Production of high-purity rutile titanium dioxide by leaching water-quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag with hydrochloric acid
-
摘要: 采用盐酸法浸取水淬含钛高炉渣,固液分离后可得到富含钛、铝等有价元素的浸取液,再通过水解、沉淀等方式可制得高纯度金红石型二氧化钛、氧化铝等产品。系统研究了酸浓度、液固比、反应温度及反应时间等工艺条件对含钛高炉渣中不同元素浸出率的影响,确定了浸出反应的优化工艺条件。当反应温度为90 ℃,盐酸浓度为33%,液固比为15∶1(mL∶g),反应时间为30 min时,钛的浸出率可达到75.3%。130 ℃条件下对浸出液进行水解、干燥,即可得到纯度为97.7%的金红石型二氧化钛。该方法可直接从水淬含钛高炉渣中回收钛元素并制得高纯度二氧化钛产品,流程短,能耗低,可为含钛高炉渣的资源化利用提供支持。Abstract: Hydrochloric acid method was used for the leaching of water-quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in this work. According to the leaching and solid-liquid separation process, valuable elements including titanium and aluminum were concentrated in the solution. With further hydrolysis and precipitation, high-purity rutile titanium dioxide and alumina oxide can be obtained. In order to obtain optimized leaching processing parameters, the effects of acid concentration, liquid-solid ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time on the leaching efficiency of different elements in titanium-bearing blast furnace slag were systematically investigated. When the leaching temperature is 90 °C, hydrochloric acid concentration is 33%, liquid-solid ratio is 15 : 1 (mL : g), and leaching time is 30 min, the leaching efficiency of titanium reaches 75.3%. By hydrolysis at 130 °C and following drying process, rutile titanium dioxide with a purity of 97.7% can be obtained. This method can be directly applied for the recovery of valuable titanium from the water-quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag and for the production of high purity titanium dioxide, with short process and low energy consumption, which can provide practical support for the resourceful utilization of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag.
-
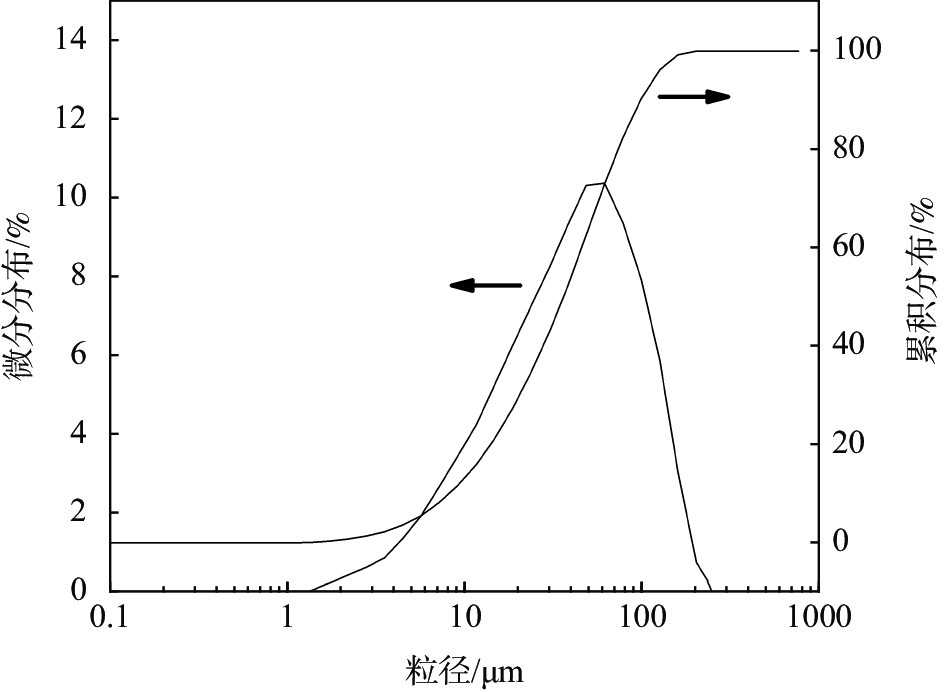
表 1 水淬含钛高炉渣的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of water-quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag
% TiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 SiO2 其它 21.50 26.66 9.18 12.96 21.75 7.95 -
[1] Li Fei. Current situation and development trend of world titanium industry[J]. Low Carbon World, 2016,(24):127−128. (李飞. 世界钛工业现状及发展趋势[J]. 低碳世界, 2016,(24):127−128.Li Fei. Current situation and development trend of world titanium industry[J]. Low Carbon World, 2016(24): 127-128. [2] Li Zheng, Chen Congxi. Development status of global titanium resource industry[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021,42(2):245−250. (李政, 陈从喜. 全球钛资源行业发展现状[J]. 地球学报, 2021,42(2):245−250.Li Zheng, Chen Congxi. Development status of global titanium resource industry[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 245-250. [3] Deng Yong, Zhen Changliang, Li Junguo, et al. Titanium enrichment process of titanium bearing blast furnace slag and utilization of titanium resources[J]. China Metallurgy, 2022,32(8):25−31. (邓勇, 甄常亮, 李俊国, 等. 含钛高炉渣钛富集工艺及钛资源利用[J]. 中国冶金, 2022,32(8):25−31. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20220124Deng Yong, Zhen Changliang, Li Junguo, et al. Titanium enrichment process of titanium bearing blast furnace slag and utilization of titanium resources[J]. China Metallurgy, 2022, 32(8): 25-31. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20220124 [4] Tan Qiyou, Chen Bo, Zhang Yushu, et al. Characteristics and current situation of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titano-magnetite resources in Panxi region[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2011,(6):6−10. (谭其尤, 陈波, 张裕书, 等. 攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿资源特点与综合回收利用现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2011,(6):6−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2011.06.002Tan Qiyou, Chen Bo, Zhang Yushu, et al. Characteristics and current situation of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titano-magnetite resources in Panxi region[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2011 (6): 6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2011.06.002 [5] Cai Y, Song N, Yang Y, et al. Recent progress of efficient utilization of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2022,29(1):22−31. doi: 10.1007/s12613-021-2323-1 [6] Liu Weizao, He Minyu, Liu Qingcai, et al. Study on the mechanism of rutile beneficiation by roasting titanium-bearing blast furnace slag with copperas[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral, 2022,42(3):75−81. (刘维燥, 何民宇, 刘清才, 等. 含钛高炉渣/绿矾协同焙烧富集金红石机理研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2022,42(3):75−81. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2022.03.011Liu Weizao, He Minyu, Liu Qingcai, et al. Study on the mechanism of rutile beneficiation by roasting titanium-bearing blast furnace slag with copperas[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral, 2022, 42(3): 75-81. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2022.03.011 [7] Montenegro-Cooper J M, Celemín-Matachana M, Cañizal J, et al. Study of the expansive behavior of ladle furnace slag and its mixture with low quality natural soils[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019,203:201−209. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.040 [8] Wang L, Chen L, Liu W, et al. Recovery of titanium, aluminum, magnesium and separating silicon from titanium-bearing blast furnace slag by sulfuric acid curing-leaching[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2022,29(9):1705−1714. doi: 10.1007/s12613-021-2293-3 [9] Wang Yu. Analysis on the separation and extraction technology of titanium components in titanium bearing blast furnace slag[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2022,(13):13−15. (王珏. 含钛高炉渣中钛组分的分离提取技术探析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2022,(13):13−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2022.13.005Wang Yu. Analysis on the separation and extraction technology of titanium components in titanium bearing blast furnace slag[J] . World Nonferrous Metals, 2022(13): 13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2022.13.005 [10] Liu Xiaohua, Sui Zhitong. Leaching of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by pressuring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002,(6):1281−1284. (刘晓华, 隋智通. 含Ti高炉渣的加压酸解[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002,(6):1281−1284. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2002.06.038Liu Xiaohua, Sui Zhitong. Leaching of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by pressuring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002(6): 1281-1284. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2002.06.038 [11] Yan Fang, Li Chun, Liang Bin. A two-step sulfuric acid leaching process of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006,(3):413−417. (严芳, 李春, 梁斌. 水淬含钛高炉渣二段酸解工艺[J]. 过程工程学报, 2006,(3):413−417. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.03.015Yan Fang, Li Chun, Liang Bin. A two-step sulfuric acid leaching process of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006(3): 413-417. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.03.015 [12] Jiang T, Dong H G, Guo Y F, et al. Study on leaching Ti from Ti bearing blast furnace slag by sulphuric acid[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2013,119(1):33−38. [13] Zhang Y. Recovery of titanium from titanium bearing blast furnace slag by sulphate melting[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2014,53(4):440−443. doi: 10.1179/1879139514Y.0000000136 [14] Wang L, Liu W, Hu J, et al. Indirect mineral carbonation of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag coupled with recovery of TiO2 and Al2O3[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018,26(3):583−592. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017.06.012 [15] Xiong Y, Aldahri T, Liu W, et al. Simultaneous preparation of TiO2 and ammonium alum, and microporous SiO2 during the mineral carbonation of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020,28(9):2256−2266. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.03.020 [16] Xiong Yao, Li Chun, Liang Bin, et al. Leaching behavior of air cooled Ti-bearing blast-furnace slag in hydrochloric acid[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008,(3):557−563. (熊瑶, 李春, 梁斌, 等. 盐酸浸出自然冷却含钛高炉渣[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008,(3):557−563. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.03.030Xiong Yao, Li Chun, Liang Bin, et al. Leaching behavior of air cooled Ti-bearing blast-furnace slag in hydrochloric acid[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008(3): 557-563. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.03.030 [17] Xiong Yao, Liang Bin, Li Chun. et al Extraction and separation of titanium from air-cooled Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008,8(6):1092−1097. (熊瑶, 梁斌, 李春. 自然冷却含钛高炉渣中钛的提取与分离[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008,8(6):1092−1097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2008.06.009Xiong Yao, Li Chun, Liang Bin, et al. Extraction and separation of titanium from air-cooled Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008, 8(6): 1092-1097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2008.06.009 [18] Zhu S, Hu J, Zhang C, et al. Process optimization and kinetics of titanium leaching from mechanically activated titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2022,(9):230−239. [19] Cao Hongyang, Fu Nianxin, Kang Changbo, et al. Pressure leaching of the modified Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by hydrochloric acid[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2008,(4):11−14. (曹洪杨, 付念新, 康常波, 等. 改性含钛高炉渣的盐酸加压浸出[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2008,(4):11−14.Cao Hongyang, Fu Nianxin, Kang Changbo, et al. Pressure leaching of the modified Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by hydrochloric acid[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2008(4): 11-14. [20] Sui Zhitong, Guo Zhenzhong, Zhang Li, et al. Green separation technique of Ti component from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006,(2):93−97. (隋智通, 郭振中, 张力, 等. 含钛高炉渣中钛组分的绿色分离技术[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2006,(2):93−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2006.02.004Sui Zhitong, Guo Zhenzhong, Zhang Li, et al. Green separation technique of Ti component from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006(2): 93-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2006.02.004 [21] Zhang Peng, Liu Daijun, Mao Xuehua, et al. Leaching of water quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in hydrochloric acid[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(5):6−9. (张鹏, 刘代俊, 毛雪华, 等. 水淬含钛高炉渣的盐酸浸取研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(5):6−9. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.05.002Zhang Peng, Liu Daijun, Mao Xuehua, et al. Leaching of water quenched titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in hydrochloric acid[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012, 33(5): 6-9. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.05.002 [22] Zhang Peng, Liu Daijun, Mao Xuehua. Study on preparation of TiO2 from aqueous TiCl4 solution by pyrohydrolysis[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013,34(5):19−22. (张鹏, 刘代俊, 毛雪华. 四氯化钛热水解制备钛白粉的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2013,34(5):19−22. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.05.004Zhang Peng, Liu Daijun, Mao Xuehua. Study on preparation of TiO2 from aqueous TiCl4 solution by pyrohydrolysis[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(5): 19-22. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.05.004 [23] Ma G Q, Cheng M. Technological study of titanium slag production from titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014,(962-965):793−796. [24] Li Xiaoying, Peng Jianrong, Zhai Zhongbiao, et al. The technical study on titanium recovery from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2018,47(6):45−48. (李小英, 彭建蓉, 翟忠标, 等. 含钛高炉渣回收钛的工艺研究[J]. 云南冶金, 2018,47(6):45−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2018.06.009Li Xiaoying, Peng Jianrong, Zhai Zhongbiao, et al. The technical study on titanium recovery from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2018, 47(6): 45-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2018.06.009 [25] Li C, Liang B, Wang H. Preparation of synthetic rutile by hydrochloric acid leaching of mechanically activated Panzhihua ilmenite[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008,91(1-4):121−129. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.11.013 [26] Li Liang, Luo Jianlin. Process mineralogy studies on V-Ti magnetite in Panzhihua region[J]. Metal Mine, 2010,(4):89−92, 109. (李亮, 罗建林. 攀枝花地区某钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2010,(4):89−92, 109.Li Liang, Luo Jianlin. Process mineralogy studies on V-Ti magnetite in Panzhihua region[J]. Metal Mine, 2010 (4): 89-92+109. [27] 遵义钛业股份有限公司, 金川集团有限公司, 云南新立有色金属有限公司, 等. 钛铁矿精矿化学分析方法, 第1部分: 二氧化钛量的测定, 硫酸铁铵滴定法[M]. 北京: 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部, 2011: 1-8.Zunyi Titanium Industry Co. , Ltd. , Jinchuan Group Co. , Ltd. , Yunnan Xinli Nonferrous Metals Co. , Ltd. , et al. Methods of chemical analysis for ilmenite concentrate, Part 1: Determination of titanium dioxide content-Ferric ammonium sulfate titration[M]. Beijing: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China, 2011: 1-8. [28] Zhang Qinghong, Gao Lian, Guo Jingkun. Preparation of nanosized TiO2 powders from hydrolysis of TiCl4[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000,(1):21−25. (张青红, 高濂, 郭景坤. 四氯化钛水解法制备纳米氧化钛超细粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000,(1):21−25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-324X.2000.01.004Zhang Qinghong, Gao Lian, Guo Jingkun. Preparation of nanosized TiO2 powders from hydrolysis of TiCl4[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-324X.2000.01.004 [29] Xu Jing, Gong Peng, Qin Ximei. Research on hydrolysis of TiCl4 characteristic[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2009,28(6):13−15. (续京, 宫鹏, 秦喜梅. 四氯化钛水解特性的研究[J]. 石油化工应用, 2009,28(6):13−15.Xu Jing, Gong Peng, Qin Ximei. Research on hydrolysis of TiCl4 characteristic[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2009, 28(6): 13-15. -





 下载:
下载: