Study on electrical removal of aluminum from Ti-Al alloys in low-temperature molten salt
-
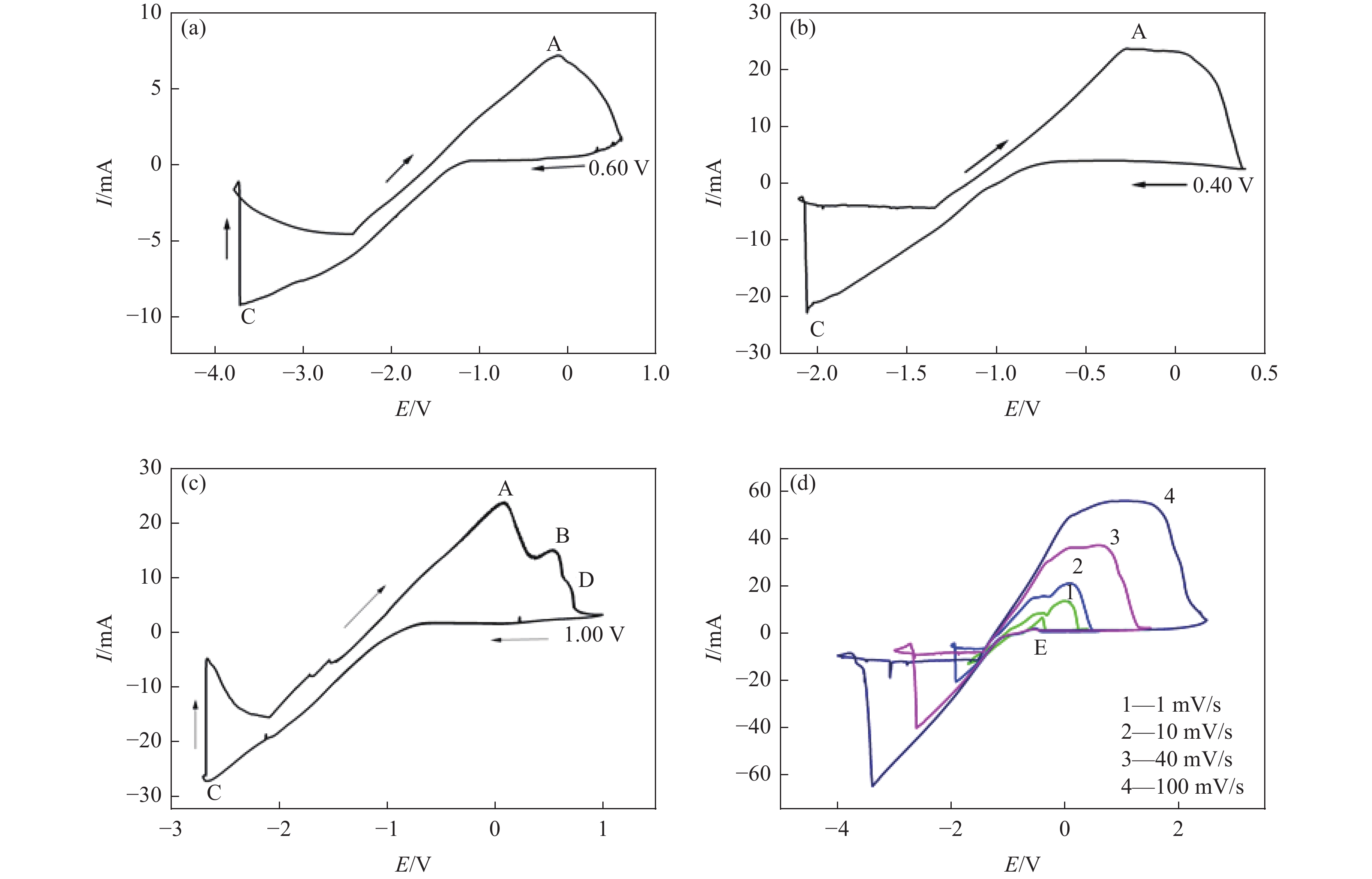
摘要: 为实现钛铝合金的二次回收与分离利用,以钛铝合金为牺牲阳极,1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑氯铝酸盐(BMIC-AlCl3)作为电解液,进行钛铝合金的脱合金化研究。采用循环伏安曲线、动电位极化和恒电位极化对电解过程的脱合金行为进行电化学分析;使用SEM对电解前后样品微区形貌进行表征,使用ICP-AES对电解前后钛铝合金样品中的Al含量进行定量分析。结果表明,钛铝合金在BMIC-AlCl3中的脱合金反应为准可逆反应,且长时间电解过程中电流保持稳定,可实现持续电解脱铝;通过扫描电子显微镜发现阴极沉积层为纯度较高且呈现多孔结构的金属铝。ICP-AES对电解前后的钛铝合金中Al元素含量的分析结果表明,电解后钛铝合金中Al元素含量相对于电解前下降10.67%。Abstract: In order to realize the secondary recycling and separation of Al-Ti alloys, the dealloying of Al-Ti alloys was studied with 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride (BMIC)-aluminum chloride (AlCl3) as the electrolyte and Ti-Al alloys as the sacrificial anode. Cyclic voltammetry, potentiodynamic polarization method, and potentiostatic polarization method were performed to analyze the dealloying behavior during electrolysis. SEM-EDS was used to characterize the micromorphology of the samples before and after electrolysis. The Al content in the Ti-Al alloy samples was quantified by ICP-AES. The results showed that the dealloying reaction of Ti-Al alloy in BMIC-AlCl3 is quasi-reversible. The current remains stable during the long-time electrolysis, indicating that the electrolytic dealloying could be achieved continuously. The cathodic deposition layer was found to be metallic aluminum with high purity and porous structure by scanning electron microscopy. The content of Al in titanium aluminum alloy after electrolysis decreased by 10.67% compared with that before electrolysis based on the ICP-AES analysis.
-
Key words:
- titanium aluminum alloy /
- ionic liquid /
- dealloying /
- electrochemical analysis /
- aluminum content
-
表 1 钛铝合金成分
Table 1. Ti-Al alloy composition
% Ti Al O 37.61 61.19 1.2 -
[1] Bolivar R, Friedrich B. Magnesiothermic reduction from titanium dioxide to produce titanium powder[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2019,5(2):219−229. doi: 10.1007/s40831-019-00215-z [2] Lee D W, Kim B K. Synthesis of nano-structured titanium carbide by Mg-thermal reduction[J]. Scripta materialia, 2003,48(11):1513−1518. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(03)00130-1 [3] Zein El Abedin S, Moustafa E M, Hempelmann R, et al. Electrodeposition of nano- and microcrystalline aluminium in three different air and water stable ionic liquids[J]. Chemphyschem:A European Journal of Chemical Physics and Physical Chemistry, 2006,7(7):1535−1543. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200600095 [4] Li Yaning, Li Guangzhong, Zhang Wenyan, et al. Nanoporous Ti alloy foam prepared by dealloying[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013,42(10):2197−2200. (李亚宁, 李广忠, 张文彦, 等. 脱合金法制备纳米多孔泡沫钛合金[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013,42(10):2197−2200.Li Yaning, Li Guangzhong, Zhang Wenyan, et al. Nanoporous Ti alloy foam prepared by dealloying[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(10): 2197-2200. [5] Jiang Weiyan, Yu Wenzhou. Classification, synthesis and application of ionic liquid[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2008,(4):51−54. (蒋伟燕, 余文轴. 离子液体的分类、合成及应用[J]. 金属材料与冶金工程, 2008,(4):51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6084.2008.04.014Jiang Weiyan, Yu Wenyou. Classification, synthesis and application of ionic liquid[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2008(4): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6084.2008.04.014 [6] Fournier C, Favier F. Zn, Ti and Si nanowires by electrodeposition in ionic liquid[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2011,13(11):1252−1255. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2011.08.031 [7] Koronaios P, Osteryoung R A. CaCl2 and MgCl2 as buffering agents for room-temperature chloroaluminate ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1999,146(8):2995. doi: 10.1149/1.1392041 [8] Wang X R, Hua Y X, Zhao Q N, et al. Electrical conductivity of AlCl3-BMIC room temperature ionic liquids[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006,16:2138−2142. [9] Armand M, Endres F, Macfarlane D R, et al. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future[J]. Nature Materials, 2009,8(8):621−629. doi: 10.1038/nmat2448 [10] Zhang Jinsheng, Tian Zhonghe, Li Lihua, et al. Application of ionic liquids in nanomaterial field[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2018,46(8):34−37. (张金生, 田中禾, 李丽华, 等. 纳米材料合成领域中离子液体的应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 2018,46(8):34−37.Zhang Jinsheng, Tian Zhonghe, Li Lihua, et al. Application of ionic liquids in nanomaterial field[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2018, 46(8): 34-37. [11] Mukhopadhyay I, Aravinda C L, Borissov D, et al. Electrodeposition of Ti from TiCl4 in the ionic liquid l-methyl-3-butyl-imidazolium bis (trifluoro methyl sulfone) imide at room temperature: study on phase formation by in situ electrochemical scanning tunneling microscopy[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005,50(6):1275−1281. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2004.07.052 [12] Mukhopadhyay I, Freyland W. Electrodeposition of Ti nanowires on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite from an ionic liquid at room temperature[J]. Langmuir, 2003,19(6):1951−1953. doi: 10.1021/la020891j [13] Endres F, Zein El Abedin S, Saad A Y, et al. On the electrodeposition of titanium in ionic liquids[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2008,10(16):2189−2199. doi: 10.1039/b800353j [14] 王喜然. BMIC-AlCl3离子液体电解精炼铝的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2006.Wang Xiran. Electrorefining of aluminum with BMIC-AlCl3 ionic liquid[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2006. [15] Zhang X, Hua Y, Xu C, et al. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide in Lewis basic AlCl3-1-butyl-3-methylimidizolium ionic liquid[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011,56(24):8530−8533. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2011.07.037 [16] Bakkar A, Neubert V. A new method for practical electrodeposition of aluminium from ionic liquids[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2015,51:113−116. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2014.12.012 [17] Jiang T, Chollier B M J, Dube G, et al. Electrodeposition of aluminium from ionic liquids: Part I—electrodeposition and surface morphology of aluminium from aluminium chloride (AlCl3)-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([EMIm]Cl) ionic liquids[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006,201(1):1−9. [18] El Abedins S Z, Moustafa E M, Hempelmann R, et al. Additive free electrodeposition of nanocrystalline aluminium in a water and air stable ionic liquid[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2005,7(11):1111−1116. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2005.08.010 [19] Tsuda T, Hussey C L, Stafford G R, et al. Electrochemistry of titanium and the electrodeposition of Al-Ti alloys in the Lewis acidic aluminum chloride-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride melt[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003,150(4):234. doi: 10.1149/1.1554915 [20] Pradhan D, Reddy R G. Dendrite-free aluminum electrodeposition from AlCl3-1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride ionic liquid electrolytes[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012,43(3):519−531. doi: 10.1007/s11663-011-9623-1 [21] Wagner K, Brankovic S R, Dimitrov N, et al. Dealloying below the critical potential[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997,144(10):3545. doi: 10.1149/1.1838046 -





 下载:
下载: