Effect of SPS sintering process on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC / 6061Al composites
-
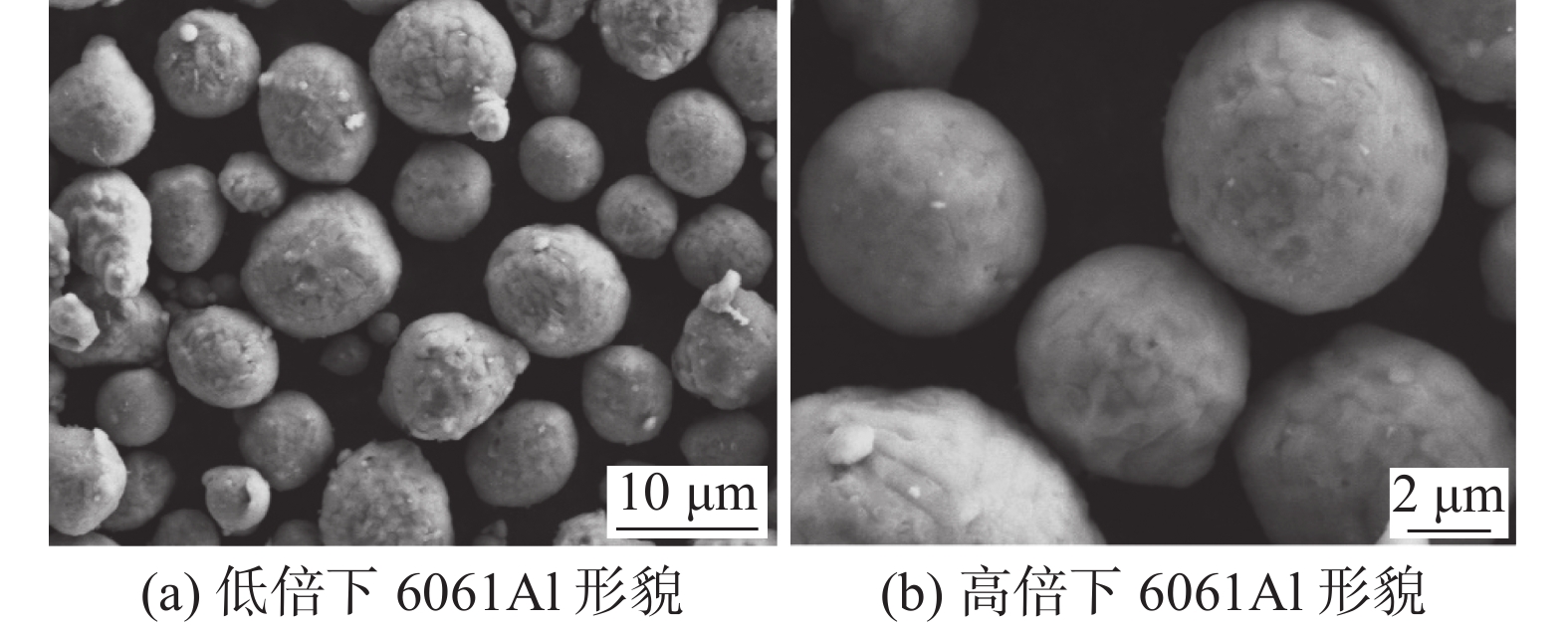
摘要: 采用低速卧式球磨法和放电等离子烧结法(SPS)制备了2%TiC/6061Al复合材料,利用光学显微镜、扫描电镜、显微硬度仪和拉伸试验研究了不同烧结温度和压力对该复合材料致密度、显微结构和力学性能的影响。结果表明,当烧结温度为500 ℃时,烧结不充分,颗粒之间结合不紧密,导致复合材料致密度过低;当烧结温度为550 ℃时,超过了Al基体的熔点,少部分熔融Al飞溅并溢出模具,导致模具内压力不平衡,从而降低了复合材料致密度。复合材料致密度和力学性能随着烧结压力的增大而增大,故选取模具所能承受的最大压力作为最佳烧结压力。故当烧结温度为525 ℃、烧结压力为40 MPa时,该复合材料的致密度、硬度和强度均达到最大值。Abstract: The 2% TiC/6061Al composites were prepared by low-speed horizontal ball milling and spark plasma sintering ( SPS ). The effects of different sintering temperatures and pressures on the density, microstructure and mechanical properties of the composites were studied by optical microscope, scanning electron microscope, microhardness tester and tensile test. The results show that when the sintering temperature is 500 ℃, the sintering is not sufficient, and the binding between the particles is not close, which leads to low density of the composite material. When the sintering temperature is 550 ℃ which exceeds melting point of Al matrix, a small amount of molten Al splashes and overflows the mold, resulting in unbalanced pressure in the mold, thereby reducing the density of the composite material. The density and mechanical properties of the composites increase with increase of the sintering pressure, so the maximum pressure that the mold can withstand is selected as the optimal sintering pressure. Therefore, when the sintering temperature is 525 ℃ and the sintering pressure is 40 MPa, the density, hardness and strength of the composite material reach the maximum values.
-
表 1 6061Al合金主要元素成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of 6061Al alloy
% Al Si Fe Cu Mn Mg Cr Zn Ti Ni Co 97.85 0.555 0.092 0.247 0.004 1.07 0.112 0.008 0.004 0.002 0.005 表 2 6061Al的主要性能参数
Table 2. Main performance parameters of 6061Al
密度/
(g·cm−3)抗拉强
度/MPa屈服强
度/MPa延伸率/
%弹性系
数/GPa抗弯强
度/MPa2.75 124 55.2 25 68.9 228 表 3 TiC的主要性能参数
Table 3. The main performance parameters of TiC
密度/
(g·cm−3)熔点/ ℃ 努氏硬度/
GPa弹性模量/
GPa热膨胀系
数/ ℃−14.93 3067 28~35 440 7.74×10−6 表 4 不同烧结温度下的2%TiC/6061Al复合材料的致密度
Table 4. The relative density of 2% TiC/6061Al composites sintered at different temperatures
T/ ℃ 理论密度/(g·cm−3) 实际密度/(g·cm−3) 致密度/% 500 2.793 2.583 92.4 525 2.793 2.732 97.8 550 2.793 2.685 96.1 表 5 不同烧结温度下制备的2%TiC/6061Al复合材料的力学性能
Table 5. Mechanical properties of 2% TiC/6061Al composites sintered at different temperatures
T/℃ 抗拉强
度/MPa屈服强
度/MPa弹性模
量/GPa延伸率/
%抗弯强
度/MPa硬度
(HV)500 246 204 62 6.4 342 63 525 281 233 78 7.8 401 75 550 263 218 69 6.6 382 66 表 6 不同烧结压力下的2%TiC/6061Al复合材料的致密度
Table 6. Density of 2% TiC/6061Al composites under different sintering pressures
压力/MPa 理论密度/(g·cm−3) 实际密度/(g·cm−3) 致密度/% 20 2.793 2.684 96.1 30 2.793 2.732 97.8 40 2.793 2.756 98.6 表 7 不同烧结压力下制备的2%TiC/6061Al复合材料的力学性能
Table 7. Mechanical properties of 2% TiC/6061Al composites sintered at different sintering pressures
压力/
MPa抗拉强
度/MPa屈服强
度/MPa弹性模
量/GPa延伸率/
%抗弯强
度/MPa硬度
(HV)20 233 193 60 4.2 337 54 30 251 208 69 6.3 351 69 40 266 220 74 7.6 386 77 -
[1] Liu Zhenshan, Li Yingdong, Zhao Jingwei, et al. Research on aluminum alloy materials and application technology for automobile lightweight[J]. Progress of Materials in China, 2022,41:786−795. (刘贞山, 李英东, 赵经纬, 等. 汽车轻量化用铝合金材料及应用技术的研究[J]. 中国材料进展, 2022,41:786−795.Liu Zhenshan, Li Yingdong, Zhao Jingwei, et al. Research on aluminum alloy materials and application technology for automobile lightweight [J]. Progress of Materials in China, 2022, 41 : 786-795. [2] Kaushal G, Bharti P K, Anas M. Mechanical and tribological behavior analysis of metal powder reinforced filled 7075 aluminum alloy composites for gear material application[J]. JETIR, 2021,8(9):756−760. [3] Patel M, Mulgaonkar S, Desai H, et al. Development and implementation of wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) based on pulse spray GMAW for aluminum alloy (AlSi7Mg)[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2021,74(5):1129−1140. doi: 10.1007/s12666-020-02154-w [4] Sakthi Sadhasivam R M, Ramanathan K, Bhuvaneswari B V, et al. A study on tribological behaviour and analysis of ZnO reinforced AA6061 matrix composites fabricated by stir casting route[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2021,73(4):642−651. doi: 10.1108/ILT-11-2020-0392 [5] Bhoi N K, Singh H, Pratap S, et al. Developments in the aluminum metal matrix composites reinforced by micro/nano particles – A review[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2020,54(6):813−833. doi: 10.1177/0021998319865307 [6] Zhou N, Yang S, Liu Y, et al. Performance evaluation on particle-reinforced rigid/flexible composites via fused deposition modeling 3D printing[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2022,139(19/20):52149. [7] Xu Shenghang, Qiu Jingwen, Zhang Huibin, et al. Friction behavior of TiC particle reinforced Ti-30Fe composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals ( English ), 2021,31:988−998. (徐圣航, 邱敬文, 张惠斌, 等. TiC颗粒强化Ti-30Fe复合材料的摩擦行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报(英文版), 2021,31:988−998.Xu Shenghang, Qiu Jingwen, Zhang Huibin, et al. Friction behavior of TiC particle reinforced Ti-30 Fe composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals ( English ), 2021, 31 : 988-998. [8] Zhai W, Zhou W, Nai S M L. In-situ formation of TiC nanoparticles in selective laser melting of 316L with addition of micronsized TiC particles[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2022,829:142179. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.142179 [9] Bagheri G A. The effect of reinforcement percentages on properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016,676:120−126. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.085 [10] Zeng X W, Zhang W G, Wei N, et al. Preparation of in situ TiCp/Ly12 composite and its microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2007,443:224−228. [11] Selcuk C, Kennedy A R. Al–TiC composite made by the addition of master alloys pellets synthesised from reacted elemental powders[J]. Materials Letters, 2006,60:3364−3366. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.021 [12] 张清泉. 纳米TiC颗粒孕育Al-Cu合金的组织演变及强韧性[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.Zhang Qingquan. Microstructure evolution and strength-toughness of Al-Cu alloy inoculated with nano-TiC particles [D]. Changchun : Jilin University, 2018. [13] 周东帅. 纳米TiC_p/Al-Cu复合材料制备和组织与力学性能的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014.Zhou Dongshuai. Preparation, microstructure and mechanical properties of nano-TiC_p / Al-Cu composites [D]. Changchun : Jilin University, 2014. [14] Yu W, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. Texture evolution, segregation behavior, and mechanical properties of 2060Al-Li (aluminium-lithium) composites reinforced by TiC (titanium carbide) nanoparticles[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023,255:110611. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110611 [15] Wu Y, Luo S, Wu J B, et al. Development and characterization of CrCoNi medium entropy alloy particles reinforced aluminum matrix composite[J]. Crystals, 2022,12:1452. doi: 10.3390/cryst12101452 [16] Zhang J, Liu Q, Yang S, et al. Microstructural evolution of hybrid aluminum matrix composites reinforced with SiC nanoparticles and graphene/graphite prepared by powder metallurgy[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2020,30:192−199. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.01.024 [17] Shi Q, Mertens R, Dadbakhsh S, et al. In-situ formation of particle reinforced aluminium matrix composites by laser powder bed fusion of Fe2O3/AlSi12 powder mixture using laser melting/remelting strategy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2022,299:117357. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117357 [18] 张学拯. 热处理对粉末触变成形SiCp/6061Al基复合材料组织和力学性能的影响及其强韧化机理研究[J]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2019.Zhang Xuezheng. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder thixoformed SiCp / 6061Al matrix composites and its strengthening and toughening mechanism [J]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2019. [19] Cohen S, Ratzker B, Kalabukhov S, et al. Diffusion bonding of transparent ceramics by spark plasma sintering (SPS) complemented by hot isostatic pressing (HIP)[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023,43:6628−6633. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2023.06.071 [20] Imran M, Deillon L, Sizova I, et al. Process optimization and study of the co-sintering behaviour of Cu-Ni multi-material 3D structures fabricated by spark plasma sintering (SPS)[J]. Materials & Design, 2022,223:111210. -





 下载:
下载: