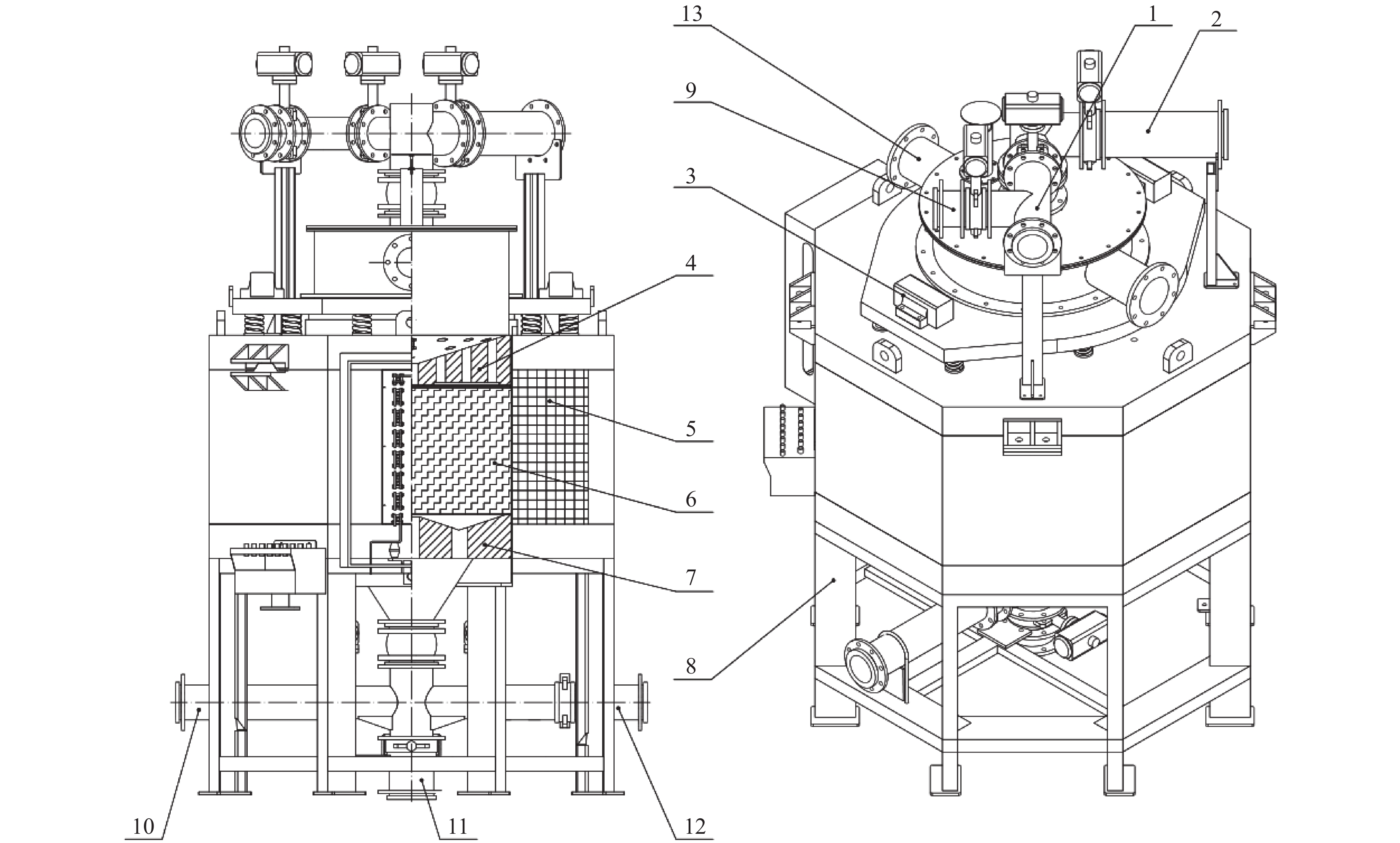
Magnetic separation and enrichment method of ultrafine-grained vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in Panxi region
-
摘要: 攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿中钛铁矿的回收普遍采用“强磁-浮选”作为原则工艺,此选钛工艺技术较为成熟、有一定的适应性,但−38 μm微细粒级钛铁矿尚未实现有效回收,大量的−38 μm粒级物料作为矿泥直接丢弃,造成选钛厂总回收率低、资源严重浪费。为提高钛铁矿的回收率,采用新型ZQS高梯度磁选机,探索了攀钢本部矿样、秀水河矿样、红格矿样三种细粒级试样的磁选富集效果,试验证明新型ZQS高梯度磁选机能高效回收超细粒级钛铁矿,精矿TiO2品位和回收率均较高,三种矿样的−0.038~0.019 mm粒级经一次磁选回收率分别达到了86.80%、82.26%、77.78%。此磁选技术工艺简单,具有良好的工业应用前景。Abstract: The recovery of ilmenite from vanadium titanomagnetite in Panxi area generally adopts “high-intensity magnetic flotation” as the principle process. This process technology is relatively mature and has certain adaptability, but the −38 μm fine ilmenite has not been effectively recovered, and a large number of −38 μm particles are directly discarded as slime, resulting in low total recovery rate and serious waste of resources. In order to improve the recovery rate of ilmenite, this paper explores the effect of magnetic separation and enrichment of three fine-grained samples of Panzhihua Iron and Steel Group Co., Ltd., Xiushui ore and Hongge ore. The test results show that the new ZQS high-gradient magnetic separator can efficiently recover ultrafine ilmenite; the grade and recovery rate of concentrate TiO2 are relatively high (86.80%, 82.26% and 77.78%, respectively, for the −0.038 to 0.019 mm grain grade). The magnetic separation technology is simple and shows a good perspective for industrial application.
-
表 1 原矿粒度组成
Table 1. Granularity composition of raw ore
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2分布率/% 负累计分布/% +0.074 1.54 2.08 0.27 100.00 −0.074~+0.045 3.89 4.95 1.68 99.72 −0.045~+0.038 5.66 8.41 4.15 98.04 −0.038~+0.019 64.36 13.05 73.23 93.89 −0.019 24.73 9.66 20.67 27.79 合计 100 11.47 100 表 2 激磁电流条件试验结果
Table 2. Experimental results under excited magnetic current conditions
激磁电流/A 精矿 尾矿品位/% 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% 600 36.02 21.22 66.65 5.98 700 43.75 20.42 77.88 4.51 800 47.47 20.19 83.56 3.59 900 53.35 18.64 86.70 3.27 表 3 磁选精矿的粒度组成
Table 3. Particle size composition of magnetic concentrate
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2金属分布率/% TiO2粒级回收率/% +0.074 1.25 3.73 0.23 68.21 −0.074~+0.045 4.38 6.45 1.40 69.65 −0.045~+0.038 6.75 11.66 3.90 78.49 −0.038~+0.019 63.62 24.14 76.07 86.80 −0.019 24.00 15.48 18.40 74.42 合计 100.00 20.19 100.00 83.56 表 4 原矿粒度组成
Table 4. Granularity composition of raw ore
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2分布率/% 负累计分布/% +0.074 12.69 6.34 9.25 100.00 −0.074~+0.045 15.80 7.08 12.86 90.75 −0.045~+0.038 13.40 7.74 11.92 77.90 −0.038~+0.019 37.80 10.86 47.18 65.97 −0.019 20.31 8.05 18.79 18.79 合计 100.00 8.70 100.00 表 5 激磁电流条件试验结果
Table 5. Experimental results under excited magnetic current conditions
激磁电流/A 精矿 尾矿品位/% 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% 600 36.32 16.82 70.22 4.07 700 38.17 16.52 72.48 3.87 800 40.32 16.28 75.45 3.58 900 42.55 15.71 76.82 3.51 表 6 磁选精矿的粒度组成
Table 6. Particle size composition of magnetic concentrate
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2金属分布率/% TiO2粒级回收率/% +0.074 11.68 10.69 7.67 62.57 −0.074~+0.045 14.88 11.97 10.94 64.20 −0.045~+0.038 13.75 12.56 10.61 67.14 −0.038~+0.019 39.71 21.09 51.44 82.26 −0.019 19.98 15.76 19.34 77.65 合计 100.00 16.28 100.00 75.45 表 7 铁、钛矿物物相分析
Table 7. Phase composition of iron and titanium minerals
铁物相 含量/% 占比/% 钛物相 含量/% 占比/% 磁性铁 14.07 72.49 钛磁性铁 1.54 18.85 赤褐铁矿 3.85 19.84 钛铁矿 5.62 68.79 硅酸铁 1.49 7.67 含钛硅酸盐 1.01 12.36 合计 19.41 100.00 合计 8.17 100.00 表 8 选钛给矿粒度组成
Table 8. Particle size composition of titanium ore feed
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2分布率/% 负累计分布/% +0.074 19.81 4.73 13.44 100.00 −0.074~+0.045 14.80 5.88 12.48 86.56 −0.045~+0.038 20.24 6.04 17.53 74.08 −0.038~+0.019 26.38 10.26 38.81 56.55 −0.019 18.77 6.59 17.74 17.74 合计 100 6.97 100 表 9 激磁电流条件试验结果
Table 9. Experimental results under excited magnetic current conditions
激磁电流/A 精矿 尾矿品位/% 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% 600 27.78 16.93 67.48 3.14 700 29.32 16.71 70.29 2.93 800 31.13 16.46 73.52 2.68 900 32.56 15.94 74.46 2.64 表 10 磁选精矿的粒度组成
Table 10. Particle size composition of magnetic concentrate
粒级/mm 产率/% TiO2品位/% TiO2金属分布率/% TiO2粒级回收率/% +0.074 17.58 9.66 10.31 56.42 −0.074~+0.045 13.31 11.03 8.92 52.52 −0.045~+0.038 23.75 14.68 21.18 88.78 −0.038~+0.019 28.39 23.82 41.07 77.78 −0.019 16.97 17.97 18.52 75.75 合计 100.00 16.46 100.00 73.50 -
[1] Sun Renbin, Wang Qiushu, Yuan Chunhua, et al. Analysis of global titanium resources situation[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019,28(6):1−6, 12. (孙仁斌, 王秋舒, 元春华, 等. 全球钛资源形势分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2019,28(6):1−6, 12. [2] Wu Jingrong, Wang Jianping, Xu Yu, et al. Current situation, problems and countermeasures of titanium resources in China[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2014,34(1):108−112. (吴景荣, 王建平, 徐昱, 等. 中国钛资源开发利用现状和存在的问题及对策[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2014,34(1):108−112. [3] Wu Xian, Zhang Jian. Geographical distribution and characteristics of titanium resources in China[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2006,(6):8−12. (吴贤, 张健. 中国的钛资源分布及特点[J]. 钛工业进展, 2006,(6):8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2006.06.004 [4] Wang Fengyu, Yang Zhaojun, Luo Rongfei, et al. Recovery increase of -38 μm ultra fine ilmenite using ZQS high gradient magnetic separator[J]. Metal Mine, 2019,(8):93−97. (王丰雨, 杨招君, 罗荣飞, 等. 采用ZQS高梯度磁选机提高超细粒级(-38μm)钛铁矿回收效果[J]. 金属矿山, 2019,(8):93−97. [5] Xue Yazhou, Wang Xuefeng, Wanghaijun, et al. On comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite resources in Panzhihua-Xichang region of Sichuan province[J]. Natural Resource Economice of China, 2017,30(4):9−13. (薛亚洲, 王雪峰, 王海军, 等. 攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿资源综合利用的思考[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2017,30(4):9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2017.04.003 [6] Li Lixia, Shen Shuaiping, Yuan Zhitao, et al. Loss mechanism of fine-grained ilmenite in magnetic separation[J]. China Mine, 2018,27(11):138−144. (李丽匣, 申帅平, 袁致涛, 等. 微细粒钛铁矿磁选回收率低原因分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2018,27(11):138−144. [7] Yang Zhaojun, Wang Fengyu, Luo Rongfei, et al. Magnetic separation and enrichment method of ultrafine-grained vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in Paxi region[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(3):26−29. (杨招君, 王丰雨, 罗荣飞, 等. 攀西超细粒级钒钛磁铁矿磁选富集方法[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(3):26−29. [8] (李政, 陈从喜. 全球钛资源行业发展现状[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(2): 245-250.)Li Zheng, Chen Congxi. Development status of global titanium resources industry[J/OL]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 245-250. [9] Chen Junming, Zhong Senglin, Xie Baohua, et al. Development and application of ZQS periodic high gradient magnetic separator[J]. Modern Mine, 2016,32(7):235−236. (陈俊明, 钟森林, 谢宝华, 等. ZQS周期式高梯度磁选机的研制和应用[J]. 现代矿业, 2016,32(7):235−236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.07.081 [10] Wu Chengcai, Zhang Chaoda, Zhong Senglin, et al. Application of ZQS-type circle high gradient magnetic separator in ironremoval purification of non-metallic mine[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2017,11(1):47−50. (吴城材, 张超达, 钟森林, 等. ZQS型周期式高梯度磁选机在非金属矿除杂提质中的应用[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2017,11(1):47−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2017.01.011 [11] Xu Limin, Chen Junming, Wang Lijuan, et al. Optimization and application of ZQS periodic high gradient magnetic separator[J]. Metal Mine, 2020,(7):187−192. (许丽敏, 陈俊明, 王丽娟, 等. ZQS周期式高梯度磁选机的优化与应用[J]. 金属矿山, 2020,(7):187−192. -





 下载:
下载: