Effect of titanium content on hydrogen embrittlement behavior of bainite/martensite dual-phase steel
-
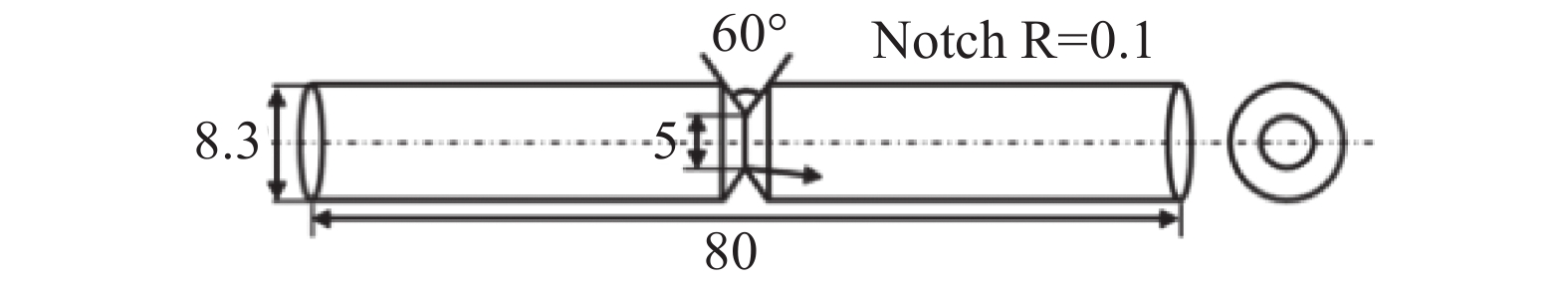
摘要: 冶炼了三种不同钛含量(0、0.9%和1.8%)的贝氏体-马氏体双相钢,通过热处理调整试样中贝氏体含量使其保持相同的强度水平,借助电化学充氢和慢应变速率拉伸试验手段研究了贝氏体含量对贝氏体-马氏体双相钢抗氢脆行为的影响。试验结果表明,钛含量为1.8%的试验钢中具有最高的贝氏体含量和最优异的抗氢脆性能,这主要归因于渗碳体-铁素体界面位错等不可逆陷阱对氢原子的俘获作用。为了提高贝氏体-马氏体双相钢的抗氢脆能力,可增加贝氏体组织中细小渗碳体颗粒的数量,为塑性变形过程中氢的迁移提供更多的不可逆氢陷阱。Abstract: Three kinds of bainite/martensite dual-phase steels with different titanium content (0, 0.9, and 1.8 wt%) were smelted in this paper. The bainite content in the samples was changed by heat treatment to maintain the same strength level. The effect of bainite content on the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of bainite/martensite dual-phase steel was studied by electrochemical hydrogen charging and a slow strain rate tensile test. The results show that the test steel with a titanium content of 1.8 wt% has the highest bainite content and the best resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, mainly due to the capture of hydrogen atoms by irreversible traps such as cementite ferrite interface dislocations. In order to improve the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of bainite/martensite dual-phase steel, the number of fine cementite particles in the bainite structure can be increased, which provides more irreversible hydrogen traps for hydrogen migration during plastic deformation.
-
Key words:
- dual-phase steel /
- titanium content /
- hydrogen trap /
- hydrogen embrittlement behavior
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of tested steels
% 编号 C Si Mn Cr V Mo Ti 1# 0.403 0.102 0.413 1.02 0.108 0.601 0.003 2# 0.398 0.100 0.406 1.01 0.107 0.596 0.902 3# 0.405 0.107 0.407 1.02 0.110 0.599 1.82 -
[1] Fang Hongsheng, Liu Dongyu, Chang Kaidi, et al. Microstructure and properties of 1500 MPa economical bainite / martensite multiphase steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2001,13(3):31−36. (方鸿生, 刘东雨, 常开地, 等. 1 500 MPa级经济型贝氏体/马氏体复相钢的组织与性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2001,13(3):31−36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2001.03.008Fang Hongsheng, Liu Dongyu, Chang Kaidi, et al. Microstructure and properties of 1500 MPa economical Bainite / martensite multiphase steel[J]. Journal of iron and steel research, 2001, 13 (3): 31-36 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2001.03.008 [2] Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng. Effect of heat treatment process on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new bainite / martensite dual phase high strength steel[J]. World Steel, 2002,2(4):23−27. (常开地, 顾家琳, 方鸿生. 热处理工艺对新型贝氏体/马氏体双相高强钢氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 世界钢铁, 2002,2(4):23−27.Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng. Effect of heat treatment process on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new bainite / martensite dual phase high strength steel[J]. World steel, 2002, 2 (4): 23-27 [3] Guo Haoran, Gao Guhui, Gui Xiaolu, et al. Effect of microstructure on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of bainite reinforcement[J]. Materials Reports, 2019,33(10):1717−1722. (郭浩冉, 高古辉, 桂晓露, 等. 显微组织对贝氏体钢筋氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2019,33(10):1717−1722. doi: 10.11896/cldb.17090254Guo Haoran, Gao guhui, GUI Xiaolu, et al. Effect of microstructure on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of bainite reinforcement[J]. Material guide, 2019, 33 (10): 1717-1722 doi: 10.11896/cldb.17090254 [4] Chen Jun, Li Chengji, Zhang Shouhua. Hydrogen embrittlement fracture behavior of ferrite granular bainite dual phase steel after cold deformation[J]. Materials Science Progress, 1988,3:68−72. (陈俊, 李承基, 章守华. 铁素体-粒状贝氏体型双相钢冷变形后的氢脆断裂行为[J]. 材料科学进展, 1988,3:68−72.Chen Jun, Li Chengji, Zhang Shouhua. Hydrogen embrittlement fracture behavior of ferrite granular bainite dual phase steel after cold deformation[J]. Advances in materials science, 1988, 3: 68-72 [5] Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng, et al. Hydrogen trap in bainite/martensite duplex high strength steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2003,28(3):20−23. (常开地, 顾家琳, 方鸿生, 等. 贝氏体/马氏体复相高强钢中的氢陷阱[J]. 金属热处理, 2003,28(3):20−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2003.03.006Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng, et al. Hydrogen trap in Bainite / Martensite Duplex high strength steel[J]. Metal heat treatment, 2003, 28 (3): 20-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2003.03.006 [6] Li Xinfeng, Zhang Jin, Shen Sicong, et al. Effect of tempering temperature and inclusions on hydrogen-assisted fracture behaviors of a low alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017,682:359−369. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.11.064 [7] Nagao Akihide, Smith Cynthia D, Dadfarnia Mohsen, et al. The role of hydrogen in hydrogen embrittlement fracture of lath martensitic steel[J]. Acta Material, 2012,60:5182−5189. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.06.040 [8] Su Liting, Zhang Fucheng, Zheng Chunlei, et al. Effect of heat treatment process and hydrogen charging on compressive properties of gcr15simoal bearing steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017,38(2):111−117. (苏丽婷, 张福成, 郑春雷, 等. 热处理工艺和充氢对GCr15SiMoAl轴承钢压缩性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017,38(2):111−117.Su Liting, Zhang Fucheng, Zheng Chunlei, et al. Effect of heat treatment process and hydrogen charging on compressive properties of gcr15 simoal bearing steel[J]. Journal of material heat treatment, 2017, 038 (2): 111-117 [9] Chen Kang, Xia Bin, Xu Le, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 2000 MPa martensitic steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017,(8):76−82. (谌康, 夏彬, 徐乐, 等. 2000 MPa级马氏体钢的氢脆敏感性[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017,(8):76−82.Chen Kang, Xia Bin, Xu Le, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 2000 mPa martensitic steel[J]. Journal of material heat treatment, 2017 (8): 76-82 [10] Pan Chuan, Li Zhengbang, Tian Zhiling, et al. Quantitative study on hydrogen embrittlement of stainless steel caused by hydrogen and hydrogen induced martensite[J]. Science in Chiana (Series E), 2002,3(3):57−63. (潘川, 李正邦, 田志凌, 等. 氢和氢致马氏体导致不锈钢氢脆的定量研究[J]. 中国科学E辑:技术科学, 2002,3(3):57−63.Pan Chuan, Li Zhengbang, Tian Zhiling, et al. Quantitative study on hydrogen embrittlement of stainless steel caused by hydrogen and hydrogen induced martensite[J]. Chinese science e: technical science, 2002, 3 (3): 57-63 -





 下载:
下载: