Simulation research of inclusive removal by argon blowing stirring during ladle tapping process
-
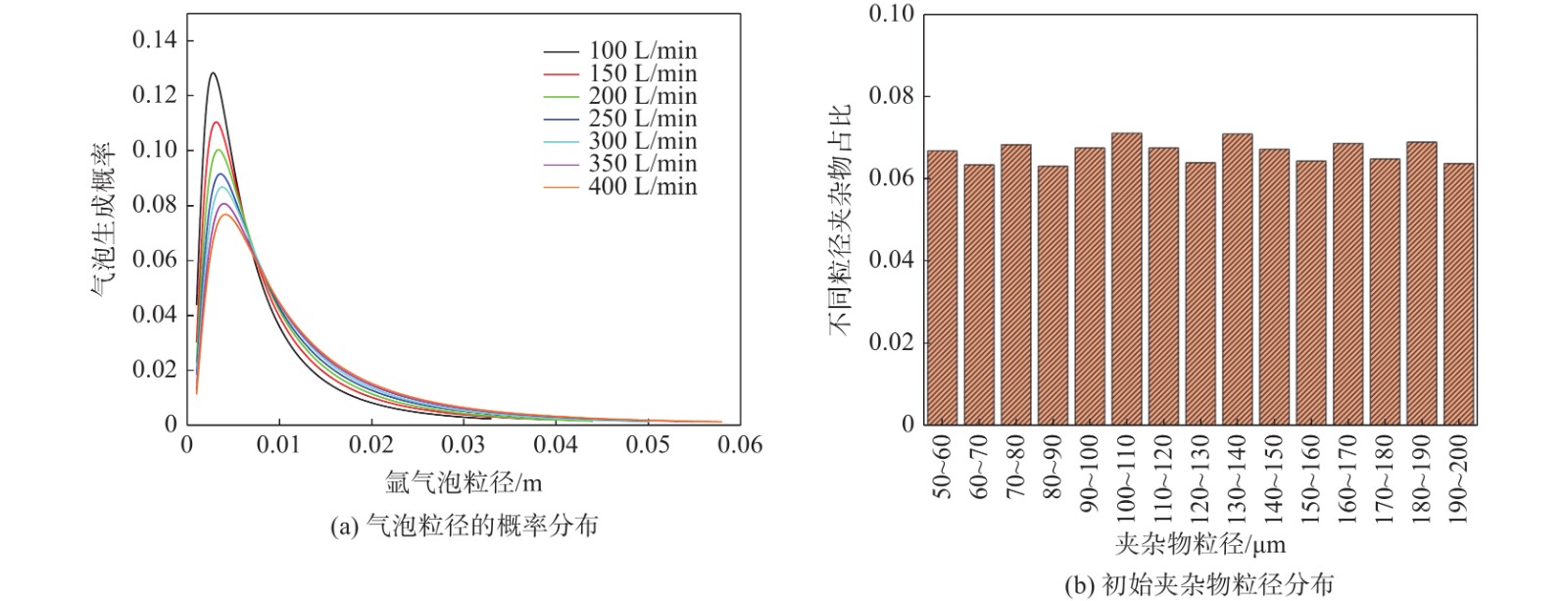
摘要: 针对钢包出钢过程建立了钢液-渣相-气相-氩气泡-夹杂物的五相数学模型,探索了钢包出钢过程中吹氩搅拌去除夹杂物的可行性,以及吹氩流量对流场、渣眼、夹杂物去除效率的影响规律。结果表明:吹氩搅拌可强化浇钢过程中钢液的流动行为,显著提升夹杂物的去除率。相较于未采用吹氩搅拌,当吹氩流量为100 L/min、出钢750 s时,夹杂物的去除率由80.74%提升至96.69%,流入中间包夹杂物的数量减少67.4%;随吹氩流量增加,渣眼尺寸增大,夹杂物去除速率增加,但去除效率变化不大,推荐吹氩流量为100 L/min。Abstract: Based on the process of ladle tapping, a five-phase numerical model including molten steel, molten slag, gas phase, argon bubble and inclusion had been established and used to investigate the feasibility of improving inclusions removal by argon blowing stirring during the tapping process, and the effect of argon blowing rate on flow field, slag-eye, and the removal efficiency of inclusions. The results show that the argon blowing stirring process can strengthen the flow of molten steel and promote the removal of inclusions. Compared with no argon blowing stirring, the removal efficiency of inclusions increases from 80.74% to 96.69% whilst the argon blowing rate is 100 L/min at 750 s, and the number of inclusions flowed into tundish is reduced by 67.4%. The size of slag-eye and the removal rate of inclusions increase with the increase of argon blowing rate, but argon blowing rate has a little effect on the removal efficiency of inclusions. The recommended argon blowing rate is 100 L/min.
-
Key words:
- ladle /
- argon blowing stirring /
- numerical simulation /
- multi-phase flow /
- inclusions /
- inclusions removal rate
-
图 3 数学模型预测值与Sheng[26]试验测得值的对比
Figure 3. Comparison between the predicted value and the measured value in Sheng’s work experiment
表 1 物性参数及计算参数
Table 1. Physical property and calculation conditions
密度/(kg.m−3) 黏度/(Pa·s) 表面张力/(N·m−1) 拉速/(m·min−1) 吹氩流量/(L·min−1) 结晶器尺寸/m 空气 氩气 钢液 渣相 夹杂物 空气 钢液 渣相 钢/渣 钢/气 渣/气 1.225 1.6228 7020 3500 3500 1.79×10−5 0.0055 0.1 1.15 1.82 0.58 1.0 0, 100, 200, 350, 500 0.23×1.6 -
[1] 张鼎瑞. 浇注钢包环出钢口吹氩新工艺去夹杂行为数学模拟研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2016.Zhang Dingrui. Numerical simulation on inclusion removal behaviors during ladle teeming with the new process of argon blowing around the tapping hole[D]. Shenyang: Northeasten University, 2016. [2] Yang Hulin, He Ping, Zai Yucun. Hydraulic model experiment on removing inclusions from molten steel by bottom blowing in ladle[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015,27(2):20−23. (杨虎林, 何平, 翟玉春. 钢包底吹去除夹杂物的水力学模型[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2015,27(2):20−23. [3] Zheng Shuguo, Zhu Miaoyong. Physical modeling of inclusion behavior in ladle with eccentric bottom blowing argon[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008,20(6):18−22. (郑淑国, 朱苗勇. 偏心底吹氩钢包内夹杂物行为的物理模拟[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2008,20(6):18−22. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.2008.06.009 [4] Cao Qing, Nastac Laurentiu. Numerical modelling of the transport and removal of inclusions in an industrial gas-stirred ladle[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2018,45(10):984−991. [5] Liu Yu, Ersson Mikael, Liu Heping, et al. A review of physical and numerical approaches for the study of gas stirring in ladle metallurgy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2019,50(1):555−577. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1446-x [6] Yang Yadi, Zhao Jing, Cui Jianzheng. Umerical simulation on interfacial behavior and mixing phenomena in three-phase argon-stirred ladles[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(5):138−148. (杨亚迪, 赵晶, 崔剑征. 三相氩气搅拌钢包内界面行为及混合现象的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(5):138−148. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.05.022 [7] Yang Zhaojun, Zeng Yanan, Li Junguo. Numerical simulation on optimization design of constructional and technical parameters of 65 t ladle[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(2):112−117. (杨赵军, 曾亚南, 李俊国. 65 t钢包精炼工艺参数优化数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(2):112−117. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.05.021 [8] Arcosgutierrez Hugo, Barretosandoval Jose, Garcia Saul, et al. Mathematical analysis of inclusion removal from liquid steel by gas bubbling in a casting tundish[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2012,(1110-757X):3800−3844. [9] Liu Heping, Qi Zhenya, Xu Mianguang. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and interfacial behavior in three-phase argon-stirred ladles with one plug and dual plugs[J]. Steel Research International, 2011,82(4):440−458. doi: 10.1002/srin.201000164 [10] Liu Yu, Ersson Mikael, Liu Heping, et al. Comparison of Euler-Euler approach and Euler-Lagrange approach to model gas injection in a ladle[J]. Steel Research International, 2019,90(5):41. [11] Tang Haiyan, Guo Xiaochen, Wu Guanghui, et al. Effect of gas blown modes on mixing phenomena in a bottom stirring ladle with dual plugs[J]. ISIJ International, 2016,12(12):123. [12] Qin Xufeng, Cheng Changgui, Li Yang, et al. Effect of annular argon blowing at upper nozzle on formation of slag eye in tundish[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(8):107−115,123. (秦绪锋, 程常桂, 李阳, 等. 上水口环形吹氩对中间包内渣眼形成的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(8):107−115,123. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190195 [13] Wu Guangjun. Development and application of argon blowing technology of the porous pocket block in continuous casting tundish[J]. Continuous Casting, 2018,43(2):12−15. (武光君. 连铸中间包透气水口座砖吹氩冶金技术开发与应用[J]. 连铸, 2018,43(2):12−15. [14] Lu Haibiao, Cheng Changgui, Zhang Feng, et al. Simulation study on process optimization of bottom argon blowing in tundish[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2018,41(1):1−7. (卢海彪, 程常桂, 张丰, 等. 中间包底吹氩工艺优化的模拟研究[J]. 武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,41(1):1−7. [15] Zhang Meijiang, Wang Houzhi, Huang Ao, et al. Mathematical simulation of inclusion movement with gas blowing at tundish bottom[J]. Continuous Casting, 2006,(6):19−21. (张美杰, 汪厚植, 黄奥, 等. 底吹氩中间罐夹杂物运动行为的数模研究[J]. 连铸, 2006,(6):19−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4006.2006.06.007 [16] Wu Yonglai, Wang Ying, Zhu Miaoyong, et al. Phenomenon of entrainment at interface between slag and metal in tundish with gas curtain[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2007,19(11):21−23. (吴永来, 王颖, 朱苗勇, 等. 气幕挡墙中间包内渣钢界面卷混现象[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2007,19(11):21−23. [17] Cheng Nailiang, Leng Xianggui, Yang Zhiwei, et al. Water model study on characteristics of fluid flow in continuous casting tundish with argon bubbling[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006,5(4):258−262. (程乃良, 冷祥贵, 杨智伟, 等. 吹氩连铸中间包内钢液流动特性的水模型实验研究[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2006,5(4):258−262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2006.04.005 [18] Launder Brian, Spalding D Brian. The numerical computation of turbulent flows[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics & Engineering, 1974,3(2):269−289. [19] Li Yang, Deng Anyuan, Yang Bin, et al. Inhibiting bulging deformation of liquid metal free surface by magnetic pressure[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2020,28(7):818−829. [20] Li Yang, Deng Anyuan, Zhang Lintao, et al. A new type of magnetic field arrangement to suppress meniscus fluctuation in slab casting: numerical simulation and experiment[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2021,298:117278. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117278 [21] Duan Haojian, Zhang Lifeng, Thomas Brian G, et al. Fluid flow, dissolution, and mixing phenomena in argon-stirred steel ladles[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,49(5):2722−2743. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1350-4 [22] Moris S A, Alexander A J. An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems[J]. J Fluid Mech, 1972,55(2):193−208. doi: 10.1017/S0022112072001806 [23] Kuo J T, Wallis G B. Flow of bubbles through nozzles[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1988,14(5):547−564. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(88)90057-2 [24] Xie Yongkun, Orsten Stefan, Oeters Franz. Behaviour of bubbles at gas blowing into liquid wood's metal[J]. ISIJ International, 1992,32(1):66−75. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.32.66 [25] Davidson J F. Bubble formation at an orifice in an inviscid liquid[J]. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng, 1960,38:335−342. [26] Sheng Y Y, Irons G A. Measurement and modeling of turbulence in the gas/liquid two-phase zone during gas injection[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1993,24(4):695−705. doi: 10.1007/BF02673185 [27] Krishnapisharody K, Irons G A. An extended model for slag eye size in ladle metallurgy[J]. ISIJ International, 2008,48(12):1807−1809. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.48.1807 -





 下载:
下载: