Forming process, microstructure, strength and toughness of Ti6Al4V alloy by laser wire-feed additive manufacturing
-
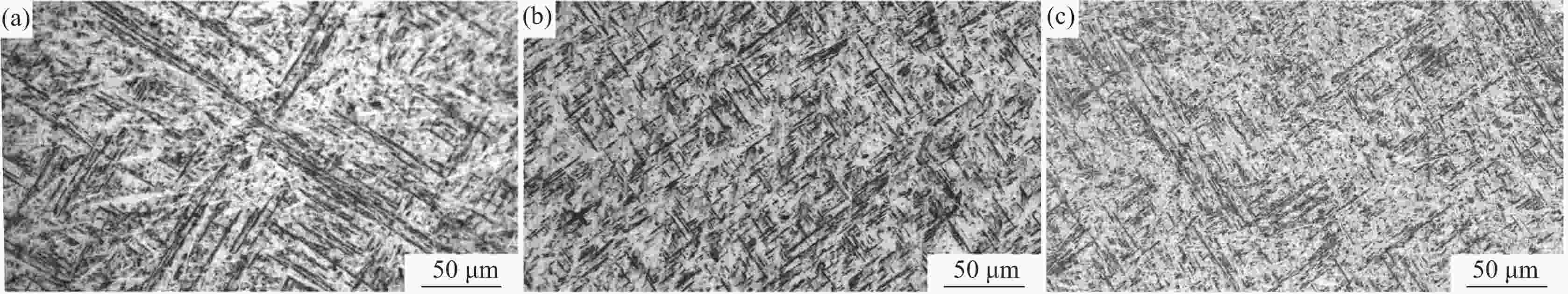
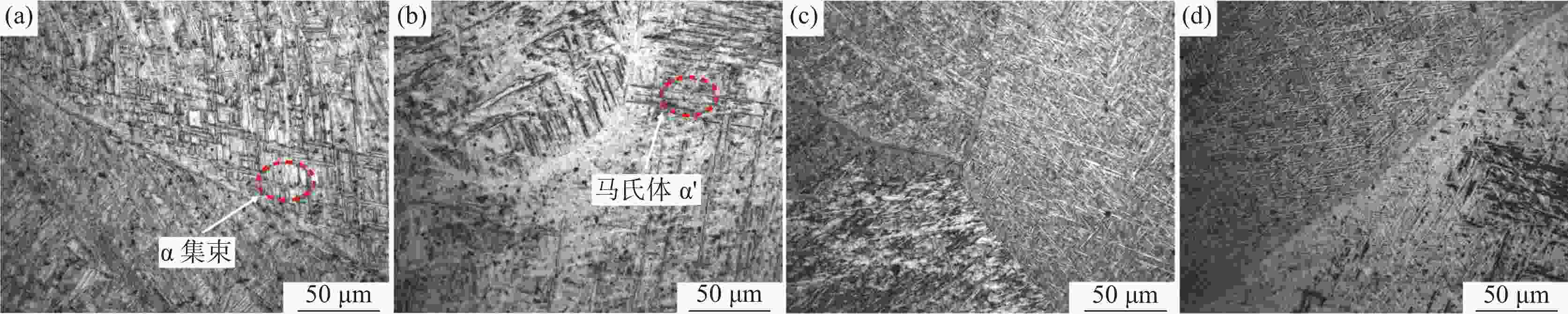
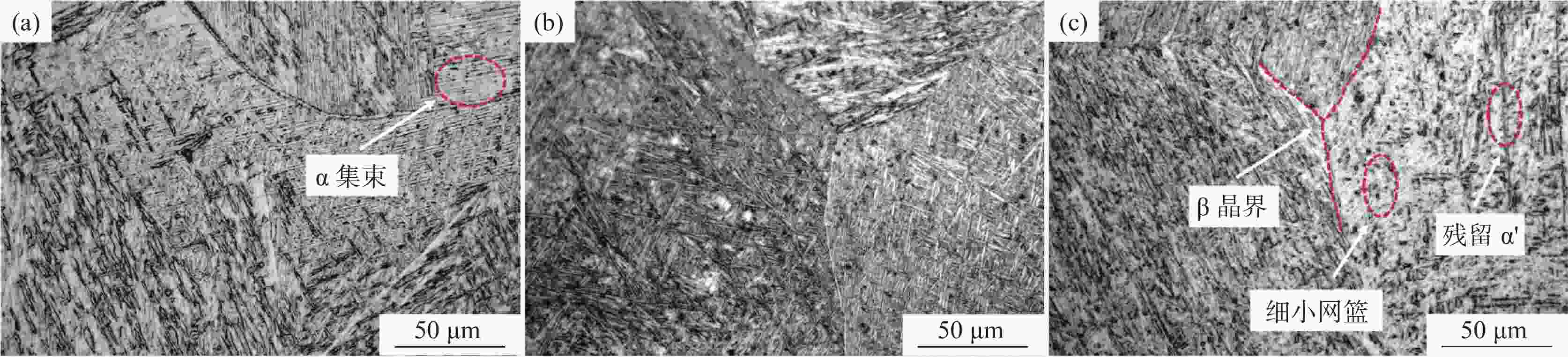
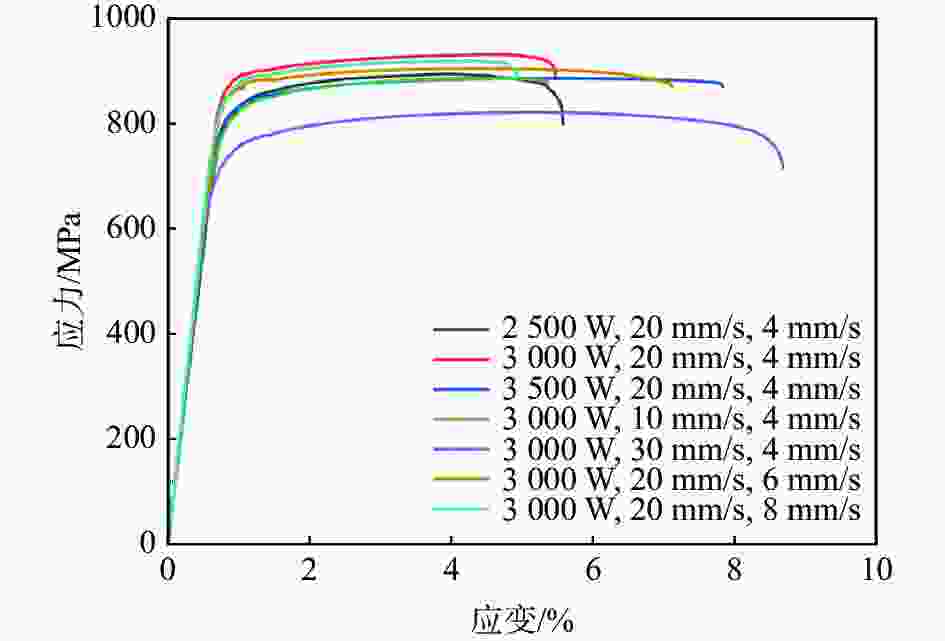
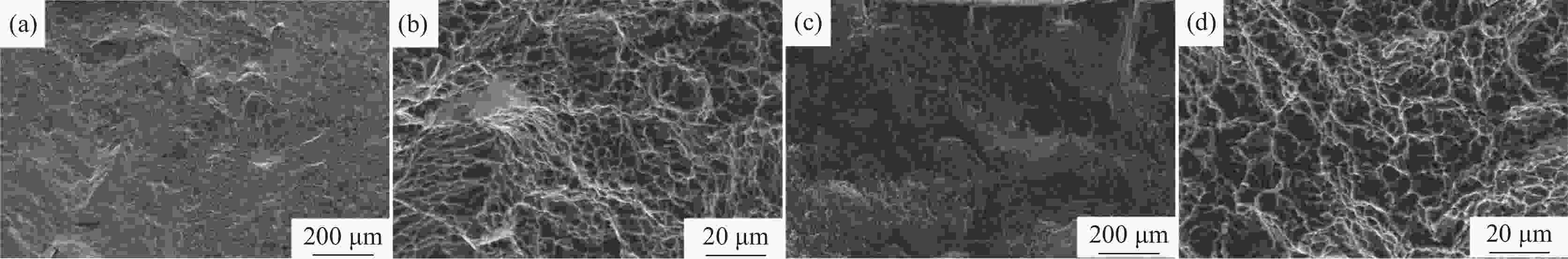
摘要: 采用激光熔丝增材制造技术制备了单道多层的Ti6Al4V合金试样,系统研究了激光功率、扫描速度及送丝速度对Ti6Al4V合金的组织形貌、拉伸性能和冲击性能的影响。单道多层沉积试样的组织由马氏体α'、α集束和网篮状α构成。激光功率提高使β晶粒尺寸增大和马氏体α'分解程度增加,激光功率从3000 W提升至3500 W时试样抗拉强度下降了约4%,但延伸率上升了50%,冲击韧性提高了约6%。送丝速度的提高增大了试样的β晶粒平均尺寸,随着送丝速度从10 mm/s增加至30 mm/s,抗拉强度下降了2%,延伸率提高了67%,冲击韧性提高了11%。扫描速度提高会增加试样内的未熔合缺陷和残留马氏体α',扫描速度6 mm/s试样相比扫描速度4 mm/s的试样延伸率提高了约45%,抗拉强度下降了2%,冲击韧性提高了11%。Abstract: In this paper, single-pass multi-layer Ti6Al4V alloy specimens were prepared by laser wire-feed additive manufacturing technology. The effects of laser power, scanning speed and wire feeding speed on the microstructure, tensile properties and impact properties of Ti6Al4V alloy were systematically studied. The microstructure of single-pass multi-layer deposition samples is composed of martensite α', α bundle and basket-weave microstructure. The increase of laser power increases the β grain size and the decomposition degree of martensite α'. When the laser power increases from 3000 W to 3500 W, the tensile strength of the sample decreases by about 4%, the elongation increases by 50%, and the impact toughness increases by about 6%. With increasing wire feeding speed, the average size of the β grains of the sample increases. As the wire feeding speed increases from 10 mm/s to 30 mm/s, the tensile strength decreases by 2%, the elongation increases by 67%, and the impact toughness increases by 11%. When the scanning speed increases, the lack-of-fusion and residual martensite α' in the sample increases. Compared with the sample with a scanning speed of 4 mm/s, the elongation rate of the sample with a scanning speed of 6 mm/s increases by about 45%, the tensile strength decreases by 2%, and the impact toughness increases by 11%.
-
表 1 Ti6Al4V丝材主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of Ti6Al4V wire
% C V Al Fe Ti H N O 0.013 4.03 6.33 0.049 90.14 0.0055 0.006 0.034 表 2 多层薄壁墙试样的沉积参数
Table 2. Deposition parameters of multi-layered thin wall specimens
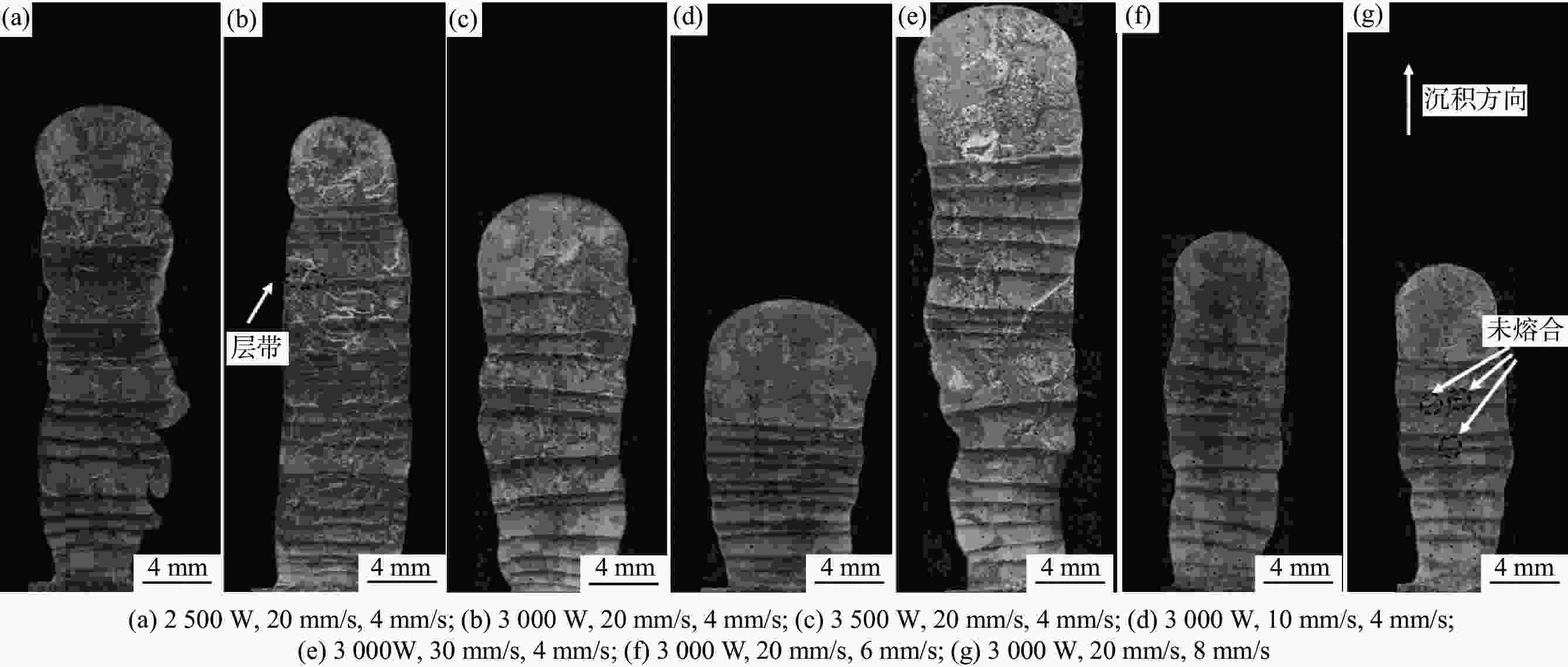
试样序号 激光功率/W 送丝速度/(mm·s−1) 扫描速度/(mm·s−1) 1 2500 20 4 2 3000 20 4 3 3500 20 4 4 3000 20 6 5 3000 20 8 6 3000 10 4 7 3000 30 4 表 3 不同工艺参数下试样的β晶粒平均尺寸
Table 3. Average sizes of β grains of samples under different process parameters
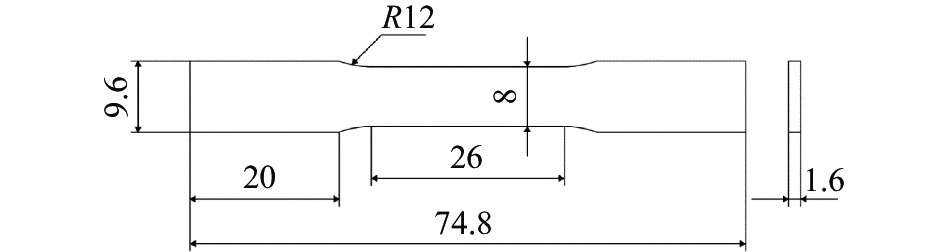
μm 试样1 试样2 试样3 试样4 试样5 试样6 试样7 981.9±4 1001.2±1 1026.5±3 942.16±2 849.11±2 774.84±2 1044.86±3 表 4 不同工艺参数的试样同一位置的拉伸性能
Table 4. Tensile properties of the samples at the same position under different process parameters
试样序号 Rp0.2/MPa Rm /MPa A/% 1 786.5 898.5 4.60 2 847.4 925.2 4.55 3 784.4 886.2 6.80 4 818.4 904.9 6.60 5 836.6 918.7 4.10 6 749.7 886.3 4.50 7 702.0 821.7 7.60 表 5 不同工艺参数试样同一位置的室温冲击性能
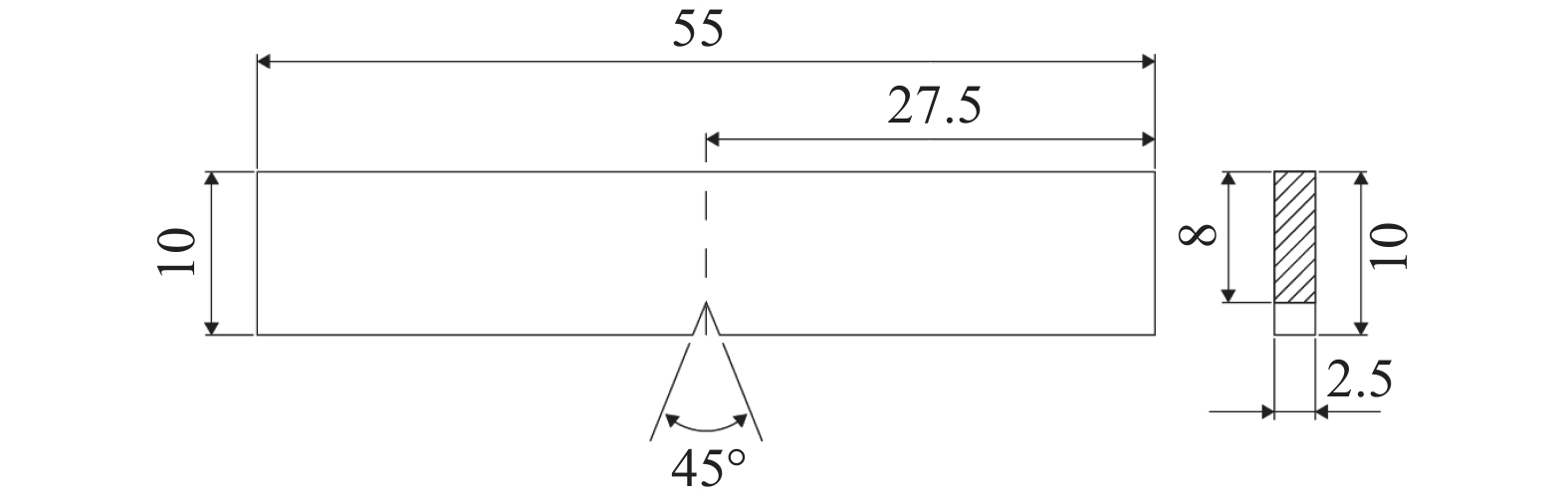
Table 5. Room temperature impact properties of the samples at the same position under different process parameters
试样序号 吸收功
Ec /J裂纹萌生
功Wi /J裂纹扩展
功Wp /J冲击韧性/
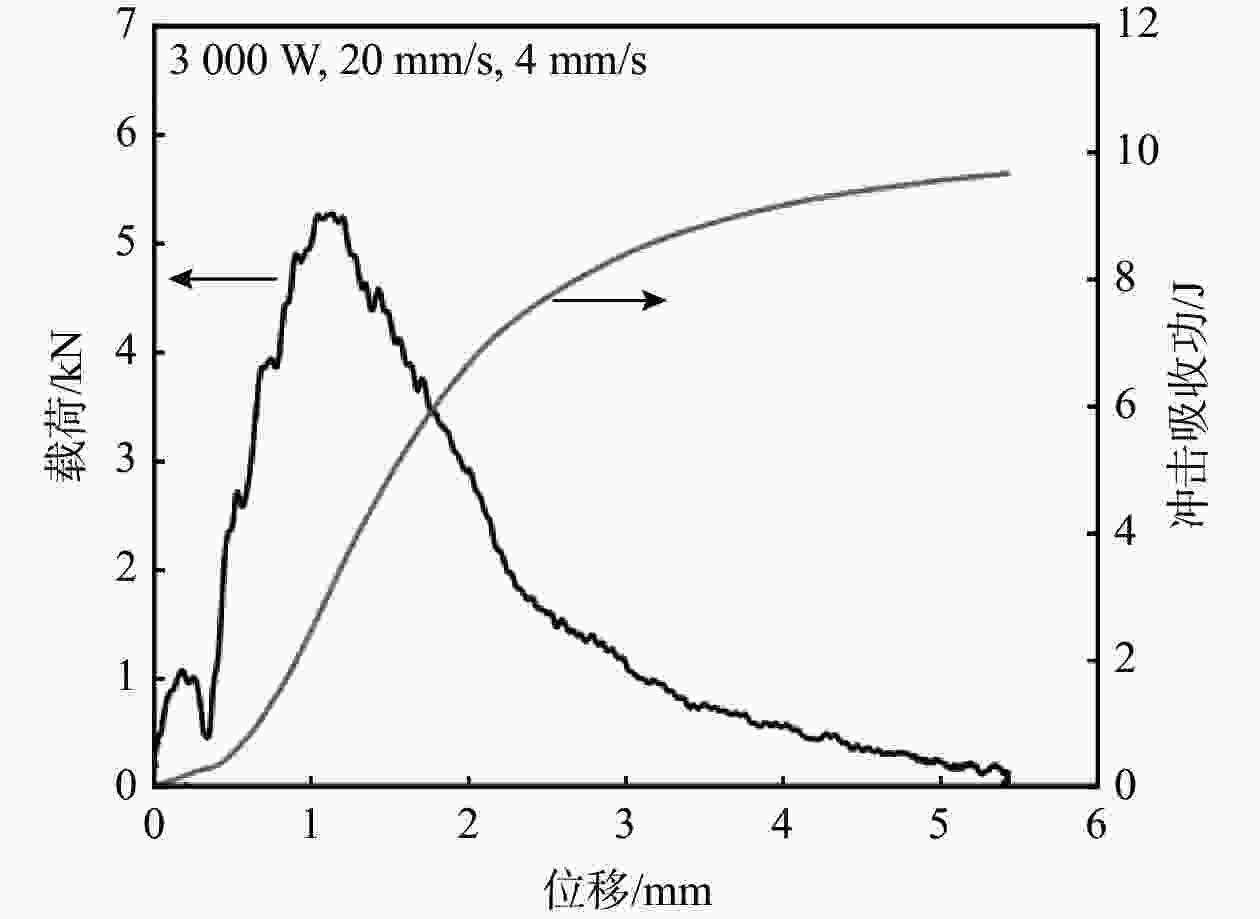
(J·cm−2)1 9.12 3.94 5.18 45.71 2 9.74 3.98 5.76 48.74 3 10.05 4.84 5.21 51.74 4 10.74 5.22 5.52 53.97 5 9.31 3.62 5.69 46.51 6 9.21 4.68 4.53 47.52 7 10.73 4.84 5.89 54.05 -
[1] Zhou Xinyuan, Zhang Weixing, Ge Futing. Overview of research status of cylindrical pressure shell structure of deep submersible[J]. Electronics Quality, 2021,(12):4. (周新院, 张卫星, 葛付婷. 深潜器柱形耐压壳结构研究现状概述[J]. 电子质量, 2021,(12):4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0107.2021.12.003Zhou Xinyuan, Zhang Weixing, Ge Futing. Overview of research status of cylindrical pressure shell structure of deep submersible[J]. Electronics Quality, 2021(12): 4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0107.2021.12.003 [2] Gorynin I V. Titanium alloys for marine application[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 1999,263(2):112−116. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01180-0 [3] Auwal S T, Ramesh S, Yusof F, et al. A review on laser beam welding of titanium alloys[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018,97(1):1071−1098. [4] Rosli Nor Ana, Alkahari Mohd Rizal, Bin Abdollah Mohd Fadzli, et al. Review on effect of heat input for wire arc additive manufacturing process[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021,11:2127−2145. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.002 [5] Murugan P Durai, Vijayananth S, Natarajan Mp, et al. A current state of metal additive manufacturing methods: A review[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2022,59:1277−1283. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.503 [6] Yuan Ding, Sun Xiaojing, Sun Laibo, et al. Improvement of the grain structure and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel fabricated by laser and wire additive manufacturing assisted with ultrasonic vibration[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2021,813:141−177. [7] Da Silva Adrien, Frostevarg Jan, Volpp Joerg, et al. Additive manufacturing by laser-assisted drop deposition from a metal wire[J]. Materials & Design, 2021,209:109987. [8] Huang Wenhao, Chen Shujun, Xiao Jun, et al. Laser wire-feed metal additive manufacturing of the Al alloy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021,134:106627. [9] Zhu Song, Nakahara You, Yamamoto Motomichi, et al. Additive manufacturing phenomena of various wires using a hot-wire and diode laser[J]. Welding in the World, 2022,66(7):1315−1327. doi: 10.1007/s40194-022-01273-w [10] Du Farui, Zhu Jinqian, Ding Xueping, et al. Dimensional characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V thin-walled parts prepared by wire-based multi-laser additive manufacturing in vacuum[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2019,25(5):849−856. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-08-2018-0207 [11] Yuan Ding, Shao Shuaiqi, Guo Chunhuan, et al. Grain refining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated by laser and wire additive manufacturing assisted with ultrasonic vibration[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2021,73:105472. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105472 [12] Ding Yaoyu, Akbari Meysam, Kovacevic Radovan. Process planning for laser wire-feed metal additive manufacturing system[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018,95:355−365. doi: 10.1007/s00170-017-1179-z [13] Hu Yaojun. Developing marine titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 1998,(4):5. (胡耀君. 发展中的船用钛合金[J]. 钛工业进展, 1998,(4):5. doi: 10.13567/j.cnki.issn1009-9964.1998.04.001Hu Yaojun. Developing marine titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 1998(4): 5 doi: 10.13567/j.cnki.issn1009-9964.1998.04.001 [14] Kelly Shawn Michael. Thermal and microstructure modeling of metal deposition processes with application to titanium aluminum vanadium[D]. USA , Virginia: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2004. [15] Kelly Sm, Babu Ss, David Sa, et al. A thermal and microstructure model for laser deposition of Ti-6Al-4V[C]//Cost-Affordable Titanium. Symposium, Dedicated to Professor Harvey Flower, 2004. Citeseer. [16] 章敏. 送粉式和送丝式的钛合金激光增材制造特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.Zhang Min. Research on laser additive manufacturing characteristics of titianium alloy with powder and wire[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. [17] Lei Lei, Zhao Yongqing, Zhao Qinyang, et al. Impact toughness and deformation modes of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with different microstructures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2021,801:140411. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140411 -




 下载:
下载: