Study on beneficiation process of a low grade ilmenite in Panxi
-
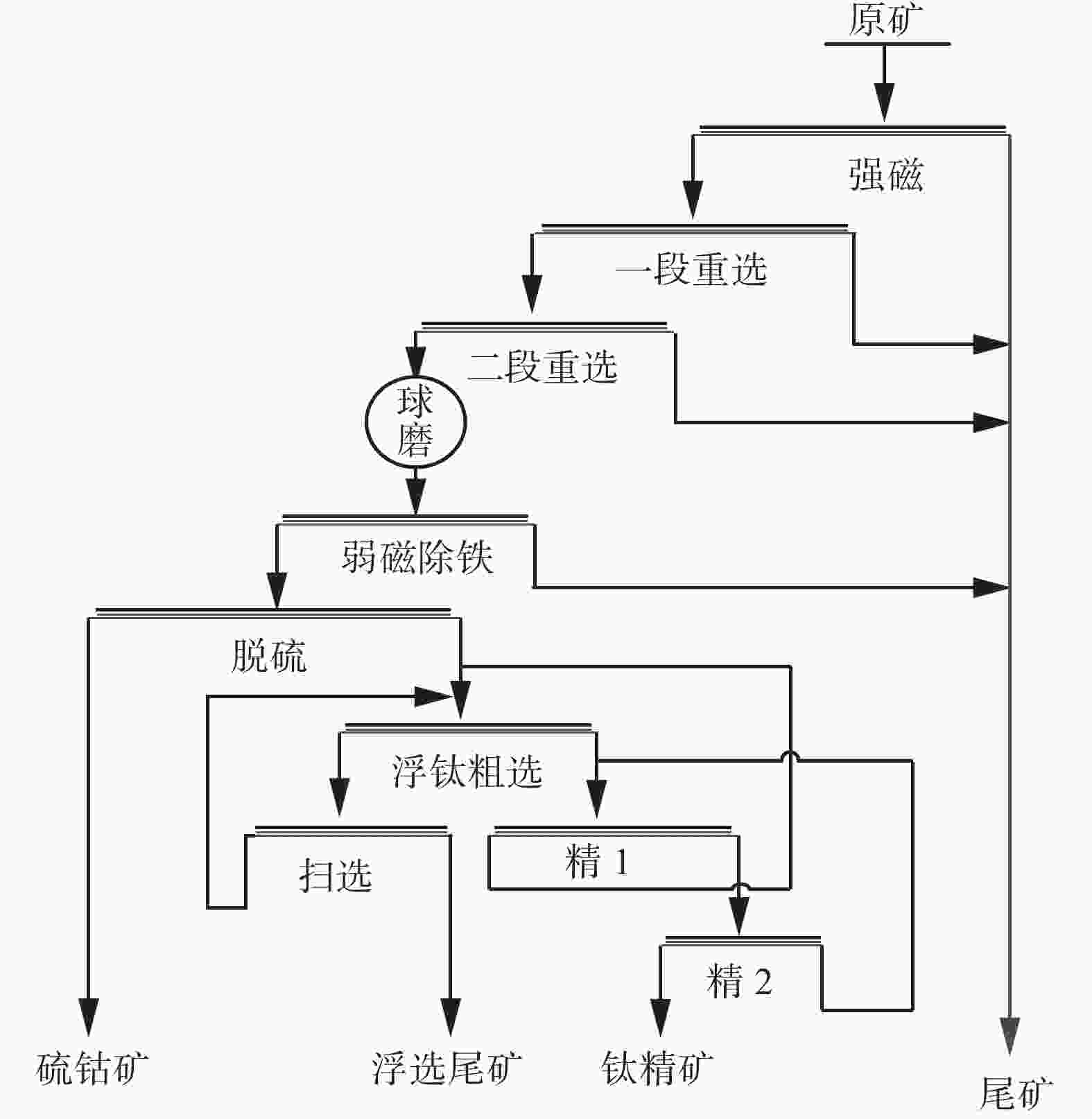
摘要: 某低品位钒钛磁铁矿,TiO2品位为6.15%,矿物组成复杂,为充分回收其中的钛铁矿,针对钛的赋存状态及粒级分布特点,制定了强磁磁选预抛尾、重选提质、细磨弱磁选除铁、反浮选脱硫与一粗一扫两精浮钛组合工艺流程,研究了磁感应强度、磁介质大小、脉动冲程、磨矿浓度、磨矿时间、浮选调整剂及捕收剂用量等的影响,在获得最优工艺条件的基础上,按“一段强磁抛尾—两段重选抛尾—磨矿—除铁—浮选”的工艺流程进行了闭路试验。试验获得了TiO2品位48.22%,回收率为35.19%的钛精矿。矿石中主要有用的矿物钛铁矿得到了有效的回收。Abstract: The TiO2 content of a low grade ilmenite in Panxi is 6.15% and its mineral composition is complex. In order to fully recover ilmenite, mineral processing experiments were carried out. According to the occurrence state and particle size distribution characteristics of titanium, the combined technological processes of pre-tail dumping by strong magnetic separation, quality improvement by gravity separation, iron removal by fine grinding and low intensity magnetic separation, reverse flotation desulfurization and one roughing-one scavenging-two cleaning titanium flotation were formulated. The effects of magnetic induction intensity, magnetic medium size, pulsating stroke, grinding concentration, grinding time, flotation regulator and collector dosage were studied. The experimental results show that after the ore dressing test is carried out by the process of "one strong magnetic throwing tail-two segment redressing-grinding-removing iron-flotation", the TiO2 grade of 48.22% and the recovery rate of 35.19% can be obtained. The main useful mineral in the ore is ilmenite, which has been effectively recovered.
-
Key words:
- ilmenite /
- strong magnetic separation /
- gravity separation /
- flotation
-
表 1 原矿化学多元素分析
Table 1. Chemical elements analysis of raw ore
% TFe FeO Fe2O3 TiO2 P S SiO2 Al2O3 V2O5 17.14 13.52 4.78 6.15 0.042 0.54 36.93 10.75 0.061 表 2 钛的化学物相分析
Table 2. Phase analysis of titanium
% 含量 分布率 钛铁矿 4.26 69.27 钛磁铁矿 0.69 11.27 硅酸盐 1.20 19.51 合计 6.15 100.00 表 3 矿物组成分析
Table 3. Analysis of mineral composition
% 钛磁铁矿 钛铁矿 硫化物 钛辉石 斜长石 绿泥石等 4.76 8.64 1.45 41.22 35.87 8.06 表 4 试验原料筛析结果
Table 4. Screening results of test material
粒级/mm 粒级产率/% 粒级品位/% 金属分布率/% 0.450 11.05 1.69 3.07 −0.450~0.280 16.14 3.18 8.44 −0.280~0.180 21.75 5.33 19.07 −0.180~0.154 17.02 8.09 22.65 −0.154~0.100 15.49 9.72 24.77 −0.100~0.074 4.13 5.33 3.62 −0.074~0.045 8.57 8.4 11.85 −0.045~0.038 2.68 4.72 2.08 −0.038 3.17 8.53 4.44 合计 100 6.07 100 表 5 磁场强度条件试验
Table 5. Condition tests of Magnetic field intensity
磁场强度/T 原矿品位/% 精矿品位/% 尾矿品位/% 精矿产率/% 回收率/% 1.2 6.22 7.98 1.38 73.33 94.08 1.0 6.22 8.05 1.25 73.09 94.59 0.8 6.22 8.61 1.12 68.09 94.25 0.6 6.22 10.61 1.28 52.95 90.32 表 6 磁介质对比试验
Table 6. Contrast tests of magnetic medium
磁介质尺寸/mm 原矿品位/% 精矿品位/% 尾矿品位/% 精矿产率/% 回收率/% 3 6.22 10.78 2.49 44.99 77.98 4 6.22 10.34 2.56 47.04 78.20 表 7 脉动冲次条件试验
Table 7. Condition tests of pulsating impulse
脉动冲次/(次·min-1) 原矿品位/% 精矿品位/% 尾矿品位/% 精矿产率/% 回收率/% 200 6.22 9.77 2.78 49.21 77.30 250 6.22 10.34 2.53 47.25 78.54 300 6.22 10.78 2.49 44.99 77.98 350 6.22 10.54 2.61 45.09 77.14 表 8 重选试验结果
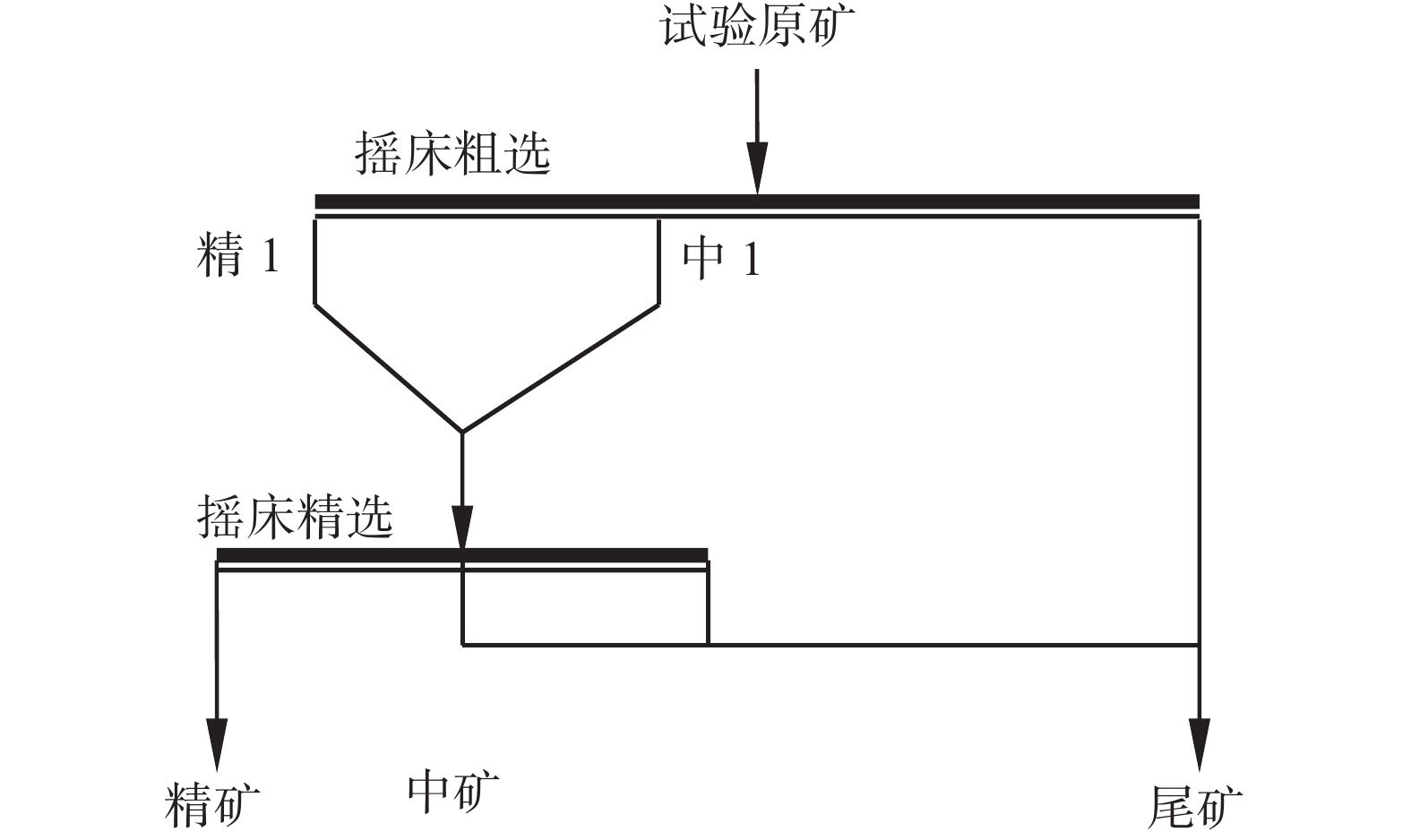
Table 8. Results of gravity separation test
% 试验条件 原矿品位 精矿品位 尾矿品位 精矿产率 回收率 一段重选 10.58 16.34 5.73 45.71 70.60 二段重选 16.34 23.12 7.48 56.65 80.16 表 9 3 min磨矿浓度对比试验
Table 9. Contrast tests of 3 min grinding concentration
粒级/mm 粒级含量/% 原矿 70%浓度 80%浓度 +0.18 42.52 16.07 2.91 +0.1 15.79 31.43 39.69 0.074 16.85 33.39 17.85 −0.074 16.28 19.11 39.55 合计 100 100 100 表 10 磨矿浓度80%条件下不同磨矿时间试验结果
Table 10. Test results of grinding time under grinding concentration of 80%
粒级/mm 不同磨矿时间下粒度分布比例 /% 原矿 2 min 3 min 5 min 8 min +0.18 42.52 6.54 2.91 0.38 0.83 +0.1 15.79 45.33 39.69 30.20 18.68 0.074 16.85 17.84 17.85 21.11 19.59 −0.074 16.28 30.30 39.55 48.31 60.90 合计 100 100 100 100 100 表 11 重选精矿除铁试验
Table 11. Iron removal tests of concentrate by gravity separation
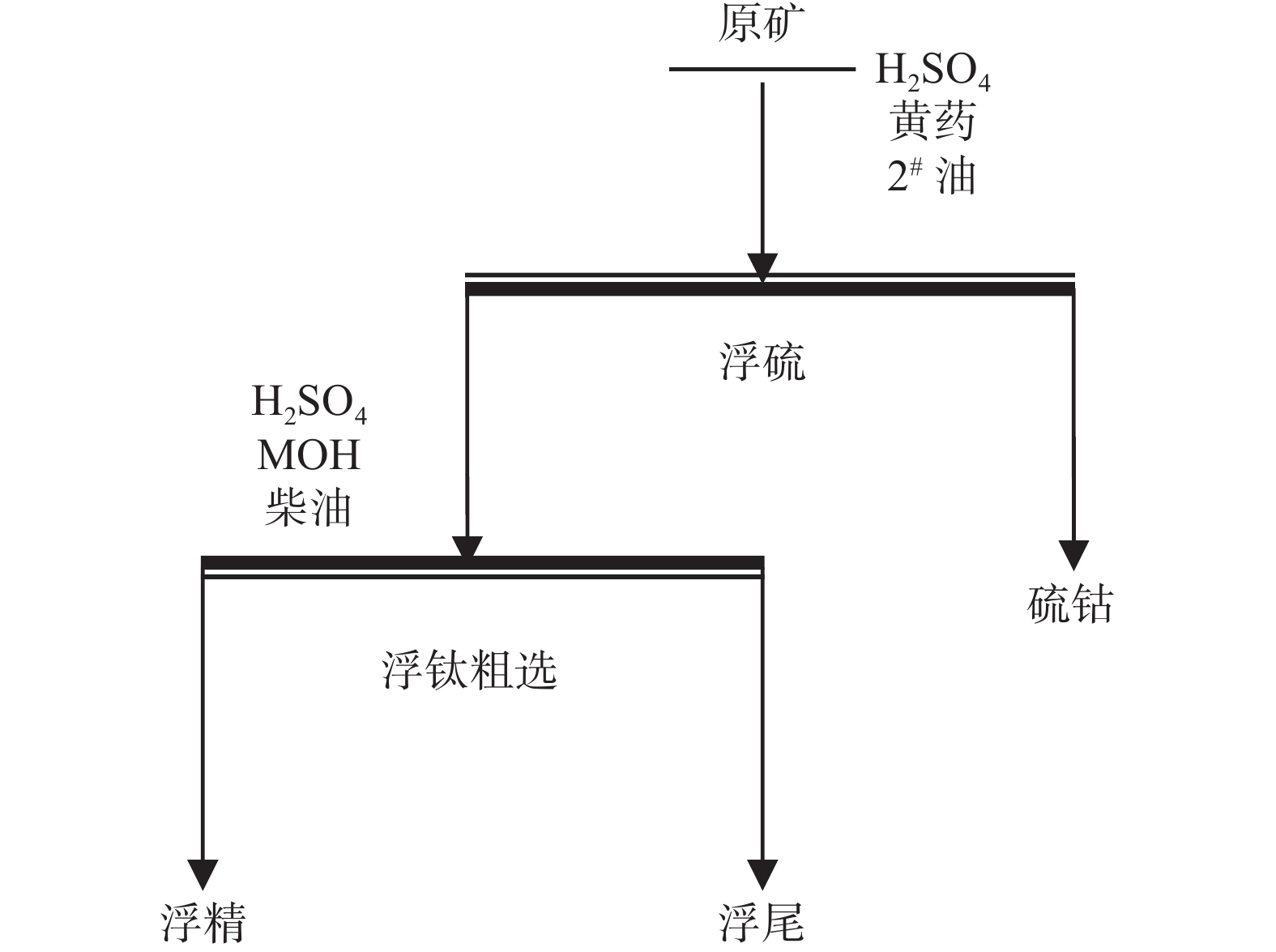
% 产品 产率 TiO2品位 TFe品位 原矿 100 23.12 铁精矿 8.90 16.45 41.85 除铁尾矿 91.10 23.77 表 12 浮钛粗选硫酸用量条件试验
Table 12. Tests of sulfuric acid dosage for coarse separation of floating titanium
硫酸用量/(g·t−1) 产品 品位/% 产率/% 回收率/% 800 浮硫精矿 10.75 3.98 1.80 钛精矿 32.48 67.63 92.41 尾矿 4.89 28.39 5.84 原矿 23.77 100 100.00 1000 浮硫精矿 10.75 3.46 1.56 钛精矿 36.68 57.88 89.23 尾矿 5.66 38.66 9.21 原矿 23.77 100.00 100.00 1300 浮硫精矿 10.27 4.21 1.82 钛精矿 39.31 50.52 83.42 尾矿 7.75 45.27 14.76 原矿 23.77 100 100.00 1600 浮硫精矿 11.03 3.27 1.52 钛精矿 41.64 44.22 77.43 尾矿 9.53 52.51 21.05 原矿 23.77 100.00 100.00 表 13 浮钛粗选捕收剂MOH用量条件试验
Table 13. Tests of MOH dosage for coarse separation of floating titanium
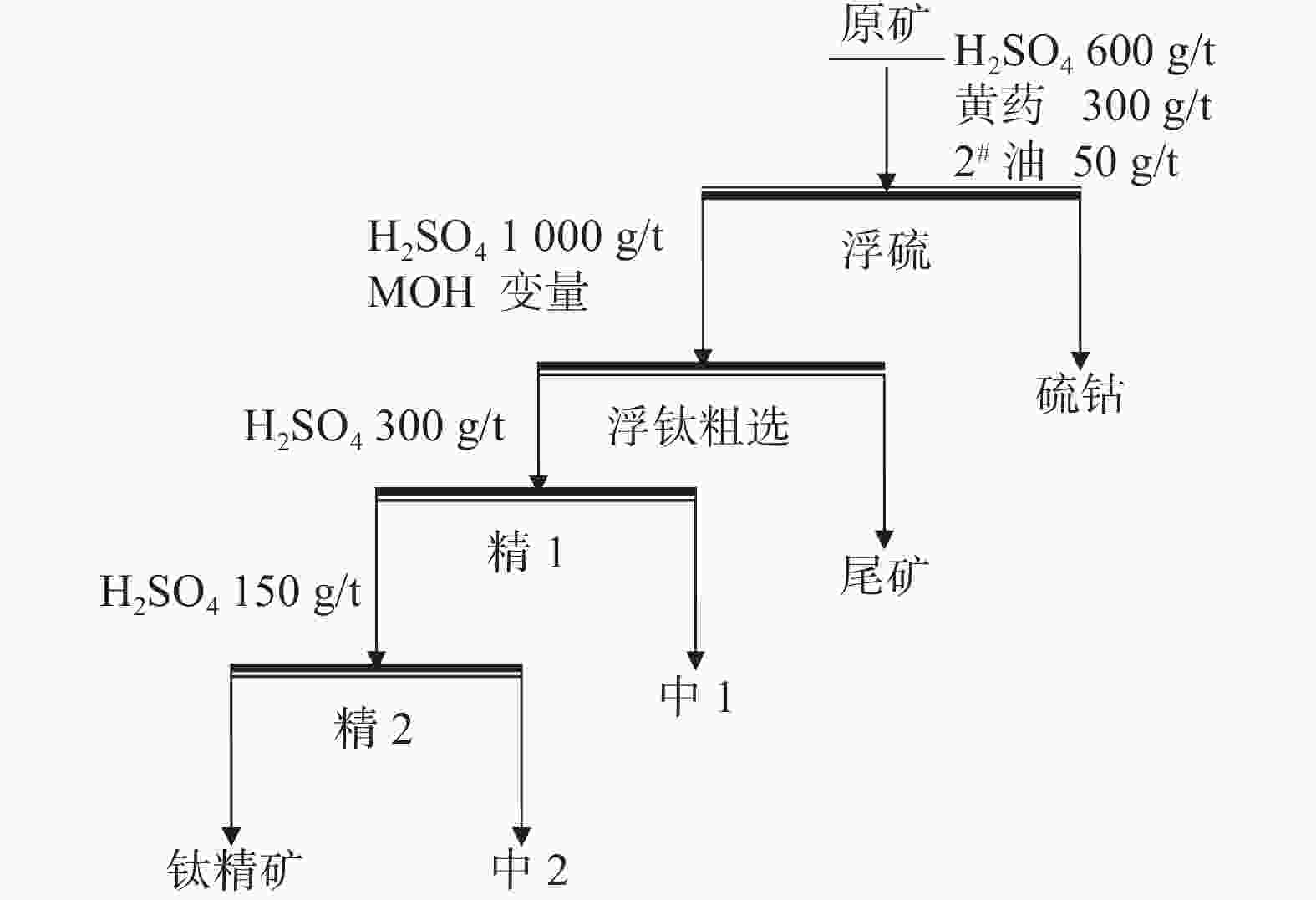
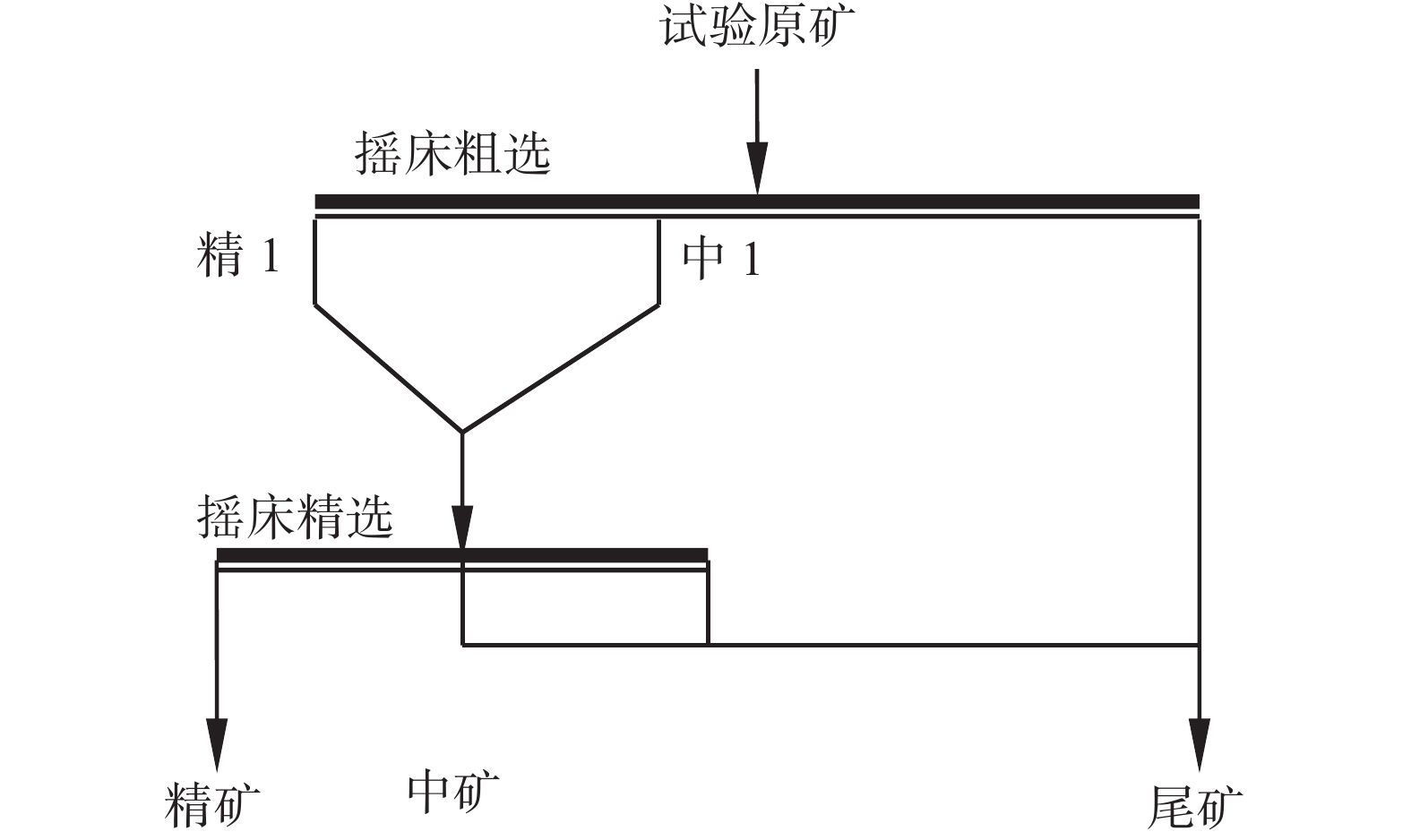
捕收剂用量/(g·t−1) 产品 品位/% 产率/% 回收率/% 1200 浮硫精矿 11.23 3.78 1.79 钛精矿 42.36 45.45 81.00 尾矿 8.28 50.77 17.68 原矿 23.77 100 100.00 1500 浮硫精矿 10.81 3.46 1.55 钛精矿 39.86 51.50 86.36 尾矿 6.38 45.04 12.09 原矿 23.77 100 100.00 1800 浮硫精矿 10.75 3.46 1.56 钛精矿 36.68 57.88 89.23 尾矿 5.66 38.66 9.21 原矿 23.77 100.00 100.00 2000 浮硫精矿 10.70 3.27 1.47 钛精矿 32.57 67.85 92.97 尾矿 4.68 28.88 5.56 原矿 23.77 100 100.00 表 14 一粗两精开路试验
Table 14. Open circuit test of one rough-two fine flotation
% 产品 品位 产率 回收率 浮硫精矿 10.6 3.65 1.62 钛精矿 48.17 39.63 79.74 中1 10.32 9.52 4.10 中2 28.13 4.23 4.96 尾矿 5.34 42.97 9.57 原矿 23.94 100 100 表 15 全流程试验结果
Table 15. Results of the whole process
% 产品名称 产率 TiO2品位 回收率 钛精矿 4.58 48.22 35.19 尾矿 95.42 4.26 64.81 原矿 100.00 6.27 100.00 -
[1] Deng Guozhu. World titanium resources and their development and utilization[J]. Progress of Titanium Industry, 2002,(5):9−12. (邓国珠. 世界钛资源及其开发利用[J]. 钛工业进展, 2002,(5):9−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2002.05.003Deng Guozhu. World titanium resources and their development and utilization [J]. Progress of titanium industry, 2002 (5): 9-12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2002.05.003 [2] USDI, USGS. Critical mineral resources of the United States—economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply[R]. 2017. [3] Chong Xiaoxiao, Luan Wenlou, Wang Fengxiang, et al. Overview of global titanium resources and titanium consumption trend in China[J]. Mineral Protection and Utilization, 2020,40(2):162−170. (崇霄霄, 栾文楼, 王丰翔, 等. 全球钛资源现状概述及我国钛消费趋势[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020,40(2):162−170.Chong Xiaoxiao, Luan Wenlou, Wang Fengxiang, et al. Overview of global titanium resources and titanium consumption trend in China [J]. Mineral protection and utilization, 2020, 40 (02): 162-170. [4] Sun Renbin, Wang Qiushu, Yuan Chunhua, et al. Analysis of global titanium resource situation[J]. China Mining, 2019,28(6):1−6,12. (孙仁斌, 王秋舒, 元春华, 等. 全球钛资源形势分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2019,28(6):1−6,12.Sun Renbin, Wang qiushu, Yuan Chunhua, et al. Analysis of global titanium resource situation [J]. China mining, 2019, 28 (06): 1-6 + 12 [5] 邓陈雄. 基于矿物交互影响的低品位钛铁矿浮选分离基础研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.Deng Chenxiong. Basic research on flotation separation of low-grade ilmenite based on mineral interaction [D]. Shengyang:Northeast University, 2015. [6] Xiao Liangchu, Wang Yong. Analysis of separation difficulties of Panzhihua Baima low grade ilmenite[J]. Modern mining, 2016,32(3):58−62. (肖良初, 王勇. 攀枝花白马低品位钛铁矿选别难点分析[J]. 现代矿业, 2016,32(3):58−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.03.024Xiao Liangchu, Wang Yong. Analysis of separation difficulties of Panzhihua Baima low grade ilmenite [J]. Modern mining, 2016, 32 (03): 58-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.03.024 -




 下载:
下载: