Microstructure evolution and processing maps of GH4169 during deformation
-
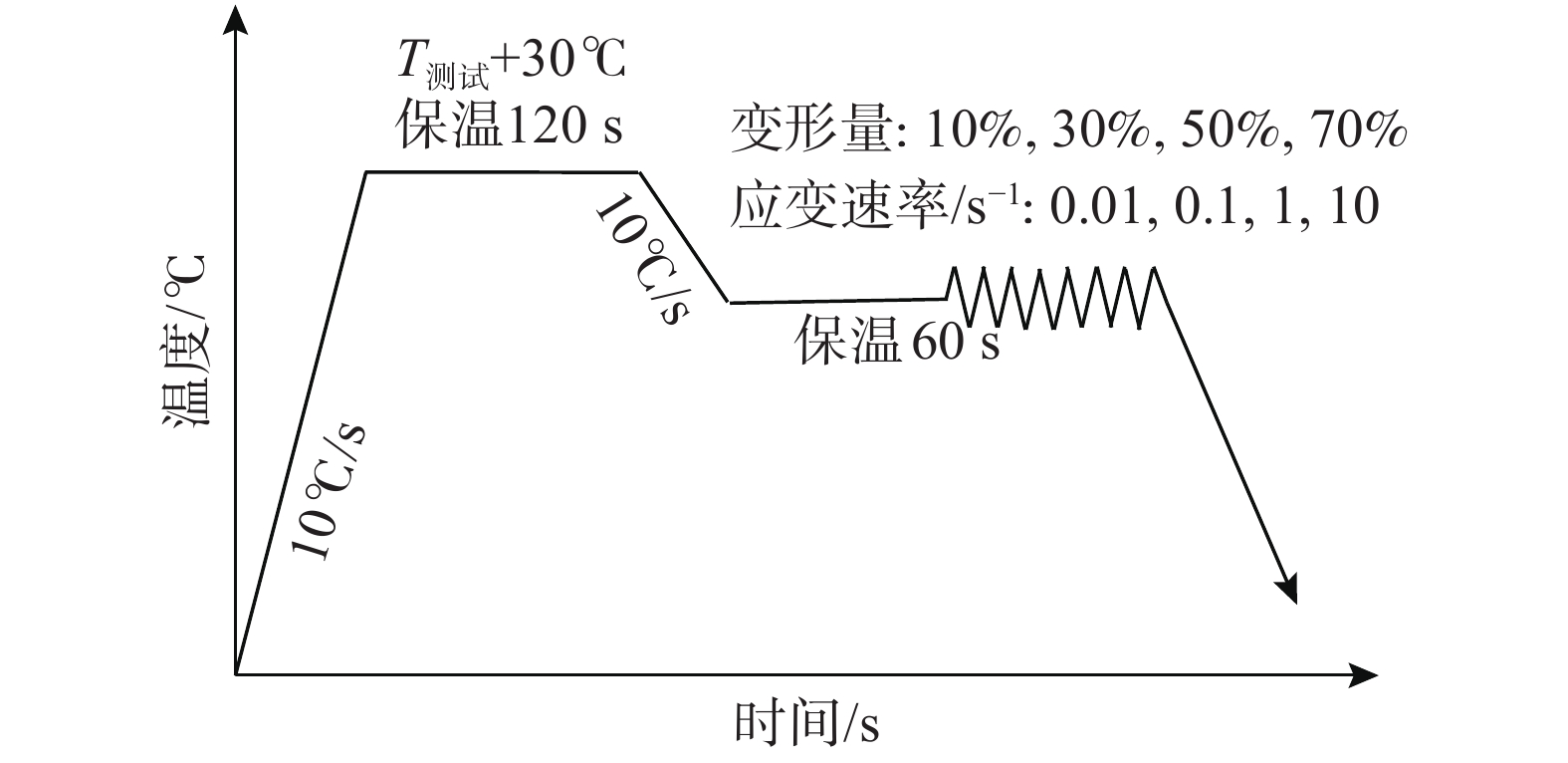
摘要: 在Gleeble-3500D热模拟机上采用单道次等温压缩试验,系统研究了GH4169合金在变形温度为900 ~1150 ℃、应变速率为0.01~10 s−1、变形量为10%~70%条件下的动态再结晶行为,确定了合金在不同变形条件下的完全再结晶条件,绘制了再结晶图,给出了该合金变形的热加工图。研究结果表明:GH4169合金随变形过程温度的升高而再结晶程度增大,变形量越大、应变速率越慢,发生完全动态再结晶的温度区间越宽;在应变速率为0.01 s−1时变形过程中经历了变形-回复-再结晶-晶粒长大的完整过程;而应变速率为10 s−1条件时,仅发生了变形-回复-(完全/部分)再结晶的过程,晶粒还未有充分长大的动力学条件;随着变形量增加,GH4169合金的易加工区间(η)和稳定加工区间(ξ
$ \left(\dot{\mathrm{\varepsilon }}\right) $ )越宽,在变形量为70%时温度为965~1134 ℃,应变速率0.02~10 s−1范围内, (ξ$ \left(\dot{\mathrm{\varepsilon }}\right) $ )大于0,处于加工稳定区。-
关键词:
- GH4169高温合金 /
- 显微组织 /
- 再结晶条件 /
- 再结晶图 /
- 热加工图
Abstract: The single-pass isothermal compression tests on a Gleeble−3500D simulated machine was carried out in this work to study the dynamic recrystallization behavior of GH4169 alloy in the temperature ranging from 900 ℃ to 1150 ℃ and strain rate ranging from 0.01 s−1 to 10 s−1 and the deformation degree ranging from 10% to 70%. Complete recrystallization condition of the alloy at a variety of different deformation conditions were identified, and recrystallization maps were plotted. Thermal processing maps of the alloy were also proposed. The results show that the recrystallization fraction of GH4169 alloy increases with the increase of deformation temperature. The larger the deformation and the slower the strain rate, the wider the temperature range of fully dynamic recrystallization; When the strain rate is 0.01 s−1, the whole process of deformation- recovery- recrystallization-grain growth occurs. When the strain rate is 10 s−1, only the process of deformation- recovery-(complete/partial) recrystallization occurs, and there is no sufficient dynamic condition for grain growth. With the increase of deformation ratio, the easy processing range (η) and stable processing range (ξ$ \left(\dot{\mathrm{\varepsilon }}\right) $ ) of GH4169 alloy are wider. When the deformation ratio is 70%, the temperature is 965 ~ 1134 ℃, and the strain rate in the range of 0.02 ~ 10 s−1, (ξ$ \left(\dot{\mathrm{\varepsilon }}\right) $ ) value is greater than 0 which indicates in the processing stable zone. -
表 1 GH4169合金主要化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of alloy GH4169
% C Mn Si Ni Cr Nb+Ta Mo 0.042 0.08 0.07 53.61 18.19 5.28 3.04 Al Ti Co Cu P S Fe 0.53 0.98 0.24 0.065 0.006 0.001 Bal -
[1] Shi Wei, Wang Yan, Shao Wenzhu, et al. Processing map of GH4169 alloy during hot plastic deformation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2012,17(3):281−289. (时伟, 王岩, 邵文柱, 等. GH4169 合金高温塑性变形的热加工图[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2012,17(3):281−289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2012.03.002 [2] Sui F L, Xu L X, Chen L Q, et al. Processing map for hot working of Inconel718 alloy[J]. J. Mater. Process Technol., 2011,(211):433−440. [3] Rezende M C, Araújo L S, Gabriel S B, et al. Oxidation assisted in-tergranular cracking under loading at dynamic strain aging temperatures in Inconel718 superalloy[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2015,643:256−259. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.279 [4] Kumar S, Rao G S, Chattopadhyay K, et al. Effect of surface nanostructure on tensile behavior of superalloy IN718[J]. Mater. Des., 2014,62:76−82. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.04.084 [5] Kundin J, Mushongera L, Emmerich H. Phase-field modeling of microstructure formation during rapid solidification in Inconel 718 superalloy[J]. Acta Mater., 2015,95:343−356. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.05.052 [6] Prasad K, Sarkar R, Ghosal P, et al. Tensile deformation behaviour of forged disc of IN 718 superalloy at 650 °C[J]. Mater. Des., 2010,31:4502−4507. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.04.019 [7] Gill A S, Telang A, Vasudevan V K. Characteristics of surface layers formed on Inconel 718 by laser shock peening with and without a protective coating[J]. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015,225:463−472. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.06.026 [8] (董建新. 镍基合金管材挤压及组织控制[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2014.)Dong Jianxin. Extrusion and microstructure control of nickel based alloy pipe[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014. -







 下载:
下载: