Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and impact properties of low-carbon high-alloy bearing steel
-
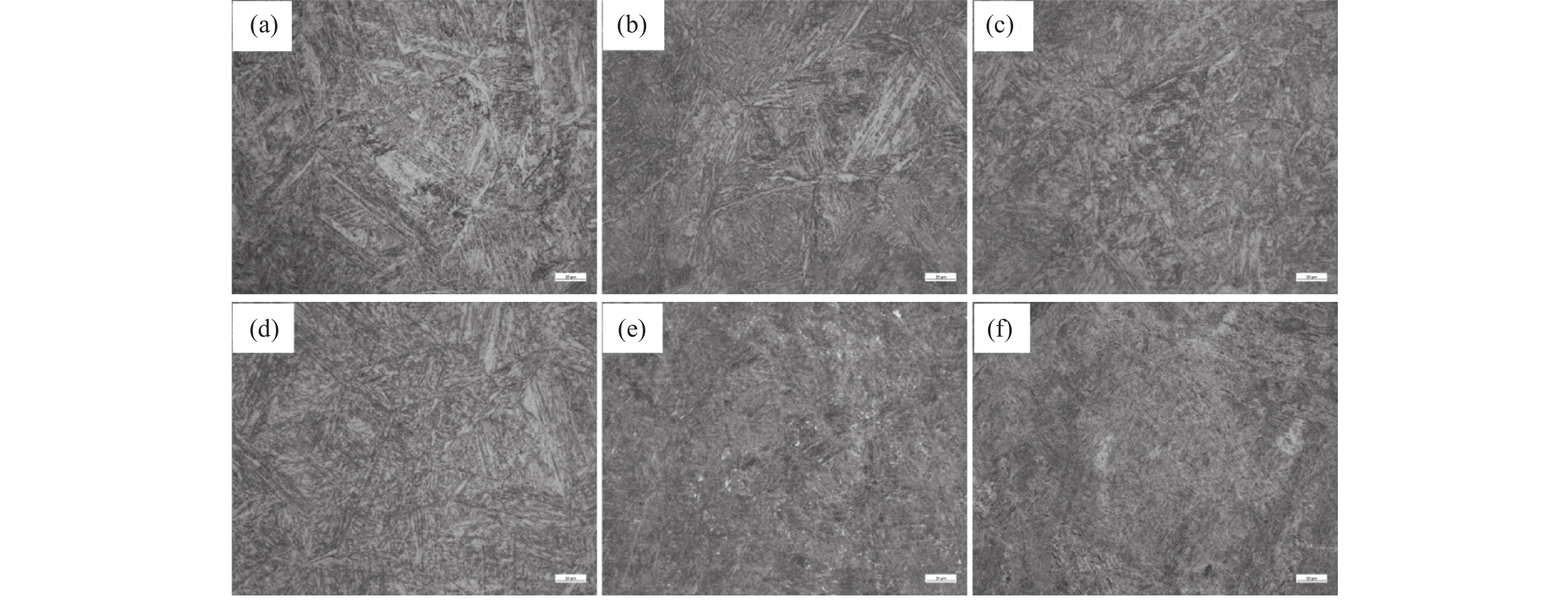
摘要: 以低碳高合金轴承钢为研究对象,通过OM、SEM、XRD等手段,研究了回火温度对显微组织和冲击韧性的影响。结果表明,低碳高合金轴承钢分别经过200、300、400、500 ℃回火处理后,金相显微组织均为回火马氏体+残余奥氏体;600 ℃和700 ℃回火处理后,马氏体组织发生退化,金相显微组织均为回火索氏体+残余奥氏体。低碳高合金轴承钢在200~700 ℃温度区间回火处理后,300 ℃回火冲击韧性最高,600 ℃回火冲击韧性最低,回火温度不宜超过500 ℃。低碳高合金轴承钢在200~500 ℃回火后断口特征均为准解离断裂,600 ℃和700 ℃回火表现为明显的脆性断裂特征。Abstract: The effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and impact toughness of low-carbon, high-alloy bearing steel was studied by OM, SEM, and XRD. The results show that the metallographic microstructure for the low-carbon, high-alloy bearing steel consisted of tempered martensite and retained austenite when the tempering temperature is 200, 300, 400, 500 ℃, respectively. Furthermore, martensite degradation occurs, and the microstructure consists of tempered soxbite and retained austenite when the tempering temperature increases to 600 ℃ and 700 ℃. After tempering at 200-700 ℃, the impact toughness of low-carbon, high-alloy bearing steel tempered at 300 ℃ is the highest, that tempered at 600 ℃ is the lowest, and the tempering temperature should not exceed 500 ℃. The fracture characteristics of low-carbon, high-alloy bearing steel after tempering at 200-500 ℃ are quasi-dissociative fractures, and the tempering at 600 ℃ and 700 ℃ are brittle fractures.
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of tested steel
% C Cr Ni Co Mo V Fe 0.14 13.5 2.0 12.5 4.6 0.60 余量 -
[1] Li Zhaokun, Lei Jianzhong, Xu Haifeng, et al. Current status and development trend of bearing steel in China and abroad[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016,28(3):1−12. (李昭昆, 雷建中, 徐海峰, 等. 国内外轴承钢的现状与发展趋势[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2016,28(3):1−12. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20150345Li Zhaokun, Lei Jianzhong, Xu Haifeng, et al. Current status and development trend of bearing steel in China and abroad[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016, 28(3): 1-12. DOI: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20150345. [2] Maloney James L, Tomasello Colleen M. Case carburized stainless steel alloy for high temperature applications: EPO, EP0664342[P]. 1995-07-26. [3] Geng Siyuan, Yang Maosheng, Zhao Kunyu. Fatigue crack initiation and propagation behavior of high cobalt molybdenum stainless bearing steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2018,30(11):906−915. (耿思远, 杨卯生, 赵昆渝. 高钴钼不锈轴承钢疲劳裂纹萌生及扩展行为[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2018,30(11):906−915. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20180053Geng Siyuan, Yang Maosheng, Zhao Kunyu. Fatigue crack initiation and propagation behavior of high cobalt molybdenum stainless bearing steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2018, 30(11): 906-915. DOI: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20180053. [4] Xiao Maoguo, Lv Xinyang, Li Donghui, et al. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms of high Cr-Co-Mo heat resistant bearing steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2018,39(9):52−57. (肖茂果, 吕新杨, 李东辉, 等. 高Cr-Co-Mo高温轴承钢的强韧化机制[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018,39(9):52−57. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2018-0176Xiao Maoguo, Lv Xinyang, Li Donghui, et al. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms of high Cr-Co-Mo heat resistant bearing steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2018, 39(9): 52-57. DOI: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2018-0176. [5] Yuan Xiaohong, Zheng Shanju, Yang Maosheng, et al. Carbide precipitation and microstructure refinement of Cr-Co-Mo-Ni bearing steel during hot deformation[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015,22(9):3265−3274. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2865-3 [6] 尹龙承. 14Cr14Co13Mo4钢Ni缓冲层法渗碳及热处理工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.Yin Longcheng. Ni buffer layer method for carburizing and heat treatment of 14Cr14Co13Mo4 steel[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. [7] 袁晓虹. 高Cr-Co-Mo轴承钢强韧机制及抗疲劳特性的多尺度研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015.Yuan Xiaohong. Multi-scale strengthening-toughening mechanisms and fatigue resistance of high-alloy Cr-Co-Mo bearing steel[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015. [8] Yuan Xiaohong, Zheng Shanju, Yin Shubiao, et al. Effect of tempering time on microstructure and properties of high temperature bearing steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2014,39(10):28−31. (袁晓虹, 郑善举, 阴树标, 等. 回火时间对高温轴承钢组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2014,39(10):28−31. doi: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2014.10.007Yuan Xiaohong, Zheng Shanju, Yin Shubiao, et al. Effect of tempering time on microstructure and properties of high temperature bearing steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2014, 39(10): 28-31. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2014.10.007. [9] Wen Tao, Hu Xiaofeng, Song Yuanyuan, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on carbide and mechanical properties in a Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo high-strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014,50(4):447−453. (温涛, 胡小锋, 宋元元, 等. 回火温度对一种Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo高强钢碳化物及其力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014,50(4):447−453. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1037.2013.00672Wen Tao, Hu Xiaofeng, Song Yuanyuan, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on carbide and mechanical properties in a Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo high-strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(4): 447-453. DOI: 10.3724/sp.j.1037.2013.00672. [10] Yu Bin, Li Xiaoyuan, Shi Jie, et al. Effect of high temperature tempering on microstructure and mechanical properties of GCr15SiMn bearing steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015,40(2):176−179. (余斌, 李晓源, 时捷, 等. 高温回火对GCr15SiMn轴承钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(2):176−179. doi: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2015.02.039Yu Bin, Li Xiaoyuan, Shi Jie, et al. Effect of high temperature tempering on microstructure and mechanical properties of GCr15 SiMn bearing steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015, 40(2): 176-179. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2015.02.039. [11] Yajima E, Miyazaki T, Sugiyama T, et al. Effects of retained austenite on the rolling fatigue life of ball bearing steels[J]. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 2007,15(3):173−179. [12] Zhang Yan, Zhao Aimin, He Jianguo, et al. Effects of tempering temperature on microstructure and properties of Cr8Ni2MoNb steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015,40(3):114−116. (张岩, 赵爱民, 何建国, 等. 回火温度对Cr8Ni2MoNb钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(3):114−116. doi: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2015.03.026Zhang Yan, Zhao Aimin, He Jianguo, et al. Effects of tempering temperature on microstructure and properties of Cr8 Ni2 MoNb steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015(3): 114-116. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2015.03.026. [13] 章守华. 合金钢[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1981.Zhang Shouhua. Alloy steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1981. [14] 黄慧玲. 含钴高性能高速钢回火组织和性能演变研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015.Huang Huiling. Study on the tempering microstructure and performance of high speed steel containing cobalt[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015. [15] Yong Qilong, Sun Xinjun, Zheng Lei, et al. Role of the second phase in iron and steel materials[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2009,(8):2−3. (雍岐龙, 孙新军, 郑磊, 等. 钢铁材料中第二相的作用[J]. 科技创新导报, 2009,(8):2−3. doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098x.2009.08.002Yong Qilong, Sun Xinjun, Zheng Lei, et al. Role of the second phase in iron and steel materials[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2009(8): 2-3. DOI:10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098 x.2009.08.002. [16] Sun Chen, Fu Paixin, Liu Hongwei, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on the low temperature impact toughness of 42CrMo4-V steel[J]. Metals, 2018,8(4):232. doi: 10.3390/met8040232 [17] Yan Peng, Liu Zhengdong, Bao Hansheng, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on the toughness of 9Cr–3W–3Co martensitic heat resistant steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2014,54:874−879. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.017 -





 下载:
下载: