Trend and control of P in FeV50 smelting process of large-scale tilting furnace
-
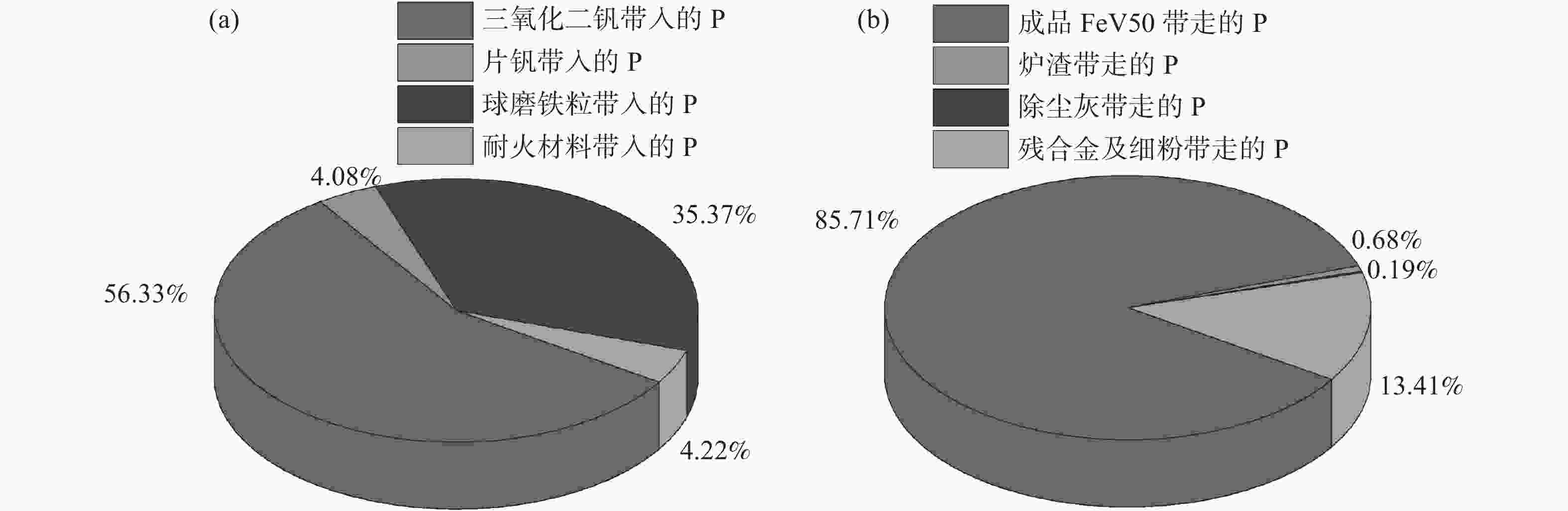
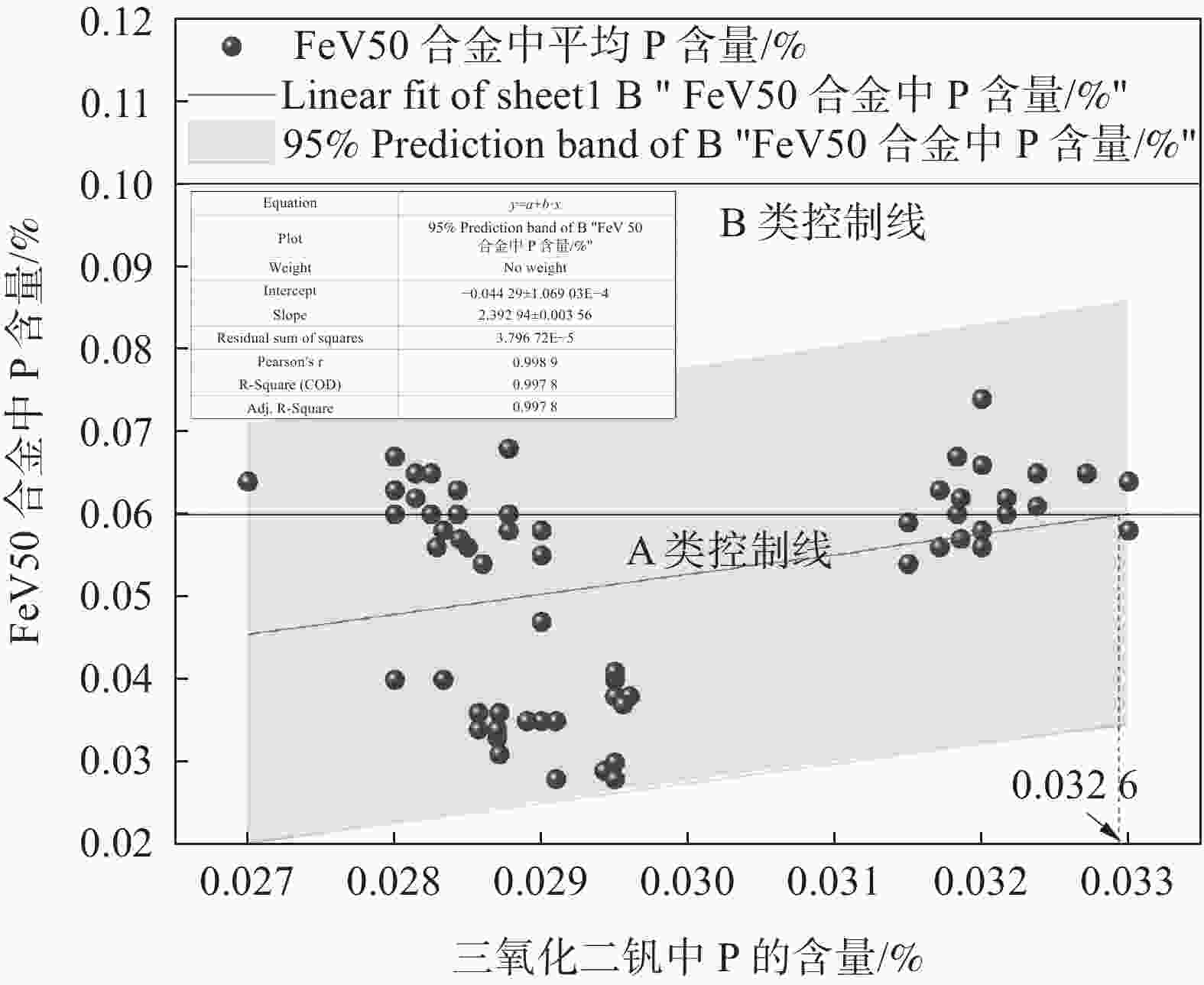
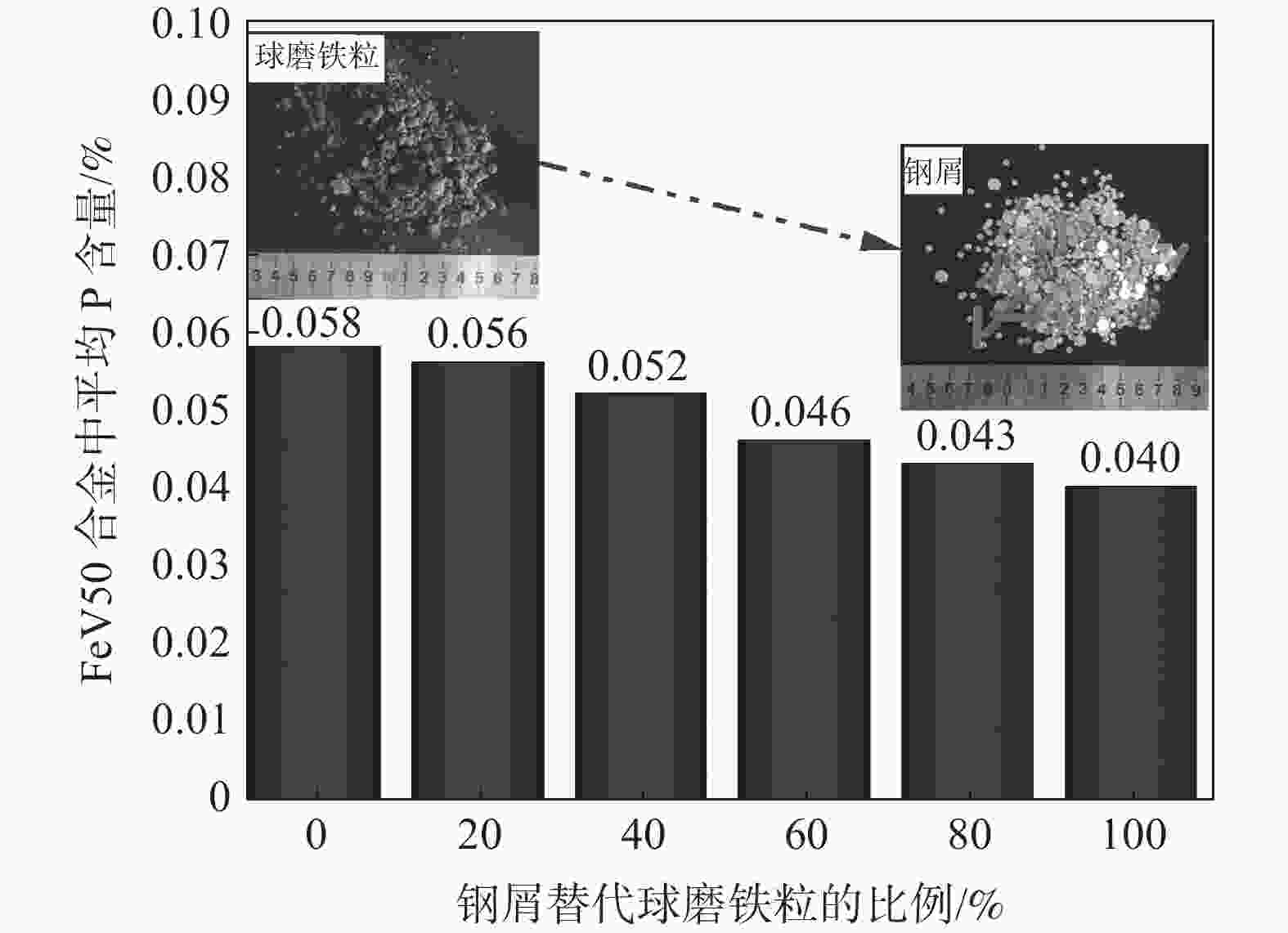
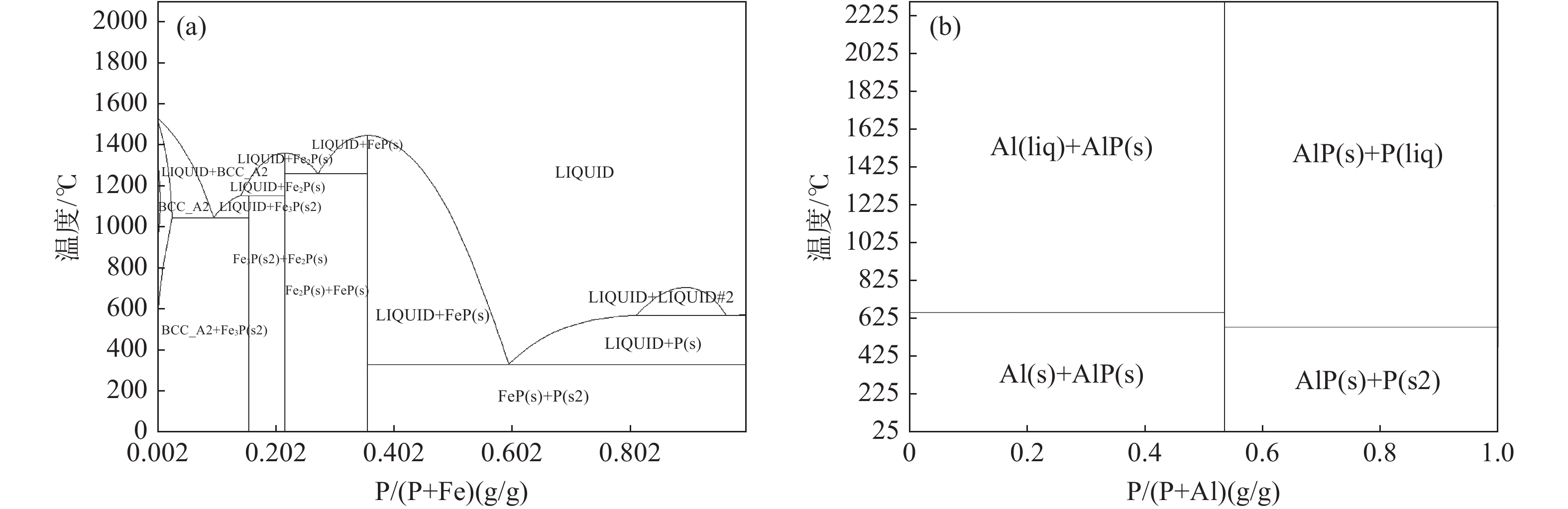
摘要: 结合理论分析、元素平衡统计和工业试验,研究了大型倾翻炉冶炼FeV50流程P元素的走向、分布与控制措施。结果表明:大型倾翻炉FeV50冶炼过程中原料带入的磷氧化物(P2O5)能充分被金属铝还原并进入合金中;三氧化二钒和球磨铁粒是P元素的主要输入源,有85.71%的P进入成品合金,13.41%的P进入残合金与细粉,进入金属相的P高达99.12%。控制三氧化二钒中P含量不超过0.0326%和采用钢屑替代球磨铁粒60%以上能控制FeV50中P含量符合A级品要求。Abstract: Combined with theoretical analysis, element balance statistics and industrial tests, the trend, distribution and control measures of P in FeV50 smelting process of large-scale tipping furnace were studied. The results show that P2O5 brought in by raw materials during FeV50 smelting in large-scale tilting furnace can be fully reduced by metallic aluminum and enter the alloy. Vanadium trioxide and ball-milled iron particles are the main input sources of P, with 85.71% of P entering the finished alloy, 13.41% of P entering the residual alloy and fine powder, and 99.12% of P entering the metal phase. The most effective method to control the P content in FeV50 is the control of P content in vanadium trioxide not exceeding 0.0326% and the replacement of more than 60% of the ball-milled iron particles with steel scraps.
-
Key words:
- tilting furnace /
- tilting furnace /
- P element /
- trend /
- steel scraps
-
表 1 现场输入物料中的平均P元素含量及物料平均消耗情况
Table 1. Average P element content and average material consumption in field input materials
物料名称 平均P元素含量/% 现场9+1配料模式下平均消耗/(kg·炉−1) 耐火材料 镁砂 0.022 1417.8 镁火泥 0.036 镁砖 0.024 球磨铁粒 0.048 5414 三氧化二钒 0.040 9000 片钒 0.052 1000 石灰 <0.01 2700 表 2 现场输入物料中的平均P元素情况
Table 2. Average total P element amount in field input materials
物料名称 总P/(kg·炉−1) 三氧化二钒 4.14 片钒 0.30 球磨铁粒 2.60 耐火材料 0.31 总计 7.35 表 3 现场输出物料中的P元素含量及平均物料产出情况
Table 3. The P content in field output materials and average material output
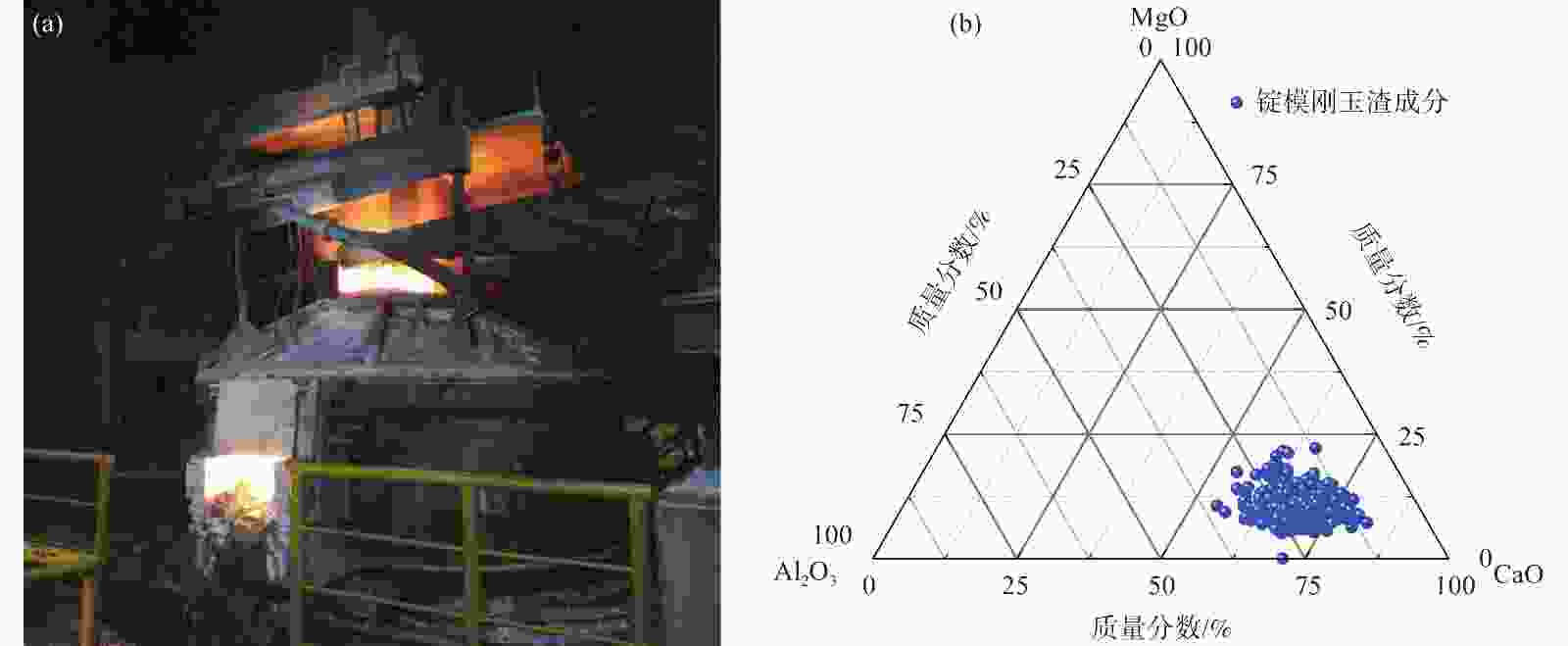
物料名称 化学元素成分/% 现场9+1配料模式下平均产出/(kg·炉−1) P MgO CaO Al2O3 成品FeV50 0.062 10156 锭模渣 <0.005 21.92 12.67 62.61 3500 渣盆渣 <0.005 10.40 24.34 62.30 7500 锅巴渣 0.016 64.32 4.71 14.58 270 黑边渣 0.050 12.57 2.92 27.31 23 旋风除尘灰 0.034 16.64 3.14 5.98 20 布袋除尘灰 0.028 35.54 1.68 5.88 25 表 4 现场输出物料中的平均P元素总量
Table 4. Average total P element amount in field output materials
物料名称 总P/(kg·炉−1) 成品FeV50 6.30 锭模渣 渣盆渣 锅巴渣 0.04 黑边渣 0.01 旋风除尘灰 0.007 布袋除尘灰 0.007 残合金与细粉 0.986 总计 7.35 表 5 球磨铁粒筛下物的元素赋存形式的分析
Table 5. Analysis of the form of elements in the sieved ball-milled iron particle
矿物 杂质元素含量/% Al C Ca Cl Cr Cu Fe K Mg P 金属铁 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 39.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 钒尖晶石 6.78 0.00 0.07 0.00 55.15 0.00 16.12 0.00 2.21 0.00 铁橄榄石 0.65 0.00 15.70 0.00 8.49 0.00 15.56 1.12 34.13 0.00 辉石 12.84 0.00 11.05 4.96 0.00 0.00 0.14 2.67 7.37 0.00 磷灰石 26.27 0.00 36.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.08 40.26 4.94 98.99 氧化铁 19.28 0.00 8.17 79.60 32.73 100.00 21.29 2.30 11.19 0.00 方镁石 0.89 0.00 0.66 15.04 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.00 27.20 0.00 玻璃质 12.23 0.00 9.84 0.00 0.39 0.00 1.27 50.12 1.53 0.00 钒酸钙 0.31 0.00 0.83 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.33 0.00 -
[1] 杨才福, 张永权, 王瑞珍. 钒钢冶金原理与应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012.Yang Caifu, Zhang Yongquan, Wang Ruizhen. Metallurgical principle and application of vanadium steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012. [2] Song Mingming, Song Bo, Cao Min, et al. Melting property of a slag for FeV alloy production by the electrical thermite method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2015,37(4):436−440. (宋明明, 宋波, 曹敏, 等. 电铝热法冶炼钒铁渣熔化性能[J]. 工程科学学报, 2015,37(4):436−440.Song Mingming, Song Bo, Cao Min, et al. Melting property of a slag for FeV alloy production by the electrical thermite method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2015, 37, 37(4): 436-440. [3] Yu Bin, Xian Yong, Sun Zhaohui, et al. Study on process of smelting ferrovanadium by tilting furnace using mixture vanadium oxides[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(4):1−6. (余彬, 鲜勇, 孙朝晖, 等. 混合钒氧化物倾翻炉钒铁冶炼工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(4):1−6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2015.04.001Yu Bin, Xian Yong, Sun Zhaohui, et al. Study on Process of Smelting Ferrovanadium by Tilting Furnace Using Mixture Vanadium Oxides[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015, 36(4): 1-6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2015.04.001 [4] 杨兴磊. 大型倾翻炉冶炼钒铁收得率提升研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019.Yang Xinglei. Study on improving the yield of smelting ferrovanadium in large tilting furnace[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019. [5] 鲜勇. Fe-V中间合金中σ相形成机理及其工业化技术应用研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2015.Xian Yong. Formation mechanism of σ phase in Fe-V alloy and its industrial application [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2015. [6] Li Mingru, Yue Feng. Trial production of HRB400 bar by microalloying process of “FeV+nitrogen enrichment agent[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2005,33(6):14−16. (李明儒, 岳峰. “钒铁+富氮剂”微合金化HRB400钢筋生产试验[J]. 钢铁研究, 2005,33(6):14−16.Li Mingru, Yue Feng. Trial production of HRB400 bar by microalloying process of “FeV+nitrogen enrichment agent[J].Research on Iron and Steel,2005, 33(6): 14-16. [7] Shi Zhixin, Yuan Tianyu, Liu Jinyan, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of vanadium spinel in the process of calcified roasting vanadium slag[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2014,23(4):95−98. (史志新, 苑天宇, 刘锦燕, 等. 钙化焙烧钒渣过程中钒尖晶石的矿物学特征[J]. 矿冶, 2014,23(4):95−98.Shi Zhixin, Yuan Tianyu, Liu Jinyan, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of vanadium spinel in the process of calcified roasting vanadium slag[J]. Mining and Metallurgy,2014, 23(4): 95-98. [8] Wang Jun, Sun Zhaohui, Su Yi, et al. Roasting and leaching of high calcium and high phosphorus vanadium slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2015,39(11):1038−1042. (王俊, 孙朝晖, 苏毅, 等. 高钙高麟钒渣焙烧浸出的研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2015,39(11):1038−1042.Wang Jun, Sun Zhaohui, Su Yi, et al. Roasting and leaching of high calcium and high phosphorus vanadium slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2015, 39(11): 1038-1042. [9] 付自碧. 高钙高磷钒渣制备氧化钒工艺研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017.Fu Zibi. Technological research on preparation of vanadium oxide from high calcium and high phosphorus vandium slag[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Science, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: