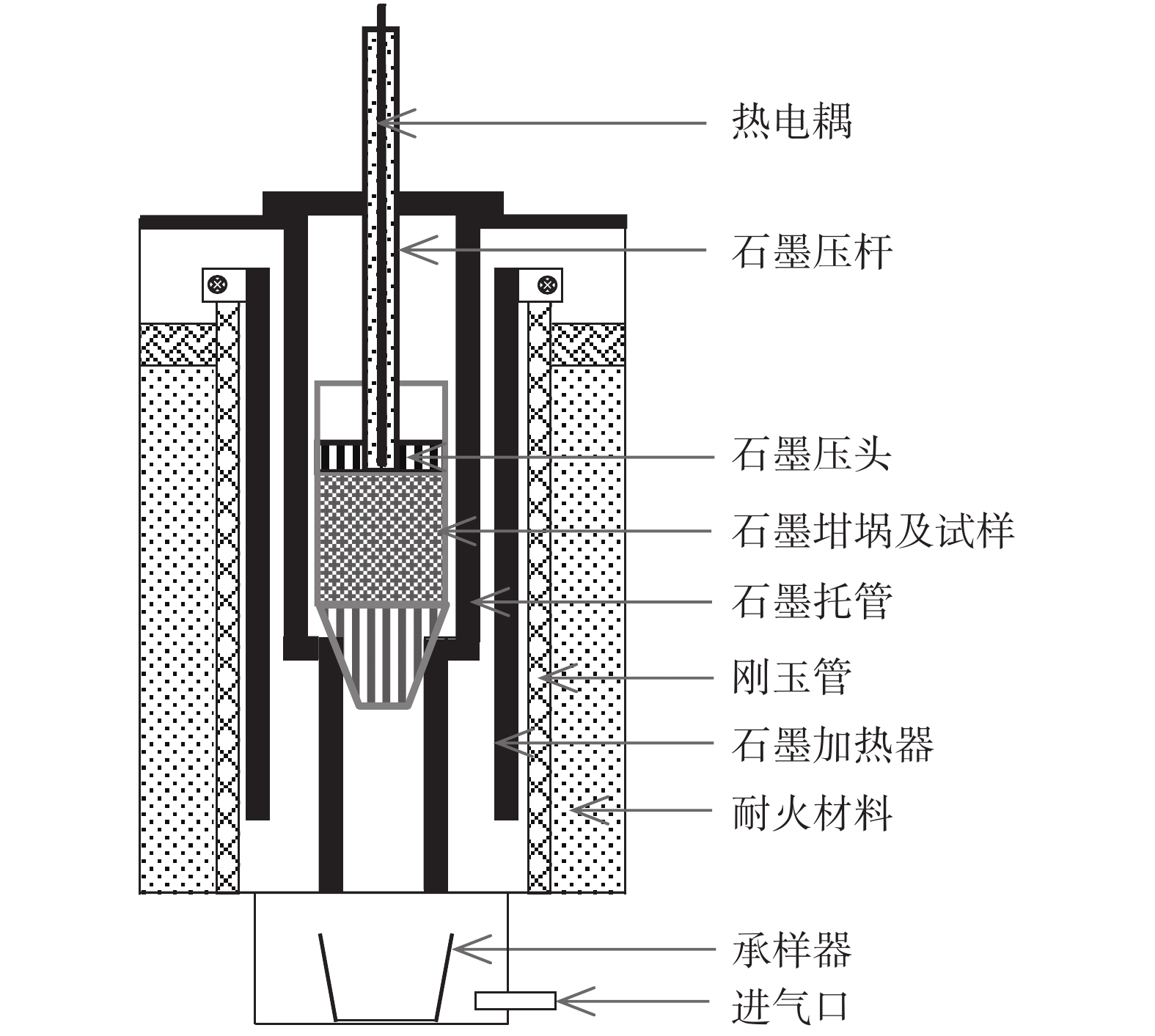
Research on the interaction mechanism between different burden for blast furnace of Pangang
-
摘要: 为探究攀钢高炉不同炉料在软熔过程中的相互作用机理,进行了单种原料及其混合矿软熔性能的测定以及由两种炉料组成的混合矿在特定温度软熔性能测定的中断试验。在试验条件下,块矿的滴落温度Td最低。与球团矿相比,烧结矿的软化终了温度T40低、滴落温度Td高、软化温度区间ΔTs窄、熔化温度区间ΔTm宽。与烧结矿和球团矿相比,混合矿的滴落温度Td明显降低。块矿软熔以后在荷重的作用下渗入烧结矿和球团矿的空隙间,促进其与烧结矿或球团矿中物相的相互侵蚀和元素在不同物相间的迁移,从而加速混合矿的软化熔融。Abstract: In order to explore the interaction mechanism between different burdens in the softening-melting process of the blast furnace in Pangang, the softening-melting properties of different single burdens and their mixed burden were tested. Meanwhile, the interrupt experiment of softening-melting properties of the mixed burden by any two kinds of single burdens at a specific temperature was carried out. Under the experimental conditions, the dropping temperature Td of lump ore is the lowest. Compared with the pellet, the sinter has a lower final softening temperature T40, a higher dropping temperature Td, a narrower softening temperature range ΔTs, and a more comprehensive melting temperature range. Compared with the sinter and pellet, the dropping temperature Td of mixed burden decreases. During softening and melting, the lump ore infiltrates into sinter or pellet under the action of load, conducive to the mutual erosion between lump ore and phases of the sinter or pellet as well as the migration of elements between different phases, thus promoting the softening and melting of mixed burden.
-
Key words:
- blast furnace /
- burden /
- softening-melting property /
- interaction
-
表 1 试验原料的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental burden
类别 TFe
/%FeO
/%SiO2
/%CaO
/%MgO
/%Al2O3
/%TiO2
/%V2O5
/%RO 烧结矿 49.19 6.62 5.52 10.23 2.23 3.30 0.347 1.85 球团矿 52.75 3.86 5.52 0.72 3.61 4.04 0.671 0.13 块矿 40.88 1.03 26.66 0.93 0.84 6.64 0.21 0 0.03 表 2 焦炭的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of experimental coke
% Fcad Mt St Vdaf Ad K2O Na2O CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 合计 85.88 0.23 0.63 1.09 0.08 0.10 0.49 7.24 0.13 3.73 1.03 12.80 表 3 铁矿石软熔性能试验条件
Table 3. Experimental conditions for the softening-melting property of iron ore
温度范围
/℃升温速率
/(℃·min−1)气体成分/% 气体流量
/(L·min−1)
Ar CO N2 0 ~ 400 6 0 0 0 3 400 ~ 900 7 100 0 0 3 900 ~ 1000 3 0 30 70 10 1000 ~ 终点 6 0 30 70 10 终点后 100 0 0 3 表 4 不同原料软熔性能
Table 4. Softening-melting properties of different burdens
样品
名称T10
/℃T40
/℃Ts
/℃Tp
/℃Td
/℃ΔTs
/℃ΔTs
/℃ΔPmax
/kPaH
/mmS
/(kPa·℃)烧结矿 1092 1158 1191 1227 1488 66 297 21.52 38.63 3340 球团矿 1055 1181 1214 1280 1442 126 228 18.83 33.77 2213 块矿 1072 1141 1114 1138 1165 69 54 2.57 15.78 119 混合矿 1075 1138 1183 1225 1390 63 207 20.43 35.79 2140 表 5 软熔炉料的化学成分
Table 5. Chemical compositions of different experimental samples
样品
编号TFe
/%FeO
/%MFe
/%CaO
/%SiO2
/%MgO
/%Al2O3
/%TiO2
/%TiC
/%TiN
/%R2 烧+块Ⅰ 59.00 61.75 7.50 4.90 9.41 2.38 3.39 4.32 <0.1 <0.01 0.52 烧+块Ⅱ 33.15 33.06 7.10 14.39 27.26 2.77 7.50 5.82 <0.1 <0.01 0.53 烧+球 49.76 41.39 17.57 8.15 8.00 4.21 5.55 12.57 <0.1 <0.01 0.98 球+块Ⅰ 52.88 55.87 5.70 1.50 12.89 3.04 4.85 9.00 <0.1 <0.01 0.10 球+块Ⅱ 41.50 46.83 4.60 2.61 26.00 3.56 6.50 7.07 <0.1 <0.01 0.12 表 6 软熔炉料造渣组分的相对含量
Table 6. Relative contents of the main slagging compositions of different experimental samples
% 样品
编号CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 烧+块Ⅰ 20.08 38.57 9.75 13.89 17.70 烧+块Ⅱ 24.92 47.21 4.80 12.99 10.08 球+块Ⅰ 4.80 41.21 9.72 15.51 28.77 球+块Ⅱ 5.71 56.84 7.78 14.21 15.46 表 7 烧结矿和块矿相互作用的微区能谱分析
Table 7. EDS analysis result of sinter and lump ore mixed ore
% 物相
编号物相
名称O Mg Al Ca Si Ti V Mn C Fe ① 钙铁橄榄石 41.8 3.66 0.32 13.68 16.70 0.46 0.21 0.78 22.39 ② 金属铁 0.97 1.18 0.67 3.93 93.25 表 8 烧结矿与球团矿相互作用的微区能谱分析
Table 8. EDS analysis result of sinter and pellet mixed ore
% 物相
编号物相
名称O Si Ca Mg Al Ti V Fe ① 钛赤铁矿 21.34 1.69 3.09 8.44 0.90 64.55 ② 磁铁矿 19.62 1.27 79.11 ③ 橄榄石 30.67 12.65 29.40 2.97 24.31 ④ 橄榄石 30.69 12.61 31.16 3.45 21.64 ⑤ 钙钛矿 30.28 0.59 31.45 0.60 31.55 5.53 表 9 球团矿与块矿相互作用的微区能谱分析
Table 9. EDS analysis result of pellet and lump ore mixed ore
% 物相
编号物相
名称O Si Ca Mg Al Ti V K Na Fe ① 浮氏体 16.96 2.11 0.92 80.01 ② 钛磁铁矿 20.46 2.66 6.72 13.99 1.91 54.26 ③ 铁橄榄石 24.10 18.05 7.11 1.32 1.43 0.90 47.09 ④ 钙铁辉石 25.43 17.85 11.24 3.09 3.38 1.24 0.89 3.22 33.66 ⑤ 玻璃相 29.44 23.26 4.40 14.27 1.80 0.70 10.38 4.64 11.11 表 10 无荷重时烧结矿与块矿相互作用的微区能谱分析
Table 10. EDS analysis result of sinter and lump ore mixed ore without load
% 物相
编号物相
名称Fe O Mg Al Ca Si Ti V ① 浮氏体 58.19 37.76 0.42 0.67 0.50 0.89 1.10 0.47 ② 铁橄榄石 35.74 44.66 1.80 0.88 0.75 14.83 0.79 0.56 表 11 无荷重时球团矿与块矿相互作用的微区能谱分析
Table 11. EDS analysis result of pellet and lump ore mixed ore without load
% 物相
编号物相
名称Fe O Mg Al Ca Si Ti V Mn K Na ① 钛赤铁矿 63.83 24.43 1.19 1.46 9.43 ② 钛铁矿 17.41 57.44 2.67 2.01 20.48 ③ 橄榄石 6.55 40.11 2.91 9.47 8.08 29.05 1.42 0.71 1.70 ④ 铁橄榄石 59.15 25.75 2.58 11.90 0.62 ⑤ 玻璃相 23.50 36.29 9.41 6.06 20.80 3.94 ⑥ 浮氏体 73.16 22.41 4.44 -
[1] 周传典. 高炉炼铁生产技术手册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2018: 127.Zhou Chuandian. Technical manual of blast furnace ironmaking[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2018: 127. [2] Du Hegui, Che Chuanren. Influence of softening-melting zone on the hard driving of blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 1980,15(4):21−27. (杜鹤桂, 车传仁. 软熔带对高炉强化冶炼的影响[J]. 钢铁, 1980,15(4):21−27. [3] Zhang Qiang, Gao Bin, Ding Jiankun, et al. Pressure field in lower region of blast furnace with different shapes of cohesive zone[J]. Research on Iron & Steel, 2012,40(4):21−24. (张强, 高斌, 丁建坤, 等. 软熔带形状参数对高炉下部压力场的影响[J]. 钢铁研究, 2012,40(4):21−24. [4] 《攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿选矿烧结高炉冶炼试验资料汇编》编写小组. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿选矿烧结高炉冶炼试验资料汇编[R]. 北京, 1978: 167-498.Writing group of 《Data compilation of beneficiation, sintering and blast furnace smelting test of Panzhihua vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite》. Data compilation of beneficiation, sintering and blast furnace smelting test of Panzhihua vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite[R]. Beijing, 1978:167-498. [5] Guha M, Sinha M. Tracking softening-melting behaviour of blast furnace burden[J]. ISIJ International, 2015,55(9):2033−2035. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2014-621 [6] 陈立杰. 高炉冶炼钒钛铁磁铁矿综合炉料熔滴性能优化研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014.Chen Lijie. Optimization on softening-dripping behaviors of blast furnace comprhensive burdens for vanadium-titanium magnetite smelting[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2014. [7] Bao Yicheng. Jia Xueqing, Song Guocai. Simulation study on reduction process of softening-melting and dripping zone in blast furnace smelting for vanadium-titanium sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993,14(2):1−11. (包毅成, 贾学庆, 宋国才. 钒钛烧结矿高炉冶炼软熔滴落带还原过程模拟研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993,14(2):1−11. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1993.02.001 [8] Diao Risheng. Difference in behaviors of V-Ti bearing and common iron ores within blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 1996,31(2):12−16,38. (刁日陞. 钒钛矿与普通矿在高炉各带行为差异的研究[J]. 钢铁, 1996,31(2):12−16,38. [9] Yang Wenkang, Yang Guangqing, Xin Hongwei, et al. Comparative study on softening-melting properties between vanadium titanium sinter and ordinary sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(4):118−122. (杨文康, 杨广庆, 邢宏伟, 等. 钒钛烧结矿与普通烧结矿软熔性能对比研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(4):118−122. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.021 [10] Gan Qin. Effect of rich ore ratio on softening-melting and dripping performance of vanadium titanium sinter[J]. Ironmaking, 1997,16(5):35−36. (甘勤. 不同富矿配比对钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落性能的影响[J]. 炼铁, 1997,16(5):35−36. [11] Gan Qin, He Qun, Wen Yongcai. Study on influence of MgO on mineral composition and metallurgical properties of V-bearing titaniferous magnetite sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(8):7−11. (甘勤, 何群, 文永才. MgO对钒钛烧结矿矿物组成及冶金性能影响的研究[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(8):7−11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2008.08.002 [12] Liu Z G, Chu M S, Wang H T, et al. Effect of MgO content in sinter on the softening–melting behavior of mixed burden made from chromium-bearing vanadium–titanium magnetite[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2016,23(1):25−32. doi: 10.1007/s12613-016-1207-2 [13] Yang Guangqing, Yang Wenkang, Li Xiaosong, et al. Comparative study of microstructure changes in vanadium titanium sinter and ordinary sinter during reduction process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(2):102−109. (杨广庆, 杨文康, 李小松, 等. 钒钛烧结矿与普通烧结矿还原过程中微观结构变化对比研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(2):102−109. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.02.017 [14] Song Guocai, Yuan Tianyuan, Chen Xiaowu. Study on phase composition of the cohesive dropping zone in BF during smelting V-bearing titanoferous magnetite sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996,17(2):25−27. (宋国才, 苑天宇, 陈小武. 高炉冶炼钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落带物相组成研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1996,17(2):25−27. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1996.02.005 [15] Wang H T, Zhao W, Chu M S, et al. Effect and function mechanism of sinter basicity on softening-melting behaviors of mixed burden made from chromium-bearing vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017,24:39−47. doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3406-z [16] Zhang Jianliang, Yang Guangqing, Guo Hongwei, et al. Microstructure change of V-Ti magnetite concentrate pellets during reduction[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013,35(1):41−48. (张建良, 杨广庆, 国宏伟, 等. 含钒钛铁矿球团还原过程中微观结构变化[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013,35(1):41−48. [17] 刘建兴. 软熔滴落带高铬型钒钛磁铁矿有价组元迁移机理[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Liu Jianxing. The migration mechanism of valuable components for high chromia vanadium-titanium magnetite in cohesive zone[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2013. [18] Liu Songli, Bai Chenguang, Hu Tu, et al. Quick and direct reduction process of vanadium and titanium iron concentrate with carbon-containing pellets at high temperature[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2011,34(1):60−65. (刘松利, 白晨光, 胡途, 等. 钒钛铁精矿内配碳球团高温快速直接还原历程[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2011,34(1):60−65. doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2011.01.010 [19] Chen Shuangyin, Tang Yu, Chu Mansheng, et al. Reduction progress of vanadium titano-magnetite with coal powder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2013,13(2):236−240. (陈双印, 唐钰, 储满生, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿的煤粉还原过程[J]. 过程工程学报, 2013,13(2):236−240. [20] Deng Chaoshu. Phase transformation of V-Ti-bearing sinter during reduction in BF[J]. Iron and Steel, 1985,20(12):46−51. (邓朝枢. 钒钛烧结矿在高炉内的还原相变[J]. 钢铁, 1985,20(12):46−51. [21] Wu Shengli, Han Hongliang, Xu Haifa, et al. Research on mechanism of interaction between sinter and lump ores in blast furnace[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010,10(Z1):37−42. (吴胜利, 韩宏亮, 许海法, 等. 高炉内烧结矿与块矿高温交互反应机理研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2010,10(Z1):37−42. -





 下载:
下载: