Effect of vanadium content on microstructure and strength plasticity of X80 pipeline steel
-
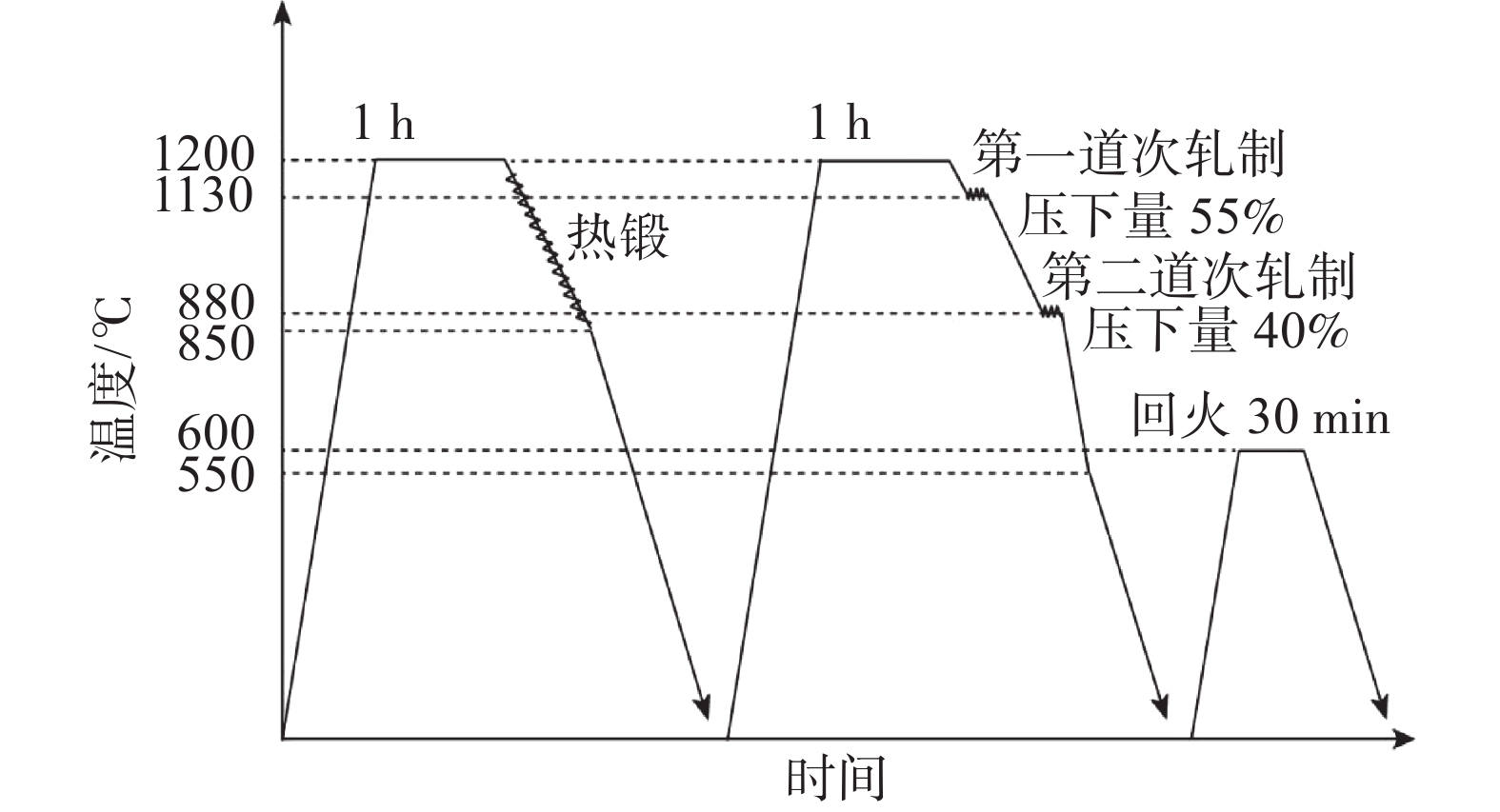
摘要: 借助高分辨透射电镜、扫描电镜、电子背散射衍射技术等手段分析了四种不同钒含量(0.036%,0.075%,0.110 %,0.150 %)X80管线钢中析出相和显微组织结构特征及对钢强塑性等性能的影响。结果表明,随着钒含量的升高,钢中纳米级析出相的数量和体积分数均呈增高趋势,四种试验钢中析出相尺寸主要集中在0~20 nm,且随着钢中钒含量的升高,尺寸小于10 nm的析出相数量增多,无论是晶内还是晶界附近析出的纳米级第二相颗粒均多为含钒的碳化物。四种不同钒含量试验钢的显微组织均由块状铁素体及粒状贝氏体组成,内部大角度晶界比例分别为23.27%、20.69%、23.13%和16.24%,钒含量最高的4#钢中的大角度晶界最少。随着钒含量由0.036%增加到0.075%,试验钢的抗拉强度和屈服强度均有明显的提高,然而钒含量进一步升高对试验钢的强度影响较小,甚至屈服强度还有一定的下降。试验钢强度的增加主要是纳米级析出相沉淀强化和细晶强化的共同作用,试验钢的塑性受钒含量变化的影响不大。Abstract: In this work, the precipitates and microstructure characteristics in four X80 pipeline steels with different vanadium contents (0.036%, 0.075%, 0.110% and 0.150%) and their effects on the strength and plasticity of the steels were investigated by means of high-resolution transmission electron microscope, scanning electron microscope and electron backscatter diffraction. The results show that with increase of the vanadium content, the number and volume fraction of nano-sized precipitates in the steel increase. The size of precipitates in four experimental steels is mainly in the range of 0~20 nm. The number of precipitates with size less than 10 nm in the steel increases with increasing the vanadium content. The nano-sized second phase particles precipitated in or near the grain boundary are mostly vanadium containing carbides. The microstructure of four experimental steels with different vanadium contents is composed of massive ferrite and granular bainite. The proportions of large angle grain boundaries in steels are 23.27%, 20.69%, 23.13% and 16.24%, respectively, and the 4# steel with the highest vanadium content has the least large angle grain boundaries. With increase of the vanadium content from 0.036% to 0.075%, the tensile strength and yield strength of the experimental steel are significantly improved. However, further increase of the vanadium content has little effect on the strength of the experimental steel, and even the yield strength has a certain decrease. The increasing strength of the experimental steel is mainly due to the combination of precipitation strengthening and fine grain strengthening of nano-sized precipitates, and the plasticity of the experimental steel is almost not affected by change of the vanadium content.
-
Key words:
- X80 pipeline steel /
- vanadium content /
- precipitate /
- microstructure /
- strength plasticity
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental steels
% 编号 C Si Mn P S Ni Mo Cr V Nb Ti Al Cu O N Fe 1# 0.05 0.17 1.77 0.004 0.0025 0.23 0.11 0.27 0.036 0.018 0.017 0.040 0.12 0.0029 0.0012 Bal. 2# 0.04 0.19 1.82 0.004 0.0025 0.24 0.11 0.27 0.075 0.027 0.020 0.032 0.11 0.0024 0.0009 Bal. 3# 0.04 0.19 1.82 0.004 0.0025 0.24 0.11 0.27 0.110 0.026 0.020 0.040 0.13 0.0020 0.0008 Bal. 4# 0.04 0.18 1.80 0.004 0.0025 0.25 0.12 0.30 0.150 0.026 0.020 0.040 0.15 0.0022 0.0008 Bal. 表 2 试验钢中析出相分析
Table 2. Analysis of precipitates in experimental steels
编号 N/个 Vf/‰ 1# 80 2.10 2# 127 2.54 3# 180 3.12 4# 343 9.95 表 3 四种试验钢的拉伸性能指标
Table 3. Tensile properties of four experimental steels
试样编号 屈服强度
σS/MPa抗拉强度
σb/MPa屈强比
(σS/σb)伸长率
δ/%断面收缩率ψ/% 1# 536.36 ± 30.70 626.57 ± 20.28 0.86 17.57 ± 2.77 78.83 ± 1.17 2# 553.62 ± 5.20 665.51 ± 4.31 0.83 20.35 ± 1.06 79.75 ± 0.54 3# 565.49 ± 22.19 673.53 ± 20.24 0.84 18.53 ± 0.47 80.01 ± 1.09 4# 545.55 ± 20.21 666.33 ± 18.97 0.82 22.8 ± 1.44 80.09 ± 0.35 -
[1] Xu Jingtao. Application and prospect of X80 steel in long-distance pipeline[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016,26(8):1−7. (徐景涛. X80管线钢在长输管道中的应用及展望[J]. 中国冶金, 2016,26(8):1−7.Xu Jingtao. Application and prospect of X80 steel in long-distance pipeline[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016, 26(8): 1-7. [2] Duan He, Shan Yiyin, Yang Ke, et al. Experimental of process, microstructure and mechanical properties of X80 high strength pipeline steel for low temperature[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020,55(2):103−112. (段贺, 单以银, 杨柯, 等. X80低温用高强度管线钢的工艺与组织性能试验[J]. 钢铁, 2020,55(2):103−112.Duan He, Shan Yiyin, Yang Ke, et al. Experimental of process, microstructure and mechanical properties of X80 high strength pipeline steel for low temperature[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(2): 103-112. [3] Wang Huihui, Song Kailan, Zuo Xiurong, et al. Fracture behavior of multi-phase heavy wall X80 pipeline steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(8):228−235. (王慧慧, 宋开兰, 左秀荣, 等. 厚规格多相组织X80管线钢的断裂行为[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(8):228−235.Wang Huihui, Song Kailan, Zuo Xiurong, et al. Fracture behavior of multi-phase heavy wall X80 pipeline steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(8): 228-235. [4] Li L F, Song B, Cai Z Y, et al. Effect of vanadium content on hydrogen diffusion behaviors and hydrogen induced ductility loss of X80 pipeline steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019,742:712−721. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.048 [5] Li L F, Song B, Yang B W, et al. Effect of tempering temperature after thermo-mechanical control process on microstructure characteristics and hydrogen-induced ductility loss in high-vanadium X80 pipeline steel[J]. Materials, 2020,13:2839. doi: 10.3390/ma13122839 [6] Li Yongliang, Wang Fuming, Li Changrong, et al. Influence of vanadium on the microstructure refinement of high strength automobile beam steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016,38(8):1108−1114. (李永亮, 王福明, 李长荣, 等. 钒对高强度汽车大梁钢组织细化的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016,38(8):1108−1114.Li Yongliang, Wang Fuming, Li Changrong, et al. Influence of vanadium on the microstructure refinement of high strength automobile beam steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(8): 1108-1114. [7] Li Mei, Wang Qiang, Gao Hongwen, et al. Effect of vanadium content on properties of new high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(6):118−122. (李梅, 王强, 高宏文, 等. 钒含量对新型高强钢性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(6):118−122.Li Mei, Wang Qiang, Gao Hongwen, et al. Effect of vanadium content on properties of new high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(6): 118-122. [8] Qing Jiasheng, Shen Houfa, Liu Ming. V-N microalloying of high strength weathering steel YQ450NQR1[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017,52(5):87−93. (卿家胜, 沈厚发, 刘明. 高强耐候钢YQ450NQR1钒氮微合金化[J]. 钢铁, 2017,52(5):87−93.Qing Jiasheng, Shen Houfa, Liu Ming. V-N microalloying of high strength weathering steel YQ450 NQR1[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017, 52(5): 87-93. [9] Liu Qingchun, Wu Lin, Zheng Zhiwang, et al. Effect of vanadium on the precipitation behavior and aging properties of higher yield strength weathering steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(2):144−149. (刘庆春, 吴林, 郑之旺, 等. 高强度热轧耐候钢的钒析出行为与时效性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(2):144−149.Liu Qingchun, Wu Lin, Zheng Zhiwang, et al. Effect of vanadium on the precipitation behavior and aging properties of higher yield strength weathering steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(2): 144-149. [10] Kim K S, Du L X, Gao C R. Influence of vanadium content on bainitic transformation of a low-carbon boron steel during continuous cooling[J]. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett. ), 2015,28(6):692−698. doi: 10.1007/s40195-015-0249-1 [11] Ma Hongxu, Li Youguo. Measurement of size distribution and volume fracture of precipitates in silicon steel[J]. Material Science & Engineering, 2002,(3):328−330. (马红旭, 李友国. 硅钢中析出物的尺寸分布以及体积分数的测定[J]. 材料科学与工程, 2002,(3):328−330.Ma Hongxu, Li Youguo. Measurement of size distribution and volume fracture of precipitates in silicon steel[J]. Material Science & Engineering, 2002(3): 328-330. [12] Li Xiaolin, Wang Zhaodong. Interphase precipitation behaviors of nanometer-sized carbides in a Nb-Ti-bearing low-carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015,51(4):417−424. (李小琳, 王昭东. 含Nb-Ti低碳微合金钢中纳米碳化物的相间析出行为[J]. 金属学报, 2015,51(4):417−424.Li Xiaolin, Wang Zhaodong. Interphase precipitation behaviors of nanometer-sized carbides in a Nb-Ti-bearing low-carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(4): 417-424. [13] Campos S S, Morales E V, Kestenbach H J. Detection of interphase precipitation in microalloyed steels by microhardness measurements[J]. Mater Charact, 2004,52:379−384. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2004.06.012 [14] Joodaki R, Alavi S R, Gheisari K, et al. Effect of annealing treatments on the microstructure and texture development in API 5L X60 microalloyed pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017,26(5):2003−2013. doi: 10.1007/s11665-017-2673-z [15] Cheng Shi, Hu Feng, Wang Yachao, et al. Effect of tempering heat treatment on low-temperature impact toughness of low-carbon high-strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2020,41(12):80−89. (程石, 胡锋, 王亚超, 等. 回火热处理对低碳高强度钢低温冲击韧性的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2020,41(12):80−89.Cheng Shi, Hu Feng, Wang Yachao, et al. Effect of tempering heat treatment on low-temperature impact toughness of low-carbon high-strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2020, 41(12): 80-89. [16] Lu Yemao, Liang Yilong, Long Shaolei, et al. Effect of the high angle boundaries on the strength for 20CrNi2Mo steel[J]. Materials Reports, 2018,32(12):4339−4346. (卢叶茂, 梁益龙, 龙绍檑, 等. 淬火20CrNi2Mo低碳钢中大角度晶界对强度的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2018,32(12):4339−4346.Lu Yemao, Liang Yilong, Long Shaolei, et al. Effect of the high angle boundaries on the strength for 20 CrNi2 Mo steel[J]. Materials Reports, 2018, 32(12): 4339-4346. [17] 雍歧龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006.Yong Qilong. The second phase in steel meterials[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006. -





 下载:
下载: