Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TC6 titanium alloy
-
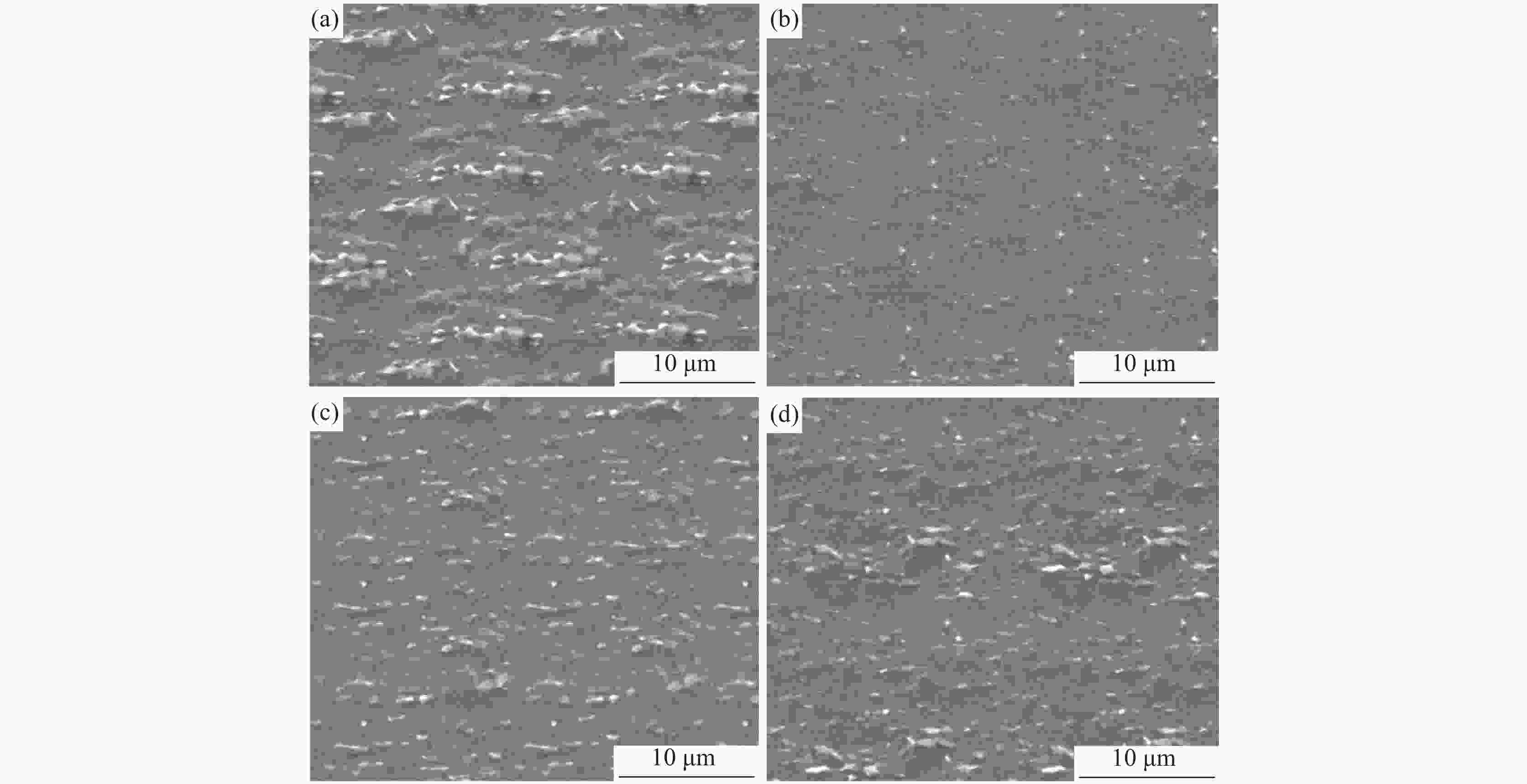
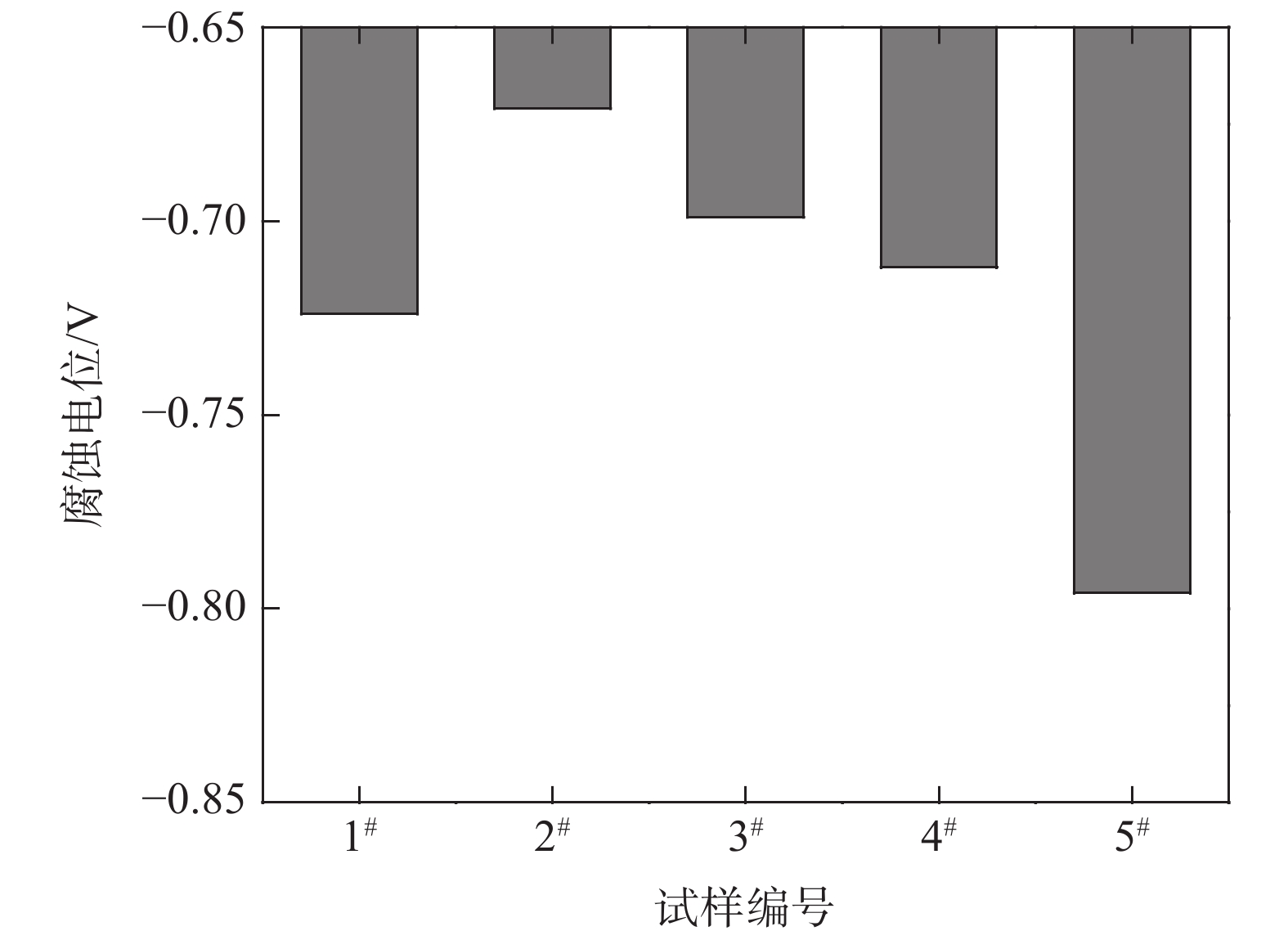
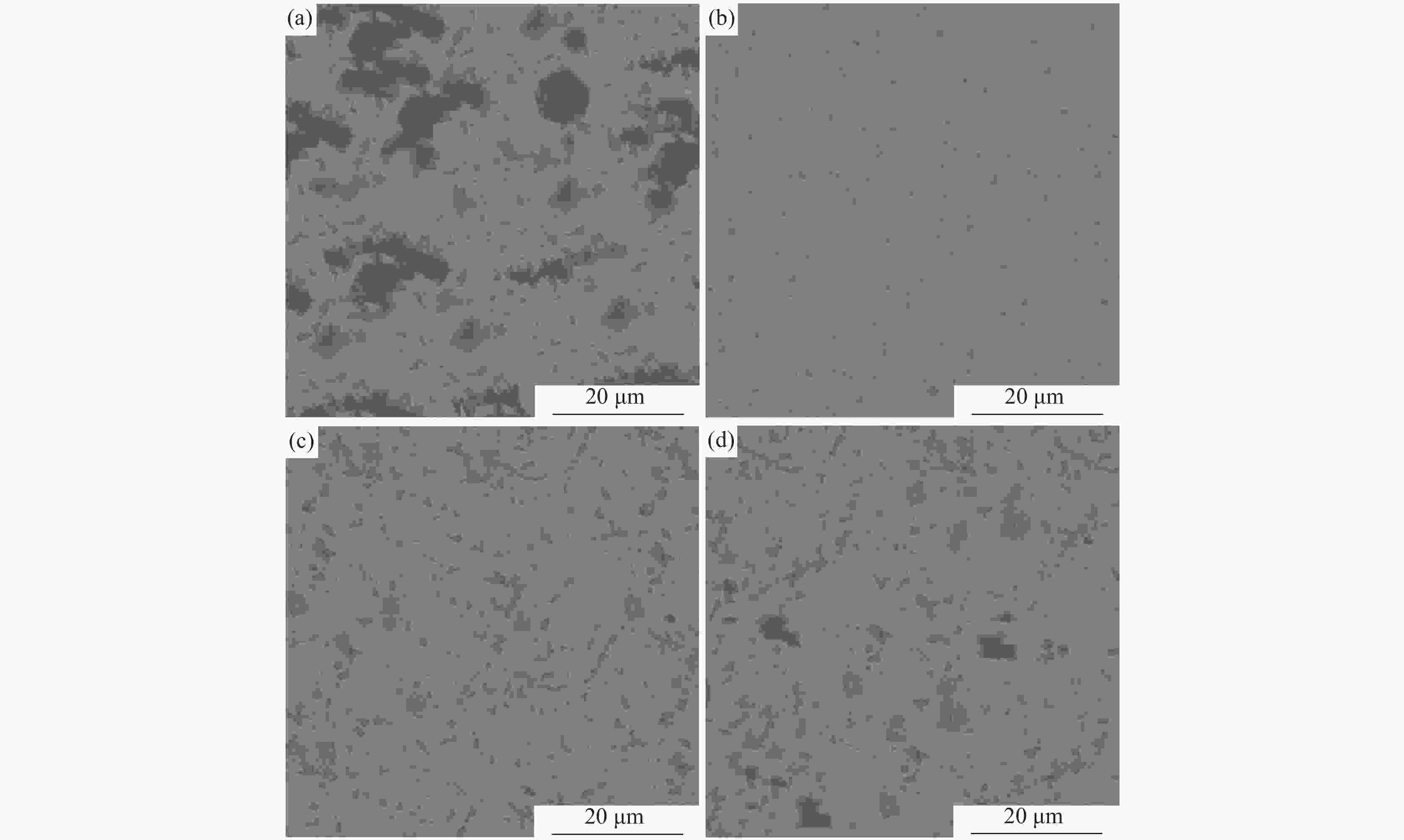
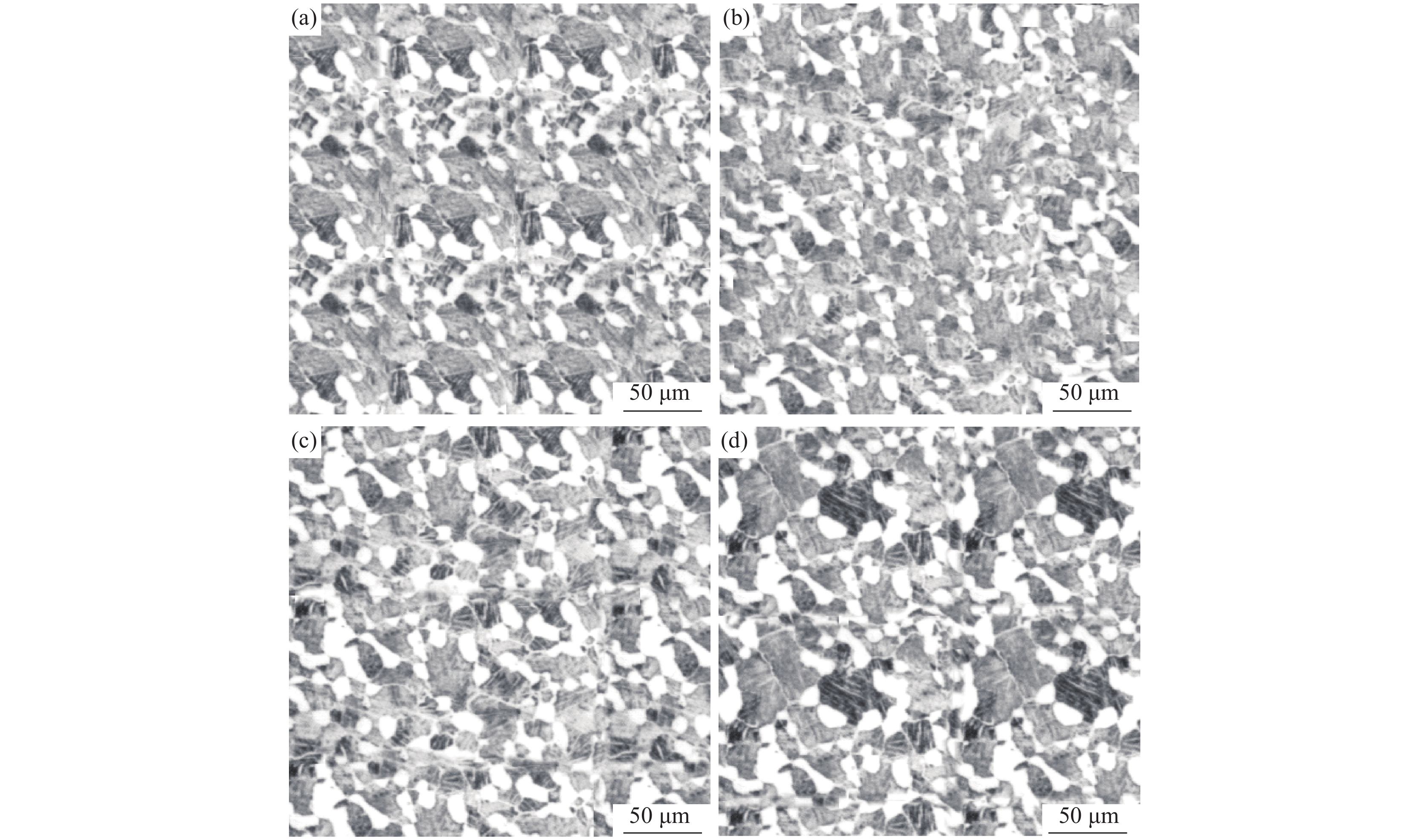
摘要: 采用四种不同热处理制度对汽车用TC6钛合金棒材进行了等温退火试验,并进行了试样显微组织、耐磨损性能和耐腐蚀性能测试与分析。结果表明,采用“870 ℃保温1.5 h,炉冷至600 ℃保温2 h,空冷”热处理制度(1#试样)时,合金的耐磨损和耐腐蚀性能最差;采用“900 ℃保温1.5 h,炉冷至600 ℃保温2 h,空冷”热处理制度(2#试样)时,合金的耐磨损和耐腐蚀性能最佳;采用“920 ℃保温1.5 h,炉冷至600 ℃保温2 h,空冷” (3#试样)和“900 ℃保温1.5 h,炉冷至620 ℃保温2 h,空冷” (4#试样)时,合金试样的腐蚀电位和耐腐蚀性能介于上述二者之间。与1#试样相比, 2#试样的磨损体积减小8×10−3 mm3、腐蚀电位正移53 mV。Abstract: TC6 titanium alloy bars were annealed by four different heat treatment processes. The microstructure, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the samples were tested and analyzed. The results show that under the heat treatment at 870 ℃ for 1.5 h, furnace cooling to 600 ℃ and insulation for 2 h followed by air cooling, the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the alloy (sample 1#) are the worst. The sample under the heat treatment at 900 ℃ for 1.5 h, furnace cooling to 600 ℃ and insulation for 2 h followed by air cooling shows the best wear resistance and corrosion resistance (sample 2#). The corrosion potential and corrosion resistance of the samples respectively under the heat treatment processes of 920 ℃ for 1.5 h furnace cooling to 600 ℃ and insulation for 2 h air cooling(sample 3#), and 900 ℃ for 1.5 h furnace cooling to 620 ℃ and insulation for 2 h air cooling (sample 4#), are between those of the sample 1# and sample 2#. Compared with sample 1#, the wear volume of sample 2# decreases by 8×10−3 mm3, and the corrosion potential shifts by +53 mV.
-
Key words:
- TC6 titanium alloy /
- heat treatment /
- isothermal annealing /
- microstructure /
- wear resistance /
- corrosion resistance
-
表 1 钛合金试样化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the TC6 sample
% Al Mo Cr Si Fe C N H Ti 检测值 6.28 2.89 1.32 0.27 0.31 0.086 0.021 0.007 Bal. 标准要求值 5.5~7 2~3 0.8~2.3 0.15~0.4 0.2~0.7 ≤0.1 ≤0.05 ≤0.015 Bal. -
[1] Ma Quan, Xin Shewei, Song Kai, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-1300 alloy by electron beam weldment[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019,48(8):2723−2728. (马权, 辛社伟, 宋凯, 等. 热处理对Ti-1300高强钛合金电子束焊接组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2019,48(8):2723−2728. [2] Cao Ze’an, Cheng Donghai, Hu De’an, et al. Effect of hydrogen heat treatment on superplastic deformation of laser welded joints of titanium alloy[J]. Transaction of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2018,39(12):129−134. (曹泽安, 程东海, 胡德安, 等. 氢热处理对钛合金激光焊接接头超塑性变形的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018,39(12):129−134. [3] Chen Zhiru, Ji Xia, Chu Ruikun, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TC4 titanium alloy by laser melting deposition[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018,43(11):144−149. (陈志茹, 计霞, 楚瑞坤, 等. 热处理工艺对激光熔化沉积TC4钛合金组织性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018,43(11):144−149. [4] Wang Chen, Xu Dong, Chen Li. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018,43(9):186−190. (王琛, 徐栋, 陈力. 热处理对TC18钛合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018,43(9):186−190. [5] Shang Jin, Cao Wei, Chen Yongchang. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion resistance of 3 D printed titanium alloy[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2020,41(5):27−29,62. (尚进, 曹玮, 陈永畅. 热处理对3 D打印钛合金耐蚀性的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2020,41(5):27−29,62. doi: 10.11973/fsyfh-202005006 [6] Li Xuefei, Huang Lijun, Huang Xu, et al. Research on heat treatment process of TB6 titanium alloy after isothermal forging[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2020,37(2):31−34. (李雪飞, 黄利军, 黄旭, 等. TB6钛合金等温锻后热处理工艺研究[J]. 钛工业进展, 2020,37(2):31−34. [7] Lu Kaikai, Zhou Lipeng, Li Minna, et al. Effect of strengthening and toughening heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA15 titanium alloy[J]. Transaction of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2020,41(1):44−49. (卢凯凯, 周立鹏, 李敏娜, 等. 强韧化热处理对TA15钛合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2020,41(1):44−49. [8] Gou Jian, Wang Zhijiang, Hu Shengsun, et al. Effects of CMT+P process and post heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TC4 component by additive manufacturing[J]. Transaction of the China Welding Institution, 2019,40(12):31−35,46. (勾健, 王志江, 胡绳荪, 等. CMT+P过程及后热处理对TC4钛合金增材构件组织和性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019,40(12):31−35,46. [9] Yuan Jingjun, Ji Zhongshuo, Zhang Maicang, et al. Correlation between structure and orientation of TC17 titanium alloy during thermal deformation and heat treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2019,41(6):772−780. (原菁骏, 姬忠硕, 张麦仓. 热变形及热处理过程中TC17钛合金组织与取向的关联性[J]. 工程科学学报, 2019,41(6):772−780. [10] Li Lifeng, Li Ganggang, Ma Tianju, et al. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on residual stress distribution of electron beam welded joints of titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(17):154−157. (李立峰, 黎刚刚, 马天驹, 等. 焊后热处理对钛合金电子束焊接接头残余应力分布的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(17):154−157. [11] Li Guoliang, Yao Zekun, Sun Pengpeng, et al. Effect of heat treatment on TC6 alloy microstructure and tensile property[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2011,36(6):125−128. (李国亮, 姚泽坤, 孙朋朋, 等. 热处理对TC6钛合金组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 锻压技术, 2011,36(6):125−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3940.2011.06.032 [12] 熊爱明, 黄维超, 陈胜晖, 等. 热处理制度对TC6钛合金显微组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(z1): 206-209.Xiong Aiming, Huang Weichao, Chen Shenghui, et al. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure of TC6 titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals. 2002, 12(z1): 206-209. -





 下载:
下载: