Experimental study on beneficiation of a low-grade refractory iron ore in Qinghai province
-
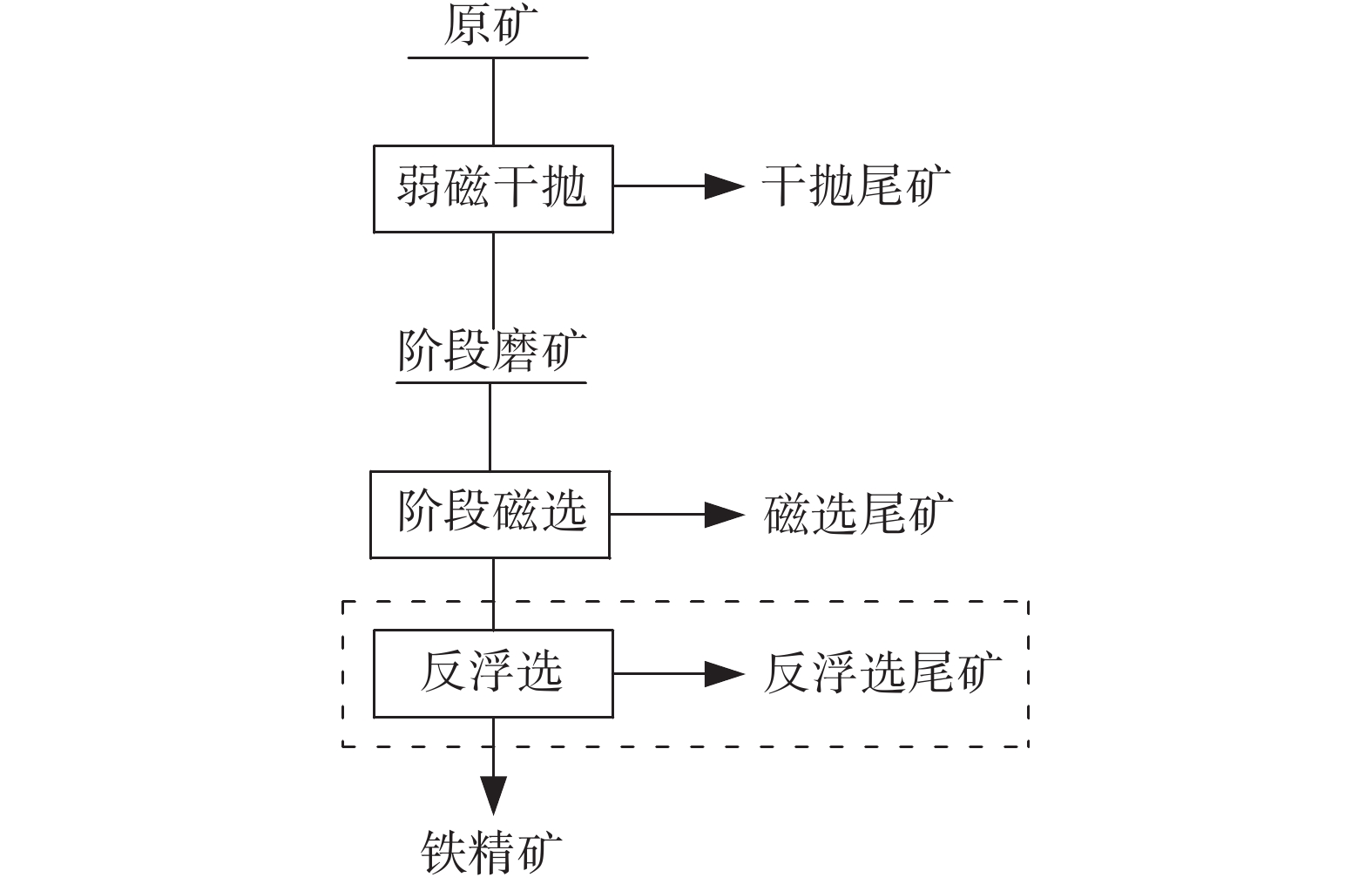
摘要: 针对青海某难选铁矿石铁品位较低,磁铁矿嵌布粒度细,与脉石矿物关系复杂的特点,采用干抛—阶段磨矿—阶段磁选的工艺流程进行试验研究,该工艺流程的主要特点是在干抛和一段磨矿作业时可以抛掉大量的尾矿,大幅度降低后续磨矿作业的入磨量。结果表明,经过四段磨矿,在最终磨矿细度−0.025 mm占95.15%时,可以获得含TFe 64.10%,TFe回收率为70.45%的铁精矿,较好地实现了该低品位难选铁矿的回收。同时,分析了四段铁精矿中的磁铁矿仍有少部分呈铁的贫连生体产出,其组成是影响铁精矿品位难以进一步提高的主要原因。Abstract: Aiming at the characteristics of low iron grade, fine distribution size of magnetite and complex relationship with gangue minerals of a refractory iron ore in Qinghai province, the technological process of dry throw-stage grinding and stage magnetic separation was adopted for experimental study. The main feature of this technological process is that a large amount of tailings can be discarded during dry throw-stage grinding and the subsequent grinding operation can greatly reduce the grinding amount. The results show that after four stages of grinding, iron concentrate containing TFe grade of 64.10% and TFe recovery rate of 70.45% can be obtained when the final grinding fineness of −0.025 mm is 95.15%. The recovery of the low-grade refractory iron ore is better realized. At the same time, it is analyzed that a small part of magnetite in the iron concentrate of the fourth section is mainly produced as iron-poor auxiliaries, and its composition is the main reason that it is difficult to further improve the grade of iron concentrate.
-
表 1 原矿化学多元素分析结果
Table 1. Results of chemical multi-element analysis of run-of-mine
% TFe FeO Fe2O3 Ni Cr2O3 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO P S 烧失 TFe/FeO 碱性系数 13.44 4.94 13.41 0.26 0.70 33.35 0.55 0.62 33.36 0.005 0.024 12.67 2.72 1.00 表 2 铁化学物相分析结果
Table 2. Results of iron chemical phase analysis
% 铁 相 磁铁矿中铁 假象赤铁矿中铁 赤(褐)铁矿中铁 碳酸盐中铁 硫化物中铁 硅酸盐中铁 合 计 含 量 9.75 1.22 1.06 0.31 0.02 1.08 13.44 分布率 72.54 9.08 7.89 2.31 0.15 8.04 100.00 表 3 矿石主要矿物的含量
Table 3. Main mineral content of ore
% 磁铁矿 磁赤铁矿 镍黄铁矿 铬尖
晶石蛇纹石 辉 石、角闪石、橄榄石 滑石、
绿泥石其 它 14.6 1.7 微量 1.4 61.4 16.1 4.6 0.2 表 4 磁铁矿的嵌布粒度结果
Table 4. The distribution size of magnetite
粒 级/
mm分布率/% 累计
分布率/%粒 级 /mm 分布率/% 累计
分布率/%≥+0.59 12.88 12.88 −0.074~+0.052 7.48 78.58 −0.59~+0.42 6.11 18.99 −0.052~+0.037 7.66 86.24 −0.42~+0.30 7.32 26.31 −0.037~+0.026 5.86 92.10 −0.30~+0.21 9.66 35.97 −0.026~+0.019 3.35 95.45 −0.21~+0.15 11.64 47.61 −0.019~+0.013 1.69 97.14 −0.15~+0.105 12.41 60.02 −0.013~+0.010 1.48 98.62 −0.105~+0.074 11.08 71.10 ≤-0.010 1.38 100.00 表 5 干抛试验结果
Table 5. Results of dry throw separation test
粒级/mm 产品名称 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% TFe MFe TFe MFe −6 干抛精矿 78.26 15.90 12.08 92.59 97.01 干抛尾矿 21.74 4.58 1.34 7.41 2.99 原矿 100.00 13.44 9.75 100.00 100.00 −12 干抛精矿 84.32 14.50 11.10 90.96 96.04 干抛尾矿 15.68 7.75 2.46 9.04 3.96 原矿 100.00 13.44 9.75 100.00 100.00 表 6 反浮选探索试验结果
Table 6. Reverse flotation test results
药剂种类及
用量/(g·t−1)产品名称 TFe作业
产率/%TFe品位/% TFe作业
回收率/%RA-715 100 浮选精矿 74.25 64.57 74.79 浮选尾矿 25.75 62.74 25.21 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 200 浮选精矿 50.64 64.73 51.14 浮选尾矿 49.36 63.45 48.86 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 400 浮选精矿 33.22 64.84 33.60 浮选尾矿 66.78 63.73 66.40 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 十二胺 100 浮选精矿 68.48 64.61 69.02 浮选尾矿 31.52 62.99 30.98 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 200 浮选精矿 48.58 64.79 49.10 浮选尾矿 51.42 63.45 50.90 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 400 浮选精矿 29.68 64.92 30.06 浮选尾矿 70.32 63.75 69.94 给矿 100.00 64.10 100.00 表 7 四段铁精矿的化学多元素分析结果
Table 7. Results of chemical multielement analysis of iron concentrate of the fourth stage
% Fe CaO MgO SiO2 Al2O3 S P Cr Mn Ni 64.10 0.061 3.23 3.50 0.14 0.0066 0.0056 1.02 0.10 0.78 表 8 四段铁精矿中磁铁矿的解离度
Table 8. Dissociation degree of magnetite in the fourth stage iron concentrate
% 单 体 连 生 体 >3/4 3/4~1/2 1/2~1/4 <1/4 94.5 0.6 1.5 2.1 1.3 表 9 全流程试验结果
Table 9. Test results of the whole process
% 产品名称 产率 TFe品位 TFe回收率 铁精矿 14.77 64.10 70.45 四段尾矿 1.61 12.69 1.52 三段尾矿 5.12 8.38 3.19 二段尾矿 5.75 4.18 1.79 一段尾矿 51.01 4.12 15.64 干抛尾矿 21.74 4.58 7.41 原矿 100.00 13.44 100.00 -
[1] Zhao Liqun, Wang Chunnv, Zhang Min, et al. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020,56(3):635−643. (赵立群, 王春女, 张敏, 等. 中国铁矿资源勘查开发现状及供需形势分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020,56(3):635−643.Zhao Liqun, Wang Chunnv, Zhang Min, et al. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(03): 635-643. [2] Ke Jiayan, Shi Yunliang, Xiao Jinxiong et al. Mineral proccessing technique for an iron ore from Russia[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2019,39(6):50−53. (柯佳焱, 石云良, 肖金雄, 等. 俄罗斯某铁矿选矿工艺研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2019,39(6):50−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.06.012Ke Jiayan, Shi Yunliang, Xiao Jinxiong et al. Mineral proccessing technique for an iron ore from Russia[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2019, 39(06): 50-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.06.012 [3] Yang Zhaojun, Xie Baohua, Zhong Senlin, et al. Experimental study on mineralogy and beneficiation of an iron ore from Australia[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(6):115−120,137. (杨招君, 谢宝华, 钟森林, 等. 澳大利亚某铁矿工艺矿物学及选矿试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(6):115−120,137.Yang Zhaojun, Xie Baohua, Zhong Senlin, et al. Experimental study on mineralogy and beneficiation of an iron ore from Australia [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(06): 115-120+137. [4] Ouyang Linli. Mineral processing test of a low-grade fine-graine iron ore in Shandong[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2022,47(2):81−87,95. (欧阳林莉. 山东某低品位微细粒铁矿选矿试验[J]. 烧结球团, 2022,47(2):81−87,95.Ouyang Linli. Mineral processing test of a low-grade fine-graine iron ore in Shandong [J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2022, 47(02): 81-87+95. [5] Huang Wusheng, Yuan Qidong, Lin Xiaofeng, et al. Experimental study on beneficiation of a foreign hematite ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2021,37(11):125−129. (黄武胜, 袁启东, 林小凤, 等. 国外某赤褐铁矿选矿试验研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2021,37(11):125−129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2021.11.033Huang Wusheng, Yuan Qidong, Lin Xiaofeng, et al. Experimental study on beneficiation of a foreign hematite ore [J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(11): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2021.11.033 [6] Xiao Wanqin, Zhu Yangge, Hu Xiaoxing, et al. Experimental study on beneficiation of a refractory iron ore with high alumina and silicon[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2022,(1):109−114. (肖婉琴, 朱阳戈, 胡晓星, 等. 某高铝高硅难选铁矿选矿试验研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2022,(1):109−114.Xiao Wanqin, Zhu Yangge, Hu Xiaoxing, et al. Experimental study on beneficiation of a refractory iron ore with high alumina and silicon [J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2022(01): 109-114. [7] Jiao Kecheng. Beneficiation process for an overseas high phosphorus-silicon oolitic iron ore[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2018,38(4):65−68. (焦科诚. 国外某高磷硅鲕状铁矿选矿工艺研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2018,38(4):65−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2018.04.016Jiao Kecheng. Beneficiation process for an overseas high phosphorus-silicon oolitic iron ore[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2018, 38(04): 65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2018.04.016 [8] Wu Peng, Guo Shunlei, Li Teng. Exploratory test of beneficiation of an iron ore in Hami, Xinjiang[J]. Modern Mining, 2020,36(7):139−141. (吴鹏, 郭顺磊, 李腾. 新疆哈密某铁矿石选矿探索试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2020,36(7):139−141.Wu Peng, Guo Shunlei, Li Teng. Exploratory test of beneficiation of an iron ore in Hami, Xinjiang [J]. Modern Mining, 2020, 36(07): 139-141. [9] Xiao Qifei, Shi Yunliang, Liu Jun. Study on new technology and process of ore dressing in Beishan site of Nanfen open pit iron mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2019,35(9):121−125. (肖启飞, 石云良, 刘军. 南芬露天铁矿北山部位矿石选矿新技术及工艺试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2019,35(9):121−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.09.035Xiao Qifei, Shi Yunliang, Liu Jun. Study on New Technology and Process of Ore Dressing in Beishan site of Nanfen Open Pit Iron Mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(09): 121-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.09.035 [10] Yang Xuanxing. Interference of magnetic coagulation in magnetic separation of Miaogou iron mine and its emeasures for its elimination[J]. Metal Mine, 1995,(9):46−48. (杨宣兴. 庙沟铁矿磁选过程中磁团聚干扰及消除措施[J]. 金属矿山, 1995,(9):46−48.Yang Xuanxing. Interference of magnetic coagulation in magnetic separation of Miaogou iron mine and its emeasures for its elimination[J]. Metal Mine, 1995(9): 46-48. -





 下载:
下载: