Evolution of microstructure and texture for Hi-B steel using low-temperature slab heating
-
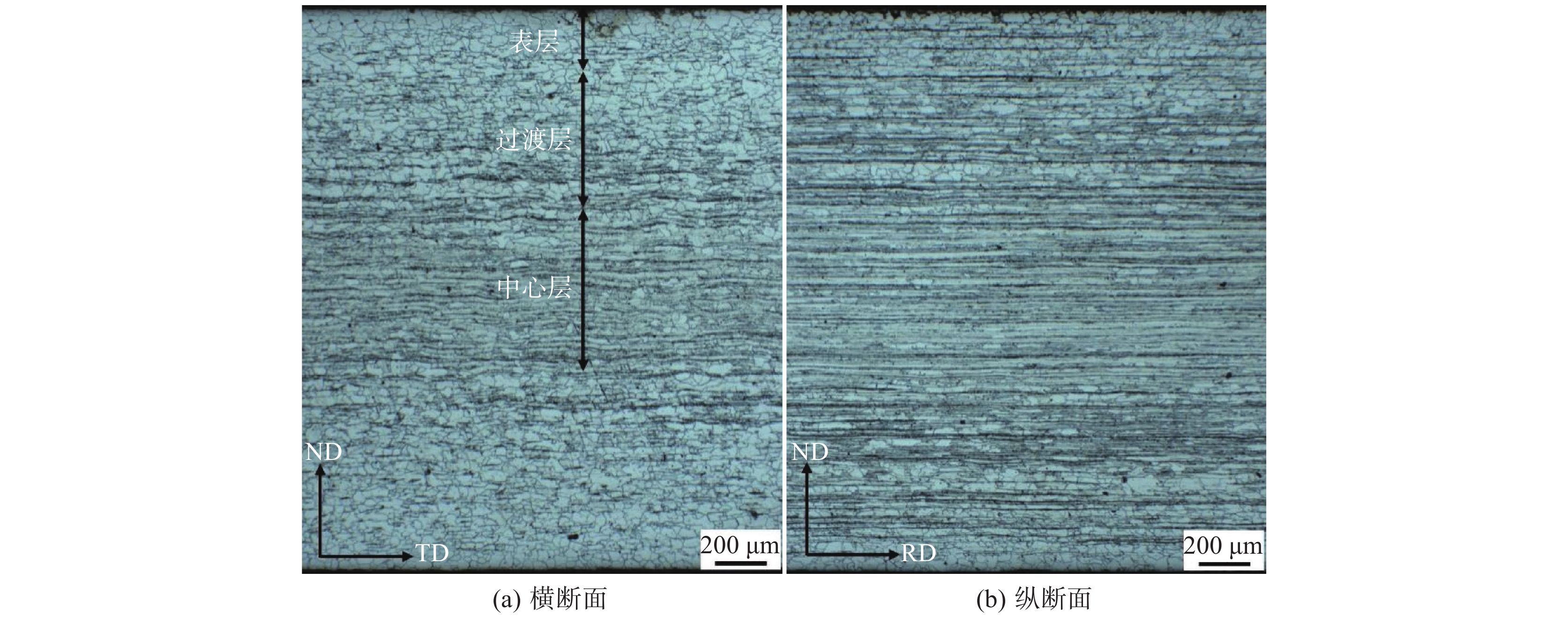
摘要: 采用光学显微镜和X射线衍射仪对低温板坯加热Hi-B钢的组织、织构的特征演变进行了研究。结果表明:从热轧板和常化板的表面到中心,组织和织构分布不均匀。热轧板组织分为表层再结晶区域、再结晶和变形晶粒混合区域和中心变形晶粒区域,并且热轧板各层的织构类型不同。常化板表层晶粒长大,过渡层和中心层的形变晶粒基本消失,常化板继承了热轧板的织构特点。冷轧板为纤维状变形组织,冷轧后形成了以{001}<110>~{111}<110>为主的α 织构。脱碳渗氮板的横断面和纵断面的晶粒平均尺寸分别为25.9 μm和25.3 μm,织构主要为{111}<112>、{114}<481>和{001}<120>织构。成品板晶粒平均尺寸为19.1 μm,成品板为单一的高斯织构。Abstract: The evolutions of microstructure and texture for Hi-B steel using low-temperature slab heating technology were studied by optical microscope and X-ray diffractometer. The results show that the distribution of microstructure and texture is not uniform from the surface to the center layer in the hot-rolled band and annealed hot-rolled band. The microstructure of the hot-rolled band consists of the surface recrystallized region, the mixed region of recrystallized and deformed grains, and the central deformed grain region. Moreover, the texture types of each layer in the hot-rolled band are different. The grains in the surface layer of the annealed hot-rolled band grow, the deformed grains in the transition layer and the center layer disappear, and the annealed hot-rolled band inherits the texture characteristics of the hot-rolled band. In addition, the cold-rolled band has a fibrous deformed structure. An α texture dominated by {001}<110>~{111}<110> is formed during cold-rolling. The average grain size of the transverse section and vertical section of the decarburized and nitrided sheet is 25.9 μm and 25.3 μm, respectively, and the textures are mainly {111}<112>, {114}<481> and {001}<120> textures. The average grain size of the final product is 19.1 μm, and the final product has a single Gaussian texture.
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of tested steel
% C Si Mn Als S N 0.05 3.2 0.095 0.0298 0.0074 0.0089 -
[1] Li Xianhao, Meng Xiaotao, Zhao Pengfei, et al. Present status and future prospect of high permeability grain-oriented silicon steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2019,29(1):1−7. (黎先浩, 孟小涛, 赵鹏飞, 等. 高磁感取向硅钢研发现状与展望[J]. 中国冶金, 2019,29(1):1−7. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20180169 [2] Qiu Shengtao, Fu Bing, Xiang Li, et al. Recent research trends and developments of production process and technology for high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2013,48(3):1−8. (仇圣桃, 付兵, 项利, 等. 高磁感取向硅钢生产技术与工艺的研发进展及趋势[J]. 钢铁, 2013,48(3):1−8. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.2013.03.002 [3] Li Jun, Sun Ying, Zhao Yu, et al. Development of low temperature slab reheating technique for grain orientedsilicon steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007,42(10):72−75. (李军, 孙颖, 赵宇, 等. 取向硅钢低温铸坯加热技术的研发进展[J]. 钢铁, 2007,42(10):72−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749x.2007.10.018 [4] 何忠治, 赵宇, 罗海文. 电工钢[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012.He Zhongzhi, Zhao Yu, Luo Haiwen. Electrical steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012. [5] Woo J S, Han C H, Hong B D, et al. The onset temperature of secondary recrystallization and the sharpness of Goss secondary recrystallization texture in the nitrided Fe–3%Si alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998,46(14):4905−4909. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00186-4 [6] Liu Gongtao, Liu Zhiqiao, Yang Ping, et al. Effect of primary recrystallized microstructure and nitriding on secondary recrystallization in grain oriented silicon steel by low temperature slab reheating[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2018,46(1):16−24. (刘恭涛, 刘志桥, 杨平, 等. 初次再结晶组织和渗氮量对低温渗氮取向硅钢二次再结晶行为的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2018,46(1):16−24. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.000178 [7] Xu Shuai, Bao Siqian, Ke Shanshan, et al. Grain boundary characteristics of non-abnormal grown Goss grains of Hi-B steel during secondary recrystallization annealing[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2020,45(9):167−171. (徐帅, 鲍思前, 柯珊珊, 等. Hi-B钢二次再结晶退火过程中未异常长大Goss晶粒晶界特征[J]. 金属热处理, 2020,45(9):167−171. doi: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2020.09.031 [8] Bao Siqian, Liu Bingbing, Zhao Gang, et al. Three-dimensional morphologies of abnormally grown goss oriented grains in Hi-B steel during secondary recrystallization annealing[J]. Acta Metall. Sin., 2018,54(6):877−885. (鲍思前, 刘兵兵, 赵刚, 等. Hi-B钢二次再结晶退火中异常长大Goss取向晶粒的三维形貌表征[J]. 金属学报, 2018,54(6):877−885. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00320 [9] Liu Zhiqiao, Yang Ping, Mao Weimin, et al. Effect of {114}< 418> texture on abnormal growth during secondary recrystallization in grain oriented steel[J]. Acta Metall. Sin., 2015,51(7):769−776. (刘志桥, 杨平, 毛卫民, 等. 取向硅钢中{114}< 418>织构对二次再结晶时晶粒异常长大的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015,51(7):769−776. [10] Wang Haijun, Fu Bing, Xiang Li, et al. Effect of nitrogen content on primary recrystallization behavior and magnetic property of Hi-B steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research(International), 2016,23(10):1080−1085. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30160-1 [11] Xiang Li, Rong Zhe, Fu Bing, et al. Characterizing microstructure and texture after recrystallization annealing of Hi-B steel with simutaneous decarburization and nitriding[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research(International), 2017,24(12):1215−1222. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(18)30020-7 -





 下载:
下载: