Microstructure and properties of vanadium microalloyed cast magnesium alloy for automobile
-
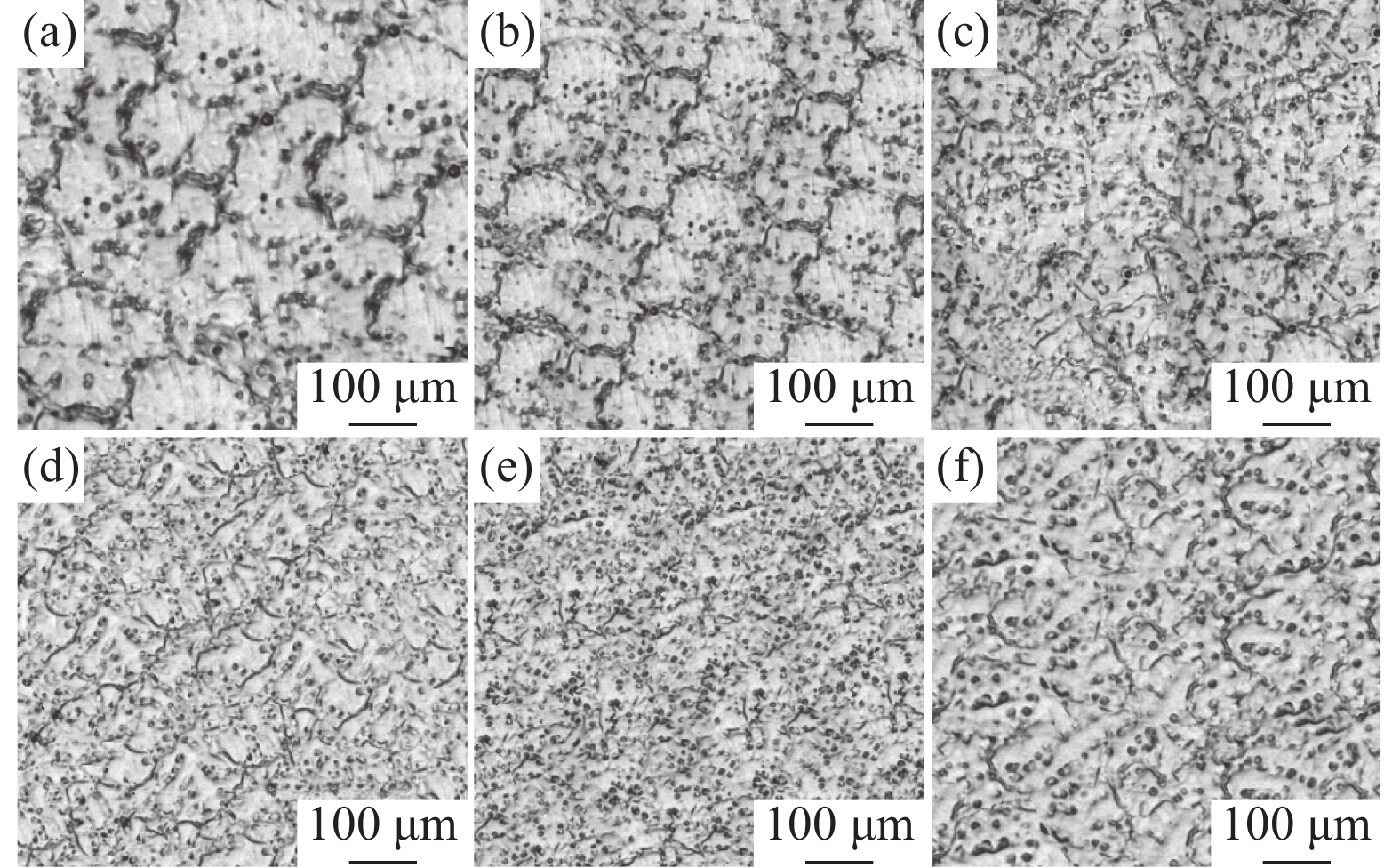
摘要: 为了研究钒微合金化汽车用铸造镁合金的显微组织、耐磨损性能和耐腐蚀性能,在铸造Mg-9Al-1Zn镁合金中添加了不同含量的合金元素钒,并进行了试验合金显微组织、力学性能、耐磨损性能和耐腐蚀性能的测试与对比分析。结果表明,合金元素钒可以有效细化合金内部组织,提高合金的耐磨损性能和耐腐蚀性能。随钒含量由0逐渐增加到0.4%时,试验合金的耐磨损性能和耐腐蚀性能均提高,进一步将钒含量增加到0.5%,则两种性能均开始下降。同不含钒的Mg-9Al-1Zn镁合金相比,当在Mg-9Al-1Zn镁合金中添加0.4%合金元素钒时,合金的磨损体积减小了12.7×10−3 mm3,减小幅度达29.8%;腐蚀电位正移了0.107 V,正移幅度达到12.2%;抗拉强度、屈服强度和断后伸长率分别增大58、58 MPa、3.3%,增大幅度分别为20.9%、36.0%、40.2%。Mg-9Al-1Zn-V镁合金的合金元素钒含量优选为0.4%。Abstract: In order to study the microstructure, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of vanadium microalloyed cast magnesium alloy for automobile, different contents of alloy element vanadium were added into the cast Mg-9Al-1Zn magnesium alloy, and the microstructure, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the test alloy were tested and compared. The results show that the alloy element vanadium can effectively refine the internal structure of the alloy and improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the alloy. With the gradual increase of vanadium content from 0 to 0.4%, both the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the test alloy have been improved. Further increasing vanadium content to 0.5% will reduce the wear and corrosion resistance. Compared with Mg-9Al-1Zn magnesium alloy without vanadium, when 0.4% alloy element vanadium is added to Mg-9Al-1Zn magnesium alloy, the wear volume of the alloy is reduced by 12.7×10−3 mm3 or 29.8%, and the positive shift of corrosion potential reaches by 0.107 V or 12.2%. The tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of the alloy are increased by 58, 58 MPa and 3.3% respectively, with relative increasing amplitude of 20.9%, 36.0% and 40.2%, respectively. The alloy element vanadium content for Mg-9Al-1Zn-V magnesium alloy is preferably at 0.4%.
-
Key words:
- cast magnesium alloy /
- vanadium microalloying /
- microstructure /
- wear resistance /
- corrosion resistance
-
表 1 Mg-9Al-1Zn-xV (x=0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5)试验合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of Mg-9Al-1Zn-xV (x=0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5) test alloys
% 试样编号 V含量 Al Zn Mn V Fe Si 其他杂质元素 Mg 1# x=0 9.034 0.998 0.231 0 0.012 0.008 <0.100 余量 2# x=0.1 9.028 0.996 0.228 0.104 0.011 0.009 <0.100 余量 3# x=0.2 9.029 0.997 0.229 0.202 0.009 0.007 <0.100 余量 4# x=0.3 9.031 1.002 0.232 0.298 0.011 0.008 <0.100 余量 5# x=0.4 9.027 0.999 0.234 0.403 0.012 0.009 <0.100 余量 6# x=0.5 9.032 0.998 0.228 0.501 0.013 0.008 <0.100 余量 表 2 Mg-9Al-1Zn-xV(x=0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5) 试验合金耐磨损与耐腐蚀性能测试结果
Table 2. Wear resistance and corrosion resistance test results of Mg-9Al-1Zn-xV(x=0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5) tested alloys
钒含量/% 磨损体积×103/mm3 腐蚀电位/V 0 42.6 −0.876 0.1 38.1 −0.828 0.2 34.7 −0.803 0.3 32.6 −0.791 0.4 29.9 −0.769 0.5 31.4 −0.814 -
[1] Yue Haiyan, Fu Penghuai, Xu Xuwen, et al. Cumulative damage behavior study of high cycle fatigue of as-cast Mg-3.0Nd-0.2Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2020,38(5):693−700. (岳海燕, 付彭怀, 徐旭文, 等. 铸造Mg-3.0Nd-0.2Zn-Zr镁合金高周疲劳累积损伤行为[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2020,38(5):693−700.Yue Haiyan, Fu Penghuai, Xu Xuwen, et al. Cumulative damage behavior study of high cycle fatigue of as-cast Mg-3.0Nd-0.2Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 38(5): 693-700. ) [2] Yue Haiyan, Fu Penghuai, Hu Bin, et al. Application of two-step aging treatment in cast Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2020,38(4):517−524. (岳海燕, 付彭怀, 胡斌, 等. 双级时效在铸造Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-Zr镁合金中的应用[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2020,38(4):517−524.Yue Haiyan, Fu Penghuai, Hu Bin, et al. Application of two-step aging treatment in cast Mg-3 Nd-0.2 Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 38(4): 517-524. [3] Huang Fang, Xu Yang. Effect of pouring temperature on microstructure and properties of new vanadium microalloyed casting magnesium alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(1):65−69. (黄芳, 徐扬. 浇注温度对新型钒微合金化铸造镁合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(1):65−69.Huang Fang, Xu Yang. Effect of pouring temperature on microstructure and properties of new vanadium microalloyed casting magnesium alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(1): 65-69. [4] Chen Rongshi, Zhou Bo, Li Jilin, et al. Contrast of microstructure, mechanical properties and casting defects between high strength and heat resistant Mg-Y-Nd(-Gd)-Zr and Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloys[J]. Foundry, 2021,70(1):15−20. (陈荣石, 周波, 李吉林, 等. 铸造高强耐热Mg-Y-Nd(-Gd)-Zr和Mg-Gd-Y-Zr系镁合金组织性能和铸造缺陷对比[J]. 铸造, 2021,70(1):15−20.Chen Rongshi, Zhou Bo, Li Jilin, et al. Contrast of microstructure, mechanical properties and casting defects between high strength and heat resistant Mg-Y-Nd(-Gd)-Zr and Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloys[J]. Foundry, 2021, 70(1): 15-20. [5] Fan Ruijun, Guan Zhiwei, Sun Cuixiang. Analysis of forging forming process for high strength magnesium alloys Mg-8Gd-1.5Y-1M containing Ti[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(5):171−174. (樊瑞军, 关志伟, 孙翠香. 含钛高强镁合金Mg-8Gd-1.5Y-0.8Ti的锻造成形工艺分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(5):171−174.Fan Ruijun, Guan Zhiwei, Sun Cuixiang. Analysis of forging forming process for high strength magnesium alloys Mg-8 Gd-1.5 Y-1 M containing Ti[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(5): 171-174. [6] Wang Zhongtang, Wu Kaiqi, Wang Minghao, et al. Study on dynamic recrystallization and microstructure evolution of magnesium alloy in process of composite deformation[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50(19):94−98. (王忠堂, 吴凯琦, 王明浩, 等. 镁合金复合变形过程中的动态再结晶及微观组织演变规律研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50(19):94−98.Wang Zhongtang, Wu Kaiqi, Wang Minghao, et al. Study on dynamic recrystallization and microstructure evolution of magnesium alloy in process of composite deformation[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(19): 94-98. [7] Gu Yuntao, Gao Xiaopeng, Dong Xiwang, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Nd, Mg-Gd and Mg-Sb binary magnesium alloys[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50(6):35−38. (顾赟涛, 高霄鹏, 董喜旺, 等. Mg-Nd、Mg-Gd和Mg-Sb二元镁合金的组织和力学性能[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50(6):35−38.Gu Yuntao, Gao Xiaopeng, Dong Xiwang, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Nd, Mg-Gd and Mg-Sb binary magnesium alloys[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(6): 35-38. [8] Xu Shubo, Sun Haibo, Liu Ting, et al. Influence of die geometry on ECAP deformation uniformity of magnesium alloy[J]. China Metalforming Equipment & Manufacturing Technology, 2021,56(2):100−105. (徐淑波, 孙海波, 刘婷, 等. 模具几何形状对镁合金ECAP变形均匀性的影响[J]. 锻压装备与制造技术, 2021,56(2):100−105.Xu Shubo, Sun Haibo, Liu Ting, et al. Influence of die geometry on ECAP deformation uniformity of magnesium alloy[J]. China Metalforming Equipment & Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 56(2): 100-105. [9] Li Quan, Jin Chaoyang. A comparative study on thermal compression flow stress of AZ80 magnesium alloy described by improved Fields-Backofen constitutive model[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2021,46(3):221−228. (李全, 金朝阳. 改进的Fields-Backofen本构模型描述AZ80镁合金热压缩流动应力的比较研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2021,46(3):221−228.Li Quan, Jin Chaoyang. A comparative study on thermal compression flow stress of AZ80 magnesium alloy described by improved Fields-Backofen constitutive model[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2021, 46(3): 221-228. [10] Xu Jingchao, Zhang Yanru, Yang Yue, et al. Analysis on microstructure and cell biological activity of new magnesium alloy by hot squeeze casting[J]. Journal of Ningbo University(Natural Science & Engineering Edition), 2022,35(1):26−32. (徐景超, 张雁儒, 杨越, 等. 热挤压铸造新型镁合金微观组织及细胞生物活性分析[J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 2022,35(1):26−32.Xu Jingchao, Zhang Yanru, Yang Yue, et al. Analysis on microstructure and cell biological activity of new magnesium alloy by hot squeeze casting[J]. Journal of Ningbo University(Natural Science & Engineering Edition), 2022, 35(1): 26-32. [11] Gao Xiaoshu, Lv Yun. Optimization of stamping process parameters of magnesium alloy sheet based on RSM and MPSO[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50(15):79− 83, 87. (高孝书, 吕云. 基于RSM和MPSO的镁合金薄板冲压工艺参数优化[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50(15):79− 83, 87.Gao Xiaoshu, Lv Yun. Optimization of stamping process parameters of magnesium alloy sheet based on RSM and MPSO[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(15): 79-83, 87. [12] Li Jilin, Feng Junning, Qin Chun, et al. Dendrite coherency point of WE54 magnesium alloy and its relation with solidification microstructure[J]. Foundry, 2021,70(11):1270−1276. (李吉林, 冯俊宁, 秦春, 等. 铸造WE54镁合金的枝晶干涉点及其与合金显微组织的关系[J]. 铸造, 2021,70(11):1270−1276.Li Jilin, Feng Junning, Qin Chun, et al. Dendrite coherency point of WE54 magnesium alloy and its relation with solidification microstructure[J]. Foundry, 2021, 70(11): 1270-1276. [13] Xiao Lv, Zhou Haitao, Wang Yanbo, et al. Linear shaped charge separation behavior and cutting mechanism of VW63Z cast magnesium alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2021,41(1):11−15. (肖旅, 周海涛, 汪彦博, 等. VW63Z铸造镁合金线型分离性能及切割机理研究[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2021,41(1):11−15.Xiao Lv, Zhou Haitao, Wang Yanbo, et al. Linear shaped charge separation behavior and cutting mechanism of VW63 Z cast magnesium alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2021, 41(1): 11-15. [14] Wang Ying, Li Guangde. Study on casting properties of two AZ magnesium alloys based on cloud model PID control[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50(3):71−73. (王瑛, 李广德. 基于云模型PID控制的两种AZ镁合金铸造性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50(3):71−73.Wang Ying, Li Guangde. Study on casting properties of two AZ magnesium alloys based on cloud model PID control[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(3): 71-73. -





 下载:
下载: