Investigation on thermal shrinkage deformation of the continuously cast slab
-
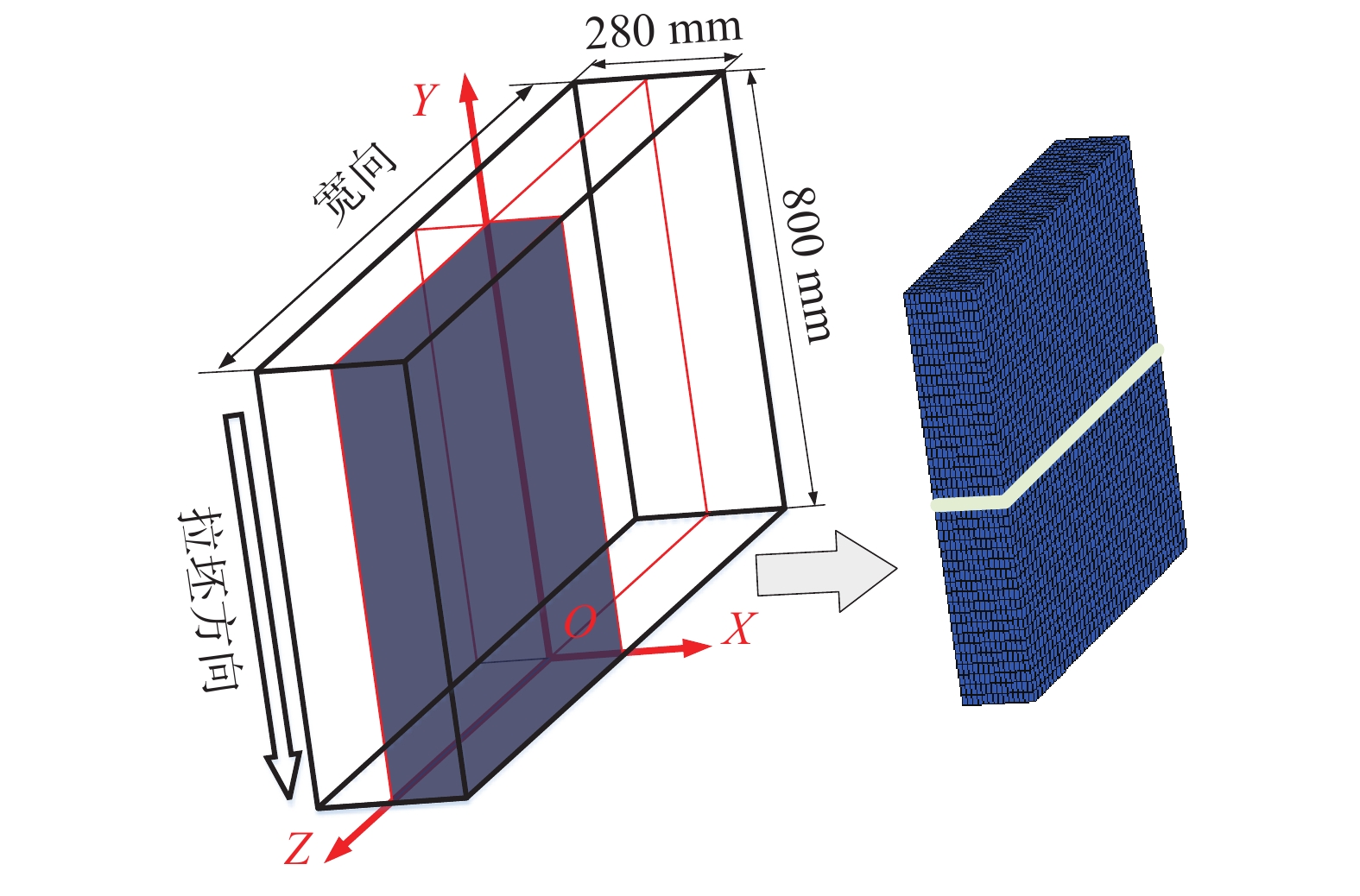
摘要: 连铸过程铸坯已凝固坯壳因冷却降温发生热收缩变形,该变形是制定连铸机基础收缩辊缝的重要依据。以板坯连铸过程为对象,建立了三维热-力耦合有限元模型,揭示了板坯连铸过程已凝固坯壳沿厚度方向热收缩变形规律。结果表明,浇铸过程中坯壳热收缩变形不断增大,在凝固终点位置热收缩出现短时加速增大趋势,铸机末端位置坯壳宽向中心位置热收缩约8 mm;板坯宽向不同位置热收缩变形存在较明显差异,由宽向中心至铸坯角部方向,已凝固坯壳厚度方向热收缩变形呈先减小后增大趋势。随着拉速增加,相同铸流位置热收缩变形减小,拉速增加0.1 m/min,铸机末端位置的坯壳宽向中心与宽向1/8位置热收缩减小约1.2 mm。研究结果为优化铸机基础收缩辊缝,改善因不合理基础辊缝导致的铸坯内部质量问题提供了数据支撑。Abstract: In the continuous casting process, thermal shrinkage deformation of the solidified shell occurs due to the temperature decrease during the cooling process, and this thermal shrinkage deformation is the important basis for designing basic shrinkage gap of the continuous casting machine. In the present work, a 3D thermal-mechanical coupling model was developed, and the thermal shrinkage deformation of the continuous casting slab was investigated. The results indicate that the thermal shrinkage deformation continuously increased during the continuous casting process and a rapidly increasing trend was observed at the solidification end of the strand. The total shrinkage of the wide surface center was ~8 mm at the exit of the continuous casting machine. The difference of the thermal shrinkage deformation along the slab width direction was obvious, and the shrinkage deformation showed a decreasing trend first and then an increasing trend from the slab surface center to its corner. The thermal shrinkage at the same strand position decreased with increasing the casting speed, and the total thermal shrinkage of the wide surface center and 1/8 width decreased ~1.2 mm with increasing the casting speed by 0.1 m/min. The present work provided data support for optimizing the basic shrinkage gap of the continuous casting machine and thus alleviating the internal quality of the continuous casting steel.
-
Key words:
- continuously cast /
- slab /
- 3D thermal-mechanical coupling /
- finite element /
- thermal shrinkage
-
表 1 冷却分区参数
Table 1. Parameters of the cooling zones
冷却分区 起始铸流位置/m 结束铸流位置/m 结晶器 0 0.80 二冷1区 0.80 1.04 二冷2区 1.04 1.60 二冷3区 1.60 2.71 二冷4区 2.71 4.26 二冷5区 4.26 6.18 二冷6区 6.18 10.02 二冷7区 10.02 13.86 二冷8区 13.86 20.49 二冷9区 20.49 30.33 表 2 模拟参数
Table 2. Simulation paraeters
Q345主要成分(w/ %) 液相线温度/℃ 固相线温度/℃ 板坯厚度/mm 板坯宽度/mm 过热度/oC 拉速/(m.min−1) C Si Mn P S 0.17 0.31 1.5 0.014 0.011 1517.7 1467.5 280 1600,1800,2000 30 0.7,0.8,0.9 -
[1] Li C S, Thomas B G. Thermomechanical finite-element model of shell behavior in continuous casting of steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2004,35(6):1151−1172. doi: 10.1007/s11663-004-0071-z [2] Song J X, Cai Z Z, Piao F Y, et al. Heat transfer and deformation behavior of shell solidification in wide and thick slab continuous casting mold[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2014,21(S1):1−9. [3] Wang T M, Cai S W, Xu J, et al. Continous casting mould for square billet optimized by solidification shrinkage simulation[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2010,37(5):341−346. doi: 10.1179/030192310X12683045806026 [4] Cai Z Z, Zhu M Y. Thermo-mechanical behavior of peritectic steel solidifying in slab continuous casting mold and a new mold taper design[J]. ISIJ International, 2013,53(10):1818−1827. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.53.1818 [5] Zhu L G, Kumar R V. Modelling of steel shrinkage and optimisation of mould taper for high speed continuous casting[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2007,34(1):76−82. doi: 10.1179/174328106X118152 [6] Wang B, Walker B N, Samarasekera I V. Shell growth, surface quality and mould taper design for high-speed casting of stainless steel billets[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2000,39(4):441−454. doi: 10.1179/cmq.2000.39.4.441 [7] Wang Weihua, Liu Yang, Wang Wenjun, et al. Numerical simulation of slab shell solidification shrinkage in continuous casting mould[J]. Research on Iron & Steel, 2014,42(6):26−29. (王卫华, 刘洋, 王文军, 等. 板坯连铸结晶器内坯壳凝固收缩的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁研究, 2014,42(6):26−29. [8] Qian Hongzhi, Du Chenwei, Hu Pijun, et al. Free thermal shrinkage behavior during the solidification process in slab casters[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016,28(8):27−32. (钱宏智, 杜辰伟, 胡丕俊, 等. 板坯连铸凝固过程中的自由热收缩行为[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2016,28(8):27−32. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20150263 [9] Chen Hongzhi, Chang Yunhe, Zhang Jiaquan, et al. Linear contraction and the related basic roller gap for stainless slab casting[J]. China Metallurgy, 2012,22(2):25−30. (陈洪智, 常运合, 张家泉, 等. 不锈钢板坯连铸自由线收缩与辊缝研究[J]. 中国冶金, 2012,22(2):25−30. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.2012.02.007 [10] Ma Changwen, Chen Songlin, Zheng Tianran, et al. Study on roll gap of slab caster based on solidification shrinkage[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(3):44−50. (马长文, 陈松林, 郑天然, 等. 基于凝固收缩的板坯铸机辊缝研究[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(3):44−50. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2008.03.010 [11] Sun Ligen, Li Xiaofei, Zhu Liguang, et al. Optimized design of roll gap for 65Mn slab caster based on solidification shrinkage[J]. Foundry Technology, 2017,38(5):1150−1154. (孙立根, 李晓斐, 朱立光, 等. 基于凝固收缩的65Mn板坯铸机辊缝优化设计[J]. 铸造技术, 2017,38(5):1150−1154. [12] Lin Qiyong, Zhu Miaoyong. Finite element modeling of nature thermal shrinkage for continuous casting slab[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2006,27(S2):8−10. (林启勇, 朱苗勇. 连铸板坯自然热收缩行为有限元模拟[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2006,27(S2):8−10. [13] Hebi Y, Man Y, Huiying Z, et al. 3D stress model with friction in and of mould for round billet continuous casting[J]. ISIJ International, 2006,46(4):546−552. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.46.546 [14] Kim K, Yeo T J, Oh K H, et al. Effect of carbon and sulfur in continuously cast strand on longitudinal surface cracks[J]. ISIJ International, 1996,36(3):284−289. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.36.284 [15] 蔡兆镇. 板坯连铸结晶器内凝固坯壳的热/力学行为研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2011.Cai Zhaozhen. Thermal and mechanical behavior of solidifying shell in slab continuous casting mold[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2011. [16] Wu C H, Ji C, Zhu M Y. Numerical simulation of bulging deformation for wide-thick slab under uneven cooling conditions[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,39(3):1346−1359. -





 下载:
下载: