Experimental study on quality improvement and impurity reduction of a vanadium-titanium iron concentrate in Panxi
-
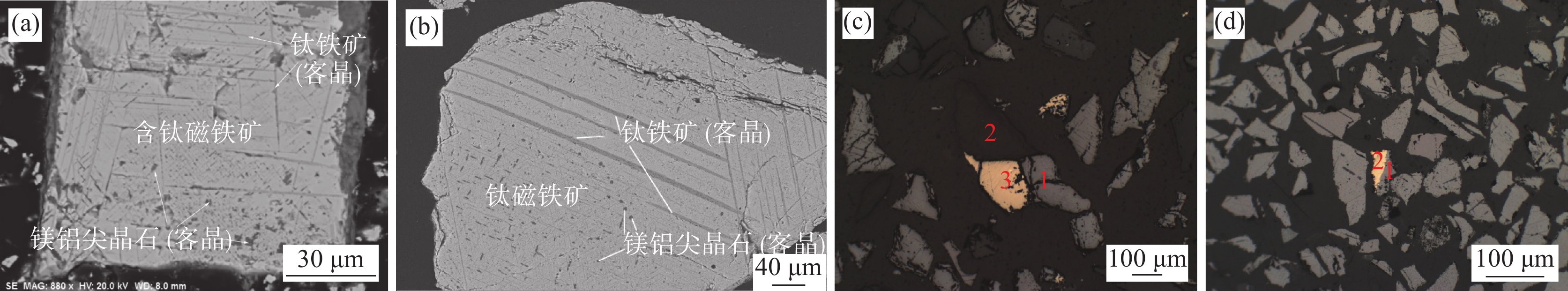
摘要: 攀西某钒钛铁精矿TFe为55.88%,主要杂质元素化学成分为TiO2、SiO2、Al2O3、MgO、CaO,粒状钛铁矿及脉石矿物等杂质组分占比达14.26%,钛铁矿主要以客晶形式嵌布于钛磁铁矿基底中,粗、细粒铁精矿中杂质组分及嵌布特征差异显著。针对该样品,在实验室开展了“预先分级—粗粒再磨磁选”“预先分级—粗粒再磨磁选—细粒磁选”“深度磁选—分级—粗粒再磨磁选”3种工艺对比试验,以及电磁湿法鼓式磁选机、高频谐波磁选机、磁选柱3种磁选设备对比试验,并对提质前后铁精矿的主要化学成分及矿物组分进行了对比分析。研究表明,以电磁湿法鼓式磁选机为选别设备,采用“预先分级(0.074 mm)-粗粒再磨(−0.074 mm占96.50%)磁选—细粒直接磁选”工艺的提质效果最优,该钒钛铁精矿经提质后TFe提升3.36个百分点,杂质组分占比累计降低了6.92个百分点,TFe/TiO2提高了3.44个百分点。Abstract: The TFe grade of a vanadium-titanium-iron concentrate in Panxi is 55.88%. The chemical composition of the main impurity elements in the sample include TiO2, SiO2, Al2O3, MgO and CaO, the proportion of impurities such as granular ilmenite and gangue minerals accountes for 14.26%. Ilmenite is mainly embedded in the titanium magnetite base in the form of guest crystals, and there are significant differences in impurity components and distribution characteristics between coarse and fine grained ferrotitanium vanadium concentrates. Three comparative experiments were conducted on the vanadium titanium iron concentrate, including "preliminary classification - coarse particle regrinding magnetic separation", "preliminary classification - coarse particle regrinding magnetic separation - fine particle magnetic separation", and "deep magnetic separation - classification - coarse particle regrinding magnetic separation". Meanwhile, magnetic separation equipment comparative tests were cared out by using electromagnetic wet drum magnetic separator, high-frequency harmonic magnetic separator and magnetic separation column. In addition, a comparative analysis was conducted on the main chemical and mineral components of the iron concentrate before and after upgrading. Research results show that using an electromagnetic wet drum magnetic separator as the sorting equipment, the process of "preliminary grading (0.074mm) - coarse particle regrinding (−0.074 mm accounting for 96.50%) magnetic separation - direct magnetic separation with fine particle" has the best quality improvement effect. After the quality improvement, the TFe grade of the vanadium titanium iron concentrate increases by 3.36 percentage points, the proportion of impurities decreases by 6.92 percentage points, and the TFe/TiO2 increases by 3.44 percentage points.
-
表 1 矿样主要化学成分分析结果
Table 1. Chemical composition analysis results of the sample
% TFe FeO TiO2 V2O5 Co S Cu Ni 55.88 32.89 9.68 0.715 0.017 0.47 0.029 0.021 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO Mn Na2O K2O 4.01 3.60 0.53 3.18 0.304 0.078 0.018 表 2 矿物组成及含量
Table 2. The mineral composition and contents of the sample
% 钛磁铁矿 磁黄铁矿 粒状钛铁矿 绿泥石 蛇纹石 镁铝尖晶石 84.41 1.33 1.35 3.54 3.47 1.47 钙长石 榍石 透闪石—阳起石 钠长石 其它脉石 合计 1.44 0.51 0.44 0.37 1.67 100.00 表 3 矿样粒度分析及主要化学成分沿粒度分布规律
Table 3. Particle size analysis and distribution of main chemical components along particle size
粒级/mm 产率/% 品位/% TFe TiO2 V2O5 S SiO2 Al2O3 MgO +0.25 1.93 34.25 6.65 0.362 0.444 22.14 7.18 10.86 −0.25~+0.15 5.78 46.06 8.96 0.562 0.484 11.05 5.09 6.88 −0.15~+0.10 8.48 51.50 9.78 0.638 0.479 7.02 4.51 5.09 −0.10~+0.074 9.89 54.69 10.13 0.696 0.476 4.58 4.05 3.89 −0.074~+0.043 16.52 56.50 10.26 0.721 0.485 3.14 3.67 3.07 −0.043~+0.038 6.96 57.50 10.14 0.734 0.492 2.67 3.56 2.83 −0.038 50.44 58.38 9.52 0.731 0.476 2.23 3.20 2.35 合计 100.00 55.88 9.68 0.701 0.478 3.94 3.68 3.31 表 4 提质工艺试验结果
Table 4. The results of improving processes test
工艺流程 产品名称 产率/% TFe品位/% TFe回收率/% 预先分级—粗粒
再磨磁选铁精矿1 20.68 59.00 21.85 铁精矿2 73.92 57.88 76.64 混合铁精矿 94.60 58.13 98.49 尾 矿 5.40 15.62 1.51 原 矿 100.00 55.83 100.00 预先分级—粗粒再磨
磁选—细粒磁选铁精矿1 20.68 59.00 21.83 铁精矿2 71.42 59.31 75.80 混合铁精矿 92.10 59.24 97.63 尾矿1 5.40 15.62 1.51 尾矿2 2.27 21.17 0.86 尾矿合计 7.67 17.27 2.37 原 矿 100.00 55.88 100.00 深度磁选—分级—粗粒
再磨磁选铁精矿1 19.15 59.12 20.27 铁精矿2 74.26 58.50 77.80 混合铁精矿 93.41 58.63 98.07 尾矿1 1.34 19.50 0.47 尾矿2 5.25 15.53 1.46 尾矿合计 6.59 16.35 1.93 原 矿 100.00 55.84 100.00 表 5 磁选设备种类试验结果
Table 5. The results of magnetic separation equipment type tests
磁选设备
种类产品名称 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% TFe TiO2 TFe TiO2 电磁湿法鼓式
磁选机铁精矿1 20.68 59.00 10.15 21.83 21.81 铁精矿2 71.42 59.31 9.78 75.80 72.58 混合铁精矿 92.10 59.24 9.86 97.63 94.39 尾矿1 5.40 15.62 6.53 1.51 3.66 尾矿2 2.27 21.17 8.25 0.86 1.95 尾矿合计 7.67 17.27 7.04 2.37 5.61 原 矿 100.00 55.88 9.62 100.00 100.00 高频谐波
磁选机铁精矿1 20.70 59.07 10.17 21.88 21.88 铁精矿2 71.35 59.22 9.74 75.61 72.23 混合铁精矿 92.05 59.19 9.84 97.49 94.10 尾矿1 5.32 15.25 6.62 1.45 3.66 尾矿2 2.63 22.38 8.18 1.05 2.24 尾矿合计 7.95 17.61 7.14 2.51 5.90 原 矿 100.00 55.88 9.62 100.00 100.00 磁选柱 铁精矿1 21.01 58.69 10.12 22.06 21.97 铁精矿2 71.17 59.05 9.81 75.18 72.13 混合铁精矿 92.18 58.97 9.88 97.24 94.09 尾矿1 5.44 17.88 6.87 1.74 3.86 尾矿2 2.38 24.00 8.33 1.02 2.05 尾矿合计 7.82 19.74 7.31 2.76 5.91 原 矿 100.00 55.90 9.68 100.00 100.00 表 6 提质前后铁精矿主要化学成分变化
Table 6. Changes of main chemical compositions of iron concentrate before and after improving quality
% TFe TiO2 V2O5 S SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 Na2O K2O TFe/TiO2 原 矿 55.88 9.62 0.715 0.47 4.01 0.53 3.18 3.60 0.078 0.018 5.81 混合铁精矿 59.24 9.86 0.743 0.37 1.84 0.25 2.18 3.23 0.036 0.009 6.01 差值(百分点) +3.36 +0.24 +0.028 −0.10 −2.17 −0.28 −1.00 −0.37 −0.042 −0.009 +0.20 表 7 提质前后铁精矿主要矿物成分变化
Table 7. Changes of main mineral compositions of iron concentrate before and after improving quality
% 钛磁铁矿 磁黄铁矿 粒状钛铁矿 绿泥石 蛇纹石 镁铝尖晶石 钙长石 榍石 透闪石—阳起石 钠长石 其他 原 矿 84.41 1.33 1.35 3.54 3.47 1.47 1.44 0.51 0.44 0.37 1.67 混合铁精矿 91.54 1.14 0.72 1.63 2.09 0.79 0.63 0.28 0.21 0.18 0.79 差值(百分点) +7.13 −0.19 −0.63 −1.91 −1.38 −0.68 −0.81 −0.23 −0.23 −0.19 −0.88 -
[1] 黑色金属矿产资源强国战略研究专题组. 黑色金属矿产资源强国战略研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.Special Research Group on the Strategy of Strengthening the Country with Ferrous Metal Mineral Resources. Research on the strategy of strengthening the country with ferrous metal mineral resources[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. [2] 马华麟. 现代铁矿石选矿[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009.Ma Hualing. Modern mineral processing of iron ores[M]. Hefei: China University of science and Technology Press, 2009. [3] Chen Fulin, Yang Xiaojun, Yang Daoguang, et al. Research on process mineralogy for a low-grade vanadium titano-magnetite in Gansu province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020,(6):64−68. (陈福林, 杨晓军, 杨道广, 等. 甘肃某低品位钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020,(6):64−68.Chen Fulin, Yang Xiaojun, Yang Daoguang, et al. Research on process mineralogy for a low-grade vanadium titano-magnetite in Gansu province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 64-68. [4] Chen Fulin, Yang Xiaojun, Cai Xianyan, et al. Experimental study on iron separation of Baima gabbro-type ultra-low-grade vanadium-titanomagnetite in Panxi area[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020,(6):26−30. (陈福林, 杨晓军, 蔡先炎, 等. 攀西地区白马辉长岩型超低品位钒钛磁铁矿选铁试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020,(6):26−30.Chen Fulin, Yang Xiaojun, Cai Xianyan, et al. Experimental study on iron separation of Baima gabbro-type ultra-low-grade vanadium-titanomagnetite in Panxi area[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 26-30. [5] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.Du Hegui. Principle of blast furnace smelting vanadium titanium magnetite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [6] Ma Jiayuan, Sun Xiwen, Sheng Shixiong. Strengthening of blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2000,35(1):1−12. (马家源, 孙希文, 盛世雄. 钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼的强化[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2000,35(1):1−12.Ma Jiayuan, Sun Xiwen, Sheng Shixiong. Strengthening of blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2000, 35(1): 1-12. [7] 吕亚男. 钒钛磁铁矿固态还原剂高效利用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009.Lv Yanan. Study on efficient utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite solid reducing agent[D]. Changsha : Central South University, 2009. [8] Rao Jiating, Wang Dunxun, Kang Bin, et al. Current situation and proposals of low cost iron-making of Pangang[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2013,35(1):7−13. (饶家庭, 王敦旭, 康斌, 等. 攀钢低成本炼铁技术现状与建议[J]. 四川冶金, 2013,35(1):7−13.Rao Jiating, Wang Dunxun, Kang Bin, et al.Current situation and proposals of low cost iron-making of Pangang[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2013, 35(1): 7-13. [9] Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Li Xiaoyu, et al. Research progress in titanium-magnetite beneficiation technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021,(3):99−105. (陈超, 张裕书, 李潇雨, 等. 钛磁铁矿选矿技术研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021,(3):99−105.Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Li Xiaoyu, et al.Research progress in titanium-magnetite beneficiation technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3): 99-105. [10] Wu Xuehong. Experimental study on improving TFe grade of iron concentrate in Midi concentrator[J]. Mining and Metallurgial Engineering, 2013,33(6):38−41. (吴雪红. 提高密地选矿厂铁精矿品位的试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2013,33(6):38−41.Wu Xuehong. Experimental study on improving TFe grade of iron concentrate in Midi concentrator[J]. Mining and Metallurgial Engineering, 2013, 33(6): 38-41. [11] Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Zhang Shaoxiang, et al. Improving quality of Panzhihua iron concentrate by magnetic separation[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018,(2):69−73,79. (陈超, 张裕书, 张少翔, 等. 攀枝花铁精矿磁选提铁降杂工艺研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018,(2):69−73,79.Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Zhang Shaoxiang, et al. Improving quality of Panzhihua iron concentrate by magnetic separation[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(2): 69-73, 79. [12] Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Zhang Shaoxiang, et al. Characteristics of Panzhihua iron concentrate and experimental study on lifting iron and reducing impurities[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018,(3):57−60. (陈超, 张裕书, 张少祥, 等. 攀枝花铁精矿特性及提铁降杂试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018,(3):57−60.Chen Chao, Zhang Yushu, Zhang Shaoxiang, et al. Characteristics of Panzhihua iron concentrate and experimental study on lifting iron and reducing impurities[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(3): 57-60. [13] Xie Meifang, Wen Shuming, Zheng Hailei, et al. Experimental study on iron improyement and desulphrization of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Metal Mine, 2010,(7):44−46,82. (谢美芳, 文书明, 郑海雷, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿精矿提铁降硫工艺试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2010,(7):44−46,82.Xie Meifang, Wen Shuming, Zheng Hailei, et al. Experimental study on iron improyement and desulphrization of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Metal Mine, 2010(7): 44-46, 82. [14] Liu Zhixiong. Research and industrial practice on improving quality and reducing impurities of Baima vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(3):104−110. (刘志雄. 白马钒钛磁铁矿提质降杂研究及工业实践[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(3):104−110.Liu Zhixiong. Research and industrial practice on improving quality and reducing impurities of Baima vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(3): 104-110. [15] Li Guoping, Zhao Hailiang, Shang Hongliang, et al. Application of the SXCT wet type high frequency harmonic magnetic separator in the separation of Panxi V-Ti magnetite[J]. Non Ferrous Metals (Beneficiation Part), 2019,(1):95−99. (李国平, 赵海亮, 尚红亮, 等. SXCT型湿式高频谐波磁场磁选机在攀西钒钛磁铁矿中的应用[J]. 有色金属:选矿部分, 2019,(1):95−99.Li Guoping, Zhao Hailiang, Shang Hongliang, et al. Application of the SXCT wet type high frequency harmonic magnetic separator in the separation of Panxi V-Ti magnetite[J]. Non Ferrous Metals (Beneficiation Part), 2019(1): 95-99. [16] Chi Dongrui, Gu Pan, Yan Weiping, et al. Study on quality improvement and impurities reduction new technology of vanadium-iron concentrate in Hongge[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020,(6):91−95. (池冬瑞, 顾畔, 严伟平, 等. 红格钒铁精矿提质降杂新技术研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020,(6):91−95.Chi Dongrui, Gu Pan, Yan Weiming, et al. Study on quality improvement and impurities reduction new technology of vanadium-iron concentrate in Hongge[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 91-95. -





 下载:
下载: