Development of gas element diffusion wear-resistant treatment technology on titanium surface
-
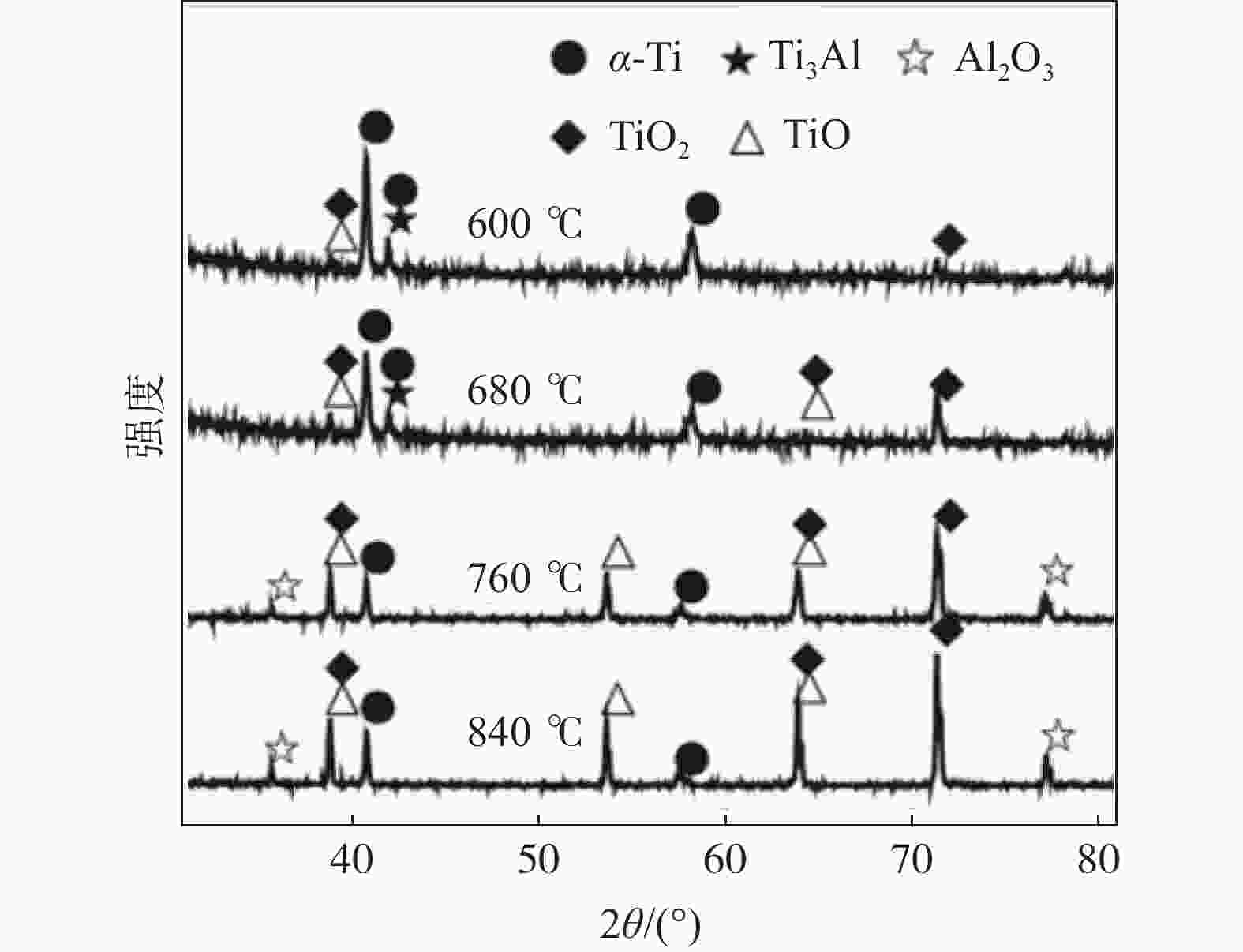
摘要: 针对近年来钛及钛合金表面气体元素扩散耐磨处理技术的研究进展进行了总结梳理。认为对钛合金表面进行渗氧、渗氮和渗碳耐磨处理,都可以起到提高表面硬度,改善表面耐磨性能的效果,结合真空和等离子体等技术,可以使得扩散层厚度增加,但需要结合工艺选择恰当的参数,不然会对材料力学性能带来较大的影响。另外耐磨状态是多样的,没有一种耐磨层能够适合于所有的摩擦环境;同时现代的服役环境更趋于复杂,不仅要求耐磨,还有耐蚀、导电等其它功能方面的要求,这样,就需要材料表面设计者,依据服役的苛刻条件,结合多场的相互作用关系,在现有表面技术的基础上设计和创新。Abstract: In this paper, the resent research progress of gas element diffusion wear treatment technology on surface of titanium and titanium alloy is summarized.It is believed that treatment technology of oxidizing, nitriding and carburizing on the surface of titanium alloy, can improve its surface hardness and wear resistance .In addition, the combination of vacuum and plasma technologies can increase the thickness of the diffusion layer, but appropriate parameters need to be selected in combination with the process, otherwise it will have a greater impact on the mechanical properties of the material.Furthermore, because the wear-resistant environment is diverse, the wear-resistant layer is difficult to adapt to all friction environments. Modern development has made the service environment of materials more complex . It requires not only wear resistance, but also corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity and other functional requirements. In this way, the material surface designer is required to design and innovate on the basis of the existing surface technology based on the harsh conditions of service and the interaction of multiple fields.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- wear-resistant treatment of gas diffusion /
- oxygenation /
- nitriding /
- carburizing /
- surface hardness
-
表 1 氮化试样的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of Ti after nitrided
试样 σb/MPa σ0.2/MPa δ/% ψ/% ak/(J·cm−2) 纯钛 521 420 27.6 62.0 78.6 钛氮化 468 361 23.2 54.8 46.5 表 2 钛金属氮化后力学性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of mechanical properties of titanium and titanium alloy after nitriding
材料 热处理 σ0.2/MPa σb/MPa Φ/ % Ψ/ %
Ti退火 246 383 39 69 氮化1) 263 384 36 64 Ti-6Al-4V 退火 900 950 7 48 氮化2) 925 974 13 45
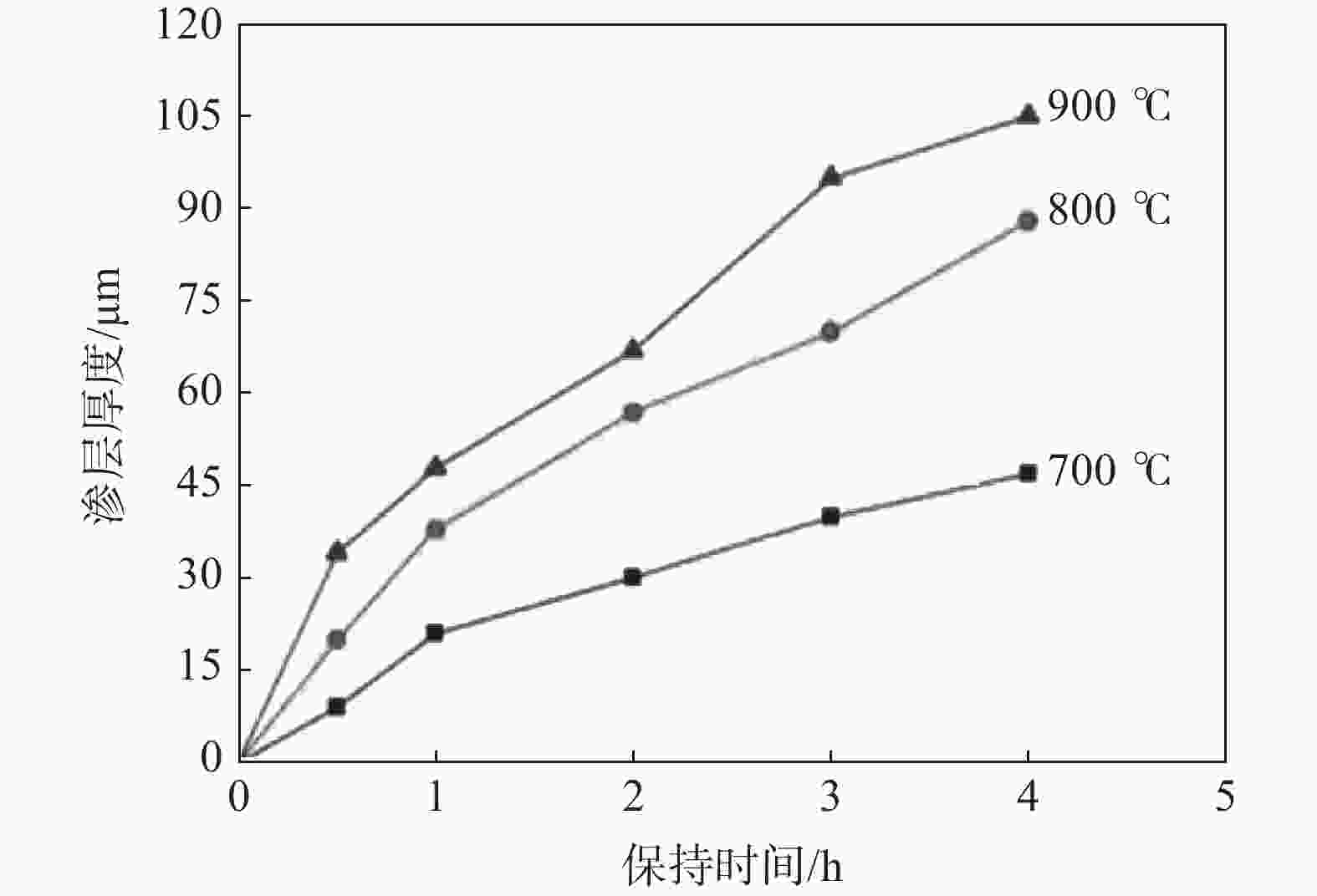
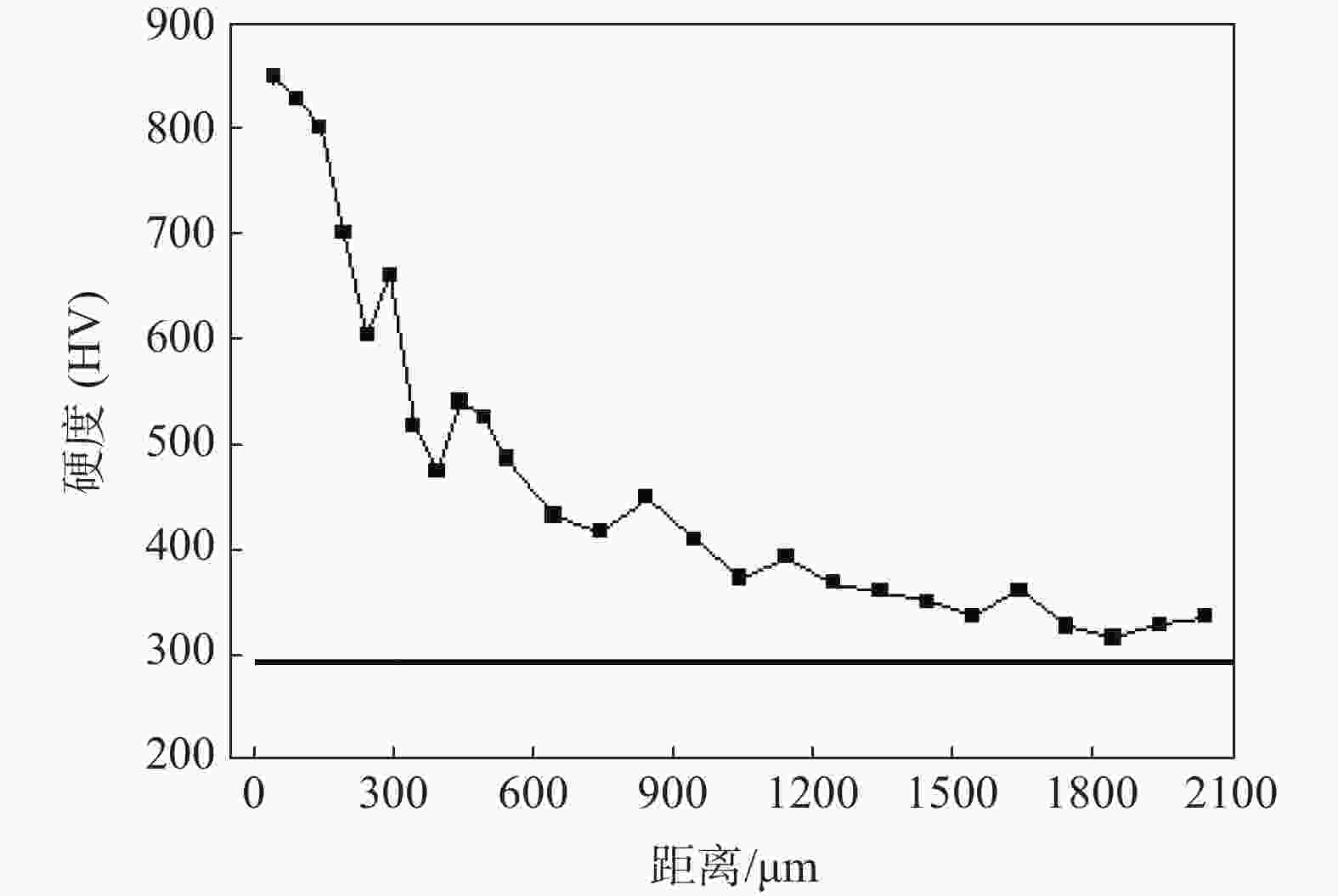
Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al退火 975 1001 13 40 氮化3) 875 901 12 47 注:渗氮工艺参数:1)为850 ℃, 9 h;2)为850 ℃, 15 h;3)为750 ℃, 60 h。 表 3 钛金属不同气体离子氮化后的表面硬度
Table 3. Surface hardness of titanium after nitriding with different gas ions
材质 处理状态 表面硬度(HV) 温度/℃ 时间/h 气源
TA2未处理 189~200 940 2 N2/H2=1 1150~1620 940 2 纯N2 1200~1450 940 2 N2/Ar=1 1385~1540
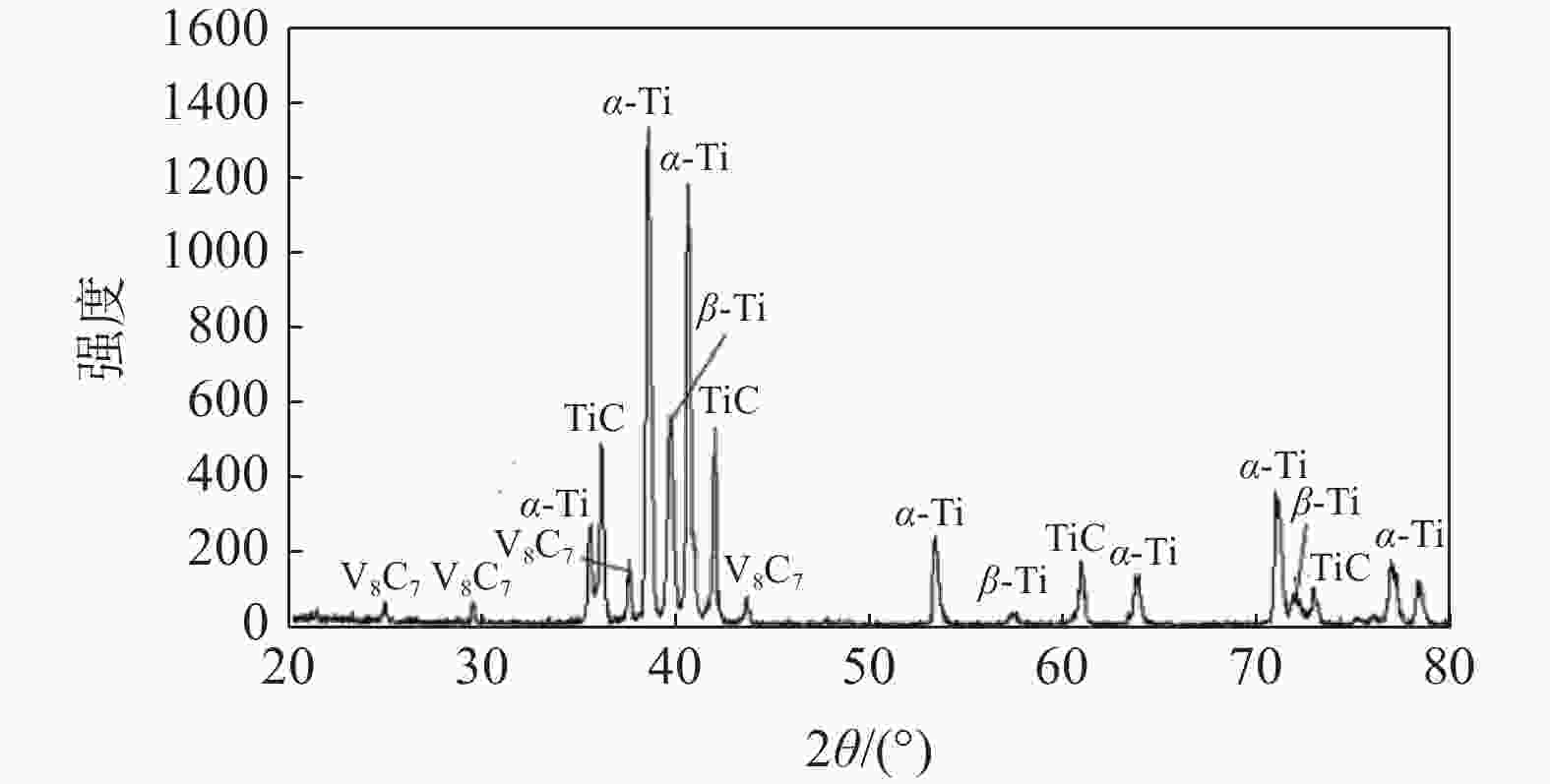
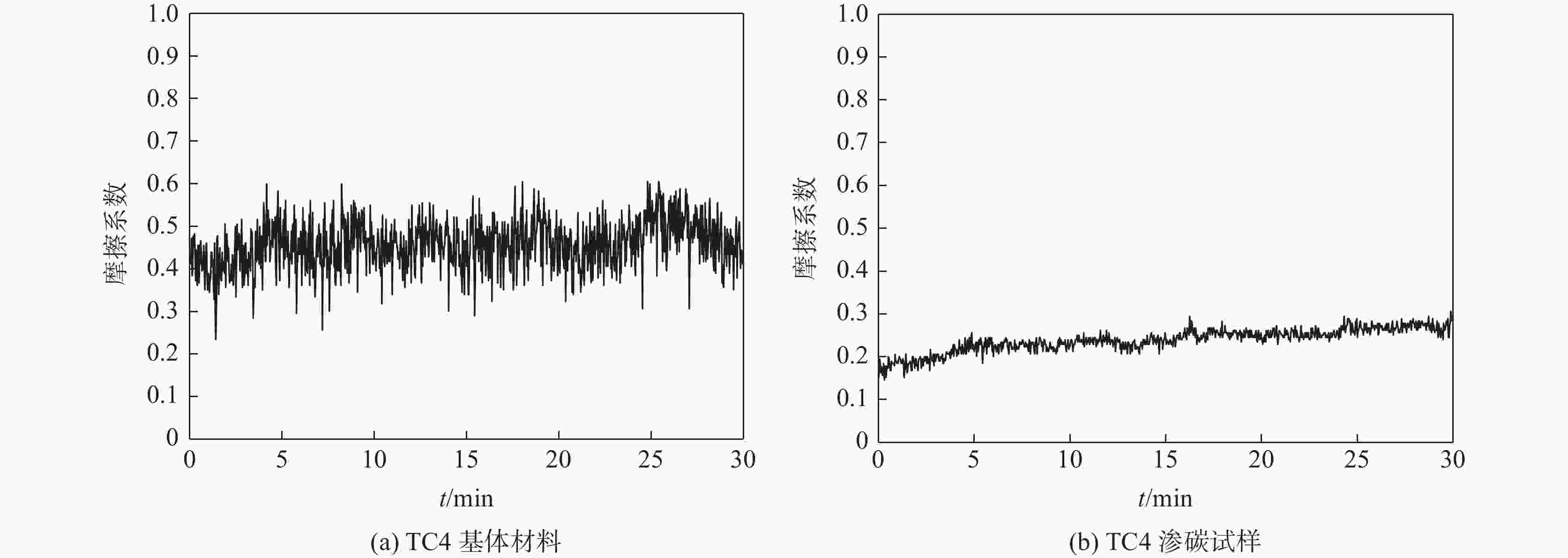
TC4未处理 380~400 800 2 N2/Ar=1 800~1100 940 2 N2/H2=1 1385~1670 表 4 钛金属无氢渗碳前后力学性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of mechanical properties of titanium alloy before and after hydrogen-free carburizing
试样 σ0.2/MPa σb/MPa Φ/ % Ψ/ % TC4 998 965 14.5 47 TC4渗碳1 1000 1049 19.0 50 TC4渗碳2 1013 1058 18.0 52 TC4渗碳3 1017 1074 17.5 49 TC4渗碳4 1035 1080 17.5 50 -
[1] 周廉, 赵永庆, 王向东, 等. 中国钛合金材料及应用发展战略研究[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012: 156.Zhou Lian, Zhao Yongqing, Wang Xiangdong, et al. Research on titanium alloy materials and application development strategy in China[M]. Bejing: Chemical Industry Press, 2012: 156. [2] Li Zhengxian, Du Jihong, Zhou Hui, et al. Double-glow discharged plasma non-hydrogen carburizing on titanium alloy surface[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004,33(12):1355−1357. (李争显, 杜继红, 周慧, 等. 钛合金表面辉光无氢渗碳的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004,33(12):1355−1357. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.12.030 [3] 辛湘杰, 薛峻峰. 钛的腐蚀、防护及工程应用[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 1988: 358.Xin Xiangjie, Xue Junfeng. Corrosion, protection and engineering application of titanium[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 1988: 358. [4] Yan Wei, Wang Xiaoxiang. Characterization of the surface oxygen-diffusion zone of the thermally oxidized titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005,34(3):471−473. (严伟, 王小祥. 热氧化处理钛表面渗氧层的组织与性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005,34(3):471−473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2005.03.034 [5] Yang Chuang, Liu Jing, Ma Yaqin, et al. Vacuum oxidation treatment on Ti6Al4V titanium alloy[J]. Surface Technology, 2017,46(5):165−170. (杨闯, 刘静, 马亚琴, 等. Ti6Al4V钛合金表面真空渗氧处理[J]. 表面技术, 2017,46(5):165−170. [6] Zheng Chuanlin, Xu Zhong, et al. Study on plasma oxygenation of titanium[J]. Journal of Beijing University of science and technology, 2002,24(1):44−46. (郑传林, 徐重, 谢锡善, 等. 钛等离子渗氧研究[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2002,24(1):44−46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2002.01.013 [7] Chen Changjun, Ma Hongyan, Zhang Min, et al. Research progress of surface oxygen diffusion hardening of titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2007,36(14):63−65. (陈长军, 马红岩, 张敏, 等. 钛合金的表面渗氧强化研究进展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2007,36(14):63−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2007.14.022 [8] Qin Jianfeng, Wang Xinbo, Zou Jiaojuan, et al. Research progress of thermal oxidation effect on improving surface properties of titanium and titanium alloy[J]. Surface Technology, 2017,46(1):1−7. (秦建峰, 王馨舶, 邹娇娟, 等. 热氧化提高钛及钛合金表面性能的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2017,46(1):1−7. [9] 贾翃, 夏志华. 钛表面气体氮化的工艺研究[J]. 稀有金属 , 1998, 22(4): 295-299.Jia Hong, Xia Zhihua. Study on processing of titanium surface nitrogenization[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1998, 22(4): 295-299. [10] 柴田英明. 朝原力など. 室化处理チタン材料[J]. 工業材料(日), 1993,41(15):114−118. [11] 贾翃. 钛合金等离子渗氮层研究[C]//钛合金文集. 上海: 科学技术出版社, 1980: 217.Jia Hong. The study of plasma nitriding layer of titanium alloy[C]//Titanium Alloy Proceedings. Shanghai: Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1980: 217. [12] Li Zhengxian, Du Jihong, Zhou Hui, et al. Double-glow plasma surface carbon implantation of non-hydrogen on titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004,33(11):1174−1177. (李争显, 杜继红, 周慧, 等. 钛表面辉光等离子无氢渗碳的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004,33(11):1174−1177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.11.013 [13] Li Zhengxian, Du Jihong, Zhou Hui, et al. Development status of titanium surface treatment technology[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2003,22(4):41−45. (李争显, 杜继红, 周慧, 等. 钛表面处理技术的发展现状[J]. 钛工业进展, 2003,22(4):41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2003.04.010 [14] 徐重. 等离子表面冶金学[M], 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 152.Xu Zhong. Plasma surface metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 152. [15] Li Zhengxian, Ji Shouchang, Wang Yanfeng, et al. Surface treatment and application on titanium alloy wheel gear[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2018,35(6):6−9. (李争显, 姬寿长, 王彦峰, 等. 钛合金齿轮的表面处理与应用[J]. 钛工业进展, 2018,35(6):6−9. [16] 姬寿长. 钛合金表面辉光等离子无氢渗碳层性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2014.Ji Shouchang. Research on properties of the nonhydrogen carburizing coating on titanium alloy by aglow plasma method[D]. Xi, an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2014. [17] 岡本善四郎, 後藤浩ニなど. チタンおよびチタン合金のプラズマ浸炭[C]//兵庫県立工業技術センター研究報告. 1998: 25. [18] 阿九津幸一 . プラズマ浸炭によるチタンの硬化処理[J].チタン , 2000, 48(2): 44-46. [19] 野田俊治, 岡部道生など. プラズマ浸炭によるTiAl金属間化合物の表面硬化処理[J]. 電気製鋼, 1994,65(4):304−306. [20] 藤原洋ニ, 岡本善四郎など. 低濃度メタンガスによりプラズマ浸炭したチタン合金の摩耗特性[C]//日本熱処理技術協会請演大会請演概要集. 1995: 29. -




 下载:
下载: