Effect of in-situ (W&Ti)C complex particles on wear behavior of high chromium cast iron
-
摘要: 采用原位法制备出(W&Ti)C复相颗粒增强高铬铸铁基复合材料,研究了增强颗粒对材料显微组织和磨损行为的影响规律。结果表明:与高铬铸铁相比,复合材料显微组织中WC和TiC颗粒的存在使其洛氏硬度(HRC)从55提高到70。在磨损过程中,高铬铸铁靠近磨损表面的M7C3型碳化物在磨料的反复作用下会产生裂纹并向基体内部扩展。破碎的碳化物更容易脱落,无法抵抗磨料对材料表面的犁削作用,从而加速材料的磨损。复合材料中相对较软的基体相在磨损时会逐渐被去除,磨损表面会暴露出大量WC和TiC颗粒。表面凸起的增强颗粒会承受来自磨料的主要破坏作用,进而有效地保护周边的基体材料。对比发现,在相同磨损条件下复合材料的磨损性能提高了1倍以上。Abstract: High chromium cast iron matrix composites reinforced with (W&Ti)C composite particles were prepared by in situ method, and the effect of reinforced particles on the microstructure and wear behavior of the material was studied. The results show that the presence of WC and TiC particles in the composite microstructure increases the Rockwell hardness (HRC) from 55 to 70 compared to high chromium cast iron (HCCI). During the wear process, the M7C3 carbides of the HCCI near the wear surface will generate cracks and expand into the matrix under the repeated action of abrasives. Broken carbides fall off more easily and cannot resist the ploughing action of abrasives on the surface of the material, thereby accelerating the wear. The relatively soft matrix in the composite is gradually removed during the wear process, and a large number of WC and TiC particles are exposed on the worn surface. The raised reinforcing particles will take the major damage from the abrasive, effectively protecting the surrounding matrix. It was found out that the wear performance of the composites increased by more than 1 times compared with traditional materials under the same wear conditions.
-
表 1 前驱体的成分配比
Table 1. Composition ratio of preform
% 石墨粉 Ti粉 W粉 Fe粉 9.52 26.67 43.81 20 表 2 高铬铸铁的化学成分
Table 2. The chemical compositions of the high chromium cast iron
% C Si Mn Cr Ni Mo S P Fe 3.17 0.15 0.34 26.96 0.42 0.39 0.02 0.01 余量 表 3 试验钢组织中物相的EDS能谱
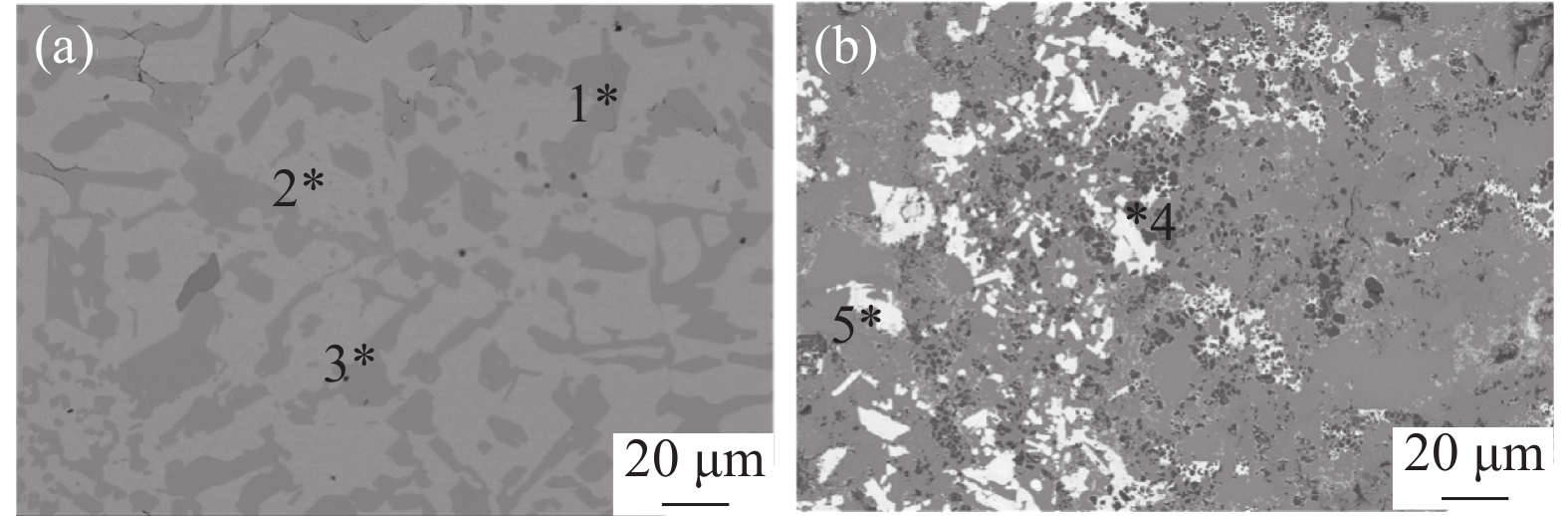
Table 3. EDS energy spectrum of indicated point in Fig.1 materials
试验钢 点 元素含量(y/%) C Si Cr Fe Mo Ti W 高铬铸铁 1 34.83 44.94 19.77 0.46 2 25.71 1.29 21.89 60.47 0.64 3 32.42 48.52 18.79 0.27 复合材料 4 51.91 0.38 47.71 5 48.94 0.14 0.16 50.76 -
[1] 郑志斌, 龙骏, 王玉辉, 等. 孪生诱发塑性钢力学性能的研究进展[J/OL].钢铁研究学报:1-22[2023-02-01].DOI: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20220049.Zheng Zhibing, Long Jun, Wang Yuhui, et al. Research progress of mechanical properties of twinning induced plasticity steel[J/OL].Journal of Iron and Steel Research: 1-22[2023-02-01].DOI:10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-096. 20220049. [2] Wang S, Zheng K H, Zheng Z B, et al. Oxidation behaviour and microstructure evolution of Zr-containing steel under continuous high-temperature exposure[J]. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2022,275:125324. [3] Wang S, Li Y M, Wang J, et al. Study on the microstructure and properties of iron-based composites locally reinforced by in-situ submicron TiC particles[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022,287:126376. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126376 [4] Yang Yi, Zheng Zhibing, Ye Zhiguo, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of lightweight high manganese steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021,33(11):1189−1197. (杨壹, 郑志斌, 叶志国, 等. 轻质高锰钢的组织及力学性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2021,33(11):1189−1197. [5] Zheng Z B, Long J, Guo Y, et al. Corrosion and impact-abrasion-corrosion behaviors of quenching-tempering martensitic Fe-Cr alloy steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2022, 29(11)1853-1863. [6] Wang F, Zheng X, Long J, et al. Effects of zirconium on the structure and mechanical properties of HSLA steels under quenched or tempered conditions[J]. Steel Research International, 2022:2200352. [7] Deng Changguang, Zhang Xiaofeng, Deng Chunming, et al. Failure mechanism of EB-PVD thermal barrier coating on turbine blades in service environment[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2022,16(1):19−28. (邓畅光, 张小峰, 邓春明, 等. 使役环境涡轮叶片EB-PVD热障涂层失效机制[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2022,16(1):19−28. [8] Li Zhi, Han Guang, Lu Xianghui, et al. Study on the properties of titanium bearing weather-proof building steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(2):60−65. (李智, 韩光, 陆向辉, 等. 含钛耐候建筑钢的耐腐蚀和耐磨损性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(2):60−65. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.02.011 [9] Sudhakar A N, Markandeya R, Srinivasa Rao B, et al. Effect of alloying elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high chromium white cast iron and Ni-hard iron[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2022,61(3):1006−1014. [10] Riki Hendra Purba, Kazumichi Shimizu, Kenta Kusumoto, et al. Effect of boron addition on three-body abrasive wear characteristics of high chromium based multi-component white cast iron[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022,275:125232. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125232 [11] Beata Białobrzeska. The influence of boron on the resistance to abrasion of quenched low-alloy steels[J]. Wear, 2022,500-501:20345. [12] Chen H, Lu Y Y, Wu K H, et al. Effect of WC addition on TiC reinforced Fe matrix composites produced by laser deposition[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2022,434:128185. [13] Gao J, Li T S, Yan Z L, et al. Research on the interface and properties of spherical ZTA particles reinforced Fe-Cr-B matrix composite[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022,19:1322−1331. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.119 [14] Dong Xiaorong, Zheng Zhibing, Long Jun, et al. Analysis of domestic patent technology of vanadium-containing cast wear-resistant steel materials[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2022,16(5):766−775. (董晓蓉, 郑志斌, 龙骏, 等. 含钒铸造耐磨钢铁材料国内专利技术分析[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2022,16(5):766−775. [15] Li C, Goei Ronn, Li Y F, et al. Fabrication and wear property of NiCo coated ZrO2-Al2O3 ceramic particles reinforced high manganese steel-based composites[J]. Wear, 2022,492-493:204235. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2022.204235 [16] Wang S, Li Y M, Wang J, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and properties of Ti/W-C reinforced Fe-based composites[J]. Vacuum, 2021,194:110617. [17] Chang Cheng, Yan Xingchen, Gardan Julien, et al. Exploration on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the selective laser melted nano-WC/CX steel[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2021,4:309−317. (常成, 闫星辰, Gardan Julien, 等. 激光选区熔化成形nano-WC/CX钢微观组织及机械性能初探[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2021,4:309−317. [18] Li C, Li Y F, Shi J, et al. Interfacial characterization and erosive wear performance of zirconia toughened alumina ceramics particles reinforced high chromium white cast irons composites[J]. Tribology International, 2022,165:107262. [19] Li J, Qiu H, Zhang X F, et al. Effects of (Ti, Mo) C particles on the abrasive wear-corrosion of low alloy martensitic steel[J]. Wear, 2022,496-497:204288. [20] Wang Tao, Hu Feng, Zhou Wen, et al. Effect of impact load on wear resistance of 10Mn steel and analysis of wear resistance mechanism[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022,34(5):478−488. (王涛, 胡峰, 周雯, 等. 冲击载荷对10Mn钢磨损性能的影响及耐磨机制分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2022,34(5):478−488. [21] Zou Y M, Tan C L, Qiu Z G, et al. Additively manufactured SiC - reinforced stainless steel with excellent strength and wear resistance[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021,41:101971. [22] Chen H Y, Gu D D, Zhang H M, et al. Novel WC reinforced iron - based composites with excellent mechanical properties synthesized by laser additive manufacturing: Underlying role of reinforcement weight fraction[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2021,289:116959. [23] Zhu H M, Ouyang Mengna , Hu J P, et al. Design and development of TiC-reinforced 410 martensitic stainless steel coatings fabricated by laser cladding[J]. Ceramics International, 2021,47(9):12505−12513. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.108 [24] Li J F, Zhu Z C, Peng Y X, et al. Phase evolution and wear resistance of in-situ synthesized (Cr, W)23C6-WC composite ceramics reinforced Fe – based composite coatings produced by laser cladding[J]. Vacuum, 2021:110242. [25] Morteza Narvan, Ali Ghasemi, Eskandar Fereiduni, et al. Laser powder bed fusion of functionally graded bi-materials: Role of VC on functionalizing AISI H13 tool steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2021,201:109503. [26] Olejnik E, Szymański Ł, Batóg P, et al. TiC-FeCr local composite reinforcements obtained in situ in steel casting[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020,275:116157. -





 下载:
下载: