Microstructure and properties of architectural TiAl alloy with heat treatment after welding
-
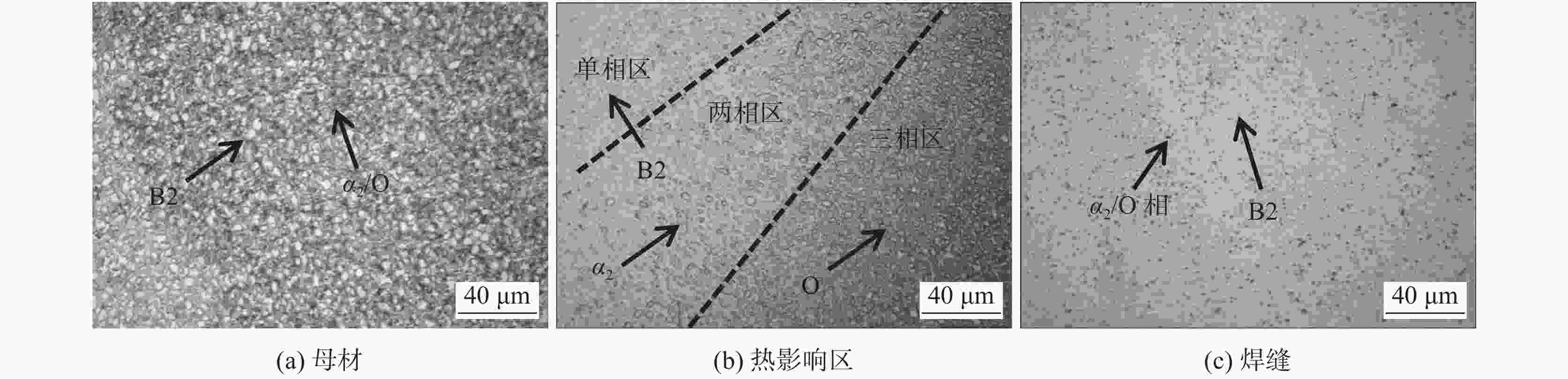
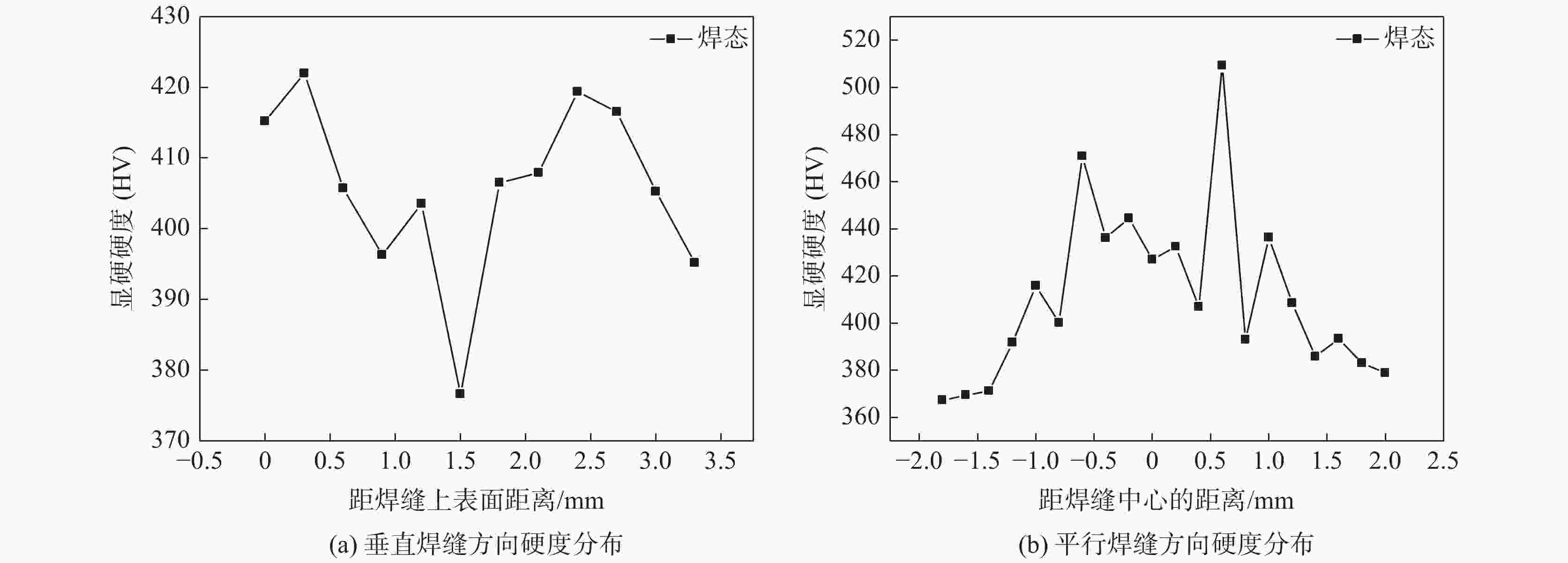
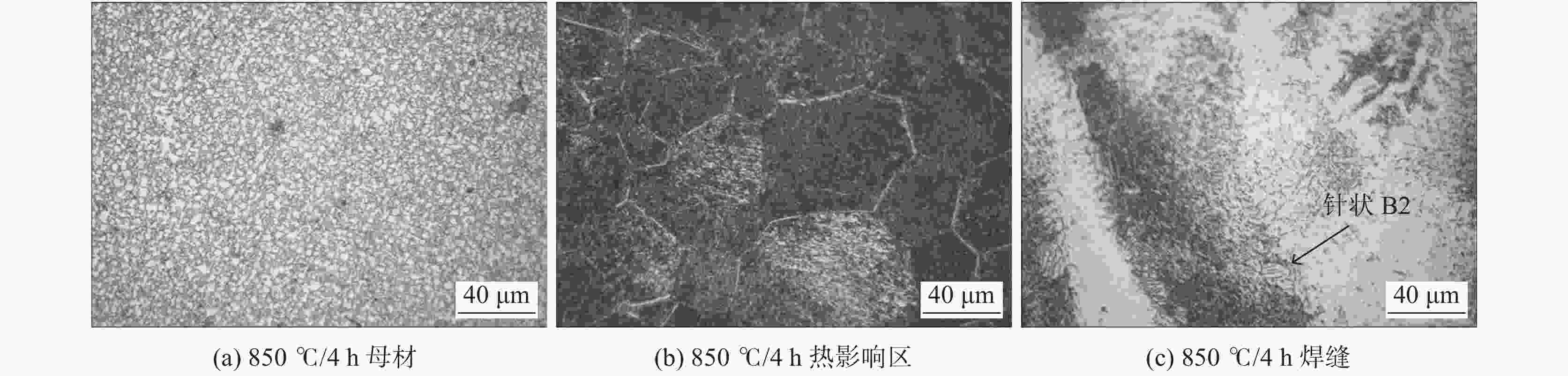
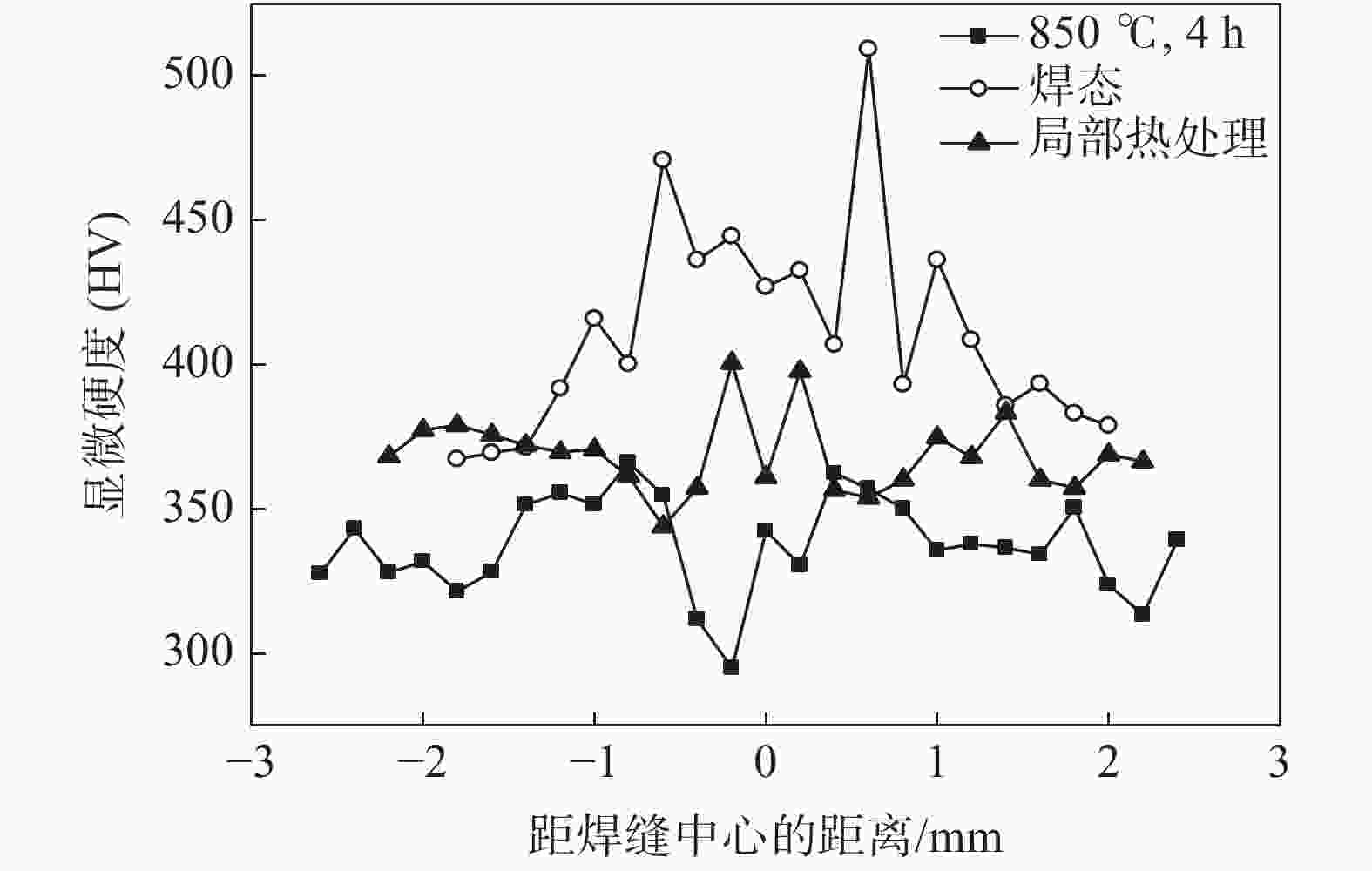
摘要: 对建筑用TiAl合金电子束焊接接头进行了两种热处理试验研究,借助金相显微镜(OM)分析了接头不同区域的显微组织,并对焊接接头进行显微硬度测试,分析了两种热处理方式对建筑TiAl合金焊接接头组织及硬度带来的变化。研究表明,TiAl合金电子束焊接后焊缝组织主要为α2相,B相与O相。焊接接头局部热处理后接头硬度较高的区域有所增加,但整体呈下降趋势;热处理后,TiAl合金电子束焊接后合金焊缝区的B2相尺寸减小,但B2相分解的O相板条尺寸变大。整体热处理后焊接接头的显微硬度整体有所降低。两种热处理均能降低焊缝区显微硬度,并分布较为平稳。Abstract: In this paper, two kinds of heat treatment were carried out on the electron beam welded joints of architectural TiAl alloy. The microstructure of different areas of the joints was analyzed with metallographic microscope (OM), and the microhardness of the welded joints was tested. The influences of the heat treatment processes on the microstructure and hardness of the welded joints of the architectural TiAl alloy were analyzed. The results show that the weld structure of TiAl alloy is composed of α2 phase, B phase and O phase. The area with higher hardness of the joint increases, but the overall trend is down after the local heat treatment. After heat treatment, the B2 phase size of TiAl alloy reduces, while the O phase plate decomposed from B2 phase becomes large. The overall microhardness of the welded joint is reduced after integral heat treatment. The microhardness of the weld zone can be reduced by two heat treatment methods, and it presents a stable distribution.
-
Key words:
- architectural TiAl alloy /
- electron beam welding /
- joints /
- heat treatment /
- microstructure /
- hardness
-
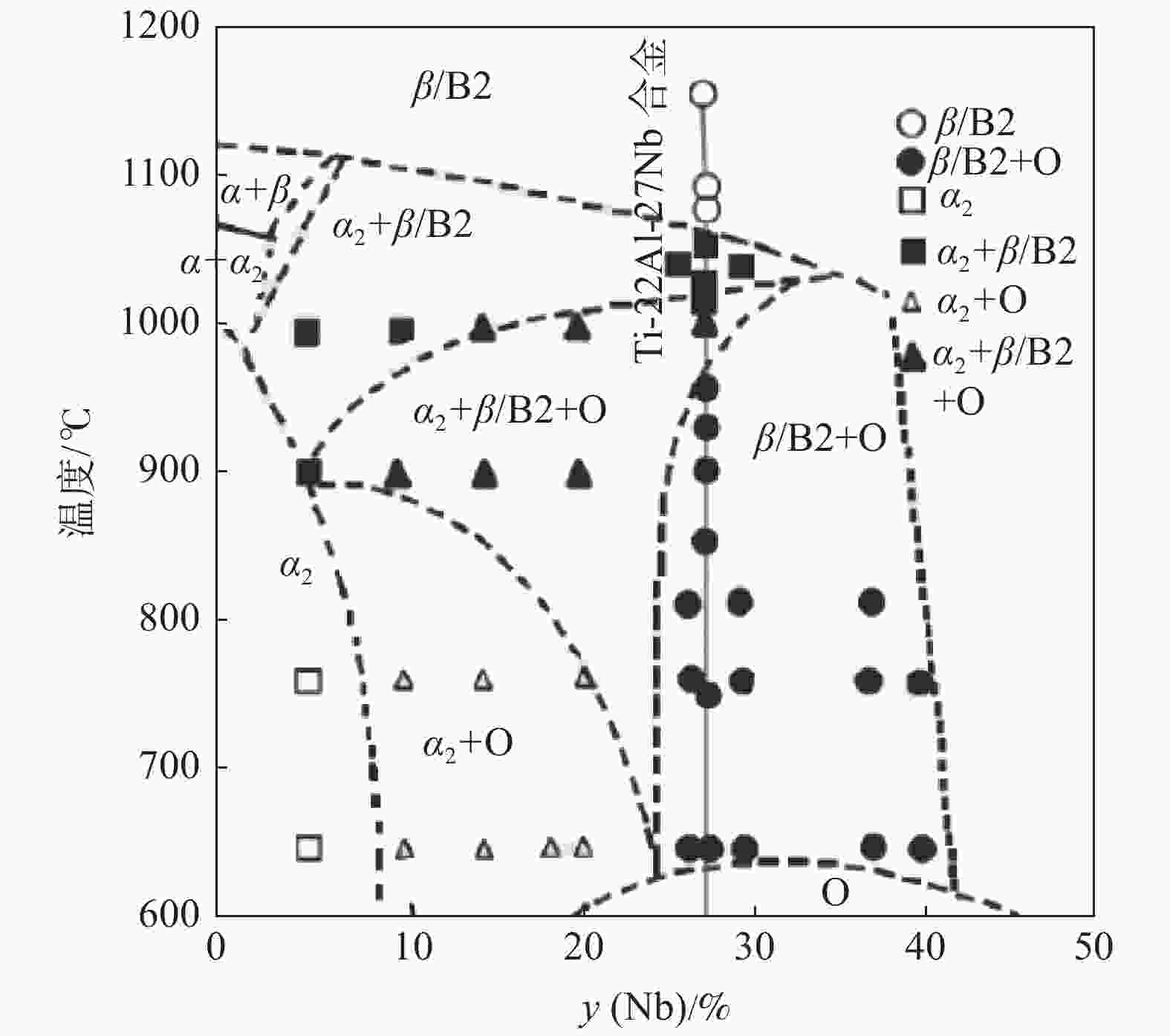
图 4 Ti-22Al-xNb合金相图[18]
Figure 4. Phase diagram of Ti-22Al-xNb alloy
表 1 Ti-12Al-25Nb合金板化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ti-12Al-25Nb plate material
% Al Nb V O H N Ti 10.62 45.22 5.42 ≤0.08 ≤0.01 ≤0.02 余量 表 2 Ti-12Al-25Nb合金基本性能
Table 2. Main properties of Ti-12Al-25Nb
温度/℃ 抗拉强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 延伸率/% 弹性模量/GPa 室温 1045 947 11.399 103 650 952 846 640 91 表 3 TiAl合金焊接与热处理工艺参数
Table 3. Process parameters of electron beam welding and heat treatment of TiAl alloy
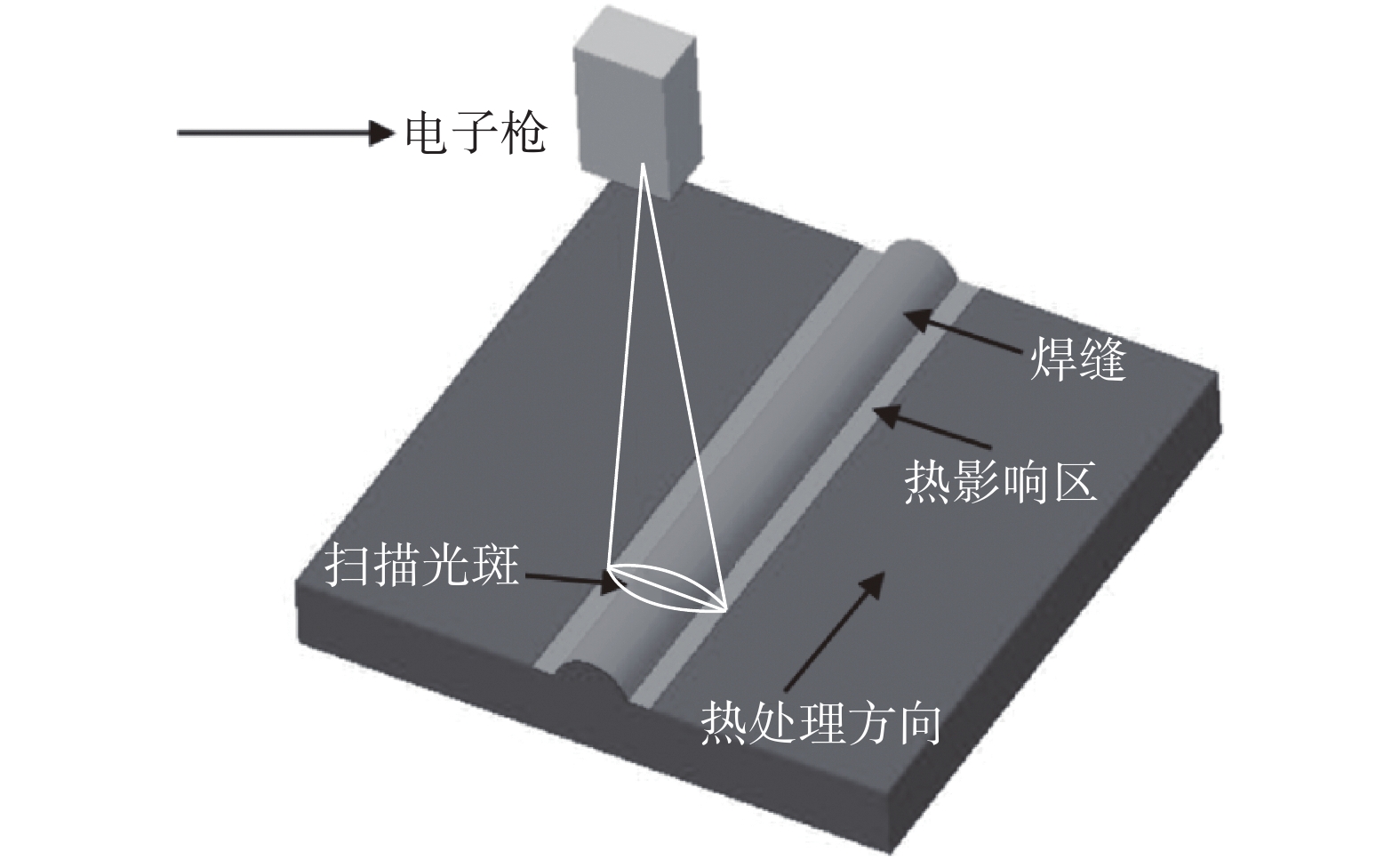
序号 工艺 加速电压
U/kV聚焦电流If/mA 电子束流Ib/mA 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) 扫描时间t/s 1 焊态 120 500 30 800 − 2 局部热处理 120 600 6 400 800 -
[1] 周戒. 房屋建筑工程专业基础知识[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2010: 42−50.Zhou Jie. Basic knowledge of housing construction engineering[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2010: 42−50. [2] Lin Junpin, Chen Guoliang. Development of TiAl intermetallic based compound[J]. Materials China, 2009,28(1):31−37. (林均品, 陈国良. TiAl基金属间化合物的发展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2009,28(1):31−37. [3] 彰国社[日]. 建筑细部集成[M]. 翻译编委会译. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社, 2000.Zhang Guoshe [Japan]. Integration of architectural details[M]. Translated by the Translation Editorial Committee. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Press, 2000. [4] Yang Hong, Chen Ganglun. Titanium and its application in architecture[J]. Industrial Architecture, 2001,32(12):81−82. (杨红, 陈纲伦. 钛金属及其在建筑上的应用[J]. 工业建筑, 2001,32(12):81−82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8993.2001.12.028 [5] Fu Pengfei, Fu Gang, Mao Zhiyong, et al. Medium pressure electron beam local heat treatment technology for TC4 titanium alloy welded joints[J]. Welding, 2005,(2):24−27. (付鹏飞, 付刚, 毛智勇, 等. TC4钛合金焊接接头中压电子束局部热处理技术[J]. 焊接, 2005,(2):24−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2005.02.006 [6] Jin Yizhen, Wen Jialing, Liu Xin, et al. In-situ observation of fatigue fracture process of electron beam welded joint of TC4-DT titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Process, 2012,41(19):11−13. (金宜振, 温家伶, 刘昕, 等. TC4-DT钛合金电子束焊接接头疲劳断裂过程的原位观测[J]. 热加工工艺, 2012,41(19):11−13. [7] Liu Pengtao, Zhao Xiujuan, Liu Xin, et al. Effect of hydrogen on fatigue fracture characteristics of electron beam welded joints of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Process, 2011,40(13):130−133. (刘鹏涛, 赵秀娟, 刘昕, 等. 氢对TC4钛合金电子束焊接头疲劳断裂特性的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2011,40(13):130−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2011.13.044 [8] Chen Guoqing, Zhang Binggang, He Jingshan, et al. Electron beam welding of TiAl based alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007,(17):36−40. (陈国庆, 张秉刚, 何景山, 等. TiAl基合金的电子束焊接[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007,(17):36−40. [9] Wu Kai, Yao Wei, Zhang Tiejun, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of electron beam welded joints of Ti2AlNb alloy[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2018,43(4):67−71. (吴凯, 姚为, 张铁军, 等. 热处理对Ti2AlNb合金电子束焊接接头组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018,43(4):67−71. [10] Ge Miaomiao, Yao Zekun, Tu Weijian, et al. Effect of annealing on microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb / TC11 electron beam welded joint[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2015,40(8):106−109. (葛苗苗, 姚泽坤, 涂唯坚, 等. 退火对Ti-22Al-25Nb/TC11电子束焊接接头组织与拉伸性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(8):106−109. [11] Luo Xin, Yao Zekun, Qin Chun, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb / TC11 double alloy welded joint[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2015,40(7):20−24. (罗鑫, 姚泽坤, 秦春, 等. 热处理对Ti-22Al-25Nb/TC11双合金焊接接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(7):20−24. [12] Yu Chen, Zhang Yupeng, Fang Weiping, et al. Effect of post weld heat treatment on residual stress of 100 mm TC4 titanium alloy electron beam welded joint[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2018,39(7):151−155. (余陈, 张宇鹏, 房卫萍, 等. 焊后热处理对100 mm TC4钛合金电子束焊接头残余应力的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018,39(7):151−155. [13] Fang Weiping, Li Xiaohui, Zhang Yupeng, et al. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of welded joint of electronbeam welding for TC4 titanium alloy with 100 mm thickness[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2017,47(6):82−87. [14] Ahn J, He E, Chen L, et al. Prediction and measurement of residual stresses and distortions in fibre laser welded Ti-6Al-4V considering phase transformation[J]. Materials and Design, 2017,115:441−457. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.078 [15] Ma Quan, Xin Shewei, Song Kai, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welding of Ti-1300 high strength titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019,48(8):2724−2728. (马权, 辛社伟, 宋凯, 等. 热处理对Ti-1300高强钛合金电子束焊接组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2019,48(8):2724−2728. [16] Wang Shiqing, Xing Bo, Zhao Qizhe, et al. Effects of different heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 / Ti60 electron beam welded joint[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2020,50(5):16−20. (王世清, 邢博, 赵启喆, 等. 不同热处理对TC4/Ti60电子束焊接头微观组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 电焊机, 2020,50(5):16−20. [17] Shen Zhengxiang, Yuan Shuqiang, Yang Hui, et al. Effect of electron beam local scanning on microstructure and impact property of 40CrMnSiB steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2017,42(1):87−90. [18] Boehlert C J. The phase evolution and microstructural stability of an orthorhombic Ti-23Al-27Nb alloy[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1999,20(2):101−108. doi: 10.1007/s11669-999-0007-z -




 下载:
下载: