Experimental study on separating ilmenite from a tailing of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite ore in Panxi region
-
摘要: 攀西地区某钒钛磁铁矿选铁尾矿含TiO2 8.25%,矿石中可回收矿物为钛铁矿,主要脉石矿物为辉石和角闪石,脉石磁性较强。矿石粒度和钛铁矿嵌布粒度较细,−38 μm粒级含量达到45.46%,TiO2分布率49.79%。为有效利用钛资源,对其进行选钛试验。结果表明,该矿经弱磁除铁—分级脱泥后,沉砂采用螺旋溜槽一粗一扫选别,细泥采用ZQS高梯度磁选机磁选,获得产率36.45%,TiO2品位15.88%,回收率70.11%的综合钛粗精矿。综合粗精矿经浮选脱硫后,以硫酸和水玻璃为调整剂,YTB-1为捕收剂进行钛浮选,经过一粗四精一扫,中矿顺序返回,最终可获得产率9.57%,TiO2品位47.23%,回收率54.79%的钛精矿,实现了钛资源的高效回收。Abstract: A vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite dressing tailing in Panxi region contents of 8.25% TiO2. In the ore, the main valuable mineral was ilmenite, and the main gangue minerals were augite and hornblende, and the gangue minerals are of stronger magnetism. Both the particle size and disseminated grain size of ilmenite are relatively fine in the ore, the fine fraction of −38 μm reaches 45.46% and contributes 49.79% TiO2. In order to utilize the titanium resources effectively, a dressing test for recovering ilmenite was carried out. In this paper, the ore was graded into two parts by particle size after the strong magnetite minerals were removed by a drum magnetic separator, then the coarse-grained ore was separated by using spiral chute and the fine-grained ore was separated by using a ZQS high-gradient magnetic separator. A comprehensive ilmenite concentrate with a yield rate of 36.45%, a TiO2 grade of 15.88% and a recovery of 70.11% was obtained. Sulfuric acid and sodium silicate were used as regulators and YTB-1 as a collector to separate ilmenite from the comprehensive concentrate which was desulphurized by flotation beforehand. After one rougher stage, four finer stages, and one scavenging stage, the medium ore are returned in sequence, and finally, an ilmenite concentrate with a yield of 9.57%, a TiO2 grade of 47.23% and a recovery of 54.79% was obtained. Ilmenite mineral resource was recovered effectively.
-
表 1 原矿化学元素组成
Table 1. Chemical element composition in the raw ore
% Fe TiO2 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO 12.95 8.25 38.8 4.24 14.51 MgO Na2O K2O P S 14.35 0.55 0.36 0.11 0.28 表 2 原矿矿物组成
Table 2. Mineral composition of the raw ore
矿物组成 含量/% 矿物组成 含量/% 钛铁矿 12.8 辉石 39.09 榍石 0.65 角闪石 34.46 钛磁铁矿 1.54 绿泥石 1.52 赤铁矿 0.26 蛇纹石 2.48 褐铁矿 0.57 黑云母 2.33 磁黄铁矿 0.33 橄榄石 1.13 黄铜矿 0.19 斜长石 0.36 磷灰石 0.38 方解石 0.34 表 3 原矿粒度组成与TiO2在各粒级分布
Table 3. Size distribution of particles and the distribution of TiO2 in different size fractions in the raw ore
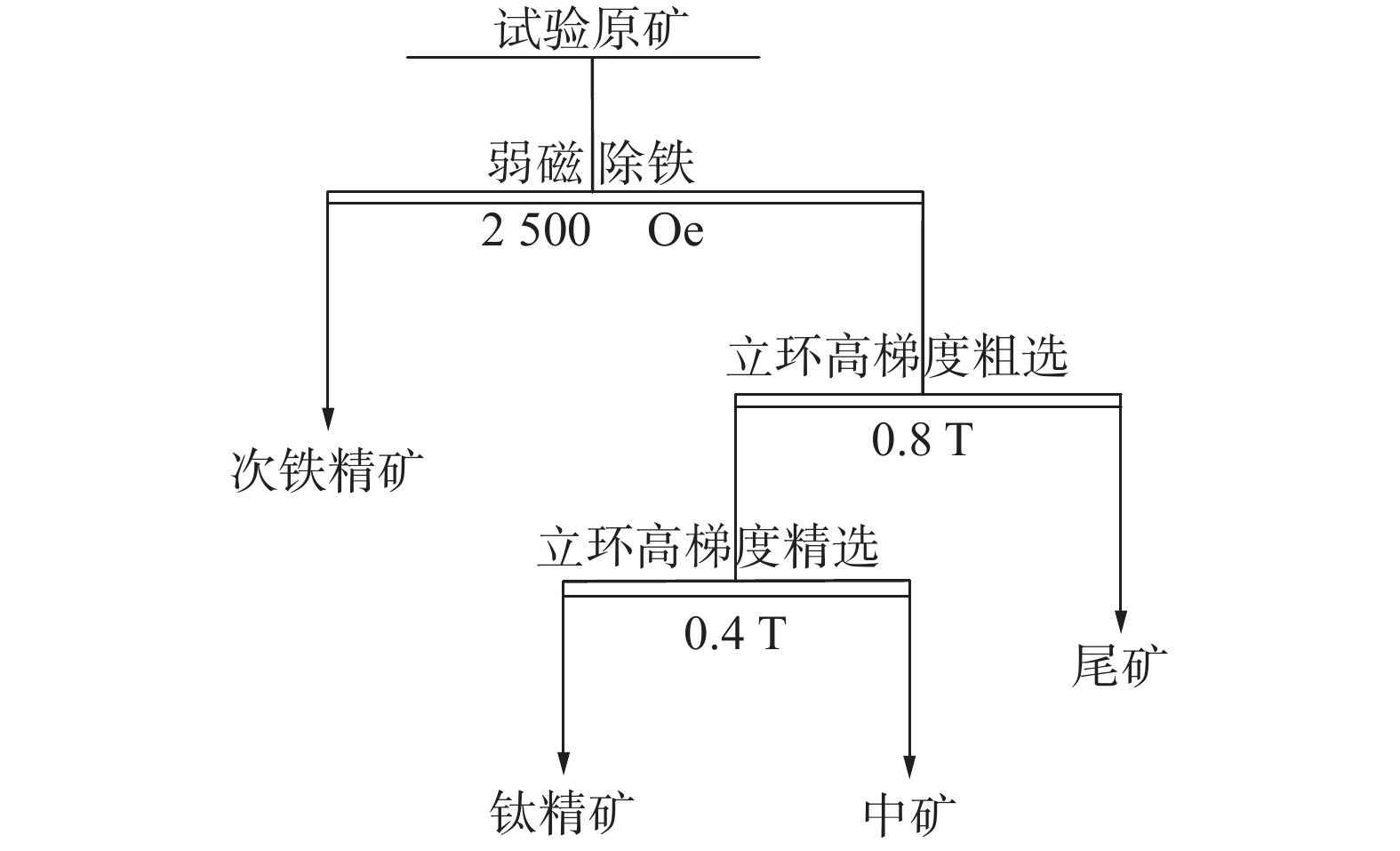
粒级/μm 产率/% TiO2品位/% 回收率/% 负累积回收率/% +200 3.65 3.80 1.66 100.00 −200~+150 3.54 4.25 1.80 98.34 −150~+74 16.90 6.81 13.80 96.53 −74~+38 30.35 9.05 32.94 82.73 −38~+19 26.85 10.28 33.10 49.79 −19 18.71 7.44 16.69 16.69 合计 100.00 8.34 100.00 表 4 立环高梯度磁选试验结果
Table 4. Separation results of vertical ring wet high-gradient magnetic separator
产品名称 产率/% TiO2品位/% 回收率/% 次铁精矿 2.21 12.12 3.24 钛精矿 27.10 13.8 45.27 中矿 28.86 6.23 21.76 尾矿 41.83 5.87 29.72 给矿 100 8.26 100 表 5 除铁—脱泥—螺旋溜槽—ZQS高梯度磁选回收细泥试验结果
Table 5. Results of high-gradient magnetic separator test via the process of low-intensity magnetic separation, desliming, spiral sluice separation, and ZQS recovering fine ilmenite
产品名称 产率/% TiO2品位/% 回收率/% 次铁精矿 2.34 12.06 3.42 螺旋精矿 20.44 16.54 40.95 螺旋尾矿 37.02 3.08 13.81 ZQS精矿 16.01 15.04 29.17 ZQS尾矿 24.19 4.32 12.66 原矿 100 8.26 100.00 表 6 全流程闭路试验结果
Table 6. Results of the whole closed-circuit process
产品名称 产率/% TiO2品位/% 回收率/% 次铁精矿 2.34 12.06 3.42 硫粗精矿 2.15 8.56 2.23 钛精矿 9.57 47.23 54.79 尾矿 85.94 3.80 39.56 原矿 100 8.25 100 -
[1] Shao Juan. Application and development of titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2007,(4):61−65. (邵娟. 钛合金及其应用研究进展[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2007,(4):61−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2007.04.015 [2] Wu Jianxin. Application of titanium alloys in marine materials[J]. Marine Equipment/Materials & Marketing, 2020,(8):5−6. (吴建新. 钛合金材料在船舶材料上的应用[J]. 船舶物资与市场, 2020,(8):5−6. [3] Gong Jiazhu. Technical progress of titanium dioxide manufacturing processes[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2012,44(8):1−4. (龚家竹. 钛白粉生产工艺技术进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2012,44(8):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2012.08.001 [4] Chong Xiaoxiao, Luan Wenlou, Wang Fengxiang, et al. Overview of global titanium resources status and titanium consumption trend in China[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020,40(2):162−170. (崇霄霄, 栾文楼, 王丰翔, 等. 全球钛资源现状概述及我国钛消费趋势[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020,40(2):162−170. [5] Sun Renbin, Wang Qiushu, Yuan Chunhua, et al. Analysis of global titanium resources situation[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019,28(6):1−6, 12. (孙仁斌, 王秋舒, 元春华, 等. 全球钛资源形势分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2019,28(6):1−6, 12. [6] Wang Hongbin, Meng Changchun. New process to recover coarse ilmenite in Midi titanium concentration plant of Panzhihua[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2011,31(4):51−54. (王洪彬, 孟长春. 攀枝花密地选钛厂粗粒钛铁矿回收新工艺研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2011,31(4):51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2011.04.014 [7] Wang Fengyu, Yang Zhaojun, Luo Rongfei, et al. Recovery increase of −38 μm ultra fine ilmenite using ZQS high gradient magnetic separator[J]. Metal Mine, 2019,(8):93−97. (王丰雨, 杨招君, 罗荣飞, 等. 采用ZQS高梯度磁选机提高超细粒级(−38 μm)钛铁矿回收效果[J]. 金属矿山, 2019,(8):93−97. -





 下载:
下载: