Study on the technology of enhanced reduction-magnetic separation of titanium and iron from calcium-based vanadium extraction tailings
-
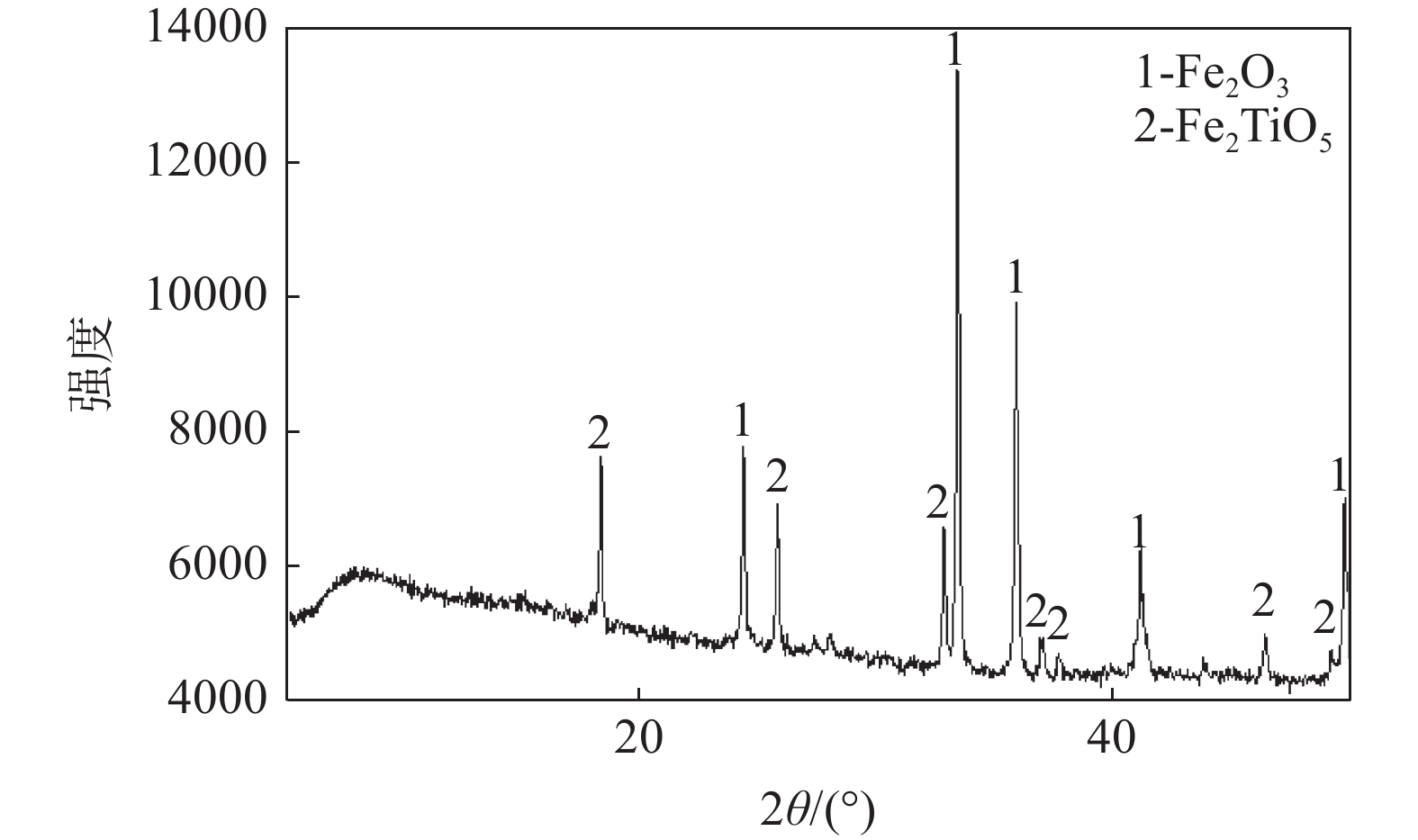
摘要: 采用直接还原-磁选方法从钒钛磁铁矿直接提钒尾渣中回收Fe,在还原温度1250 ℃、还原时间2 h、还原剂用量为尾渣质量的20%的条件下,球团的金属化率为92.71%。在球团中加入5% CaCO3并延长保温时间至6 h后,Fe晶粒的平均直径从14.53 μm增加至25.39 μm。通过对Fe晶粒的生长速率拟合发现,加入CaCO3后,晶粒生长速率常数从0.26 μm2/min提高至1.45 μm2/min。加入CaCO3的直接还原球团经过磁选后,可以得到TFe含量为90.72 %的直接还原铁和TiO2含量为41.75 %的含钛渣,Fe的回收率达到了91.05%,大幅提高了钒钛磁铁矿的资源利用率。Abstract: In this paper, the direct reduction-magnetic separation method was used to recover Fe from vanadium titano-magnetite (VTM) tailings. Under the conditions of reduction temperature 1250 ℃, reduction time 2 h and reducing agent dosage 20% of the mass of the tailings, the metallization rate of pellets was 92.71%. After adding 5% CaCO3 and prolonging the holding time to 6 h, the average diameter of Fe grains increased from 14.53 μm to 25.39 μm. By fitting the growth rate of Fe grains, it was found that the grains growth rate constant increased from 0.26 μm2/min to 1.45 μm2/min after adding CaCO3. After magnetic separation, the direct reduced iron with TFe content of 90.72% and the titanium slag with TiO2 content of 41.75% could be obtained. The recovery rate of Fe reached 91.05%, which greatly improved the resource utilization of VTM.
-
表 1 提钒尾渣的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of vanadium extraction tailings
% V2O5 SiO2 Fe2O3 TiO2 CaO Al2O3 MgO MnO Na2O S 0.47 1.58 73.78 12.39 1.26 3.76 0.73 0.25 0.01 0.017 表 2 不同添加剂对TFe含量和铁回收率的影响
Table 2. Effect of different additives on TFe content and iron recovery rate
添加剂 加入量/% 磁选后TFe含量/% Fe回收率/% CaCO3 3 82.26 87.79 MgCO3 3 83.52 76.93 3CaO·Al2O3 3 73.86 71.11 Na2SiO4 3 86.59 82.69 CaO 3 85.24 81.32 表 3 磁性物相和非磁物相成分分析
Table 3. Analysis of phase composition of magnetic materials and non-magnetic materials
% V2O5 SiO2 TFe TiO2 CaO Al2O3 MgO Cr2O3 MnO SO3 非磁性物料 1.36 6.05 5.99 41.75 11.17 19.90 1.95 0.69 0.53 3.387 磁性物料 0.14 2.20 90.72 2.43 1.27 0.71 0.12 0.07 0.09 -
[1] Elkasabgy T. Effect of alkalis on reduction behavior of acid iron ore pellets[J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1984,24(8):612−621. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational1966.24.612 [2] El-Geassy A A, Shehata K A, NASR M I, et al. Effect of alkalies on the performance of blast furnace[J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1986,26(10):865−874. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational1966.26.865 [3] Han Jiqing, Zhang Li, Cui Dong, et al. Study on direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate extracted vanadium[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2018,17(2):101−106,113. (韩吉庆, 张力, 崔东, 等. 提钒后钒钛磁铁精矿直接还原研究[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2018,17(2):101−106,113. doi: 10.14186/j.cnki.1671-6620.2018.02.004 [4] 郭宇峰, 隋裕雷, 姜涛, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿钠化提钒尾渣还原磨选铁钛分离研究[C]//2014年非高炉炼铁学术年会论文集. 中国金属学会, 2014: 254-259.Guo Yufeng, Sui Yulei, Jiang Tao, et al. The research on reduction-magnetic separation foe the slag of sodiumization-vanadium extraction from titanomagnetite[C]// Symposium of 2014 Annual Conference of Non-blast Furnace Ironmaking . China Metal Society, 2014: 254-259. [5] 景丽丽. 提钒尾渣直接还原制备金属铁粉研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2010.Jing Lili. Recovery iron from vanadium tailings with coal based direct reduction followed magnetic separation[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010. [6] Sui Yulei, Guo Yufeng, Andrew Yakovlevich Travyanov, et al. Reduction roasting–magnetic separation of vanadium tailings in presence of sodium sulfate and its mechanisms[J]. Rare Metals, 2015,35(12):954−960. [7] Zeng Guanwu, Hao Jianzhang. Research on removing sodium from extracted vanadium residue[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(1):78−82,104. (曾冠武, 郝建璋. 提钒尾渣脱钠技术研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(1):78−82,104. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.01.014 [8] 张海平. 钠化提钒尾渣脱钠试验研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015.Zhang Haiping. Experimental study on eliminating sodium from extracted vanadium tailings[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015. [9] Gao Feng, Du Hao, Wang Shaona, et al. A comparative study of extracting vanadium from vanadium titano-magnetite ores: Calcium salt roasting vs sodium salt roasting[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2022:1−13. doi: 10.1080/08827508.2022.2069105 [10] Zhang Qingcen, Qiu Guanzhou. The effect of coal-kind on coal-based direct reduction of low grade iron ore[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1997,(2):27−30. (张清岑, 邱冠周. 煤种对低品位铁矿煤基直接还原的影响[J]. 中南工业大学学报, 1997,(2):27−30. [11] Zhu Deqing, Xiao Yongzhong, Chun Tiejun, et al. Growth behavior of metal iron grain during direct reduction of low grade hematite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013,23(11):3242−3247. (朱德庆, 肖永忠, 春铁军, 等. 低品位赤铁矿直接还原过程中铁晶粒的长大行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013,23(11):3242−3247. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.11.031 [12] Shi Xuefeng, Xu Hongjun, Zhang Yingyi, et al. The experimental study on direct reduction of shaft furnace based gas of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(1):52−56. (师学峰, 徐红军, 张颖异, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿气基竖炉直接还原试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(1):52−56. [13] 黄道鑫. 提钒炼钢[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000.Huang Daoxin. Vanadium recovery steelmaking[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000. [14] 刘玉芹. 硅酸盐陶瓷相图[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2011.Liu Yuqin. Phase diagram of silicate ceramics[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011. [15] Hillert M. On the theory of normal and abnormal grain growth[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1965,13(3):227−238. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(65)90200-2 [16] 何希. 纳米SnO2, TiO2, BaTiO3的合成及晶粒生长动力学研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007.He Xi. Synthesis of nanocrystalline SnO2, TiO2 and BaTiO3 and growth kinetics of nanocrystalline materials[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007. [17] Zhang Kai, Ding Yazhuo. Study on iron particles growth characteristic in the processing of deep reduction for a vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Metal Mine, 2021,(11):110−114. (张凯, 丁亚卓. 某钒钛磁铁矿精矿深度还原铁颗粒长大特性研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2021,(11):110−114. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202111017 -





 下载:
下载: