Research on the effect of Nb-V composite microalloying on austenite recrystallization of pipeline steel
-
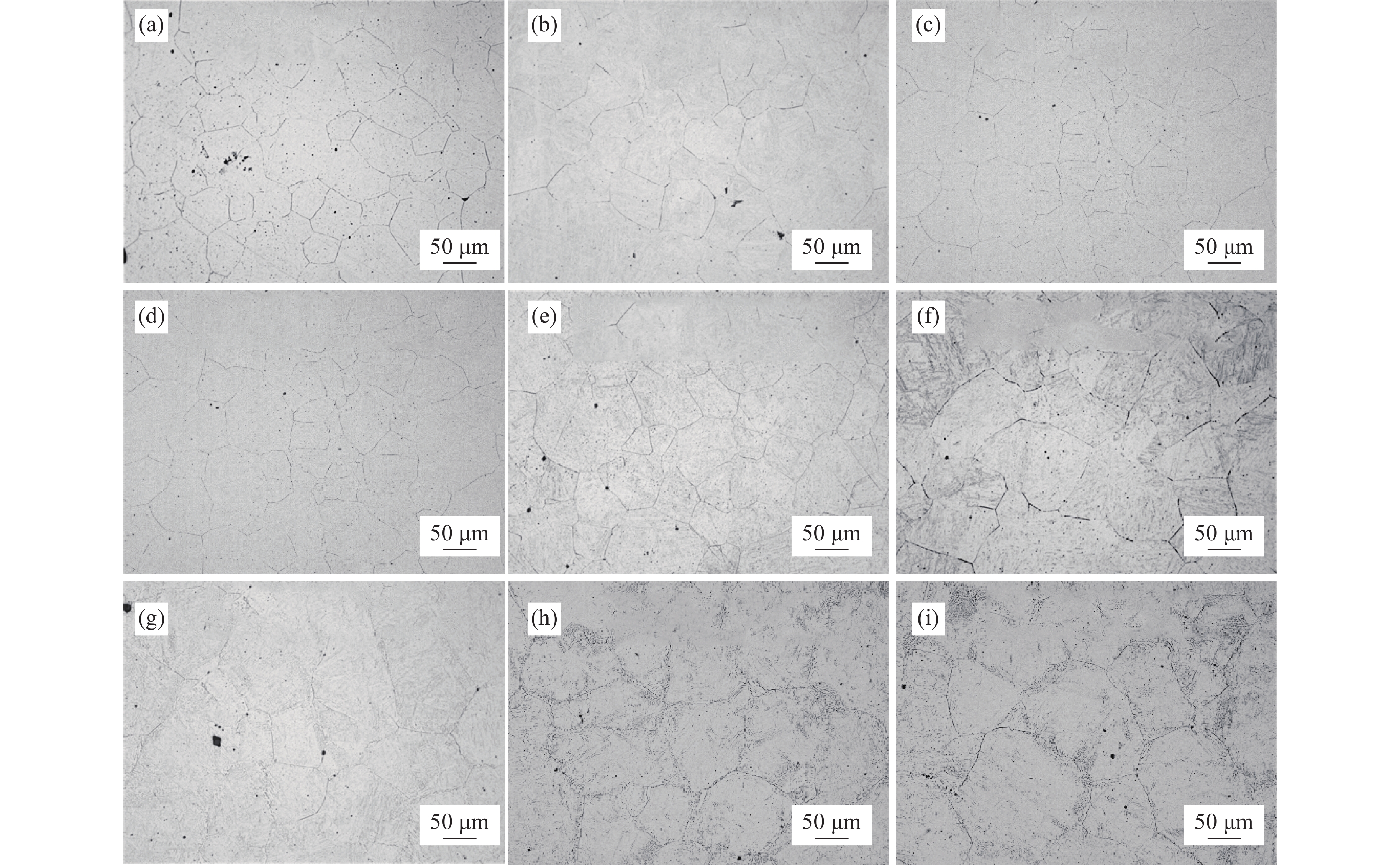
摘要: 借助光学显微镜(OM)、高分辨透射电镜(HRTEM)等分析手段,通过热处理试验,热力学模型计算及therme-cacl软件分析等,研究了再加热过程中管线钢奥氏体晶粒尺寸和微合金元素溶解和析出行为之间的耦合关系。结果表明,试验钢在再加热温度1180 ℃、保温1.5 h时,此时奥氏体晶粒尺寸存在以下规律:Nb钢(61.14 μm±5.59 μm)<Nb-V钢(63.84 μm±5.52 μm)<V钢(71.89 μm±6.8 μm),此时Nb钢奥氏体中Nb元素的固溶量为0.064%,而Nb-V试验钢的固溶量为0.05%,此时两种试验钢在奥氏体中固溶的Nb含量差仅有0.014个百分点。通过建立热力学模型计算发现,在1050~1250 ℃温度区间内奥氏体晶粒长大激活能关系为QNb钢>QNb-V钢>QV钢,进一步证实在该阶段奥氏体晶粒的长大主要与Nb元素固溶量成正相关。在再加热温度1180 ℃、保温1.5 h下Nb-V试验钢和Nb钢原奥氏体晶粒尺寸、Nb固溶量都在相近的范围内,从再加热阶段进一步验证了含V管线钢的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 管线钢 /
- Nb-V复合微合金化 /
- 奥氏体晶粒尺寸 /
- 第二相析出 /
- 激活能
Abstract: Through heat treatment test, microstructure observation, thermodynamic model calculation and thermo-cacl software, the austenite grain size as well asthe dissolution and precipitation behavior of microalloying elements in pipeline steel during reheating had been investigated.. The results show that when the test steel is reheated at 1180 ℃ and held for 1.5 hours, the austenite grain size order is as follows: Nb steel (61.14 μm±5.59 μm)<Nb-V steel (63.84 μm±5.52 μm)<V steel (71.89 μm ±6.8 μm) . Under this condition, the solid solution Nb content of Nb steel is 0.064%, while the solid solution Nb content of Nb-V test steel is 0.05%. The difference between the solid solution Nb content of the two test steels in austenite is only 0.014%. The predication from established thermodynamic model shows that the activation energy of austenite grain growth in the temperature range of 1050 ℃ to 1250 ℃ exists in QNb steel>QNb-V steel>QV steel, which further confirms that the growth of austenite grains at this stage is mainly positively correlated with the solid solution amount of Nb element. Under investigated reheating condition, the prior austenite grain size and solid solution Nb content in Nb-V test steel is similar to that of Nb steel, which confirms the feasibility of Nb-V microalloying pipeline steel from the prospective of reheating stage. -
表 1 试验钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of experimental steel
% 钢种 Ac3/℃ C Mn Si Nb V Ti Cr+Mo+Cu+Ni Nb 830 0.054 1.73 0.214 0.080 0.012 0.62 Nb-V 833 0.055 1.73 0.221 0.050 0.031 0.010 0.62 V 838 0.043 1.70 0.205 0.073 0.007 0.62 -
[1] Qiao Guiying, Han Yang, Han Xiulin, et al. Microstructure and properties of welding heat-affected zone of high-niobium and high-strength pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2014,26(10):40−45. (乔桂英, 韩杨, 韩秀林, 等. 高铌高强管线钢焊接热影响区的组织与性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2014,26(10):40−45. [2] Mitchell P S, Hart P H M, Morrison W B. The effect of microalloying on HAZ toughness[C]// Microalloying 95. Korchynsky M. ed. . , I&SS, Pittsburgh, USA, 1995: 149-162. [3] Yu Quancheng, Gu Daqing, Ma Heng. Study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of welding heat-affected zone of V-N microalloy steel[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2021,43(3):39−45. (于全成, 顾大庆, 麻衡. V-N微合金钢焊接热影响区组织与力学性能研究[J]. 山东冶金, 2021,43(3):39−45. [4] Erfan Abbasi, William Mark Rainforth. Microstructural evolution of Nb-V-Mo and V containing TRIP-assisted steels during thermomechanical processing[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2017,33(4):311−320. [5] He Feiyu, Dong Jian, Sun Yanhui. Thermodynamic calculation and verification of ternary carbon and nitrogen precipitates in low carbon steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(4):144−151. (贺飞羽, 董健, 孙彦辉. 低碳钢三元碳氮析出物的热力学计算及验证[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(4):144−151. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.04.027 [6] Yu Yinjun, Zhao Shiyu, Zhang Ke, et al. The effect of isothermal cooling time on microstructure transformation and hardness of Ti-V-Mo composite microalloyed steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021,46(6):95−101. (于银俊, 赵时雨, 张可, 等. 等温冷却时间对Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢组织转变及硬度的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2021,46(6):95−101. [7] Xian Kang, Huo Xiangdong, Fang Menglong, et al. Thermal simulation study on the mechanism of titanium strengthening low carbon steel[J]. Journal of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021,42(8):144−152. (鲜康, 霍向东, 方梦龙, 等. 钛元素强化低碳钢机理的热模拟研究[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2021,42(8):144−152. [8] Chen Zihao, Zhang Ke, Fu Xibin, et al. Effect of V content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-V composite microalloyed steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021,21(7):827−835. (陈子豪, 张可, 付锡彬, 等. V含量对Ti-V复合微合金钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021,21(7):827−835. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.221107 [9] Huang Jie, Xu Zhou. Formation mechanism of composite microalloyed precipitates during hot deformation of V-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2005,(6):16−19. (黄杰, 徐洲. V-Ti微合金钢热变形过程中复合微合金析出相的形成机制[J]. 上海金属, 2005,(6):16−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2005.06.004 [10] Liu Shuai, Wang Fuming, Li Yongliang. Effects of microalloying elements Nb and Ti on low-temperature impact properties of high-strength engineering structural steels[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Science, 2018,40(S1):41−46. (刘帅, 王福明, 李永亮. 微合金元素Nb和Ti对高强工程结构钢低温冲击性能的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018,40(S1):41−46. [11] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 361.Yong Qilong. Secondary phase in steels[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 361. [12] Qiu Yubin, Lin Dawei, Han Anchang. The effect of hot rolling temperature parameters on the mechanical properties of Nb-Ti and Nb-V microalloyed steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2007,(1):48−52. (邱昱斌, 林大为, 韩安昌. 热轧温度参数对Nb-Ti和Nb-V微合金钢力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2007,(1):48−52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2007.01.011 [13] Luo Yanzhao, Zhang Jiongming, Xiao Chao, et al. The evolution of the precipitation process of low carbon Nb-Ti binary microalloyed steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012,34(7):775−782. (罗衍昭, 张炯明, 肖超, 等. 低碳Nb-Ti二元微合金钢析出过程的演变[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2012,34(7):775−782. [14] 李远远. Nb-Ti低碳微合金钢的组织及析出控制研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Li Yuanyuan. Research on the structure and precipitation control of Nb-Ti low-carbon microalloyed steel[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2013. [15] Lewis M H, Hattersley B. Precipitation of M23C6 in austenitic steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1965,13(11):1159−1168. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(65)90053-2 [16] Fu Liming, Shan Aidang, Wang Wei. Effects of Nb solute dragging and precipitation NbC pinning on recrystallized grain growth in low carbon Nb microalloyed steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010,46(7):832−837. (付立铭, 单爱党, 王巍. 低碳 Nb 微合金钢中 Nb 溶质拖曳和析出相 NbC 钉扎对再结晶晶粒长大的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2010,46(7):832−837. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00832 [17] Adrian H, Pickering F B. Effect of titanium additions on austenite grain growth kinetics of medium carbon V–Nb steels containing 0.008%-0.018%N[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1991,7(2):176−182. doi: 10.1179/mst.1991.7.2.176 [18] Renata Staśko, Henryk Adrian, Anna Adrian. Effect of nitrogen and vanadium on austenite grain growth kinetics of a low alloy steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2006,56(4):340−347. [19] Staśko R, Adrian H, Adrian A. Effect of nitrogen and vanadium on austenite grain growth kinetics of a low alloy steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2006,56(4-5):340−347. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2005.09.012 [20] Chang K, Feng W, Chen L Q. Effect of second-phase particle morphology on grain growth kinetics[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009,57(17):5229−5236. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2009.07.025 [21] Gladman T. On the theory of the effect of precipitate particles on grain growth in metals[C]// Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1966, 294(1438): 298-309. [22] Sellars C M, Mc Tegart W J. On the mechanism of hot deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966,14(9):1136−1138. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(66)90207-0 [23] Pang Q, Guo J, Li W, et al. Complex precipitation mechanism of Ti-Nb-V microalloyed bainitic base high strength steel[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2019,34(6):1444−1450. doi: 10.1007/s11595-019-2211-y [24] 张可, 孙新军, 张明亚, 等. Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ/α中沉淀析出的动力学[J]. 金属学报, 2018, 54(8): 1122-1130.Zhang Ke, Sun Xinjun, Zhang Mingya, et al. Kinetics of (Ti, V, Mo)C precipitation in γ/α in Ti-V-Mo composite microalloyed steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Metals, 2018, 54(8): 1122-1130. [25] Li X, Wang Z. Interphase precipitation behaviors of nanometer-sized carbides in a Nb-Ti-bearing low-carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metall. Sin., 2015,51(4):417−424. [26] Shanmugam S, Tanniru M, Misra R D K, et al. Precipitation in V bearing microalloyed steel containing low concentrations of Ti and Nb[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2005,21(8):883−892. doi: 10.1179/174328405X47564 [27] Solis-Bravo G, Merwin M, Garcia C I. Impact of precipitate morphology on the dissolution and grain-coarsening behavior of a Ti-Nb microalloyed linepipe steel[J]. Metals, 2020,10(1):89. doi: 10.3390/met10010089 -





 下载:
下载: