Effect of coiling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ti-Nb microalloyed steel
-
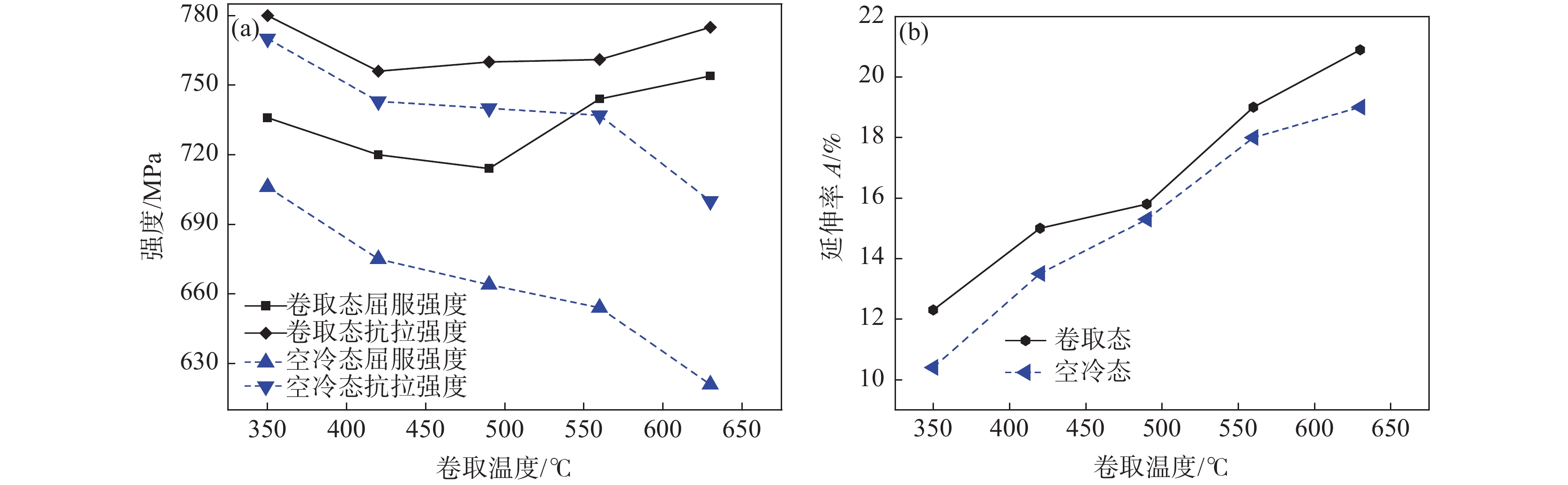
摘要: 利用试验轧机和热处理炉进行了低碳Ti-Nb微合金钢的模拟轧制和卷取试验,研究卷取温度对微观组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明,随着卷取温度的降低,钢的相变过程逐步由扩散型相变过渡到切变型相变,微观组织由等轴铁素体依次转变为多边形铁素体、粒状贝氏体、板条贝氏体;由于析出强化和相变强化的综合作用,卷取态试验钢强度先降低后升高,延伸率持续降低;卷取过程微合金碳氮化物的析出强化导致卷取态试验钢强度高于空冷态试验钢,且随着卷取温度的降低,卷取态试验钢较空冷态试验钢强度的增量逐步降低;Ti-Nb微合金钢的卷取温度设定在560~630 ℃时,钢屈服强度744~754 MPa,延伸率19%~20.9%,可获得良好的综合性能。Abstract: The effect of coiling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical property of a Ti-Nb microalloyed steel was studied by simulated hot rolling and coiling tests conducted on a pilot hot rolling mill and heat treatment furnace. The results show that the phase transformation process of steel gradually changes from diffusion-type phase transformation to shear-type phase transformation, and the microstructure changes from equiaxed ferritic grain to polygonal ferrite, granular bainite, and lath bainite with the coiling temperature decreases. In addition, the strength first decreases and then increases, while the elongation decreases due to precipitation strengthening and phase transformation strengthening. The strength of the steel at the coiling state is higher than that of the steel after air-cooled due to the precipitation and strengthening of micro-alloy carbonitride during the coiling. With the decrease in coiling temperature, the strength increment of steel at the coiling state gradually decreases compared with the steel after air-cooled. The yield strength is 744~754 MPa, and the elongation is 19%~20.9%, which can obtain good comprehensive properties when the coiling temperature of Ti-Nb microalloyed steel is set at 560~630 ℃.
-
Key words:
- Ti-Nb microalloyed steel /
- coiling temperature /
- mechanical property /
- microstructure
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of the experimental steel
% C Si Mn Nb Ti P S Al N 0.08 0.15 1.81 0.05 0.11 0.0038 0.0043 0.018 0.0050 表 2 试验钢板的拉伸性能
Table 2. The tensile properties of the tested plates
编号 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率/% C630 754 775 20.9 C560 744 761 19.0 C490 714 760 15.8 C420 720 756 15.0 C350 736 780 12.3 A630 621 700 19.0 A560 654 737 18.0 A490 664 740 15.3 A420 675 743 13.5 A350 706 770 10.4 -
[1] Yang Hongbo, Wang Hao, Zhao Xu, et al. Research progress on nano-scale interphase precipitation behavior of microalloyed high-strength steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021,56(12):10−21. (杨洪波, 王豪, 赵旭, 等. 微合金高强钢纳米相间析出行为研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(12):10−21. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210124 [2] Jiang Rong. Microstructure and mechanical properties of micro-alloyed steel with V, Nb, and Ti[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2009,(9):13−15. (蒋蓉. 含V, Nb, Ti微合金钢的微观结构及力学性能[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2009,(9):13−15. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2009.09.004 [3] Gladman T. Precipitation hardening in metals[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1999,15(1):30−36. doi: 10.1179/026708399773002782 [4] Li Fan, Ge Zhangqi, Xing Jun, et al. Effect of prior austenite grain size on critical strain of dynamic recrystallization of hot rolled low carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021,42(11):51−58. (李凡, 葛章琦, 邢军, 等. 奥氏体晶粒尺寸对热轧低碳微合金钢动态再结晶临界应变的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2021,42(11):51−58. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2021-0227 [5] Hui Yajun, Pan Hui, Li Wenyuan, et al. Study on the heating schedule of 1 000 MPa grade Nb-Ti microallyed ultra-high strength steel[J]. Actametalica Sinica, 2017,(2):3−13. (惠亚军, 潘辉, 李文远, 等. 1 000 MPa级Nb-Ti微合金化超高强度钢加热制度研究[J]. 金属学报, 2017,(2):3−13. [6] Ding Zhimin, Fang Jianfei, Liang Bo, et al. Kinetics of austenite grain growth of V-Nb-(Ti) microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013,34:88−91. (丁志敏, 方建飞, 梁博, 等. V-Nb-(Ti)微合金化钢奥氏体晶粒长大的动力学[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2013,34:88−91. [7] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 145-147.Yong Qilong. Secondary phases in steels[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 145-147. [8] Liang Wen, Wu Run, Hu Jun, et al. Effect of heating process on Nb-Ti micro-alloyed high strength steel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019,(9):2063−2073. (梁文, 吴润, 胡俊, 等. 加热工艺对Nb-Ti微合金化高强钢的影响[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2019,(9):2063−2073. [9] Wu Xinlang, Zhao Zhenzhi, Tian Yun, et al. Phase transformation and second-phase precipitation behavior of Nb-Ti microalloyed steel during cooling after deformation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2008,29(1):66−70. (吴新朗, 赵征志, 田允, 等. Nb-Ti微合金钢热变形后组织演变及第二相粒子析出行为[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2008,29(1):66−70. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2008.01.013 [10] Zhang Hesong, Kang Yonglin, Tang Xingchang. Nano-precipitates in Nb-Ti microalloy X100 pipeline steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2015,36(11):138−143. (张鹤松, 康永林, 唐兴昌. Nb-Ti微合金化X100管线钢中的纳米析出规律[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,36(11):138−143. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2015.11.024 -





 下载:
下载: