Study on hydrogen embrittlement resistance of vanadium molybdenum microalloyed 32MnB5 hot formed steel
-
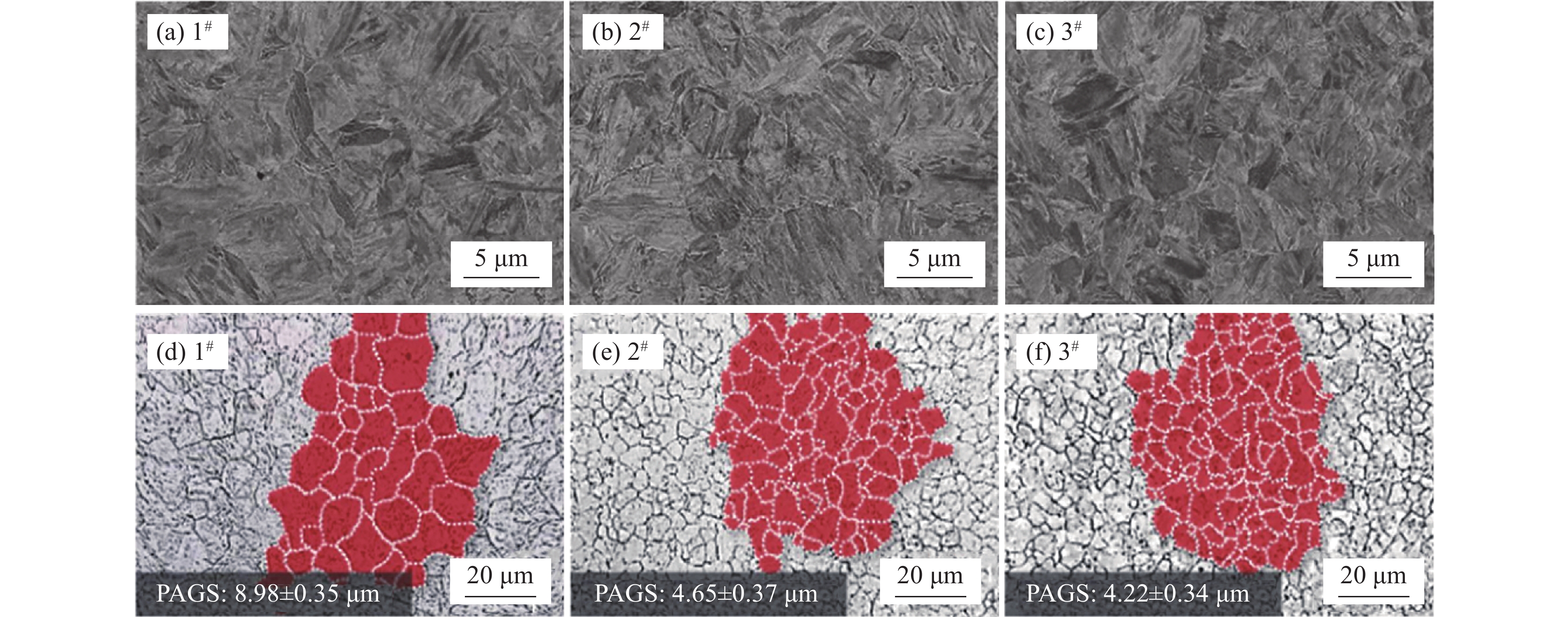
摘要: 在实验室条件下通过在传统32MnB5热成形钢基础上添加不同含量的V和Mo,利用慢应变速率拉伸试验来评价材料的氢脆敏感性,并结合氢渗透试验对微合金化热成形钢的抗氢脆性能变化机理进行了探讨。试验结果表明:添加V和Mo合金元素均有利于提高材料的抗氢脆性能,材料充氢后的塑性损失均出现降低。其中V与Mo复合添加相对于单一添加V样品,其原奥氏体晶粒尺寸及纳米级析出相尺寸更为细小,可以有效捕获氢原子,阻碍了氢原子的扩散,因此表现出最佳的抗氢脆性能,氢扩散系数降至7.3×10−11 m2/s,可扩散氢浓度减少至4100 mol/m3。Abstract: Different contents of vanadium and molybdenum were added into the traditional 32MnB5 hot formed steel under laboratory conditions, the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of the microalloyed material was evaluated by slow strain rate tensile test, and the change mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement resistance of microalloyed hot formed steel was discussed combined with results from hydrogen penetration test. It is found out that addition of V and Mo alloy elements is conducive to improve the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of the material, and the plastic loss of the material after hydrogen charging is reduced. Compared with the V-added only sample, the original austenite grain size and nano precipitate size of V-Mo combinated addition are smaller, which can effectively capture hydrogen atoms and hinder the diffusion of hydrogen atoms. Therefore, the V-Mo steel shows the best resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, and the hydrogen diffusion coefficient is reduced to 7.3×10−11 m2/s, the diffusible hydrogen concentration is reduced to 4100 mol/m3.
-
Key words:
- hot formed steel /
- 32MnB5 /
- microalloying /
- vanadium /
- molybdenum /
- hydrogen embrittlement
-
表 1 热成形钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the three hot-stamping steels used in this study
% C Si Al Mn Cr Ti Mo V 1# 0.32 0.25 0.04 1.2 0.12 0.03 2# 0.32 0.25 0.04 1.2 0.12 0.03 0.05 3# 0.32 0.25 0.04 1.2 0.12 0.03 0.1 0.05 -
[1] Jin Xuejun, Gong Yu, Han Xianhong, et al. Research status and prospect of manufacturing and application of advanced hot formed automotive steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(4):411−428. (金学军, 龚煜, 韩先洪, 等. 先进热成形汽车钢制造与使用的研究现状与展望[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):411−428. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00381 [2] Li Jinxu, Wang Wei, Zhou Yao, et al. Research progress on hydrogen embrittlement of advanced high strength steel for automobile[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(4):444−458. (李金许, 王伟, 周耀, 等. 汽车用先进高强钢的氢脆研究进展[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):444−458. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00427 [3] Chen Xiuli, Lv Lidong, Jia Huihui, et al. Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength steel B1500HS after hot forming[J]. Casting Technology, 2017,38(7):3. (陈秀丽, 吕利栋, 贾慧慧, 等. 高强钢B1500HS热成形后的显微组织和力学性能研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2017,38(7):3. [4] Lu Hongzhou, Zhao Yan, Feng Yi, et al. Development and application progress and prospect of microalloyed hot formed steel[J]. Mechanical Engineering Materials, 2020,44(12):10. (路洪洲, 赵岩, 冯毅, 等. 微合金化热成形钢开发应用进展及展望[J]. 机械工程材料, 2020,44(12):10. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202012001 [5] Fang Xiaofen, Wang Jingxia. Tensile properties and hydrogen embrittlement fracture analysis of cold rolled Fe-17Mn-0.05C high manganese steel for automobile lightweight[J]. Forging Technology, 2019,44(1):5. (方晓汾, 王静霞. 汽车轻量化用冷轧Fe-17Mn-0.05C高锰钢拉伸性能和氢脆断裂分析[J]. 锻压技术, 2019,44(1):5. [6] Zhao Xiaoli, Zhang Yongjian, Hui Weijun, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 0.1C-5Mn medium manganese steel with different rolling and annealing treatments[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(11):11. (赵晓丽, 张永健, 惠卫军, 等. 不同轧制及退火处理0.1C-5Mn中锰钢的氢脆敏感性[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(11):11. [7] Gu Hairong, Lu Xiqian, Liu Yonggang, et al. Effect of microalloyed elements Nb and V on microstructure and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of hot formed steel[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2018,35(4):6. (谷海容, 卢茜倩, 刘永刚, 等. 微合金元素Nb, V对热成形钢组织及氢脆敏感性影响[J]. 安徽工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2018,35(4):6. [8] Koyama M, Tasan C C, Akiyama E, et al. Hydrogen-assisted decohesion and localized plasticity in dual-phase steel[J]. Acta Mater., 2014,70:174−187. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.048 [9] Yamasaki S, Bhadeshia H. Modelling and characterisation of Mo2C precipitation and cementite dissolution during tempering of Fe-C-Mo martensitic steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003,19:723−731. doi: 10.1179/026708303225002929 -





 下载:
下载: