Research on prediction accuracy of the flow stress of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel based on machine learning
-
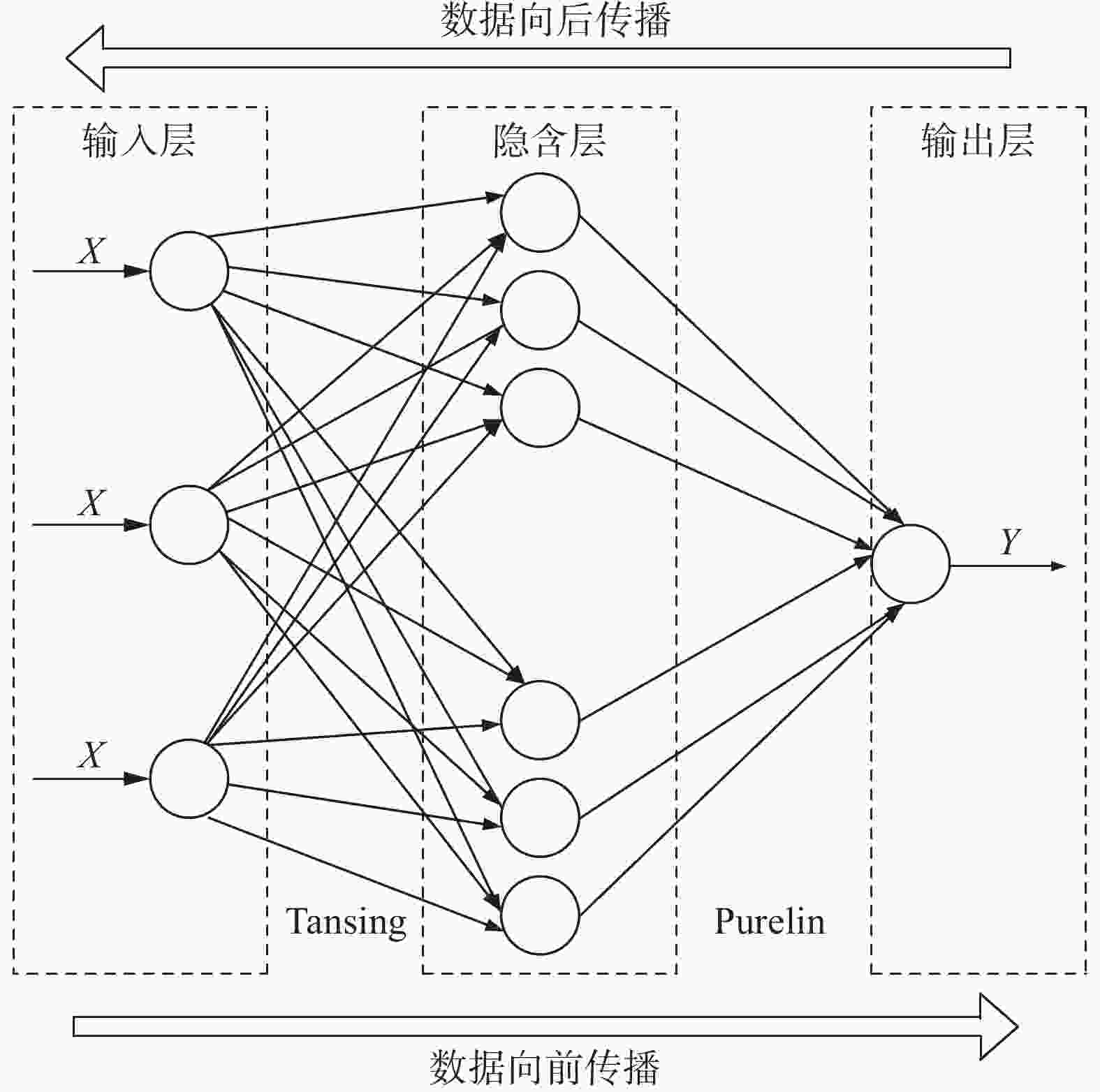
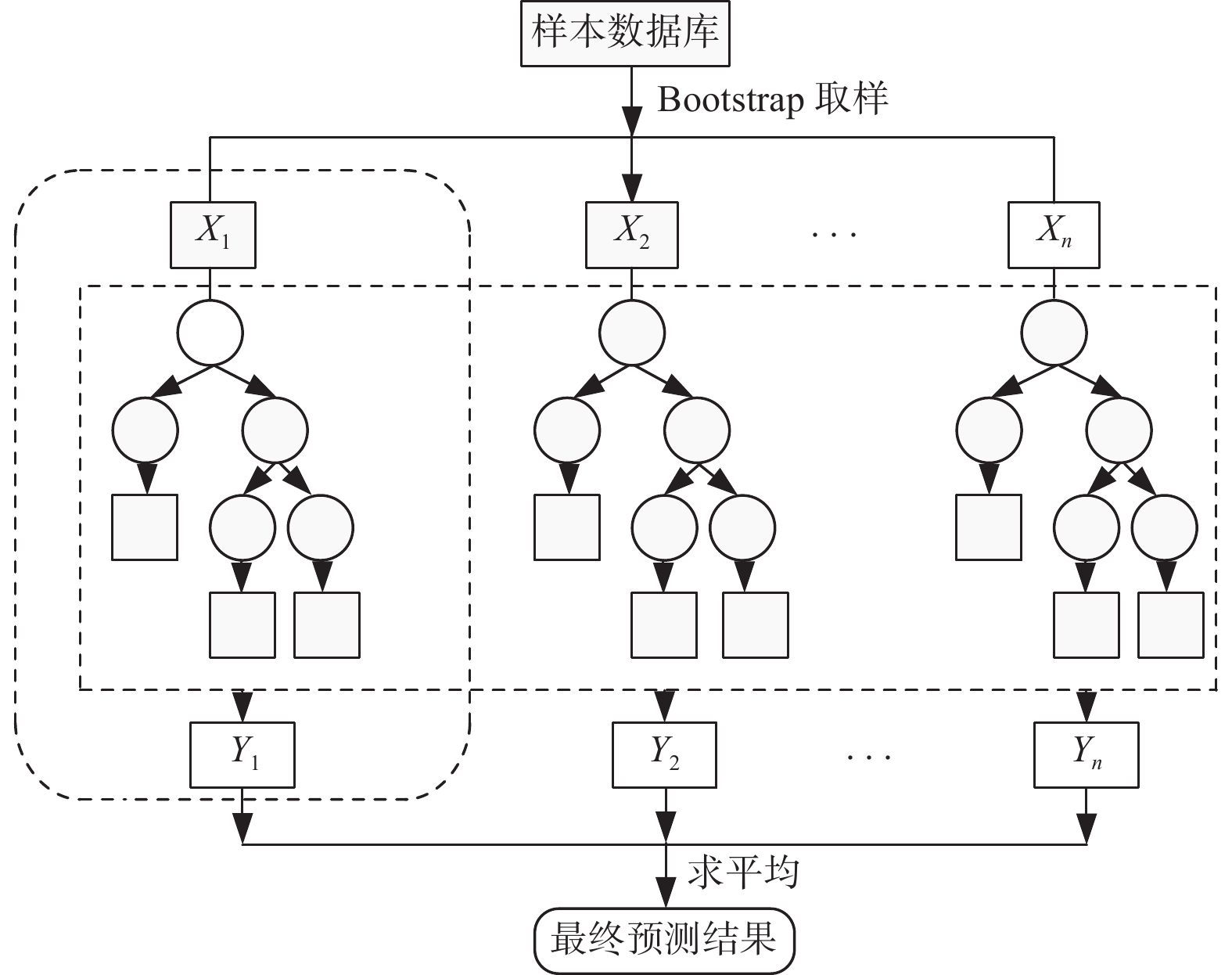
摘要: 以0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢为例,提出一种基于粒子群优化BP神经网络预测流变应力的新模型。以常温下的准静态(0.001 s−1)压缩试验数据、四种温度(25、350、500、300 ℃)和六种应变率(750、1500、2 000、2600、3500、4500 s−1)的冲击试验数据为基础,构建了 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢流变应力的随机森林预测模型、粒子群优化随机森林预测模型、Back Propagation(BP)神经网络预测模型以及粒子群优化BP神经网络预测模型,采用统计学的决定系数(R2)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方差(MSE)和均方误差平方根(RMSE)四个指标分析评价上述四种模型,得出四种模型预测的综合性能依次是粒子群优化BP神经网络模型、BP神经网络模型、粒子群优化随机森林模型、随机森林模型。粒子群优化BP神经网络模型决定系数R2=0.9997、平均绝对误差MAE=1.5773、均方差MSE=5.5053和均方误差平方根RMSE=2.3463,该模型能够很好预测 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢流变应力。
-
关键词:
- 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢 /
- 流变应力 /
- 预测模型 /
- 机器学习 /
- 粒子群优化BP神经网络
Abstract: A new model for predicting rheological stresses based on particle swarm optimization BP neural network is proposed for 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel as an example. Based on the quasi-static (0.001 s−1) compression testing data at room temperature and the impact testing data at four temperatures (25, 350, 500 and 300 ℃) and six strain rates (750, 1500, 2000, 2600, 3500 and 4500 s−1), a random forest prediction model for rheological stress of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel, a Particle Swarm Optimized Random Forest prediction model, a Back Propagation (BP) neural network, and a Particle Swarm Optimized BP neural network are constructed. Four indicators including the statistical coefficient of determination (R2), mean absolute error (MAE), mean square error (MSE) and root mean square error (RMSE) are used to analyze and evaluate the four models mentioned above. The comprehensive performance of the prediction models is in sequence of particle swarm optimization BP neural network model, BP neural network model, particle swarm optimization random forest model, and the random forest model. The coefficient of determination R2=0.9997, mean absolute error MAE=1.5773, mean squared error MSE=5.5053 and root mean squared error RMSE=2.3463 are determined for the particle swarm optimized BP neural network model, which can predict the rheological stress of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel very well. -
表 1 不锈钢0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel
% C Si Cr Ni Mn P S Cu Nb Fe 0.05 0.80 16.25 3.60 0.82 0.03 0.02 3.83 0.28 Bal. 表 2 随机森林预测能力评价指标
Table 2. Random forest predictive capability evaluation index
ntree R2 MAE MSE ESE 5 0.9477 24.4079 1069.2639 32.3405 10 0.9500 23.9846 1022.4408 31.2505 15 0.9526 23.4958 969.3096 30.9611 20 0.9645 20.9364 725.6117 26.8710 25 0.9629 21.1896 759.2660 27.4315 30 0.9676 19.5587 661.3547 25.6921 35 0.9672 20.1650 671.3218 25.9012 40 0.9664 20.2319 687.3605 26.1867 45 0.9684 19.7709 645.1419 25.3661 50 0.9667 20.0062 680.3112 26.0351 55 0.9666 20.1374 681.8699 26.1012 60 0.9647 20.6059 721.0314 26.8389 表 3 粒子群优化随机森林预测能力评价指标
Table 3. Particle swarm optimization random forest prediction capability evaluation index
ntree R2 MAE MSE ESE 16 0.9672 20.0205 670.9482 25.8998 表 4 不同神经元个数训练下的评价指标
Table 4. Evaluation metrics under different training numbers of neurons
神经元数量 R2 MAE MSE ESE 3 0.9777 16.5449 455.9399 21.3527 5 0.9802 15.4572 404.0375 20.1007 7 0.9951 7.4794 100.2042 10.0102 9 0.9968 6.0398 65.4811 8.092 11 0.9982 4.4221 36.8969 6.0743 13 0.9978 4.7259 45.1895 6.7223 表 5 不同隐含层个数训练下的评价指标
Table 5. Evaluation metrics under different training numbers of implied layers
隐含层层数 R2 MAE MSE ESE 1 0.9982 4.4194 36.9513 6.0788 2 0.9993 2.5569 14.4780 3.8050 3 0.9996 2.0898 8.9598 2.9933 4 0.9995 2.1464 10.3096 3.2109 5 0.9995 2.0498 9.7388 3.1207 6 0.9997 1.5773 5.5429 2.3543 表 6 粒子群优化BP神经网络训练下的评价指标
Table 6. Evaluation metrics under particle swarm optimization BP neural network training
隐含层结构 R2 MAE MSE ESE 12 0.9969 5.8513 63.677 7.9798 12×12 0.9995 2.1863 10.9691 3.312 12×12×8 0.9997 1.4770 5.5053 2.3463 9×11×12×12 0.9997 1.6695 6.6039 2.5698 12×11×10×12×11 0.9996 1.7680 7.3263 2.7067 12×12×12×12×12×12 0.9997 1.5030 5.6700 2.3812 -
[1] Wang Jianxing, Yang Gang, Zhang Zhongmo, et al. Effect of ECAP deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2018,25(1):119−124. (王剑星, 杨钢, 张忠模, 等. ECAP变形对0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2018,25(1):119−124.Wang Jianxing , Yang Gang , Zhang Zhongmo, et al. Effect of ECAP deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb stainless steel[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2018, 25(1): 119-124. [2] Wang Jianxing, Yang Gang, Liu Tianmo, et al. Effect of Ni content on mechanical properties of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010,31(12):56−60. (王剑星, 杨钢, 刘天模, 等. Ni含量对0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2010,31(12):56−60.Wang Jianxing, Yang Gang, Liu Tianmo, et al. Effect of Ni content on mechanical properties of 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb stainless steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010, 31(12): 56-60 [3] Wang Hanxiao, Bai Bing, Zhang Changyi, et al. Micro-structure and properties analysis of nuclear power stem material 17-4PH stainless steel at different service time[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2018,38(2):318−325. (王瀚霄, 白冰, 张长义, 等. 核电阀杆材料17-4PH不锈钢服役不同时间的组织性能分析[J]. 核科学与工程, 2018,38(2):318−325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2018.02.022Wang Hanxiao, Bai Bing, Zhang Changyi, et al. Micro-structure and properties analysis of nuclear power stem material 17-4 PH stainless steel at different service time[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2018, 38(2): 318-325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2018.02.022 [4] Huang Jing, Ma Yuan, Wang Mingjie, et al. Investigation and optimization of investment casting 0Cr17Ni4Cu3Nb stainless steel parts aero-engines[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2019,39(2):159−162. (黄静, 马原, 王明杰, 等. 精密铸造0Cr17Ni4Cu3Nb不锈钢航空发动机零件[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2019,39(2):159−162.Huang Jing, Ma Yuan, Wang Mingjie, et al. Investigation and optimization of investment casting 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu3 Nb stainless steel parts aero-engines[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2019, 39(2): 159-162 [5] Sun Jianxin, Liu Yongsheng, Guo Baofeng, et al. Hot deformation behavior and hot processing map of 17-4PH stainless steel for oil fracturing valve box[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2022,29(4):112−118. (孙建新, 刘永胜, 郭宝峰, 等. 石油压裂阀箱用17-4PH不锈钢热变形行为及热加工图[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2022,29(4):112−118.Sun Jianxin, Liu Yongsheng, Guo Baofeng, et al. Hot deformation behavior and hot processing map of 17-4 PH stainless steel for oil fracturing valve box [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2022, 29(4): 112-118. [6] Zhang Jilin, Jia Haishen, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Effect of high temperature and high strain rate on the dynamic mechanical properties of 06Cr19Ni10 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(1):145−151. (张继林, 贾海深, 易湘斌, 等. 高温高应变率对06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢动态力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(1):145−151.Zhang Jilin, Jia Haishen, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Effect of high temperature and high strain rate on the dynamic mechanical properties of 06 Cr19 Ni10 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(1): 145-151. [7] Jia Haishen, Zhang Jilin, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Experimental study on rheological behavior of 022Cr18Ni14Mo2 stainless steel at high temperature and high strain rate[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2022,44(3):600−606. (贾海深, 张继林, 易湘斌, 等. 高温、高应变率下022Cr18Ni14Mo2不锈钢流变行为的试验研究[J]. 机械强度, 2022,44(3):600−606.Jia Haishen, Zhang Jilin, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Experimental study on rheological behavior of 022 Cr18 Ni14 Mo2 stainless steel at high temperature and high strain rate[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2022, 44(3): 600-606 [8] Jia Haishen, Luo Wencui, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022Cr18Ni14Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(2):178−185. (贾海深, 罗文翠, 张继林, 等. 冲击载荷下022Cr18Ni14Mo2不锈钢动态力学特性及其本构模型研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(2):178−185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027Jia Haishen, Luo Wencui, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022 Cr18 Ni14 Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 178-185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027 [9] Duan Xinmin, Sun Peiqiu, Xu Zhiqiang, et al. Study on the integral forming technology of front /rear interfacering for 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2016,41(5):44−48. (段新民, 孙培秋, 徐志强, 等. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb前/后接口套圈整体成形技术研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2016,41(5):44−48.Duan Xinmin , Sun Peiqiu , Xu Zhiqiang, et al. Study on the integral forming technology of front /rear interfacering for 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2016, 41(5): 44-48. [10] Ding Jun, Gu Yuchuan, Huang Xia, et al. Research on prediction accuracy of flow stress of 304 stainless steel based on artificial neural network optimized by improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022,58(10):78−86. (丁军, 古愉川, 黄霞, 等. 基于改进遗传算法优化人工神经网络的304不锈钢流变应力预测准确性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022,58(10):78−86.Ding Jun , Gu Yuchuan , Huang Xia, et al. Research on prediction accuracy of flow stress of 304 stainless steel based on artificial neural network optimized by improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(10): 78-86. [11] Zhong Mingjun, Wang Kelu, Lu Shiqiang, et al. Study on high temperature deformation behavior and BP neural network constitutive model of MoNb alloy[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2020,27(12):177−182. (钟明君, 王克鲁, 鲁世强, 等. MoNb合金高温变形行为及BP神经网络本构模型研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2020,27(12):177−182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2020.12.025Zhong Mingjun, Wang Kelu, Lu Shiqiang, et al. Study on high temperature deformation behavior and BP neural network constitutive model of MoNb alloy[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2020, 27(12): 177-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2020.12.025 [12] Luo Rui, Cao Yun, Qiu Yu, et al. Investigation of constitutive model of as-extruded spray-forming 7055 aluminum alloy based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2021,41(1):35−44. (罗锐, 曹赟, 邱宇, 等. 基于BP人工神经网络喷射成形7055铝合金的本构模型[J]. 航空材料学报, 2021,41(1):35−44.Luo Rui , Cao Yun , Qiu Yu, et al. Investigation of constitutive model of as-extruded spray-forming 7055 aluminum alloy based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2021, 41(1): 35-44. [13] Wu Xiongxi. Model of constitutive relationship and processing map for 7050 aluminum alloy based on BP neural network[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2014,34(10):1011−1015. (吴雄喜. 基于BP神经网络的7050铝合金本构关系模型及加工图[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2014,34(10):1011−1015. doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2014.10.001Wu Xiongxi. Model of constitutive relationship and processing map for 7050 aluminum alloy based on BP neural network[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2014, 34(10): 1011-1015. doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2014.10.001 [14] Zhou Feng, Wang Kelu, Lu Shiqiang, et al. Flow behavior and BP neural network high temperature constitutive model of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Y alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2019,47(8):141−146. (周峰, 王克鲁, 鲁世强, 等. Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Y合金流变行为及BP神经网络高温本构模型[J]. 材料工程, 2019,47(8):141−146. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2017.001548Zhou Feng , Wang Kelu , Lu Shiqiang, et al. Flow behavior and BP neural network high temperature constitutive model of Ti-22 Al-24 Nb-0.5 Y alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2019, 47(8): 141-146. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2017.001548 [15] Zhang Qing, Li Ping, Xue Kemin. Model of constitutive relationship for TB8 alloy based on BP neural network[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2010,35(1):130−133. (张青, 李萍, 薛克敏. 基于BP神经网络的TB8合金高温本构关系模型[J]. 锻压技术, 2010,35(1):130−133.Zhang Qing , Li Ping , Xue Kemin. Model of constitutive relationship for TB8 alloy based on BP neural network[J]. [16] Wang Tianxiang, Lu Shiqiang, Wang Kelu, et al. Flow stress behavior and artificial neural network constitutive model of Ti60 alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2020,40(9):1019−1023. (王天祥, 鲁世强, 王克鲁, 等. Ti60合金的流变应力行为及人工神经网络本构模型[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2020,40(9):1019−1023. doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2020.09.022Wang Tianxiang, Lu Shiqiang, Wang Kelu, et al. Flow stress behavior and artificial neural network constitutive model of Ti60 alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2020, 40(9): 1019-1023 doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2020.09.022 [17] An Zhen, Li Jinshan, Feng Yong, et al. Modeling constitutive relationship of Ti-555211 alloy by artificial neural network during high-temperature deformation[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015,44(1):62−66. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(15)30013-8 [18] Wang Chunhui, Sun Zhihui, Zhao Jiaqing, et al. Creep deformation constitutive model of BSTMUF601 superalloy using BP neural network method[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(6):1885−1893. [19] He Long, Zhang Ranyang, Zhao Gangyao, et al. Constitutive model of GH5188 superalloy based on BP neural network[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloyss, 2021,41(2):223−226. (何龙, 张冉阳, 赵刚要, 等. 基于BP神经网络的GH5188高温合金本构模型[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2021,41(2):223−226. doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2021.02.020He Long , Zhang Ranyang, Zhao Gangyao, et al. Constitutive model of GH5188 superalloy based on BP neural network[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloyss, 2021, 41(2): 223-226. doi: 10.15980/j.tzzz.2021.02.020 [20] Qiu Qian, Wang Kelu, Li Xin, et al. Constitutive relationship of SP700 titanium alloy based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021,28(11):167−172. (邱仟, 王克鲁, 李鑫, 等. 基于BP神经网络的SP700钛合金本构关系[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021,28(11):167−172.Qiu Qian, Wang Kelu, Li Xin, et al. Constitutive relationship of SP700 titanium alloy based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021, 28(11): 167-172. [21] Lei Jinwen, Xue Xiangyi, Zhang Siyuan, et al. High-precision constitutive model of Ti6242s alloy hot deformation based on artificial neural network[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2021,50(6):2025−2032. (雷锦文, 薛祥义, 张思远, 等. 基于人工神经网络的高精度Ti6242s合金热变形本构模型[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2021,50(6):2025−2032.Lei Jinwen, Xue Xiangyi, Zhang Siyuan, et al. High-precision constitutive model of Ti6242 s alloy hot deformation based on artificial neural network[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2021, 50(6): 2025-2032. [22] Zhang Pin, Yin Zhenyu, Jin Yinfu, et al. A novel hybrid surrogate intelligent model for creep index prediction based on particle swarm optimization and random forest[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020,265:628−638. [23] Wang Jie, Cheng Xuexin, Peng Jinzhu. A weighted random forest model based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2018,50(1):72−76. (王杰, 程学新, 彭金柱. 一种基于粒子群算法优化的加权随机森林模型[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版), 2018,50(1):72−76. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6841.2017006Wang Jie, Cheng Xuexin, Peng Jinzhu. A weighted random forest model based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 50(1): 72-76. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6841.2017006 [24] Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001,45(1):5−32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [25] Wang Weitong, Fan Haidong, Liang Chengsi, et al. Predictive modeling of NOx outlet of hedged boiler based on random forest[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022,51(4):96−104. (王伟同, 范海东, 梁成思, 等. 基于随机森林算法的对冲锅炉出口NOx排放量预测模型研究[J]. 热力发电, 2022,51(4):96−104.Wang Weitong, Fan Haidong, Liang Chengsi, et al. Predictive modeling of NOx outlet of hedged boiler based on random forest[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51(4): 96-104. [26] Wu Xianguo, Liu Pengcheng, Chen Hongyu, et al. Prediction of concrete strength based on random forest[J]. Concrete, 2022,(1):17−20,24. (吴贤国, 刘鹏程, 陈虹宇, 等. 基于随机森林的高性能混凝土抗压强度预测[J]. 混凝土, 2022,(1):17−20,24.Wu Xianguo, Liu Pengcheng, Chen Hongyu, et al. Prediction of concrete strength based on random forest[J]. Concrete, 2022(1): 17-20, 24. [27] Yan Liangming, Shen Jian, Li Zhoubing, et al. Modelling for flow stress and processing map of 7055 aluminum alloy based on artificial neural networks[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(7):1296−1301. (闫亮明, 沈健, 李周兵, 等. 基于神经网络的7055铝合金流变应力模型和加工图[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(7):1296−1301. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2010.07.008Yan Liangming, Shen Jian, Li Zhoubing, et al. Modelling for flow stress and processing map of 7055 aluminum alloy based on artificial neural networks[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(7): 1296-1301. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2010.07.008 [28] Lv Zhe, He Lile, Lin Yuyang, et al. Parameters prediction of BP neural network based on constitutive model of aluminum alloy powder forming[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2022,51(4):46−50. (吕哲, 贺利乐, 林育阳, 等. 基于铝合金粉末成形本构模型的BP神经网络参数预测[J]. 热加工工艺, 2022,51(4):46−50.Lv Zhe, He Lile, Lin Yuyang, et al. Parameters prediction of BP neural network based on constitutive model of aluminum alloy powder forming[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2022, 51(4): 46-50. [29] Feng Xi, Li Qing, Quan Wei, et al. Overview of multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021,43(6):745−753. (冯茜, 李擎, 全威, 等. 多目标粒子群优化算法研究综述[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021,43(6):745−753.Feng Xi, Li Qing, Quan Wei, et al. Overview ofmultiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(6): 745-753. [30] Li Hejian, Xu Xiaowei, Wang Ke, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis model based on particle swarm optimization and random forest[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology(Natural Sciences), 2021,46(3):94−101. (李鹤健, 徐肖伟, 王科, 等. 基于粒子群优化随机森林的变压器故障诊断模型[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021,46(3):94−101. doi: 10.16112/j.cnki.53-1223/n.2021.03.451Li Hejian, Xu Xiaowei, Wang Ke, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis model based on particle swarm optimization and random forest[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology(Natural Sciences), 2021, 46(3): 94-101. doi: 10.16112/j.cnki.53-1223/n.2021.03.451 [31] Li Le, Shu Yuechao, Wu Jianpeng, et al. A damage prediction model of wet friction elements based on PSO-BP neural network[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022,42(12):1246−1255. (李乐, 舒越超, 吴健鹏, 等. 基于PSO-BP神经网络湿式摩擦元件损伤预测模型[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2022,42(12):1246−1255. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.347Li Le, Shu Yuechao, Wu Jianpeng, et al. A damage prediction model of wet friction elements based on PSO-BP neural network[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022, 42(12): 1246-1255. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.347. [32] Fan Shengxu, Yang Chunxi, Yang Qiliang, et al. Prediction model of Panax notoginseng leaf area growth based on particle swarm-optimization random forest algorithm and meteorological data[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022,53(10):3103−3110. (范升旭, 杨春曦, 杨启良, 等. 基于粒子群-随机森林算法和气象数据的三七叶面积生长预测模型[J]. 中草药, 2022,53(10):3103−3110. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.10.021Fan Shengxu, Yang Chunxi, Yang Qiliang, et al. Prediction model of Panax notoginseng leaf area growth based on particle swarm-optimization random forest algorithm and meteorological data[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(10): 3103-3110. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.10.021 [33] 程学新. 粒子群优化加权随机森林算法研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2017.Cheng Xuexin. Research on particle swarm optimization weighted random forest algorithm[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2017. [34] 李超. 粒子群优化算法改进策略及其应用研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021.Li Chao. Improvement strategies for particle swarm optimization algorithms with applications[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021. [35] Chang Ruohan, Cai Zhongyi, Cheng Liren, et al. Flow stress prediction model and processing map of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy based on GA-BP network[J]. Materials Reports, 2017,31(6):136−139,146. (常若寒, 蔡中义, 程丽任, 等. 基于遗传BP网络的Mg-Sm-Zn-Zr合金应力预测模型及加工图[J]. 材料导报, 2017,31(6):136−139,146. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.06.027Chang Ruohan, Cai Zhongyi, Cheng Liren, et al. Flow stress prediction model and processing map of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy based on GA-BP network[J]. Materials Reports, 2017, 31(6): 136-139, 146. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.06.027 [36] Zhang Jilin, Jia Haishen, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and comparison of two constitutive models for martensitic stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Materials Research Express, 2021,8(10):106501. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac29f5 [37] Hu Yi, Zhang Lushan, Yuan Fuyin, et al. Prediction of concrete strength based on random forest[J]. Construction Technology, 2020,49(17):89−94. (胡毅, 张陆山, 袁福银, 等. 基于随机森林的混凝土强度预测研究[J]. 施工技术, 2020,49(17):89−94.Hu Yi, Zhang Lushan, Yuan Fuyin, et al. Prediction of concrete strength based on random forest[J]. Construction Technology, 2020, 49(17): 89-94. [38] Zou Dafang, Wang Zidong, Zhang Leimin, et al. Deep field relation neural network for click-through rate prediction[J]. Information Sciences, 2021,577:128−139. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.06.079 -





 下载:
下载: