Precipitation kinetics of composite carbides of Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloyed steel
-
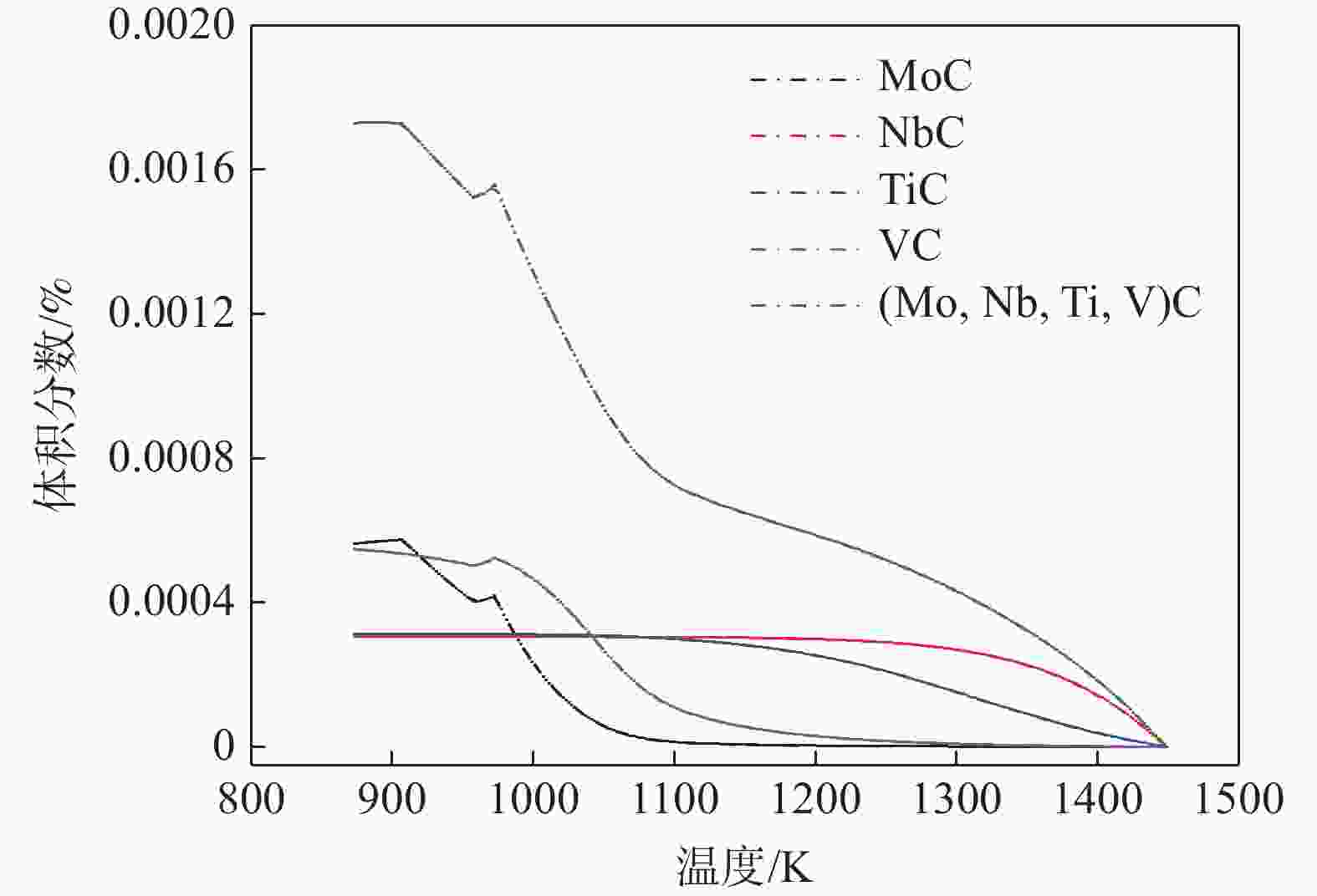
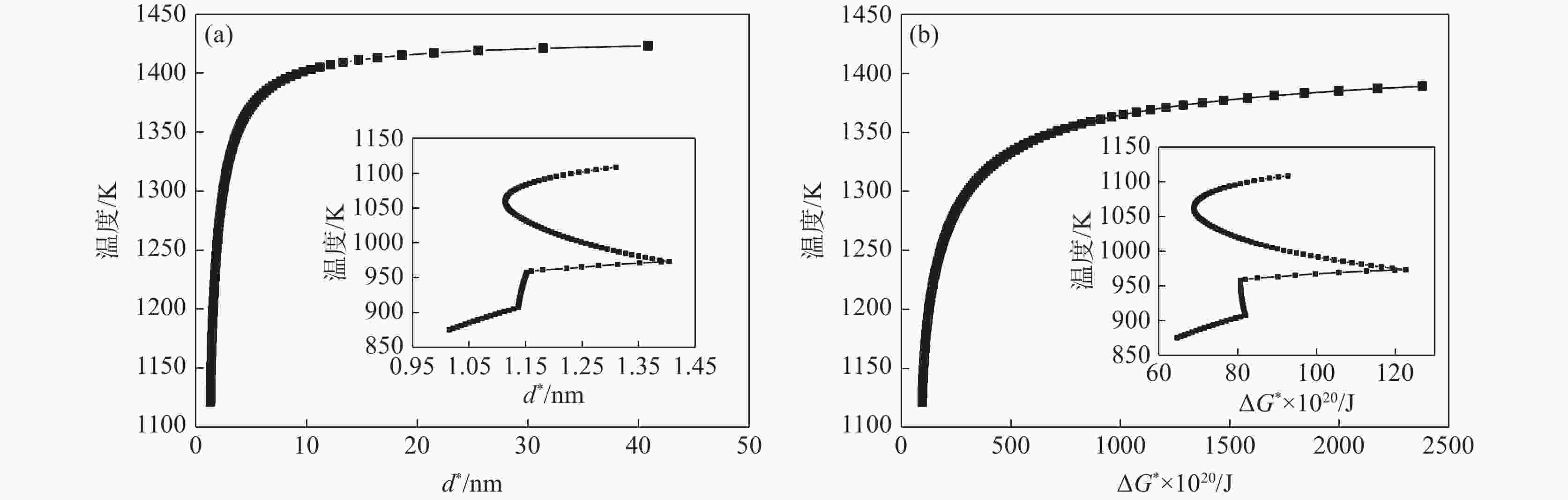
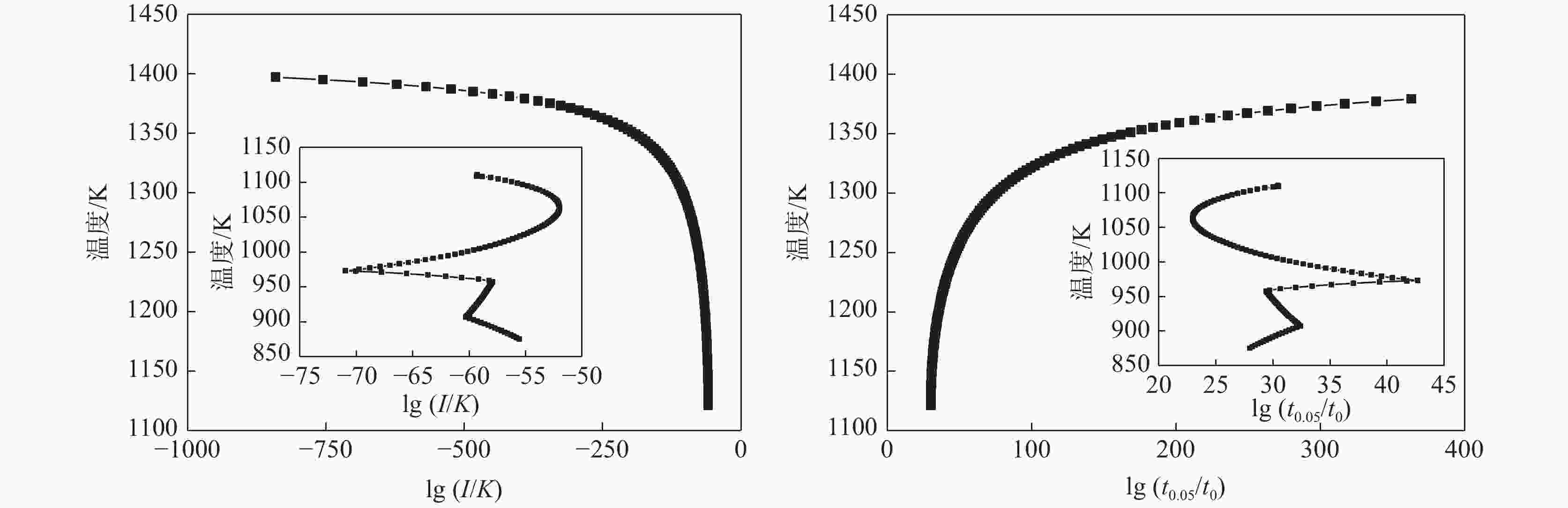
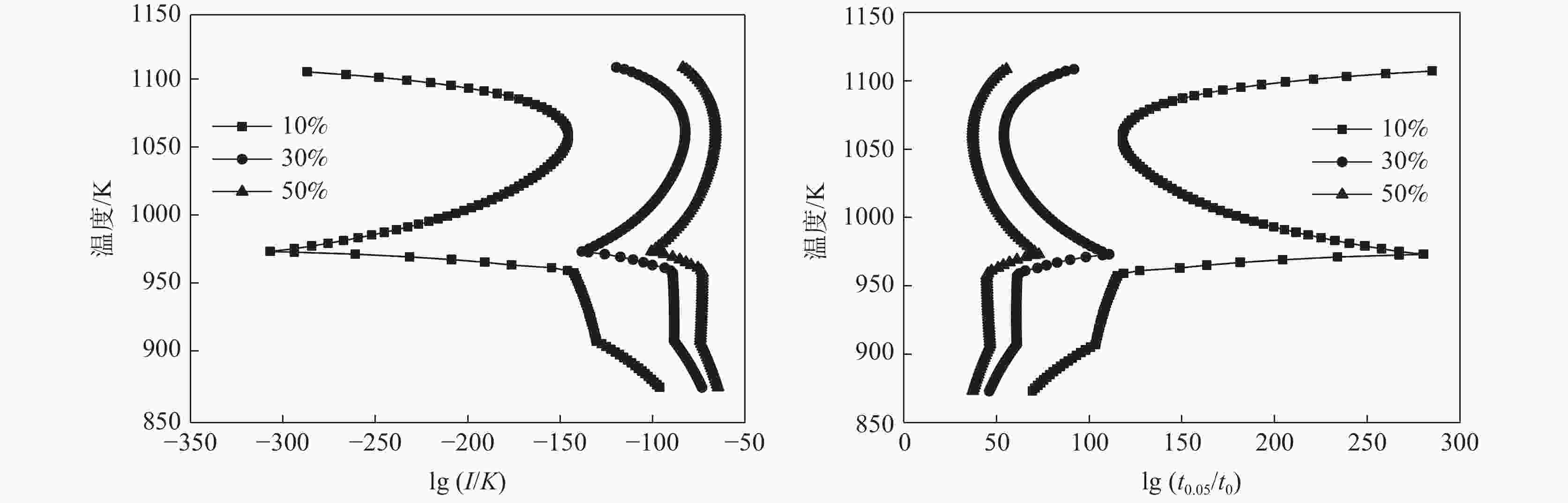
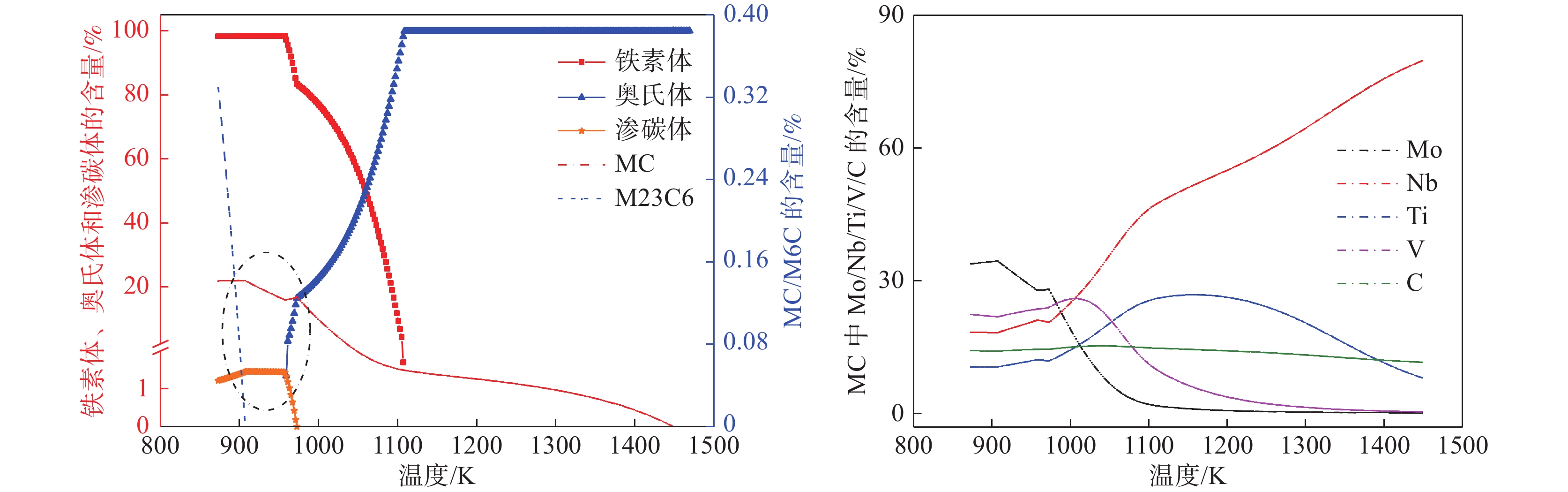
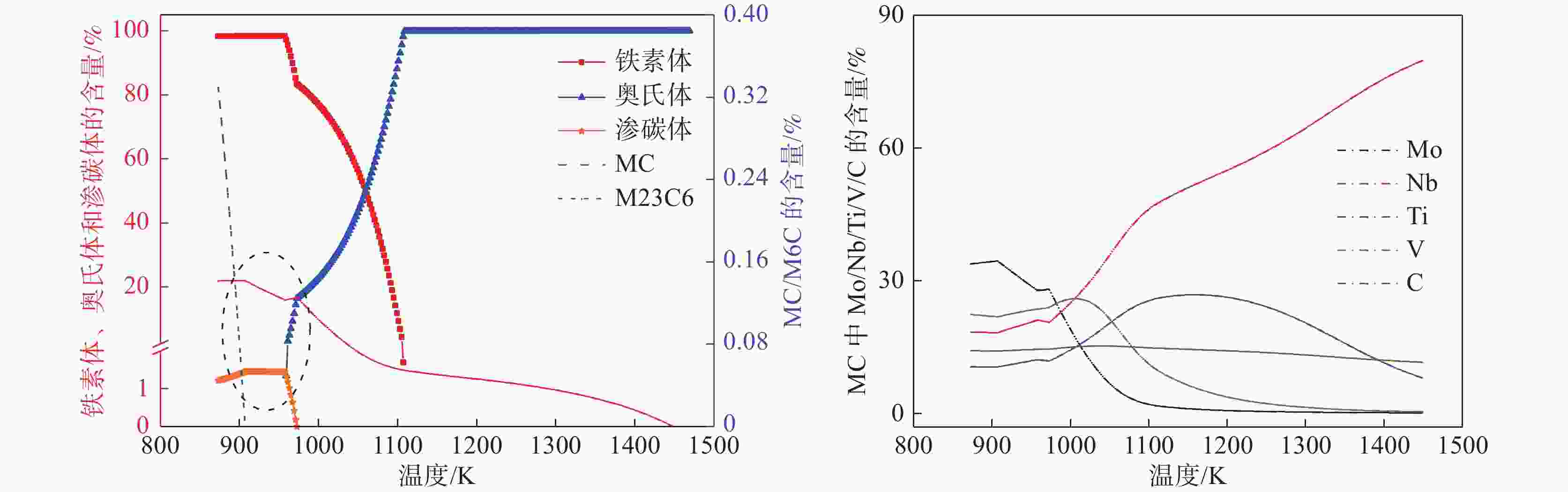
摘要: 结合JmatPro热力学软件对Nb-Ti-V-Mo微合金化E460海工钢中多元复合析出相的固溶热力学计算和经典形核长大动力学理论,研究了(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C在奥氏体和铁素体中沉淀析出规律,探讨了奥氏体形变储能和形变诱导析出量对(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C沉淀析出动力学的影响。研究表明,(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C在1448.6 K时开始析出。在奥氏体相区,随着温度的降低,临界形核功逐渐降低,NrT曲线和PTT曲线呈单调变化趋势。在奥氏体和铁素体两相区,(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C的最快沉淀析出温度为1062.6 K。随着形变储能的增加,相对形核率呈增加趋势,析出孕育期缩短。随形变诱导析出量增加,PTT曲线向左移动,最大形核率温度和最快析出温度为1058.3~ 1063.8 K。
-
关键词:
- Nb-Ti-V-Mo微合金钢 /
- 碳化物 /
- 析出动力学 /
- PTT曲线 /
- NrT曲线
Abstract: The precipitation thermodynamics of the multi-element composite precipitates in the Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloy E460 off shore steel was calculated by JmatPro thermodynamics software, in combination with the classical nucleation and growth kinetic theory, were used to study precipitation law of (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C in austenite and ferrite. The influence of austenite deformation storage and deformation-induced precipitation on (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C precipitation and precipitation kinetics were also discussed. The results indicate that (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C begins to precipitate at 1 448.6 K. In austenite region, as the temperature decreases the critical nucleation energy gradually decreases, and the NrT curve and the PTT curve show a monotonous trend. In the two-phase region of austenite and ferrite, the fastest precipitation temperature of (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C is 1 062.6 K. Relative nucleation rate increases, and both precipitation and incubation period shorten with the increase of deformation energy storage. As the amount of precipitation induced by deformation increases, the PTT curve shifts to the left, and the maximum nucleation rate temperature and the fastest precipitation temperature are between 1058.3 K and 1063.8 K.-
Key words:
- Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloyed steel /
- carbide /
- precipitation kinetics /
- PTT curve /
- NrT curve
-
表 1 Nb-Ti-V-Mo微合金化试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloyed steel
% C N Si Mn P Al Cr 0.11~0.13 0.0030~0.0040 0.20~0.30 1.1~1.3 0.010~0.012 0.030~0.05 0.16~0.20 Ni Mo Cu Ti Nb V Fe 0.20~0.30 0.18~0.22 0.15~0.18 0.013~0.017 0.024~0.028 0.030~0.036 余量 表 2 碳化物在γ和α相中的动力学计算相关参数
Table 2. Relevant parameters for kinetic calculation of MC in austenite [18]
析出相 固溶度积 M元素的扩散系数/(cm2·s−1) 晶格常数/ nm NbC γ 3.70−9100/T 530 exp(−344000/RT) 0.4470 α 3.90−9930/T 50.2 exp(−252000/RT) TiC γ 2.75−7000/T 0.15 exp(−251000/RT) 0.4318 α 4.40−9575/T 3.15 exp(−248000/RT) MoC γ 1.29−523/T 0.036 exp(−240000/RT) 0.4277 α 3.19−4649/T 1.3 exp(−229000/RT) VC γ 6.72−9500/T 0.28 exp(−264000/RT) 0.4182 α 2.72−6080/T 3.92 exp(−241000/RT) 表 3 位错条件下不同形变储能下复合碳化物(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C形核参量的计算结果
Table 3. Nucleation parameters of (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C at different deformation energies under dislocation nucleation
位错形核温度/K 形变储能=0 J/mol 形变储能=2 000 J/mol 形变储能=4 000 J/mol lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d 1373 −325.62 297.57 −325.56 297.44 −325.51 297.31 1323 −131.38 102.52 −131.33 102.39 −131.28 102.26 1273 −86.54 57.32 −86.49 57.18 −86.43 57.05 1223 −69.23 39.91 −69.18 39.77 −69.12 39.63 1173 −61.65 32.44 −61.60 32.30 −61.54 32.15 1123 −59.24 30.31 −59.18 30.15 −59.12 30.00 1073 −52.20 23.22 −52.13 23.06 −52.07 22.90 1023 −55.46 26.58 −55.39 26.41 −55.32 26.24 973 −70.95 42.69 −70.88 42.51 −70.81 42.33 923 −59.42 31.31 −59.35 31.12 −59.27 30.94 873 −55.55 27.97 −55.47 27.77 −55.39 27.57 表 4 不同形变诱导析出量时铁素体中元素的初始含量(1073 K)
Table 4. Initial content of elements in ferrite at different deformation induced precipitation (1 073 K)
% MC Mo Nb Ti V C 析出量 0.0563 0.00214 0.0233 0.0131 0.00915 0.00851 10% 0.198 0.00507 0.00320 0.0248 0.112 30% 0.199 0.00972 0.00583 0.0266 0.114 50% 0.199 0.0144 0.00845 0.0284 0.116 表 5 形变诱导析出量10%、30%和50%时(Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C在铁素体中形核参量的计算结果
Table 5. Calculation results of nucleation parameters of (Nb,Ti,Mo,V)C in ferrite under strain induced precipitation 10%, 30% and 50%
位错形核温度/K 10% 30% 50% lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05/t0)d 1093 −199.43 172.21 −94.80 66.78 −72.07 43.69 1073 −152.28 124.73 −83.74 55.51 −66.53 37.97 1053 −146.15 118.51 −82.76 54.47 −66.26 37.65 1033 −158.57 131.02 −87.64 59.42 −69.40 40.87 1013 −183.63 156.28 −96.93 68.89 −75.28 46.91 993 −226.61 199.55 −112.18 84.39 −84.81 56.68 973 −306.99 280.33 −138.23 110.78 −100.62 72.81 953 −141.22 113.88 −88.93 61.06 −72.95 44.81 933 −135.54 108.38 −88.35 60.70 −73.30 45.39 913 −131.36 104.40 −88.24 60.83 −73.94 46.28 893 −113.42 86.58 −81.14 53.88 −69.68 42.21 873 −96.14 69.40 −73.23 46.13 −64.55 37.26 -
[1] Zhang D Q, Liu G, Zhang K, et al. Effect of Nb microalloying on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021,824:1−13. [2] 张正延. 高Nb低碳钢中Mo对纳米级析出相及组织性能的影响研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.Zhang Zhengyan. Effect of Mo on the nanometer-sized precipitates, microstructure and properties of high Nb low carbon steel[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. [3] Li Jing, Yuan Shaoqiang, Chu Xiangzhi. Dissolution behavior of second phase in Nb-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Foundre Technology, 2017,38(9):2087−2089,2095. (李敬, 苑少强, 褚祥治. Nb-Ti微合金钢中第二相的溶解行为[J]. 铸造技术, 2017,38(9):2087−2089,2095.Li Jing, Yuan Shaoqiang, Chu Xiangzhi. Dissolution behavior of second phase in Nb-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Foundre Technology, 2017, 38(9): 2087-2089, 2095. [4] Yang Qing, Zhang Liwen, Zhang Chi, et al. Austenite grain growth behavior of low carbon Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel X70[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(4):1−5. (杨清, 张立文, 张驰, 等. 低碳Nb-V-Ti微合金钢X70的奥氏体晶粒长大行为[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(4):1−5.Yang Qing, Zhang Liwen, Zhang Chi, et al. Austenite grain growth behavior of low carbon Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel X70[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(4): 1-5. [5] Chen Xin, Liu Chunming. Effects of V and Mo on precipitation of second phase in microalloyed bainite steel[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2011,10(3):209−211,236. (陈昕, 刘春明. 钒和钼对微合金化贝氏体钢第二相析出的影响[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2011,10(3):209−211,236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.03.012Chen Xin, Liu Chunming. Effects of V and Mo on precipitation of second phase in microalloyed bainite steel[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2011, 10(3): 209-211, 236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.03.012 [6] Zhou Dan, Chai Xiyang, Liang Fengrui, et al. Influence of V, V-N and V-Nb microalloying on microstructure and properties of high strength steel for shipbuilding[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(6):60−64. (周丹, 柴希阳, 梁丰瑞, 等. V, V-N与V-Nb微合金化对高强船板钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(6):60−64.Zhou Dan, Chai Xiyang, Liang Fengrui, et al. Influence of V, V-N and V-Nb microalloying on microstructure and properties of high strength steel for shipbuilding[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(6): 60-64. [7] Fang Fang, Yong Qilong, Yang Caifu, et al. Precipitating kinetics of V(C, N) in ferrite of V-N microalloying steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009,45(5):625−629. (方芳, 雍岐龙, 杨才福, 等. V(C, N)在V-N微合金钢铁素体中的析出动力学[J]. 金属学报, 2009,45(5):625−629. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.05.019Fang Fang, Yong Qilong, Yang Caifu, et al. Precipitating kinetics of V(C, N) in ferrite of V-N microalloying steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(5): 625-629. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.05.019 [8] Zhao Mengjing, Wang Feng, Xi Xiaojun, et al. Effect of Y on inclusions characteristics and tensile properties in EH36 shipbuilding steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(7):61−67. (赵梦静, 王峰, 习小军, 等. 钇对EH36船板钢夹杂物特性和拉伸性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(7):61−67.Zhao Mengjing, Wang Feng, Xi Xiaojun, et al. Effect of Y on inclusions characteristics and tensile properties in EH36 shipbuilding steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(7): 61-67. [9] Zhou Yutao, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe, et al. Inclusions evolution of high-grade ship plate steel in practical production processes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(1):33−42. (周宇涛, 杨树峰, 李京社, 等. 高级别船板钢生产过程中夹杂物的演变规律[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(1):33−42.Zhou Yutao, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe, et al. Inclusions evolution of high-grade ship plate steel in practical production processes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(1): 33-42. [10] Wang Hongtao, Tian Yong, Ye Qibin, et al. Development of heavy ship plate in extremely cold environment[J]. Steel Rolling, 2018,35(5):48−53. (王红涛, 田勇, 叶其斌, 等. 极寒环境下厚规格船舶用钢的发展[J]. 轧钢, 2018,35(5):48−53.Wang Hongtao, Tian Yong, Ye Qibin, et al. Development of heavy ship plate in extremely cold environment[J]. Steel Rolling, 2018, 35(5): 48-53. [11] Yang Kaisheng. Effect of heat treatment process and NbV-N microalloying on mechanical property and microstructure of grade ship plate steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017,27(10):34−39. (阳开生. 热处理及NbV-N微合金化对船板钢组织性能的影响[J]. 中国冶金, 2017,27(10):34−39.Yang Kaisheng. Effect of heat treatment process and NbV-N microalloying on mechanical property and microstructure of grade ship plate steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017, 27(10): 34-39. [12] Vanovsek W, Bernhard C, Fiedler M, et al. Effect of titanium on the solidification and postsolidification microstructure of high-strength steel welds[J]. Welding in the World, 2013,57(5):665−674. doi: 10.1007/s40194-013-0063-1 [13] Zou X D, Zhao D P, Sun J C, et al. An integrated study on the evolution of inclusions in EH36 shipbuilding steel with Mg addition: From casting to welding[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, B, 2018,49(2):481−489. doi: 10.1007/s11663-017-1163-x [14] Wang Bingxing, Wu Zhongzi, Lou Haonan, et al. Effect of oxide metallurgy on microstructure and properties of HAZ in EH36 Steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(2):239−246. (王丙兴, 武仲子, 娄号南, 等. 氧化物冶金工艺对EH36钢HAZ组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(2):239−246.Wang Bingxing, Wu Zhongzi, Lou Haonan, et al. Effect of oxide metallurgy on microstructure and properties of HAZ in EH36 Steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019, 31(2): 239-246. [15] Shi Minghao, Duan Zhengtao, Zhang Pengyan, et al. Effect of inclusions on formation of acicular ferrite in Ti and Zr micro-alloying steel[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2012,33(10):1424−1427. (石明浩, 段争涛, 张朋彦, 等. 夹杂物对Ti, Zr微合金钢中针状铁素体形成的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,33(10):1424−1427. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2012.10.014Shi Minghao, Duan Zhengtao, Zhang Pengyan, et al. Effect of inclusions on formation of acicular ferrite in Ti and Zr micro-alloying steel[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2012, 33(10): 1424-1427. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2012.10.014 [16] Adrian H. Thermodynamic model for precipitation of carbonitrides in high strength low alloy steels containing up to three microalloying elements with or without additions of aluminium[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1992,8(5):406−420. doi: 10.1179/mst.1992.8.5.406 [17] Zhang Ke, Sun Xinjun, Zhang Mingya, et al. Kinetics of (Ti, V, Mo)C precipitated in γ/α matrix of Ti-V-Mo complex microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2018,54(8):1122−1130. (张可, 孙新军, 张明亚, 等. Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ/α中沉淀析出的动力学[J]. 金属学报, 2018,54(8):1122−1130. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00011Zhang Ke, Sun Xinjun, Zhang Mingya, et al. Kinetics of (Ti, V, Mo)C precipitated in γ/α matrix of Ti-V-Mo complex microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2018, 54(8): 1122-1130. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00011 [18] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006.Yong Qilong. Second phase in iron and steel materials [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006. [19] Wang X J, Sun X J, Song C, et al. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical properties during solution treatment of a Ti–V–Mo-containing high-manganese cryogenic steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018,135:287−294. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.11.054 [20] Duan Xiugang, Cai Qingwu, Wu Huibin, et al. Precipitation law of ultra fine carbides in ferrite matrix Ti-Mo micro-alloy steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012,34(6):644−650. (段修刚, 蔡庆伍, 武会宾, 等. 铁素体基Ti-Mo微合金钢超细碳化物析出规律[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2012,34(6):644−650.Duan Xiugang, Cai Qingwu, Wu Huibin, et al. Precipitation law of ultra fine carbides in ferrite matrix Ti-Mo micro-alloy steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012, 34(6): 644-650. -




 下载:
下载: