量,有助于BiVO4进一步转化为单斜相。硅藻土含量为5%~30%的样品的光降解率比BiVO4有不同程度的提升,硅藻土的最佳含量为10%。在煅烧温度450 ℃,光催化时间2 h,罗丹明B浓度10 mg/L的条件下,复合材料的去除率和光降解率分别高达100%和60.41%。空穴是材料光降解罗丹明B的主要活性物种,复合材料光催化性能提升可归因于硅藻土良好的吸附性、对BiVO4的分散性以及形成的单斜相BiVO4/四方相BiVO4/SiO2混相p-n异质结,其提升了材料对罗丹明B的吸附,增大了表面活性位点和比表面积,加速了光生载流子的分离与传输,在有机污染物废水处理方面具有较好的应用前景。Abstract: The diatomite/BiVO4 composite materials with different diatomite content (5%~80%) were prepared by liquid precipitation method. The samples were characterized by XRD and UV-Vis. The results show that the composite consists of monoclinic BiVO4, tetragonal BiVO4 and SiO2. BiVO4 can be transformed into monoclinic phase by increasing the calcination temperature, and at a higher calcination temperature, the increase of diatomite content is conducive to the further transformation of BiVO4 into monoclinic phase. Compared with BiVO4, the photodegradation efficiencies of the composites with the diatomite contents of 5%~30% are improved in different degrees, and the optimum content of the diatomite is 10%. Under the conditions of calcination temperature of 450 ℃, photocatalytic time of 2 h, rhodamine B concentration of 10 mg/L, the removal and photodegradation efficiencies of the sample for rhodamine B can reach 100% and 60.41%, respectively. Holes are the main active species for the photodegradation of rhodamine B. The enhanced photocatalytic performance of the composite materials can be attributed to the good adsorption of the diatomite, the good dispersion of BiVO4 and the formation of monoclinic BiVO4/tetragonal BiVO4/SiO2 miscible p-n heterojunctions, which improve the adsorption for rhodamine B, increase the surface active site and specific surface area, and accelerate the separation and transmission of photoinduced carriers, with promising application for the treatment of organic pollutant wastewater.
-
Key words:
- BiVO4 /
- photocatalytic /
- diatomite /
- liquid phase precipitation /
- degradation rate
-
表 1 L9(34)正交试验因素及水平
Table 1. The factors and levels of L9(34) orthogonal test
水平 因素A
(煅烧温度/℃)因素B
(光催化时间/min)因素C
(罗丹明B浓度/(mg·L−1))1 450 120 10 2 500 90 5 3 400 60 15 表 2 L9(34)正交试验方案及结果
Table 2. L9 (34) orthogonal test schemes and results
序号 因素A 因素B 因素C 空列 降解率/% 1 1(450) 1(120) 1(10) 1 60.41 2 1(450) 2(90) 2(5) 2 49.77 3 1(450) 3(60) 3(15) 3 35.86 4 2(500) 1(120) 2(5) 3 46.72 5 2(500) 2(90) 3(15) 1 32.23 6 2(500) 3(60) 1(10) 2 47.16 7 3(400) 1(120) 3(15) 2 34.74 8 3(400) 2(90) 1(10) 3 46.83 9 3(400) 3(60) 2(5) 1 38.51 K1 1.46 1.42 1.54 1.31 K2 1.26 1.29 1.35 1.32 K3 1.20 1.22 1.03 1.29 极差R 0.26 0.20 0.51 0.03 因素主→次 CAB 优方案 A1B1C1 -
[1] Kudo A, Ueda H K, Mikami I. Photocatalytic O2 evolution under visible light irradiation on BiVO4 in aqueous AgNO3 solution[J]. Catalysis Letters, 1998,53(3-4):229−230. [2] Tokunaga S, Kato H, Kudo A. Selective preparation of monoclinic and tetragonal BiVO4 with scheelite structure and their photocatalytic properties[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2001,13(12):4624−4628. doi: 10.1021/cm0103390 [3] Kudo A, Omori K, Kato H. A novel aqueous process for preparation of crystal form-controlled and highly crystalline BiVO4 powder from layered vanadates at room temperature and its photocatalytic and photophysical properties[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1999,121(49):11459−11467. doi: 10.1021/ja992541y [4] Monfort O, Plesch Gustav. Bismuth vanadate-based semiconductor photocatalysts: a short critical review on the efficiency and the mechanism of photodegradation of organic pollutants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25: 19362-19379. [5] Chen S, Huang D L, Xu P, et al. Facet-engineered surface and interface design of monoclinic scheelite bismuth vanadate for enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(2): 1024-1059. [6] Liu Jingjing, Zhang Zelan, Li Shi, et al. Research progress on modification of bismuth vanadate visible light photocatalytic materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2021,35(17):17163−17177, 17184. (刘景景, 张泽兰, 李诗, 等. 钒酸铋可见光催化材料的改性研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021,35(17):17163−17177, 17184. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20040162 [7] Liu Jingjing, Zhao Wei. Research progress on rare earth modified bismuth vanadate photocatalytic materials[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021,33(11):2081−2095. (刘景景, 赵伟. 稀土改性钒酸铋光催化材料的研究进展[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2021,33(11):2081−2095. [8] He Hongbo, Luo Yimin, Luo Zhuangzhu, et al. Diatomite-based material as an adsorbent or photocatalyst for water treatment[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2019,31(4):561−570. (何洪波, 罗一旻, 罗荘竹, 等. 硅藻土基吸附与光催化材料在水处理中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2019,31(4):561−570. doi: 10.7536/PC180919 [9] Hu Hongliang, Gao Haoyue. Research progress of diatomaceous earth based photocatalytic composites[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021,50(7):2002−2007. (胡洪亮, 高皓月. 硅藻土基光催化复合材料研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021,50(7):2002−2007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.07.055 [10] Yu Yinghao, Zhang Ting, Wang Zekang, et al. Research progress on treatment of organic pollutants by diatomite and its complexes[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2022,50(1):308−312. (于颖浩, 张婷, 王泽康, 等. 硅藻土及其复合物处理有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2022,50(1):308−312. doi: 10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2022.01.062 [11] 崔天晴. BiVO4/硅藻土复合光催化剂的水热制备及其光催化性能研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.Cui Tianqing. Hydrothermal fabrication of BiVO4/diatomtite composite photocatalysts and their photocatalytic performance[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021. [12] Hua C L, Liu S X, Ren S X, et al. Preparation of visible light-responsive photocatalytic paper containing BiVO4@diatomite/MCC/PVBCFs for degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020,202:110897. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110897 [13] 王燕南. 可见光响应型铋系光催化剂的制备及性能研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2014.Wang Yannan. The preparation performance study of visible-light-responsive bismuth-base photocatalysts[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2014. [14] Xiao Liguang, Zhang Xiaotong, Yan Gang, et al. Preparation and the photocatalytic properties of diatomite/TiO2/graphene oxide composite materials[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2019,48(4):712−717, 724. (肖力光, 张晓彤, 闫刚, 等. 硅藻土/TiO2/氧化石墨烯复合材料的制备及其光催化性能研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2019,48(4):712−717, 724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.04.025 [15] 王敏, 朱彤, 吕春梅. 钒酸铋光催化剂及其应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017.Wang Min, Zhu Tong, Lv Chunmei. BiVO4 photocatalyst and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industy Press, 2017. [16] Xiao Liguang, Zhang Yichao, Pang Bo, et al. Effect of low temperature second calcination on pore size distribution and component of diatomite[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018,37(10):3201−3205. (肖力光, 张艺超, 庞博, 等. 低温二次焙烧对硅藻土孔径分布及组分的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018,37(10):3201−3205. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2018.10.031 [17] Xiao Liguang, Zhang Yichao. Acid leaching and roasting treatment of diatomite and its influence on functionality[J]. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University, 2017,34(6):4−8. (肖力光, 张艺超. 硅藻土的酸浸和焙烧处理及对其功能性的影响[J]. 吉林建筑大学学报, 2017,34(6):4−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0185.2017.06.002 [18] Liu Jingjing, Zhang Zelan, Zhao Wei. Synthesis and properties of Tb modified BiVO4/BiOCl composite photocatalysts[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(4):39−46. (刘景景, 张泽兰, 赵伟. Tb改性BiVO4/BiOCl复合光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(4):39−46. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.04.007 [19] GuoTianzhong, Xu Zhiyong. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of nano TiO2/diatomite composite material[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2017,49(4):79−82. (郭天中, 徐志永. 纳米二氧化钛/硅藻土复合材料制备及光催化性能研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(4):79−82. -





 下载:
下载: