Study on migration and transformation behavior of elements during vanadium extraction by calcification
-
摘要: 试验结合XRD、XPS、SEM-EDS和ICP-OES等分析手段,研究了不同pH值条件下酸性铵盐沉钒产物的物相组成及形貌,并分析了沉钒pH值等于2.20时V、Fe和Mn三种元素的迁移转化行为。结果表明,沉钒pH值显著影响产物的组成和形貌,较低pH值沉钒滤饼为无定形结构,随着pH值的升高,晶型逐渐确定。V在提钒尾渣中以CaV2O6形式存在,在滤饼中以多聚钒酸根形式存在,终产品中则以V2O5的形式存在;Fe在尾渣中的主要存在形式为Fe2O3和Fe2TiO5,在沉钒滤饼和终产品中含量较少;Mn在尾渣中以MnSO4形式存在,沉钒过程中主要进入到上清液中,滤饼中则以MnV2O6·4H2O形式存在,终产品中有0.210%。Abstract: Combined with XRD, XPS, SEM-EDS and ICP-OES characterizations, the phase composition and morphology of acid ammonium salt precipitation vanadium products under different pH values were studied; also the migration and transformation behavior of V, Fe and Mn were analyzed when the pH value of vanadium precipitation was 2.20. The results show that the pH value of vanadium precipitation significantly affects the composition and morphology of the product. The filter cake of vanadium precipitation is amorphous at low pH value, and the crystal form is gradually determined with the increase of pH value. V exists in the form of CaV2O6 in vanadium extraction tailings, polyvanadate in filter cake, and V2O5 in the final product. The main forms of Fe in tailings are Fe2O3 and Fe2TiO5, which are less abundant in vanadium filter cake and final product. Mn exists in the form of MnSO4 in the tailings, and mainly enters the supernatant during vanadium precipitation, while MnV2O6·4H2O exists in the filter cake and with 0.210% in the final product.
-
表 1 钙化焙烧熟料XRF成分分析
Table 1. XRF component analysis of calcified roasted clinker
% O Fe Si Ti V Mn Cr Al Mg Ca Na P 34.83 30.92 4.03 5.90 8.47 7.35 1.04 0.799 0.555 5.36 0.168 0.045 表 2 钙化酸浸液的主要成分
Table 2. Main composition of calcified acid leaching solution
g/L V Mn Ca Al Fe Mg Cr Ti 30.3 13.6 0.99 0.251 0.0417 0.809 0.0134 0.0340 表 3 沉钒上清液的主要成分
Table 3. Main compositions of vanadium precipitation supernatant
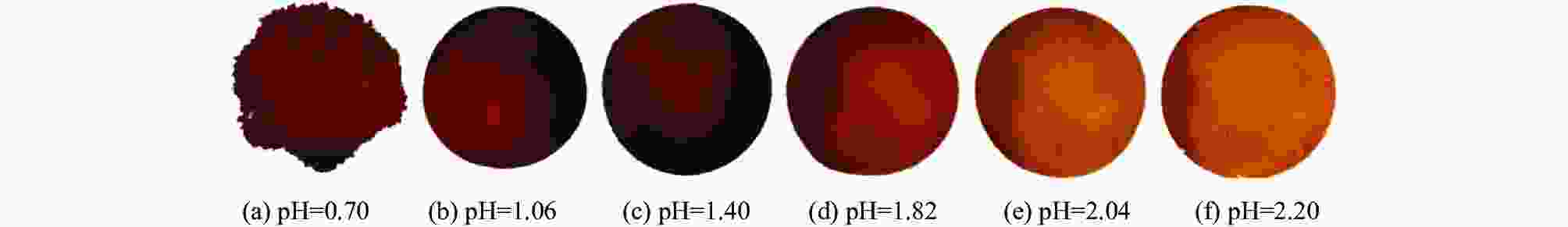
pH 含量/(g·L−1) V Mn Ca Al Fe Mg Cr Ti 0.70 7.73 12.8 1.01 0.0404 0.0435 0.772 0.00947 0.00887 1.06 4.68 13.2 1.35 0.0855 0.0610 0.797 0.0171 0.00704 1.40 3.15 17.5 1.03 0.0594 0.0460 0.999 0.0139 0.00577 1.82 1.77 15.5 0.843 0.0506 0.0233 0.909 0.00942 0.00456 2.04 0.619 19.5 0.950 0.0986 0.0186 1.14 0.00525 0.00367 2.20 0.432 21.3 0.815 0.0865 0.0238 1.22 0.00643 0.00416 表 4 XRF氧化物含量分析
Table 4. XRF oxide content analysis
% 试样 V2O5 Fe2O3 MnO SO3 SiO2 CaO TiO2 Al2O3 MgO Na2O P2O5 K2O Cr2O3 CALT① 5.81 47.98 6.57 8.90 8.35 7.24 10.78 1.52 0.594 0.209 0.124 0.0642 1.61 PVFC② 98.36 0.0979 0.274 0.253 0.0118 0.211 0.0771 0.0203 0.127 0.0893 0.0319 0.0075 V2O5 98.49 0.0947 0.271 0.201 0.0115 0.198 0.0801 0.0201 0.118 0.0918 0.0357 0.0074 注:CALT①:钙化酸浸尾渣;PVFC②:沉钒滤饼。 表 5 XRF元素含量分析
Table 5. XRF element content analysis
% 试样 V Fe Mn Ti S Si K Ca O Al Mg Na P Cr CALT① 3.25 33.55 5.08 6.46 3.56 3.90 0.0533 5.18 36.27 0.805 0.358 0.155 0.0540 1.10 PVFC② 55.09 0.0685 0.212 0.0462 0.101 0.0055 0.0062 0.151 43.79 0.0108 0.0765 0.0663 0.0139 V2O5 55.17 0.0662 0.210 0.0480 0.0806 0.0054 0.0061 0.141 43.80 0.0106 0.0714 0.0681 0.0156 -
[1] Anjass Montaha H, Kastner Katharina, Naegele Florian, et al. Stabilization of low-valent iron(I) in a high-valent vanadium(V) oxide cluster[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2017,56(46):14749−14752. doi: 10.1002/anie.201706828 [2] Cha Woojoon, Chin Sungmin, Park Eunseuk, et al. Photocatalytic performance of V2O5/TiO2 materials prepared by chemical vapor condensation and impregnation method under visible-light[J]. Powder Technology, 2014,258:352−357. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.03.012 [3] Gao Feng, Olayiwola Afolabi Uthmon, Liu Biao, et al. Review of vanadium production part I: Primary resources[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2021,43(4):466−488. [4] He Zhangxing, Li Manman, Li Yuehua, et al. Electrospun nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber as negative electrode for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019,469:423−430. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.220 [5] Chen Desheng, Zhao Hongxin, Hu Guoping, et al. An extraction process to recover vanadium from low-grade vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015,294:35−40. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.054 [6] Gilligan Rorie, Nikoloski Aleksandar N. The extraction of vanadium from titanomagnetites and other sources[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020,146:18. [7] Dong Yingbo, Liu Yue, Lin Hai, et al. Improving vanadium extraction from stone coal via combination of blank roasting and bioleaching by ARTP-mutated Bacillus mucilaginosus[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019,29(4):849−858. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64995-2 [8] Zhao Yunliang, Wang Wei, Zhang Yimin, et al. In-situ investigation on mineral phase transition during roasting of vanadium-bearing stone coal[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2017,28(3):1103−1107. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2016.12.019 [9] Ma Zhiyuan, Liu Yong, Zhou Jikui, et al. Recovery of vanadium and molybdenum from spent petrochemical catalyst by microwave-assisted leaching[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2019,26(1):33−40. doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1707-y [10] Deng Rongrui, Xiao Hao, Xie Zhaoming, et al. A novel method for extracting vanadium by low temperature sodium roasting from converter vanadium slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020,28(8):2208−2213. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.03.038 [11] Li Hongyi, Fang Haixing, Wang Kang, et al. Asynchronous extraction of vanadium and chromium from vanadium slag by stepwise sodium roasting–water leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015,156:124−135. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.06.003 [12] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Liu Yajing, et al. Extraction behavior of vanadium and chromium by calcification roasting-acid leaching from high chromium vanadium slag: Optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2018,40(1):56−66. [13] Peng Hao, Li Bing, Shi Wenbing, et al. Efficient recovery of vanadium from high-chromium vanadium slag with calcium-roasting acidic leaching[J]. Minerals, 2022,12(2):342. [14] Li Hongyi, Wang Chengjie, Yuan Yiheng, et al. Magnesiation roasting-acid leaching: A zero-discharge method for vanadium extraction from vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020,260:121091. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121091 [15] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Wang Junpeng, et al. An efficient utilization of high chromium vanadium slag: Extraction of vanadium based on manganese carbonate roasting and detoxification processing of chromium-containing tailings[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019,378:120733. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.06.010 [16] Xiang Junyi, Huang Qingyun, Lv Xuewei, et al. Effect of mechanical activation treatment on the recovery of vanadium from converter slag[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(5):2759−2767. doi: 10.1007/s11663-017-1033-6 [17] Wu Zhenxiu, Jiang Lin. Study on vanadium precipitation by hydrolysis of chromium-vanadium solution[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titamium, 2020,41(5):22−26. (伍珍秀, 蒋霖. 钒铬溶液水解沉钒试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(5):22−26. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.05.004Wu Zhenxiu, Jiang Lin. Study on vanadium precipitation by hydrolysis of chromium-vanadium solution [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titamium, 2020, 41(5): 22-26. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.05.004 [18] Li He, Liu Xuheng, He Lihua. Thermodynamic study on vanadium precipitation with calcium salt[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2014,42(1):15−19. (李贺, 刘旭恒, 何利华. 钙盐沉钒的热力学研究[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2014,42(1):15−19.Li He, Liu Xuheng, He Lihua. Thermodynamic study on vanadium precipitation with calcium salt [J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2014, 42(1): 15-19. [19] Li Dabiao. Experiment of acidic precipitation of vanadate-leaching solution[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2003,3(1):53−56. (李大标. 酸性铵盐沉钒条件实验研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2003,3(1):53−56.Li Dabiao. Experiment of acidic precipitation of vanadate-leaching solution [J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2003, 3(1): 53-56. [20] Ma Lei, Zhang Yiming, Liu Tao, et al. Enhancing effect of precipitating vanadium in acid ammonium salt[J]. Rare Metals, 2009,33(6):936−939. (马蕾, 张一敏, 刘涛, 等. 提高酸性铵盐沉钒效果的研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2009,33(6):936−939.Ma Lei, Zhang Yiming, Liu Tao, et al. Enhancing effect of precipitating vanadium in acid ammonium salt [J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 33(6): 936-939. [21] Zhan Lianlian, Zhang Yang, Zheng Shili, et al. Crystallization kinetics of ammonium polyvanadate[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2019,526:125218. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2019.125218 [22] Zhang Juhua, Liang Yue, Zhang Wei, et al. Recovery of manganese from the mother liquor after vanadium precipitation during vanadium extraction with calcified roasting and acid leaching process[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2020,20(10):1174−1181. (张菊花, 梁月, 张伟, 等. 钙化-酸浸提钒沉钒母液中锰的回收[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020,20(10):1174−1181.Zhang Juhua, Liang Yue, Zhang Wei, et al. Recovery of manganese from the mother liquor after vanadium precipitation during vanadium extraction with calcified roasting and acid leaching process [J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(10): 1174-1181. [23] Chen Liang. Effects of pH and temperature on acidic ammonium salt precipitation of vanadate leaching solution[J]. Rare Metals, 2010,34(6):924−929. (陈亮. pH值和温度对酸性铵盐沉钒影响研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2010,34(6):924−929.Chen Liang. Effects of pH and temperature on acidic ammonium salt precipitation of vanadate leaching solution [J]. Rare Metals, 2010, 34(6): 924-929. [24] Wang Yanrong, Li Dabiao, Zhang Hong, et al. Discussion on the main factors affecting vanadium precipitation by acidic ammonium salt and its countermeasures[J]. Ferroalloy, 2012,43(4):12−16. (王艳戎, 李大标, 张宏, 等. 影响酸性铵盐沉钒主要因素及对策探讨[J]. 铁合金, 2012,43(4):12−16.Wang Yanrong, Li Dabiao, Zhang Hong, et al. Discussion on the main factors affecting vanadium precipitation by acidic ammonium salt and its countermeasures [J]. Ferroalloy, 2012, 43(4): 12-16. -





 下载:
下载: