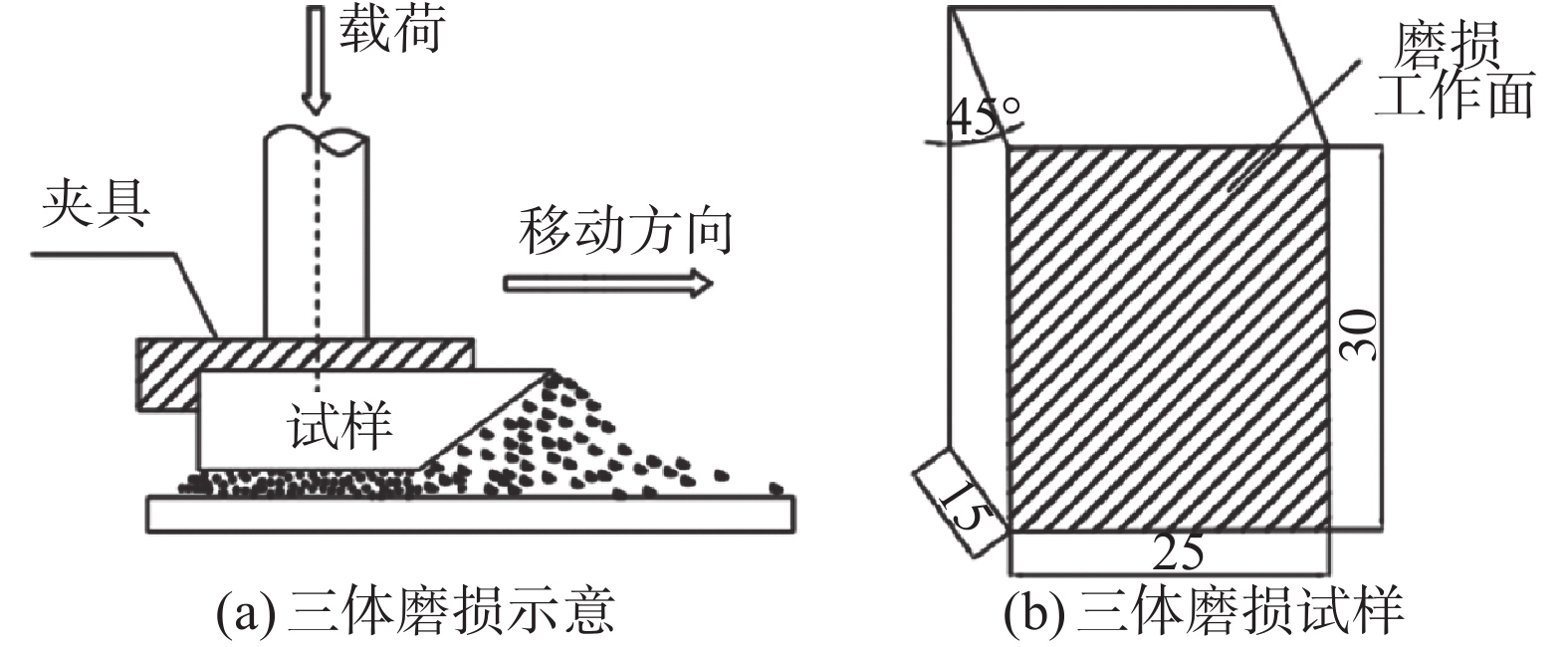
Wear properties of TiC particle reinforced iron matrix composites prepared by casting sintering method
-
摘要: 通过铸造烧结法制备TiC颗粒增强高铬铸铁基复合材料,采用EDS、SEM等检测手段研究增强颗粒对材料显微组织和磨损行为的影响规律。结果表明,与高铬铸铁相比,复合材料中由于TiC颗粒的存在使其洛氏硬度(HRC)从49提高到了60。在磨损过程中,高铬铸铁表面的M7C3型碳化物在磨粒的反复作用下出现了明显的裂纹,并逐渐向基体内扩展。破碎后的碳化物容易脱落,不能有效阻止磨粒在材料表面的犁削作用,加剧了材料的磨损。而在复合材料中,随着较软的基体相优先被磨料削除,会裸露出大量的TiC颗粒。这些表面凸起的TiC颗粒承担磨粒的主要破坏作用,从而有效保护基体材料。对比发现,在相同的磨损条件下,复合材料的耐磨性与高铬铸铁相比提高了1.95倍。Abstract: TiC particles reinforced high chromium cast iron matrix composites were prepared by casting sintering method. The effects of reinforced particles on the microstructure and wear behavior of the composites were studied by EDS and SEM. The results showed that the Rockwell hardness (HRC) of the composites increases from 49 to 60 compared with high chromium cast iron, due to the presence of TiC particles. During the wear process, the M7C3 carbides on the surface of high chromium cast iron appeared obvious cracks under the repeated action of abrasive particles, and gradually expanded into the matrix. The broken carbides are easy to fall off, which cannot effectively prevent the ploughing effect of abrasive particles on the surface of the material and aggravate the wear of the material. In the composites, a large number of TiC particles are exposed as the softer matrix phase is preferentially removed by the abrasive. These surface convex TiC particles bear the main damage of the abrasive particles, thus effectively protecting the matrix material. Through experimental comparison, it is found that the wear resistance of the composites is 1.95 times higher than that of high chromium cast iron under the same wear conditions.
-
表 1 高铬铸铁的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of high chromium cast iron
% C Si Mn Cr Ni Mo S P Fe 3.1~3.3 0.1~0.5 0.3~0.6 25~26 0.2~0.4 0.3~0.6 0.021 0.023 余量 表 2 试验钢组织中物相的EDS能谱
Table 2. EDS energy spectra of phase in the microstructure of test steel
试验钢 点 y/% C Si Ti Cr Fe 高铬铸铁 1 36.08 42.98 20.94 2 19.32 1.24 10.05 63.39 3 36.21 41.54 21.77 复合材料 4 41.05 56.68 1.21 1.06 5 38.8 0.18 53.38 4.27 3.37 -
[1] Olejnik E, Szymanski L, Tokarski T, et al. Local composite reinforcements of TiC/FeMn type obtained in situ in steel castings[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2019,19(4):997−1005. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2019.05.004 [2] Wang S, Li Y, Wang J, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and properties of Ti/W–C reinforced Fe-based composites[J]. Vacuum, 2021,194:110617. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110617 [3] Yang Yi, Yang Haokun, He Qiang, et al. Effect of aging treatment on the mechanical and impact properties of solid soluted Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight high manganese steel[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2023,17(2):303−309. (杨壹, 杨浩坤, 何强, 等. 时效热处理对Fe-Mn-Al-C轻质高锰钢拉伸和冲击性能的影响[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2023,17(2):303−309.Yang Yi, Yang Haokun, He Qiang, et al. Effect of aging treatment on the mechanical and impact properties of solid soluted Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight high manganese steel[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2023, 17(2): 303-309. [4] He Qiang, Jie Xiaohua, Zheng Zhibin, et al. Effect of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of medium chromium alloy steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023,35(5):586−594. (何强, 揭晓华, 郑志斌, 等. 碳含量对中铬合金钢组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2023,35(5):586−594.He Qiang, Jie Xiaohua, Zheng Zhibin, et al. Effect of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of medium chromium alloy steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023, 35(5): 586-594. [5] Dong Xiaorong, Zheng Zhibin, Long Jun, et al. Analysis of domestic patent technology of vanadium-containing cast wear-resistant steel materials[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2022,16(5):766−775. (董晓蓉, 郑志斌, 龙骏, 等. 含钒铸造耐磨钢铁材料国内专利技术分析[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2022,16(5):766−775.Dong Xiaorong, Zheng Zhibin, Long Jun, et al. Analysis of domestic patent technology of vanadium-containing cast wear-resistant steel materials[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2022, 16(5): 766-775. [6] Zheng Zhibin, Long Jun, Wang Yuhui, et al. Research progress of mechanical properties of twinning induced plasticity steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023,35(2):115−130. (郑志斌, 龙骏, 王玉辉, 等. 孪生诱发塑性钢力学性能的研究进展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2023,35(2):115−130.Zheng Zhibin, Long Jun, Wang Yuhui, et al. Research progress of mechanical properties of twinning induced plasticity steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023, 35(2): 115-130. [7] Huang L, Deng X, Li C, et al. Effect of TiC particles on three-body abrasive wear behaviour of low alloy abrasion-resistant steel[J]. Wear, 2019,434-435:202971. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2019.202971 [8] Huang L, Pan Y, Zhang J, et al. Densification, microstructure and mechanical performance of TiC/Fe composites by spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020,9(3):6116−6124. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.014 [9] Zhu M, Jiang Y, Sui Y, et al. Study on microstructure and abrasive wear properties of in-situ TiC reinforced high chromium cast iron matrix composite[J]. Materials Research Express, 2022,9(3):036517. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac5b02 [10] Wang S, Li Y, Wang J, et al. Effect of in-situ (Ti&W)C multiphase particles on three-body abrasive wear of high chromium cast iron[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2023,295:127161. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.127161 [11] Zhong L, Wei J, Bai H, et al. Effects of soaking time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-NbC/Fe core–shell rod-reinforced cast-iron-matrix composite fabricated through two-step in situ solid-phase diffusion[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020,9(6):12308−12317. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.095 [12] Lee J, Lee D, Song M H, et al. In-situ synthesis of TiC/Fe alloy composites with high strength and hardness by reactive sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018,34(8):1397−1404. [13] Wang Shuai, Zheng Zhibin, Li Yingmin, et al. Effect of W/Ti content on the microstructure and phase transformation of iron matrix composites[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2023,17(1):109−117. (王帅, 郑志斌, 李英民, 等. W/Ti含量对钢铁基复合材料微观组织和相变的影响规律[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2023,17(1):109−117.Wang Shuai, Zheng Zhibin, Li Yingmin, et al. Effect of W/Ti content on the microstructure and phase transformation of iron matrix composites[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2023, 17(1): 109-117. [14] Chen H, Lu Y, Sun Y, et al. Coarse TiC particles reinforced H13 steel matrix composites produced by laser cladding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020,395:125867. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125867 [15] Liang Y, Zhao Q, Zhang Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of TiC particulate locally reinforced steel matrix composites from Cu–Ti–C system with various C particles[J]. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2018,2(3):281−288. [16] Jiang J, Li S, Zhang W, et al. In situ formed TiCx in high chromium white iron composites: Formation mechanism and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,788:873−880. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.292 [17] Olejnik E, Szymański Ł, Batóg P, et al. TiC-FeCr local composite reinforcements obtained in situ in steel casting[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020,275:116157. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.03.017 [18] Wang Shuai, Li Yingmin, Zheng Zhibin, et al. Effect of in-situ (W&Ti)C complex particles on wear behavior of high chromium cast iron[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(1):151−157. (王帅, 李英民, 郑志斌, 等. 原位(W&Ti)C复相颗粒对高铬铸铁磨损行为的影响规律[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(1):151−157. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.024Wang Shuai, Zheng Zhibin, Wang Juan, et al. Effect of in-situ (W&Ti)C complex particles on wear behavior of high chromium cast iron[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(1): 151-157. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.024 [19] Qiu F, Zhang H, Li C L, et al. Simultaneously enhanced strength and toughness of cast medium carbon steels matrix composites by trace nano-sized TiC particles[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2021,819:141485. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141485 [20] Guan D, He X, Zhang R, et al. Tribological and corrosion properties of PM 316L matrix composites reinforced by in situ polymer-derived ceramics[J]. Vacuum, 2018,148:319−326. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.12.003 -





 下载:
下载: