Flow field distribution of stirring tank for hydrometallurgical vanadium extraction
-
摘要: 为提高湿法提钒浸出率、掌握机械搅拌反应釜内液相流动和固相分布的规律,使用Fluent软件,基于计算流体力学理论,利用多重参考系法对浸钒搅拌釜内计算区域进行处理,建立多相流欧拉-欧拉模型和标准k-ε湍流模型,研究了搅拌速度v、桨叶离底高度L和带孔挡板对搅拌釜内流场分布的影响。结果表明:随着搅拌速度v的增大,搅拌釜内液相速度先逐渐增大,然后基本保持不变;根据桨叶离底高度L高低对搅拌釜内液相速度分布的影响,将最适宜离底高度选作L=0.4D1;安装带孔挡板有助于消除流场的漩涡现象,改善流场分布。Abstract: In order to improve the leaching rate of vanadium and understand the liquid flow and solid distribution in the mechanical stirring tank for hydrometallurgical vanadium extraction, the software Fluent was used to establish the Euler-Euler model of multi-phase flow and the standard k-ε turbulence model, by dealing with the calculation area in the stirring tank via multi-reference system method based on the theory of computational fluid dynamics. The influences of stirring speed v, the height of blade from the bottom L and the perforated baffle on the flow field distribution in the stirring tank were investigated. The results show that the liquid phase velocity in the stirring tank gradually increases first and then basically stabilizes with the increase of stirring velocity v. Based on the influence of the height of the blade from the bottom L on the liquid velocity distribution, the most suitable value was determined at L=0.4D1, where D1 refers to the blade diameter. The perforated baffle is helpful to eliminate the vortex in the flow field and improve the flow field distribution.
-
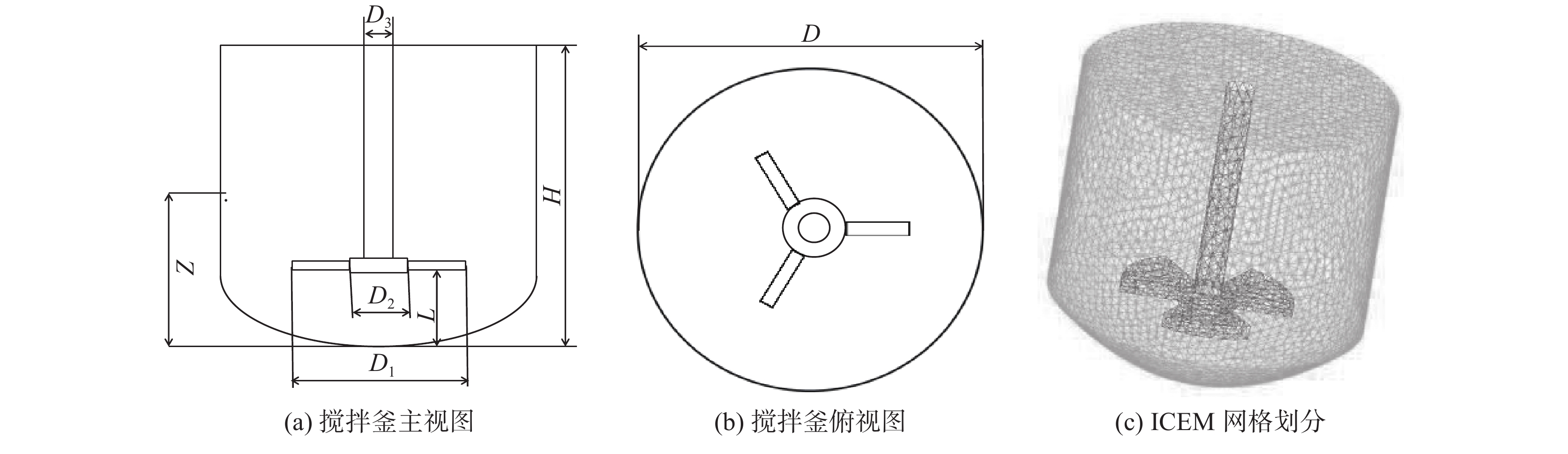
表 1 搅拌釜结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of stirring tank
搅拌釜直径
D/mm搅拌釜高度
H/mm桨叶直径
D1/mm桨叶离底高度
L/mm轮毂直径
D2/mm搅拌轴直径
D3/mm桨叶个数/
个纵向高度
Z/mm110 105 60 0.25D1,0.4D1,0.55D1,0.7D1 20 10 3 52.5 表 2 基本物性参数
Table 2. Main material parameters
物料 直径dp/μm 密度$\rho $/(kg∙m−3) 粘度$\eta $/(Pa∙s) 体积分数α/% 钒钛磁铁矿颗粒 75~150 4500~6000 5~20 NaOH溶液 1000 0.001~0.007 80~95 -
[1] (陈家镛, 杨守志. 湿法冶金的研究与发展[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998: 258−264.)Chen Jiayong, Yang Shouzhi. Research and development of wet metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998: 258−264. [2] Altway H Setyawan, Margono S Winardi. Effect of particle size on simulation of three dimensional solid dispersion in stirred tank[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2001,79(8):1011−1016. doi: 10.1205/02638760152721578 [3] Maurice S Onyango. Mixing in a tank stirred by a Rushton turbine at a low clearance[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 2008,(47):842−851. [4] Tamburini A Cipollina, Micale G, Brucato A, et al. CFD simulations of dense soid liquid suspensions in baffled stirred tanks: Prediction of solid particle distribution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013,223:857−890. [5] Wang Chunlin, Ma Qingyong, Li Tingting, et al. Numerical simulation of solid liquid two phase flow stirring in stirred slurry tank[J]. Irrigation and Drainage Machinery, 2007,25(6):18−22. (王春林, 马庆勇, 李婷婷, 等. 搅拌浆液池固液两相流搅拌的数值模拟[J]. 排灌机械, 2007,25(6):18−22. [6] Chen Zhuo, Zhou Ping, Li Peng, et al. Numerical simulation and structure optimization of solid liquid two phase flow in mechanically stirred zinc leaching tank[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012,22(6):1836−1841. (陈卓, 周萍, 李鹏, 等. 机械搅拌式锌浸出槽内固液两相流的数值模拟与结构优化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012,22(6):1836−1841. [7] Hervey P S, Greaves M. Turbulence flow in an agitated vessel, partI: A predictive model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1982,60(4):195−201. [8] Hervey P S, Greaves M. Turbulence flow in an agitated vessel, partII: Numerical solution and model prediction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1982,60(8):201−210. [9] Brucato A, Ciofalo M, Grisafi F, et al. Numerical prediction of flow fields in baffled stirred vessels: A comparison of altermative modeling approaches[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998,53(5):365−368. [10] Luo J Y, Gosman A D, Issa R I, et al. Full flow field computation of mixing in baffled stirred reactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1993,71(10):342−344. [11] Jaworski Z, Bujalski W, Qtomo N, et al. CFD study of homogenization with dual rushton turbines comparison with experimental results[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2000,78(13):327−333. [12] Luo J Y, Gosman A D, Issa R I, et al. Prediction of impeller induced flows in mixing vessels using multiple frames of reference[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1994,52(6):549−556. [13] (李鹏飞, 徐敏义, 王飞飞. 精通CFD工程仿真与案例实战[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2011: 162−186.)Li Pengfei, Xu Minyi, Wang Feifei. Fluent in CFD engineering simulation and case combat[M]. Beijing: Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2011: 162−186. [14] (盖得. 希特斯洛尼. 多相流动和传热手册[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1993: 15−23.)Hitsloni G. Handbook of multiphase flow and heat transfer[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1993: 15−23. [15] Mao Zaisha. Particle swarm optimization: the basis of multi-scale numerical simulation of multiphase flow[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2008,8(4):645−659. (毛在砂. 颗粒群研究: 多相流多尺度数值模拟的基础[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008,8(4):645−659. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2008.04.003 [16] Cheng Jingcai, Mao Zaisha, Yang Chao. Numerical simulation of liquid solid solid three phase flow in stirred tank[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2008,24(2):97−102. (程景才, 毛在砂, 杨超. 搅拌槽内液固固三相流数值模拟研究[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2008,24(2):97−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7631.2008.02.001 -





 下载:
下载: