Study on wear resistance of nitriding coatings of Ti-Al base multielement alloys
-
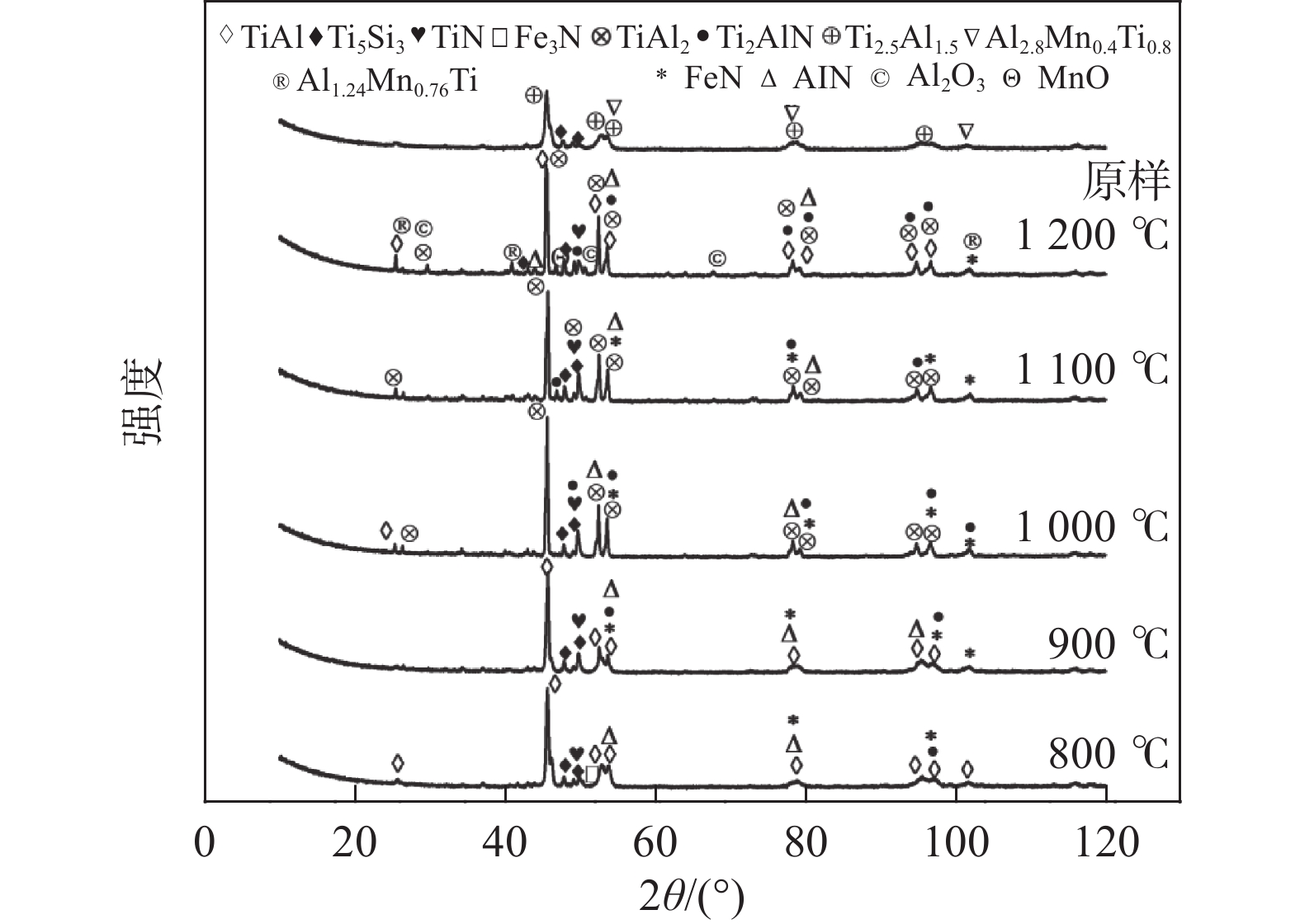
摘要: 以攀枝花酸溶性钛渣、铝粉、氧化钙为原料制备钛铝基多元合金,并将钛铝基多元合金在不同温度不同时间条件下直接氮化处理,得到氮化层。采用扫描电镜、X射线衍射仪、显微硬度计、摩擦磨损试验机、三维形貌仪等对制得的氮化层的性能进行检测分析。结果表明,在不同条件下对钛铝基多元合金进行直接氮化,均能提高合金的表面硬度及耐磨性。氮化温度对合金硬度及耐磨性能的影响较大,氮化时间为2 h时,适宜的氮化温度为800 ℃,此时氮化层的平均硬度(HV)高达698.8,平均摩擦系数为0.120,往复摩擦的磨损率为19.44 mm3/(N·m),表面粗糙度为0.731 μm;氮化温度为900 ℃时,适宜的氮化时间为3 h,此时得到的氮化层硬度(HV)为682.6,平均摩擦系数为0.059,往复摩擦的磨损率为9.48 mm3/(N·m),表面粗糙度为0.601 μm。Abstract: In this paper, the titanium-aluminum-based multi-component alloy was prepared from Panzhihua acid-soluble titanium slag, aluminum powder and calcium oxide. After directly nitriding treatment at different temperatures and different time, a nitrided layer was obtained. Scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometer, microhardness tester, friction and wear testing machine, and three-dimensional topography instrument were used to detect and analyze the properties of the nitriding layer. The results show that the surface hardness and wear resistance of Ti-Al based multielement alloy can be improved by direct nitriding under different conditions. The nitriding temperature has a great effect on the hardness and wear resistance of the alloy. When the nitriding time is 2 h, the optimum nitriding temperature is 800 ℃, the average hardness (HV) of the nitriding layer is up to 698.8, the average friction coefficient is 0.120, the reciprocating friction wear rate is 19.44 mm3/(N·m), and the surface roughness is 0.731 μm. When the nitriding temperature is 900 ℃ and the optimum nitriding time is 3 h, the hardness (HV) of nitriding layer is 682.6, the average friction coefficient is 0.059, the reciprocating friction wear rate is 9.48 mm3/(N·m), and the surface roughness is 0.601 μm.
-
Key words:
- Ti-Al base multi-element alloy /
- direct nitriding /
- nitriding layer /
- wear resistance
-
表 1 钛铝基多元合金化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of Ti-Al base multielement alloy
% Ti Al Fe Si Mn O 50.11 38.16 6.88 1.43 3.35 0.07 表 2 氮化温度不同制得的氮化层的磨损量、磨损体积及磨损率
Table 2. Wear amount, wear volume and wear rate of coatings prepared at different nitriding temperatures
氮化温度/℃ 磨损量/g 磨损体积/mm3 磨损率/[mm3·(N·m)−1] 原样 0.00017 8.69×10−3 34.76 800 0.00006 4.86×10−3 19.44 900 0.00009 7.91×10−3 31.64 1000 0.00013 6.30×10−3 25.2 1100 0.00011 7.05×10−3 28.2 1200 0.00013 6.47×10−3 25.88 表 3 氮化时间不同的氮化层的磨损量、磨损体积及磨损率
Table 3. Wear amount, wear volume and wear rate of nitriding coatings with different nitriding time
氮化时间/h 磨损量/g 磨损体积/mm3 磨损率/[mm3·(N·m)−1] 原样 0.00017 8.69×10−3 34.76 1 0.00016 8.60×10−3 34 2 0.00009 7.91×10−3 31.64 3 0.00004 2.37×10−3 9.48 4 0.00010 6.97×10−3 27.88 5 0.00007 3.36×10−3 13.44 -
[1] Guo Li, He Weixia, Zhou Peng, et al. Research status and development prospect of titanium and titanium alloy products in China[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020,49(22):22−28. (郭鲤, 何伟霞, 周鹏, 等. 我国钛及钛合金产品的研究现状及发展前景[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020,49(22):22−28.Guo Li, He Weixia, Zhou Peng, et al. Research status and development prospect of titanium and titanium alloy products in China[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(22): 22-28. [2] Narayana P L, Li C L, Kim S W, et al. High strength and ductility of electron beam melted β stabilized γ-TiAl alloy at 800 °C[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019,756:41−45. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.114 [3] Chen R, Wang Q, Yang Y H, et al. Brittle-ductile transition during creep in nearly and fully lamellar high-Nb TiAl alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2018,93:47−54. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2017.11.009 [4] Song L, Hu X G, Zhang T B, et al. Precipitation behaviors in a quenched high Nb-containing TiAl alloy during annealing[J]. Intermetallics, 2017,89:79−85. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2017.05.025 [5] Chen G, Peng Y B, Zheng G, et al. Polysynthetic twinned TiAl single crystals for high-temperature applications[J]. Nature Materials, 2016,15:876−882. doi: 10.1038/nmat4677 [6] Wu H, Fan G H, Geng L, et al. Nanoscale origins of the oriented precipitation of Ti3Al in Ti-Al systems[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2016,125:34−38. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.037 [7] Appel F, Clemens H, Fischer F D. Modeling concepts for intermetallic titanium aluminides[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2016,81:55−124. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.01.001 [8] 潘健生, 胡明娟. 热处理工艺学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009: 514-527.Pan Jiansheng, Hu Mingjuan. Heat treatment technology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009: 514-527. [9] 马鹏飞, 李美兰. 热处理技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009: 116-127.Ma Pengfei, Li Meilan. Heat treatment technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 116-127. [10] Stappen M Van, Stals L M, Kerkhofs M, et al. State of the art for the industrial use of ceramic PVD coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1995,74-75(2):629−633. [11] Zhang Minghai, Yang Gangbin. Research progress of Lanxide materials[J]. Journal of Luoyang Technical College, 2006,(1):5−7. (张明海, 杨刚宾. Lanxide材料及其研究进展[J]. 洛阳工业高等专科学校学报, 2006,(1):5−7.Zhang Minghai, Yang Gangbin. Research progress of Lanxide materials[J]. Journal of Luoyang Technical College, 2006(1): 5-7. [12] 史程程. P/M 钛铝基合金的热变形行为与等温锻造/扩散连接工艺[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.Shi Chengcheng. Thermal deformation behavior and isothermal forging/diffusion bonding process of P/M Ti-Al base alloys[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [13] Li Yong, Wang Qiulin, Zhu Jinbo, et al. Technology status and prospect of titanium aluminum alloy prepared by powder metallurgy[J]. Journal of Chengdu Aeronautical Vocational and Technical College, 2020,36(3):74−77,80. (李勇, 王秋林, 朱金波, 等. 粉末冶金制备钛铝合金技术现状及展望[J]. 成都航空职业技术学院学报, 2020,36(3):74−77,80.Li Yong, Wang Qiulin, Zhu Jinbo, et al. Technology status and prospect of titanium aluminum alloy prepared by powder metallurgy[J]. Journal of Chengdu Aeronautical Vocational and Technical College, 2020, 36(3): 74-77+80. [14] Li Jun, Wu Enhui, Yang Shaoli, et al. Study on vacuum magnetic levitation refining of titanium aluminum alloy prepared by electrothermic reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(2):41−49. (李军, 吴恩辉, 杨绍利, 等. 电铝热还原法制备的钛铝合金真空磁悬浮精炼研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(2):41−49.Li Jun, Wu Enhui, Yang Shaoli, et al. Study on vacuum magnetic levitation refining of titanium aluminum alloy prepared by electrothermic reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(2): 41-49. [15] Li Jun, Lu Xiongang, Yang Shaoli, et al. Theoretical and experimental study on preparation of TiAl alloy by electrothermic reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(5):46−52. (李军, 鲁雄刚, 杨绍利, 等. 电铝热还原法制备TiAl合金理论及试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(5):46−52.Li Jun, Lu Xiongang, Yang Shaoli, et al. Theoretical and experimental study on preparation of TiAl alloy by electrothermic reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(5): 46-52. [16] Piao Rongxun, Yang Shaoli, Ma Lan, et al. Vacuum electromagnetic levitation melting of Ti-Al based alloy prepared by aluminothermic reduction of acid soluble Ti bearing slag[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2020,26:130−142. doi: 10.1007/s12540-019-00295-2 [17] Li Y M, Yue Q B, He H B, et al. Friction and wear characteristics of 20Cr steel substrate and TiAlN coating under different lubrication conditions[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2018,19(10):1521−1528. doi: 10.1007/s12541-018-0179-8 -





 下载:
下载: