Experimental research on the recycling of valuable metal elements with the extracted-vanadium residues reduced by biomass
-
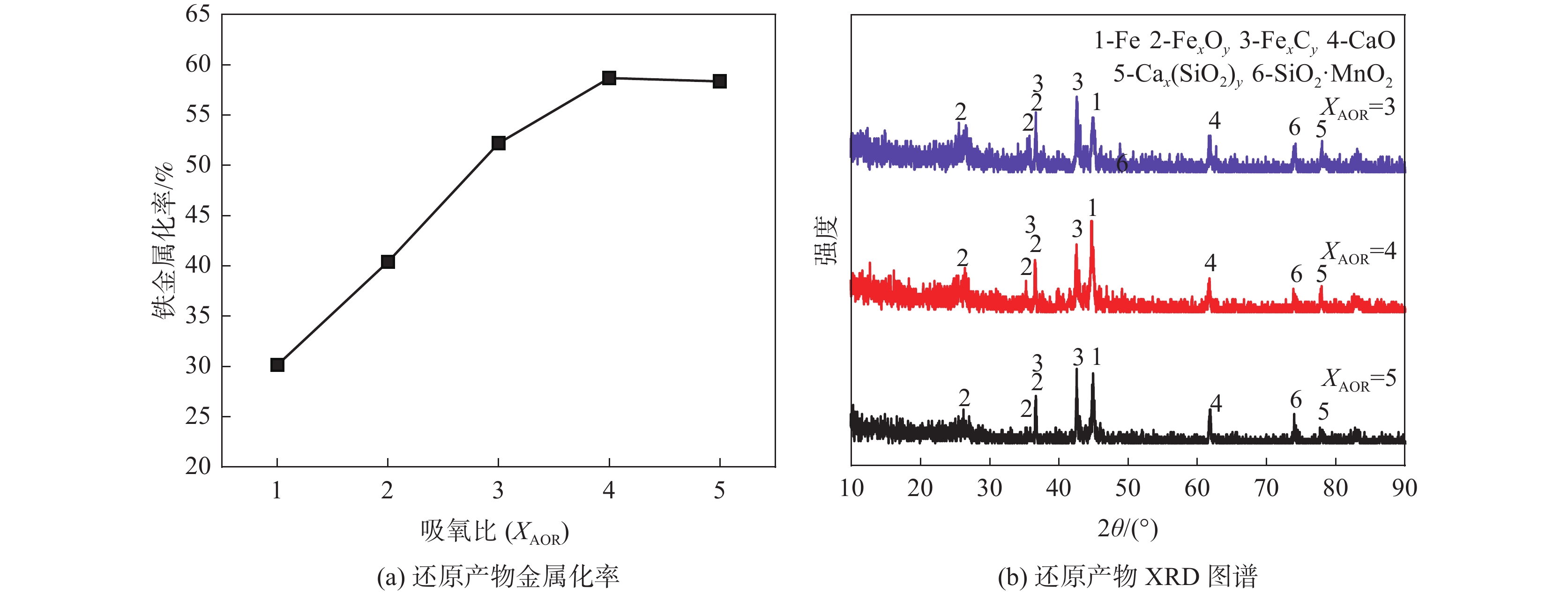
摘要: 为解决提钒废渣堆积造成的土地资源浪费、污染环境等问题,以两种提钒废渣为研究对象,采用生物质作为还原剂进行高温还原试验,对还原产物进行组分分析、物相分析等,探究吸氧比、时间、温度对还原过程、产物金属化率的影响。结果表明,水浸提钒废渣在吸氧比为4、还原温度为1450 ℃、还原时间为2 h的条件下,铁金属化率可达到58.67%;沉钒废渣在吸氧比为1.75、还原温度为1550 ℃、还原时间为4 h的条件下,铬金属化率可达到99.19%。将两种提钒废渣混合,进行了生物质高温还原制备铬铁合金的初步试验验证,对在吸氧比4、还原时间3 h、反应温度1550 ℃条件下所得的还原产物进行熔分,合金中铬含量为61.51%,铁含量为31.05%,元素含量满足FeCr65C4.0牌号合金的国家标准要求。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of land resources waste and environmental pollution caused by accumulation of vanadium extraction tailings, two kinds of vanadium extraction tailings were studied in this paper. Biomass was used as reducing agent for high temperature reduction experiment, and the component analysis and phase analysis of reduction products were carried out to explore the influences of oxygen absorption ratio, time and temperature on metallization rate of reduction products. The results show that the iron metallization rate can reach 58.67% when the oxygen absorption ratio is 4, the reduction temperature is 1450 ℃ and the reduction time is 2 h. The chromium metallization rate of vanadium-precipitated waste slag can reach 99.19% when the oxygen absorption ratio is 1.75, the reduction temperature is 1550 ℃ and the reduction time is 4 h. Two kinds of vanadium extracting tailings were mixed to prepare ferrochromium alloy by high temperature reduction of biomass. The preliminary experiment proved that the reduction product was melted under the condition of oxygen absorption ratio of 4, reduction time of 3 hours and reaction temperature of 1550 ℃. The content of chromium in the alloy was 61.51%, the content of iron was 31.05%, and the content of elements met the national standard requirements of FeCr65C4.0 alloy.
-
表 1 水浸提钒废渣主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of extracted-vanadium residues from water-immersed
% Fe2O3 SiO2 TiO2 MnO Cr2O3 CrO3 Al2O3 CaO MgO Na2O 49.37 14.93 12.17 8.32 7.58 0.60 3.55 1.65 1.09 0.73 表 2 沉钒废渣主要化学成分
Table 2. Main chemical composition of extracted-vanadium residues from sediment of vanadium
% Cr2O3 (NH4)2SO4 SiO2 V2O5 Na2O CaO K2O MgO Fe2O3 CrO3 67.46 17.49 9.57 1.78 1.19 1.02 0.12 0.09 0.05 1.22 表 3 花生壳元素分析
Table 3. Element analysis of peanut shells
% C H O N S 总计 47.22 5.66 46.11 0.93 0.08 100 表 4 还原条件与金属化率
Table 4. Reduction conditions and metallization rate
还原条件 铁金属化率/% 铬金属化率/% 吸氧比 还原时间/h 还原温度/℃ 4 3 1550 99.31 59.08 表 5 合金主要化学成分与FeCr65C4.0牌号合金的国家标准
Table 5. Chemical composition of alloy and national standard of FeCr65C4.0
% Cr Fe C Si S 国家标准 60~70 ≤4 ≤3 ≤0.05 测试含量 61.51 31.05 2.3 2.72 0.04 -
[1] Qing Xuemei, Xie Bing, Li Danke, et al. Study on the oxidation of vanadium in molten iron and the formation of ferrovanadium spine[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2009,9(z1):122−126. (青雪梅, 谢兵, 李丹柯, 等. 铁水中钒氧化及钒铁尖晶石形成的研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009,9(z1):122−126.Qing Xuemei, Xie Bing, Li Danke, et al. Study on the oxidation of vanadium in molten iron and the formation of ferrovanadium spinel[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9 ( z1 ): 122-126 [2] Liu Jinsheng, Ding Xueyong, Xue Xiangxin, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of vanadium slag[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021,56(7):152−160. (刘金生, 丁学勇, 薛向欣, 等. 提钒废渣资源化综合利用的研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(7):152−160.Liu Jinsheng, Ding Xueyong, Xue Xiangxin, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of vanadium slag[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56 (7): 152-160 [3] Taylor P R, Shuey S A, Vidal E E, et al. Extractive metallurgy of vanadium-containing titaniferous magnetite ores: a review[J]. Minerals & Metallurgical Processing, 2006,23(2):80−86. [4] Meng Lipeng, Zhao Chu, Wang Shaona, et al. Research progress on vanadium re-extraction technology from vanadium extraction slag in China[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(3):49−56. (孟利鹏, 赵楚, 王少娜, 等. 国内提钒废渣再提钒技术研究进展[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(3):49−56. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2015.03.011Meng Lipeng, Zhao Chu, Wang Shaona, et al. Research progress on vanadium re-extraction technology from vanadium extraction slag in China[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015, 36 (3): 49-56 doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2015.03.011 [5] Hou Jing, Wu Enhui, Li Jun. Research status and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction residue[J]. Mineral Protection and Utilization, 2017,(6):103−108. (侯静, 吴恩辉, 李军. 提钒尾渣的综合利用研究现状及进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017,(6):103−108.Hou Jing, Wu Enhui, Li Jun. Research status and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction residue[J]. Mineral Protection and Utilization, 2017, (6): 103-108 [6] Yang Huifen, Wang Jingjing, Jing Lili, et al. Effect of roasting temperature on coal-based direct reduction of high-iron vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2010,32(10):1258−1263. (杨慧芬, 王静静, 景丽丽, 等. 焙烧温度对高铁提钒废渣煤基直接还原效果影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2010,32(10):1258−1263.Yang Huifen, Wang Jingjing, Jing Lili, et al. Effect of roasting temperature on coal-based direct reduction of high-iron vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2010, 32 (10): 1258 - 1263 [7] Wu Enhui, Zhu Rong, Yang Shaoli, et al. Thermodynamic analysis and experiment on smelting reduction of carbon-containing pellets from vanadium slag by electric arc furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(5):41−46. (吴恩辉, 朱荣, 杨绍利, 等. 提钒废渣含碳球团电弧炉熔融还原热力学分析与试验[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(5):41−46.Wu Enhui, Zhu Rong, Yang Shaoli, et al. Thermodynamic analysis and experiment on smelting reduction of carbon-containing pellets from vanadium slag by electric arc furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015, 36(5): 41-46 [8] Bu Qingjie, Luo Siyi, Ma Chen, et al. Experimental study of biomass tar reduction of iron ore[J]. Steel Research, 2015,43(2):1−4,13. (卜庆洁, 罗思义, 马晨, 等. 生物质焦油还原多孔铁矿粉试验研究[J]. 钢铁研究, 2015,43(2):1−4,13.Bu Qingjie, Luo Siyi, Ma Chen, et al. Experimental study of biomass tar reduction of iron ore[J]. Steel Research, 2015, 43 (2): 1-4, 13 [9] Hu Lile, Li Liang, Li Junsheng. Characteristics and environmental effects of biomass energy[J]. Energy and Environment, 2012,(1):47−49. (胡理乐, 李亮, 李俊生. 生物质能源的特点及其环境效应[J]. 能源与环境, 2012,(1):47−49.Hu Lile, Li Liang, Li Junsheng. Characteristics and environmental effects of biomass energy[J]. Energy and Environment, 2012, (1): 47-49 -





 下载:
下载: