Research on Johnson-Cook constitutive model of 06Cr19Ni10 austenitic stainless steel at high strain rate
-
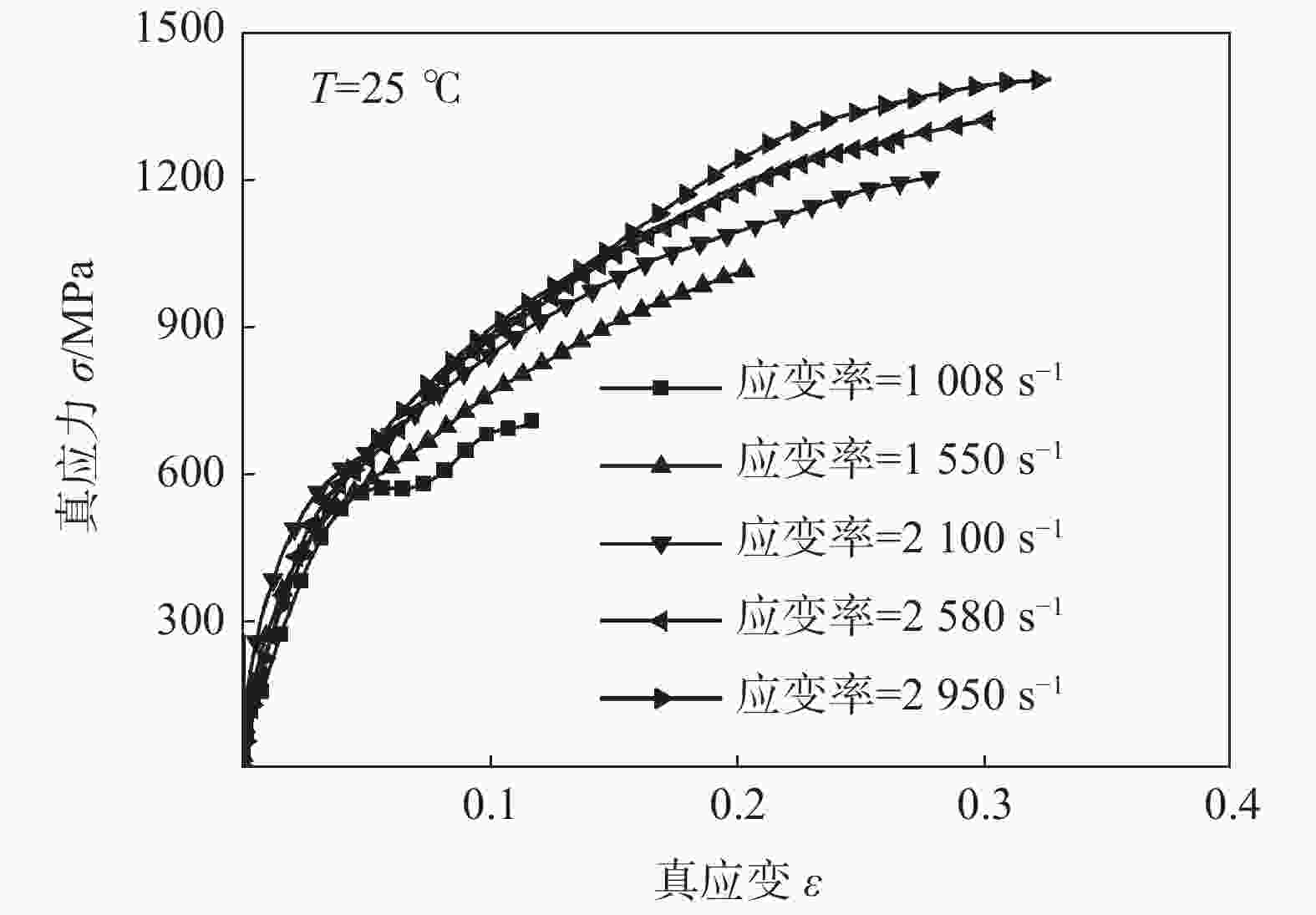
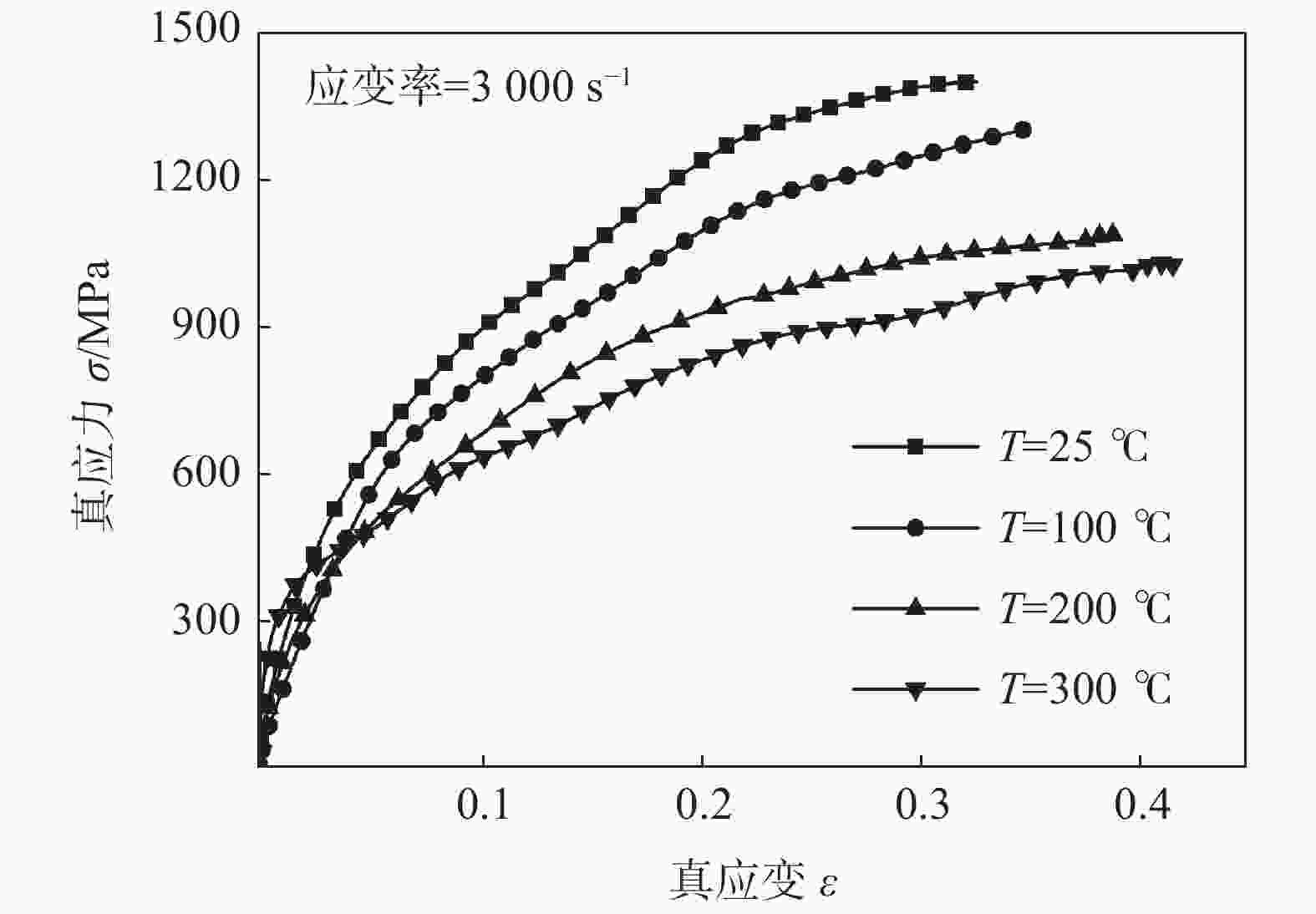
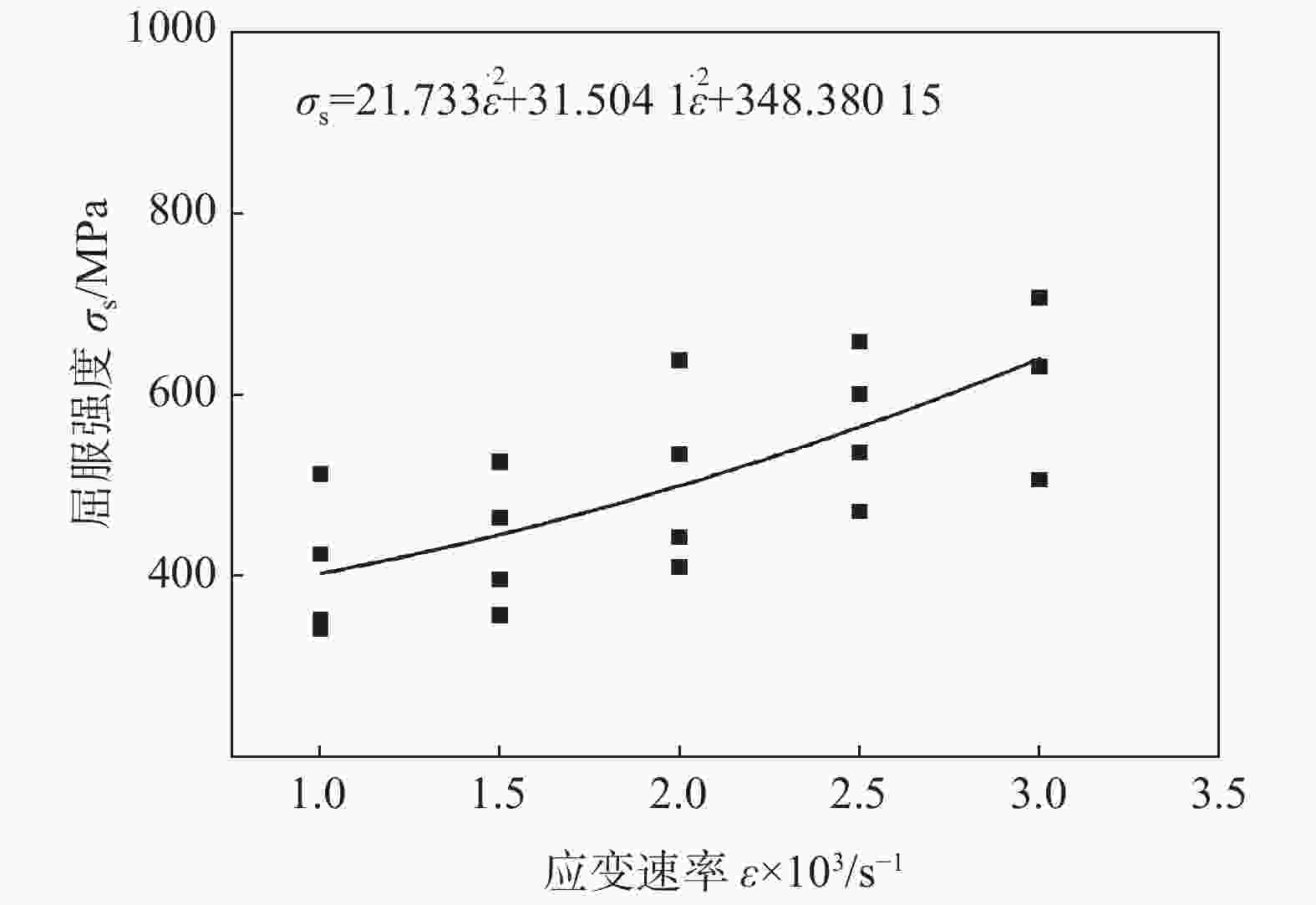
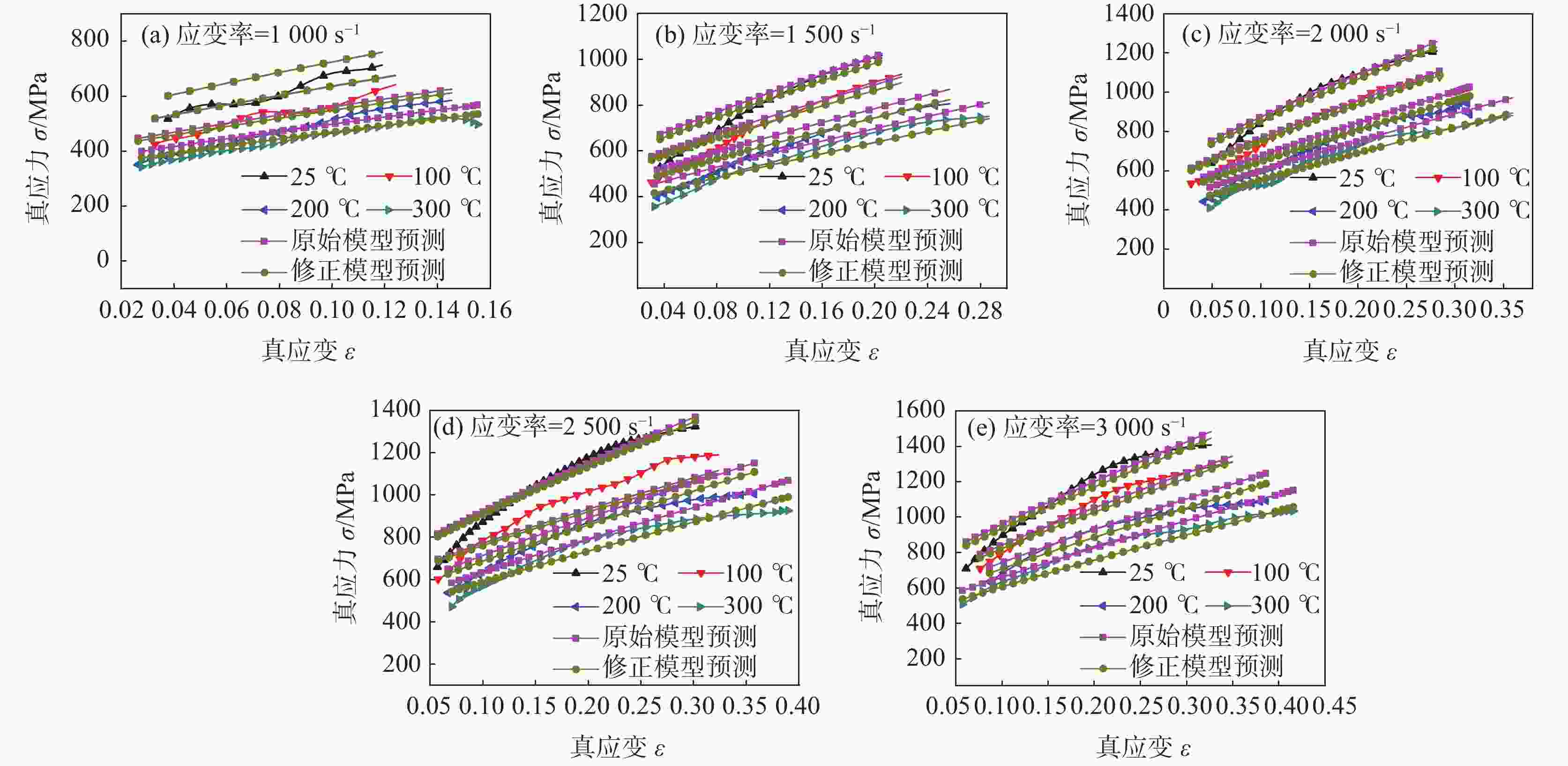
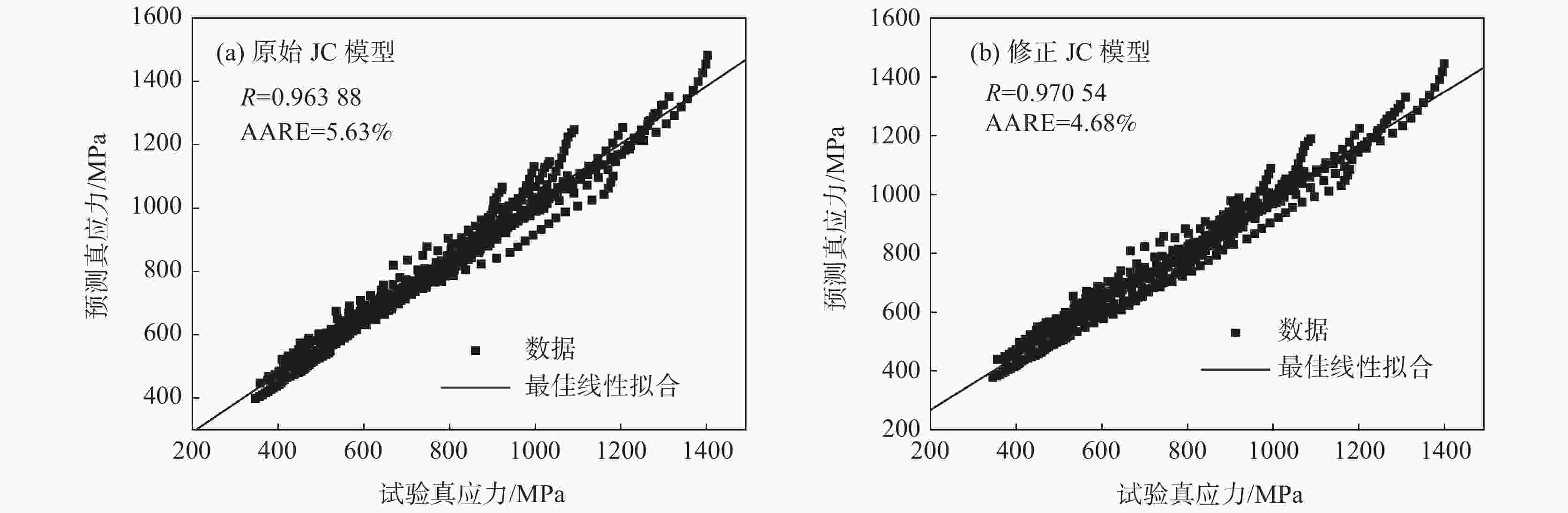
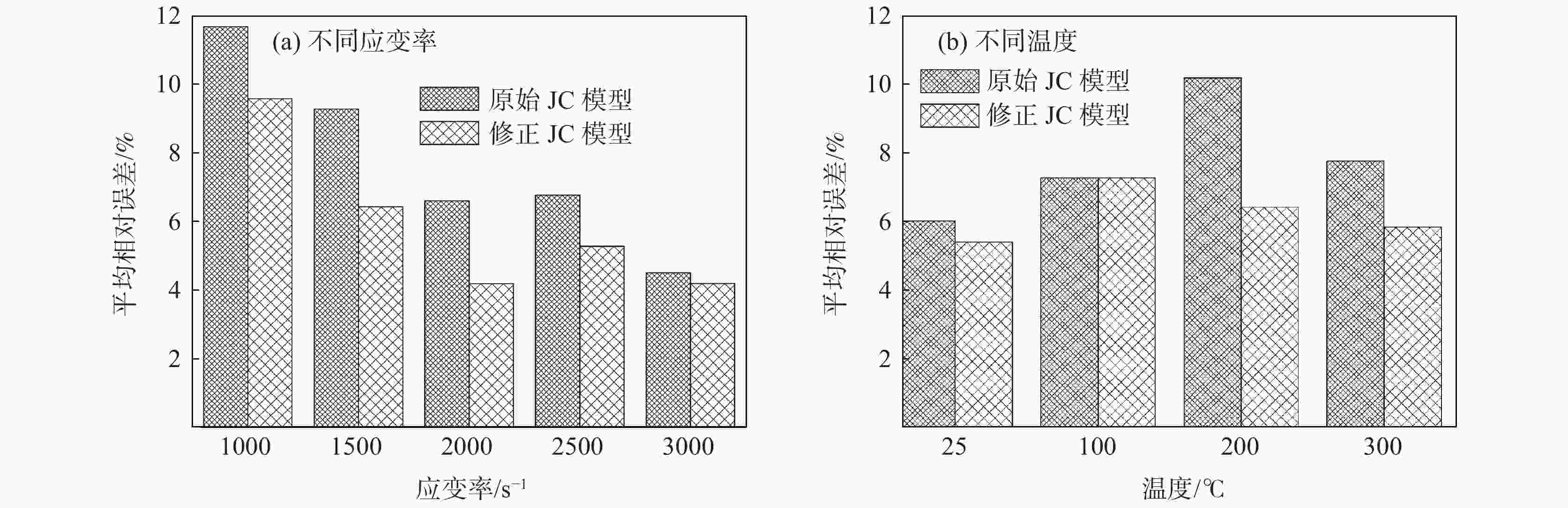
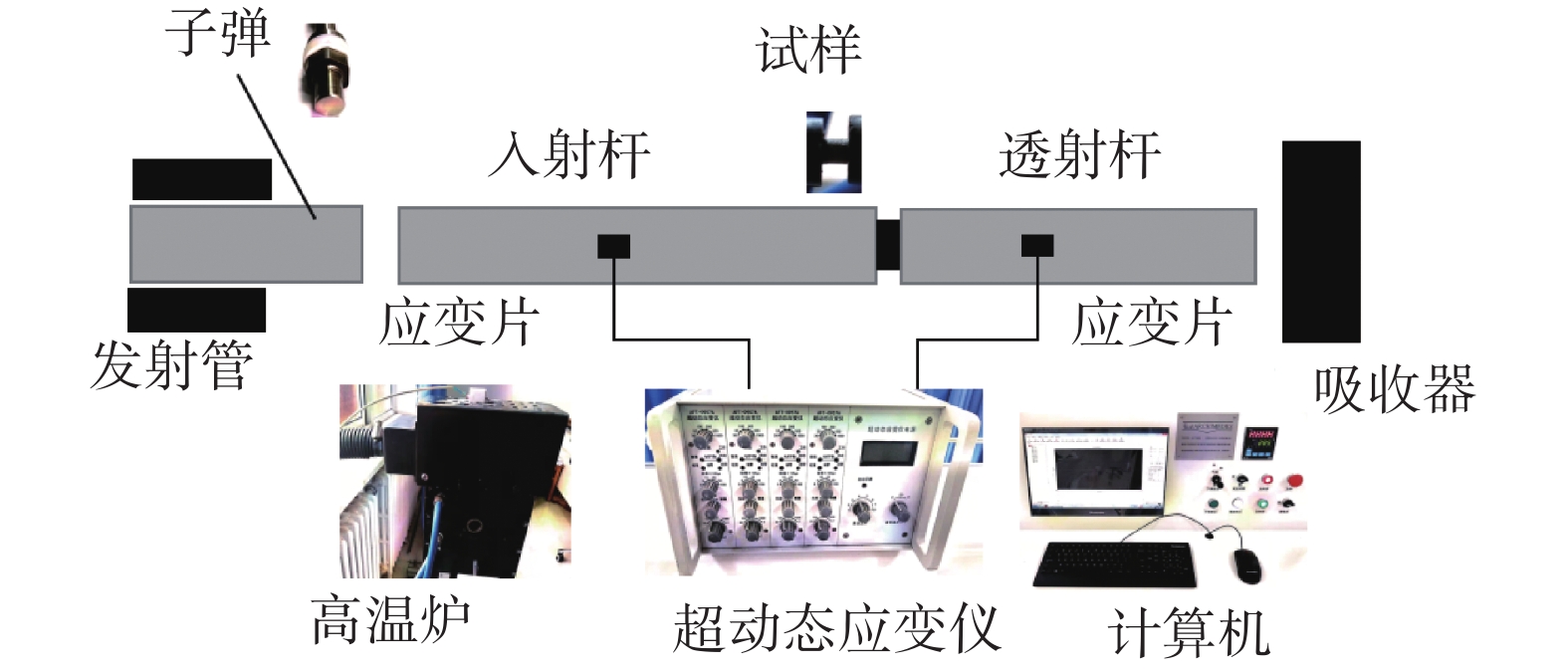
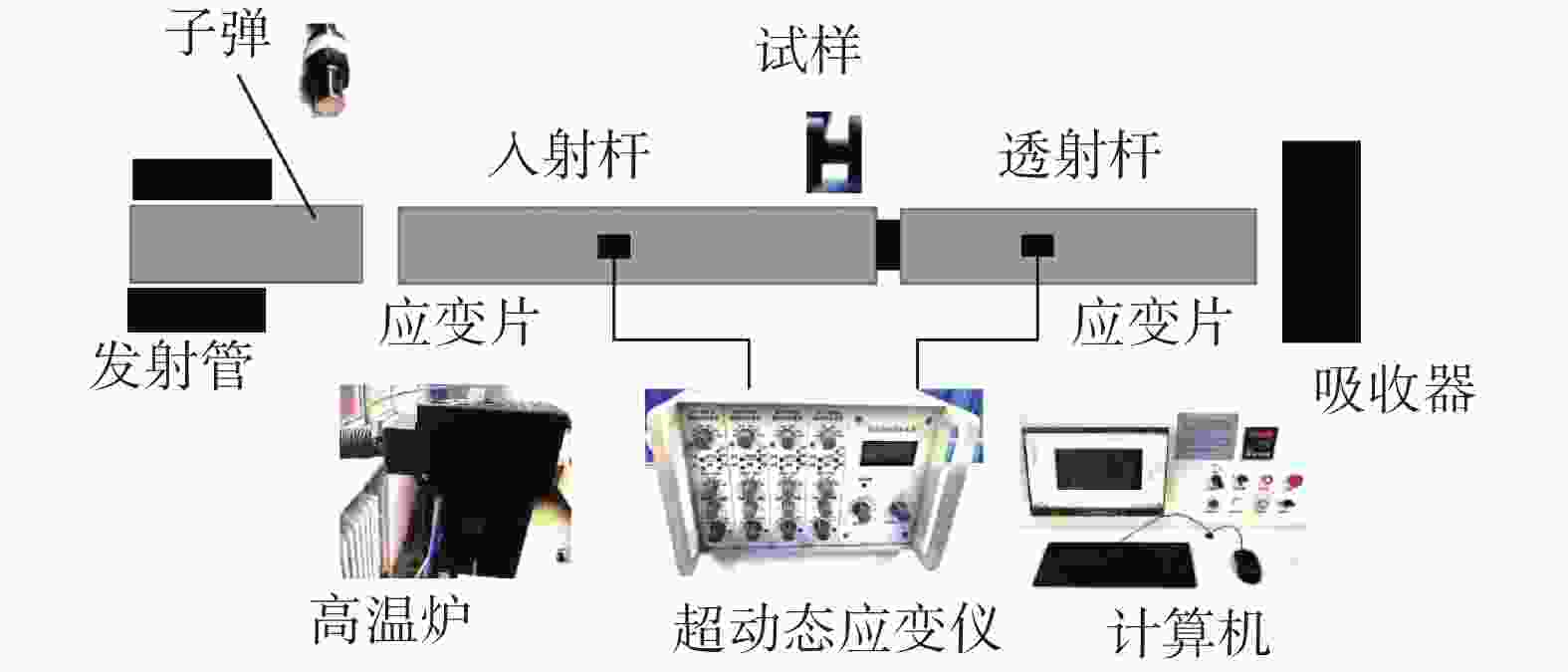
摘要: 为了探讨06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢在大应变和高应变率下成形的流动规律,借助高温分离式霍普金森(High Temperature Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar)动态试验装置,进行不同温度和应变率冲击试验。分析试验数据表明,该材料具有增塑、应变率强化和温度软化现象,并建立了Johnson-Cook本构模型。考虑应变率强化效应,依据试验数据进行了JC本构模型的修正,对比修正前后模型预测值和试验值,吻合程度好。运用统计分析,对比修正前后模型的相关系数(R)和平均相对误差(AARE),修正前、后相关系数(R)分别为0.96388、0.97054;修正前、后平均相对误差(AARE)分别为5.63%、4.68%,修正后的模型预测精度优于修正前。结果表明,修正后的模型可以更加精确预测06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢应力与应变、应变率和温度的关系。Abstract: In order to explore the flow behavior of 06Cr19Ni10 austenitic stainless steel under large strain and high strain rate forming, impact tests had been carried out under different temperature and strain rate with the help of high temperature split hopkinson pressure bar dynamic experimental device. Impact test results show that the material has plasticization, strain rate strengthening and temperature softening phenomena, and the Johnson-Cook (JC) constitutive model has been established. Taking into account the strain rate strengthening effect the JC constitutive model was modified and both the model prediction values before and after the correction showed good agreement with experimental value. The correlation coefficients (R) before and after the model correction were 0.963 88 and 0.970 54, respectively, and the average relative error (AARE) before and after the correction were 5.63 %, 4.68 %, respectively. This indicated that the revised model achieved better prediction accuracy than origin model. The revised model could be used to predict the relationship among stress, strain, strain rate and temperature of 06Cr19Ni10 austenitic stainless steel more accurately.
-
图 9
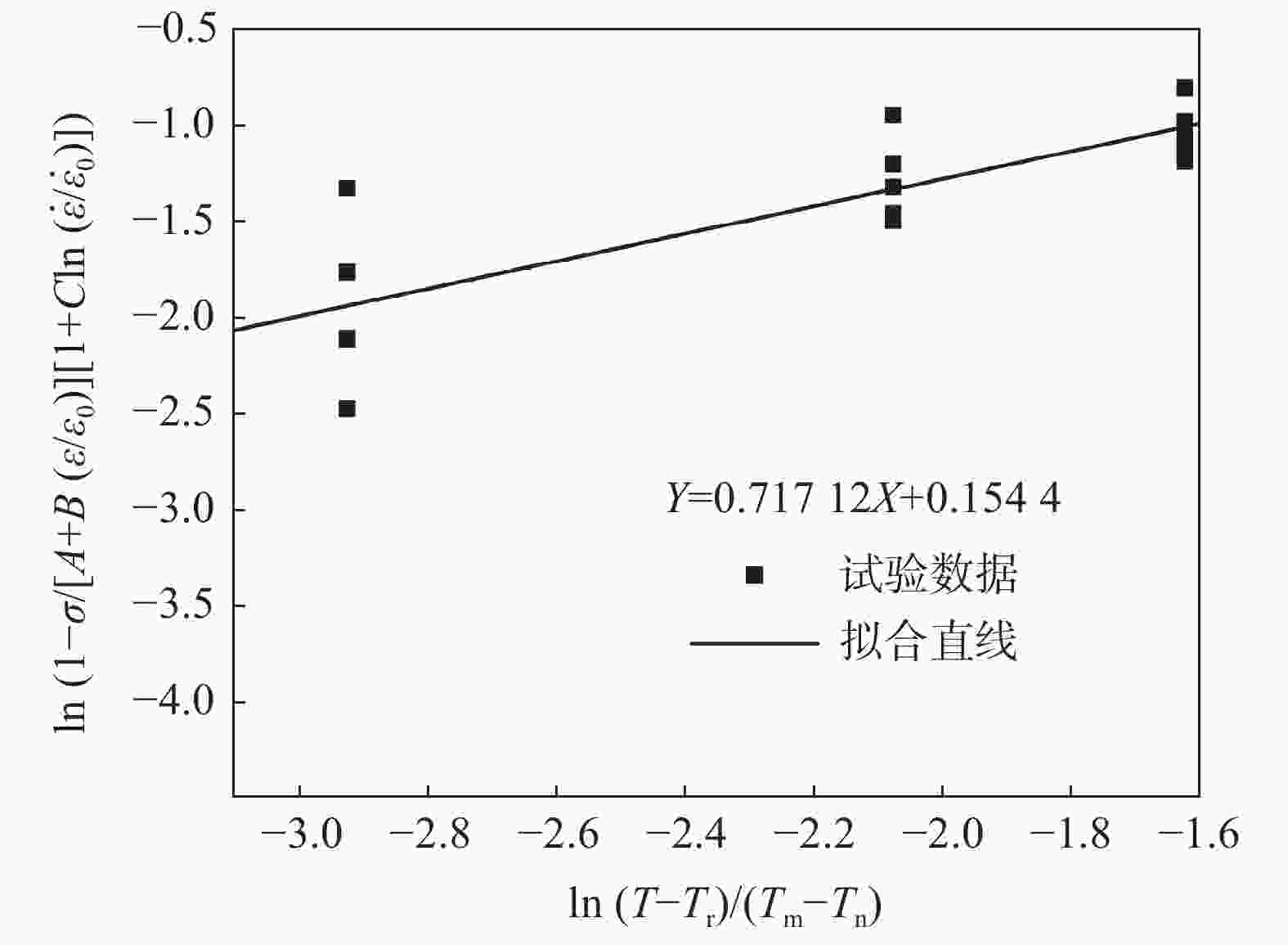
$ \ln (1 - \sigma /[A + B(\varepsilon /{\varepsilon _0})][1 + C\ln (\dot \varepsilon /{\dot \varepsilon _0})]) $ 和$ \ln [(T - {T_{\text{r}}})/({T_{\text{m}}} - {T_{\text{n}}})] $ 的关系Figure 9. Relationship between
$ \sigma /[A + B(\varepsilon /{\varepsilon _0})] - 1 $ and ln$ [(T - {T_{\text{r}}})/({T_{\text{m}}} - {T_{\text{n}}})] $ 图 11
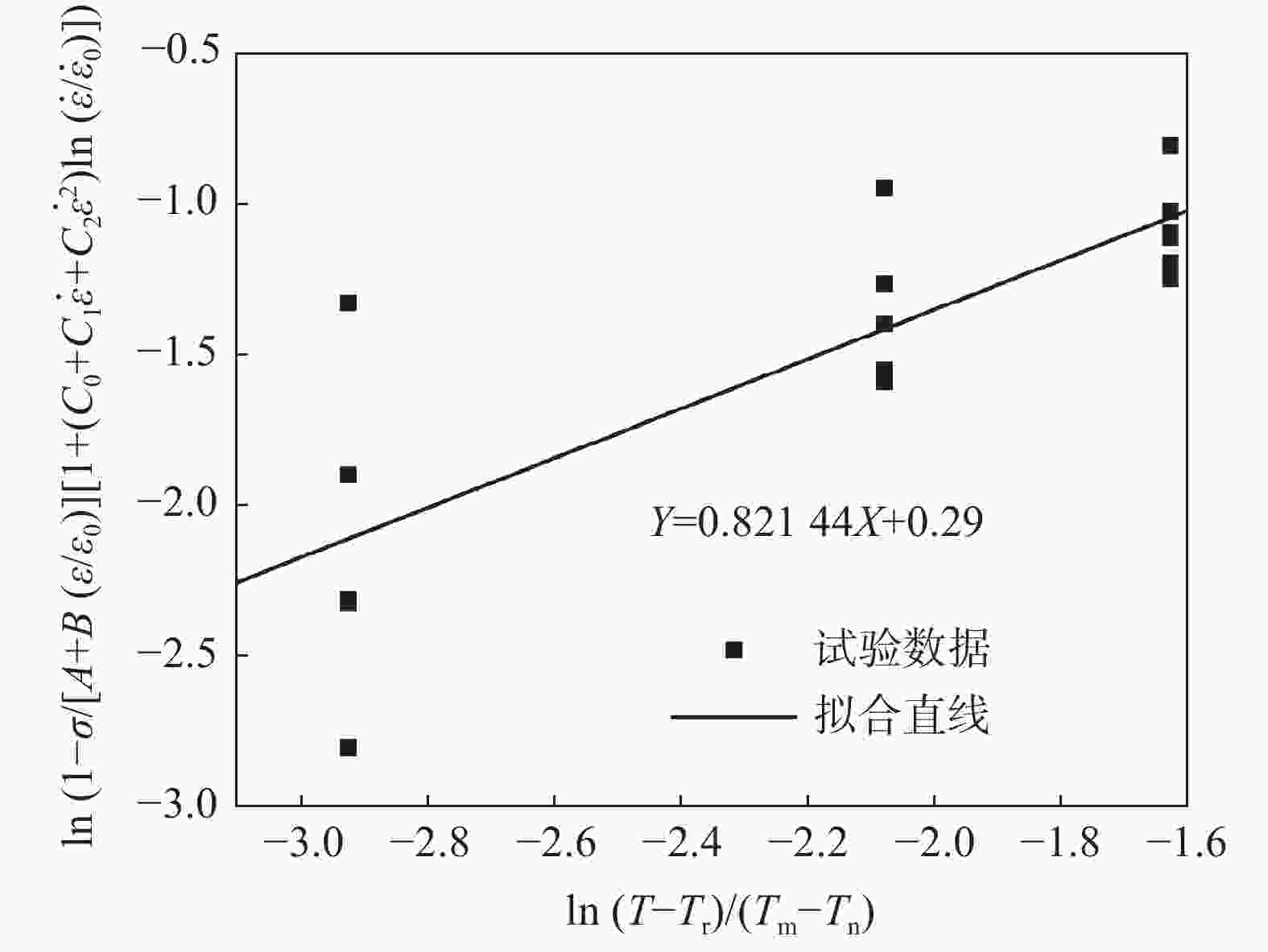
$ \mathrm{ln}(1-\sigma /[A+B(\varepsilon /{\varepsilon }_{0})][1+({C}_{0}+{C}_{1}\dot{\varepsilon }+{C}_{2}{\dot{\varepsilon }}_{2}) $ $\mathrm{ln}(\dot{\varepsilon }/{\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0})]) $ 和$ \ln [(T - {T_{\text{r}}})/({T_{\text{m}}} - {T_{\text{n}}})] $ 的关系Figure 11. Relationship between
$ \mathrm{ln}(1-\sigma /[A+B(\varepsilon /{\varepsilon }_{0})][1+ $ $({C}_{0}+{C}_{1}\dot{\varepsilon }+{C}_{2}{\dot{\varepsilon }}_{2})\mathrm{ln}(\dot{\varepsilon }/{\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0})]) $ and$ \ln [(T - {T_{\text{r}}})/$ $({T_{\text{m}}} - {T_{\text{n}}}) $ ]表 1 06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 06Cr19Ni10 stainless steel
% C Si Mn P S Ni Cr Fe 0.08 0.75 2.00 0.045 0.03 8.22 18.89 Bal 表 2 Johnson-Cook模型参数
Table 2. Parameters for the Johnson-Cook model
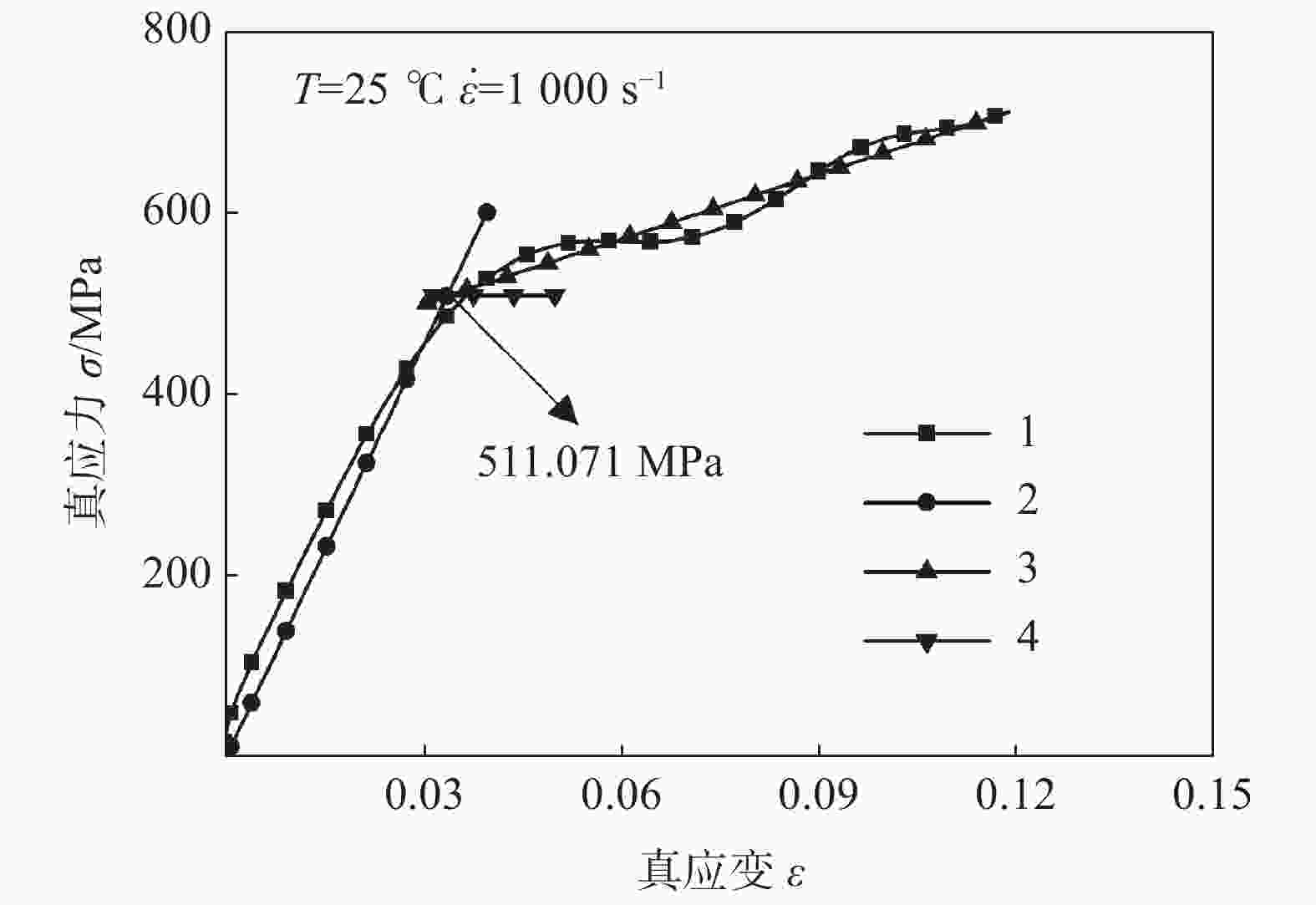
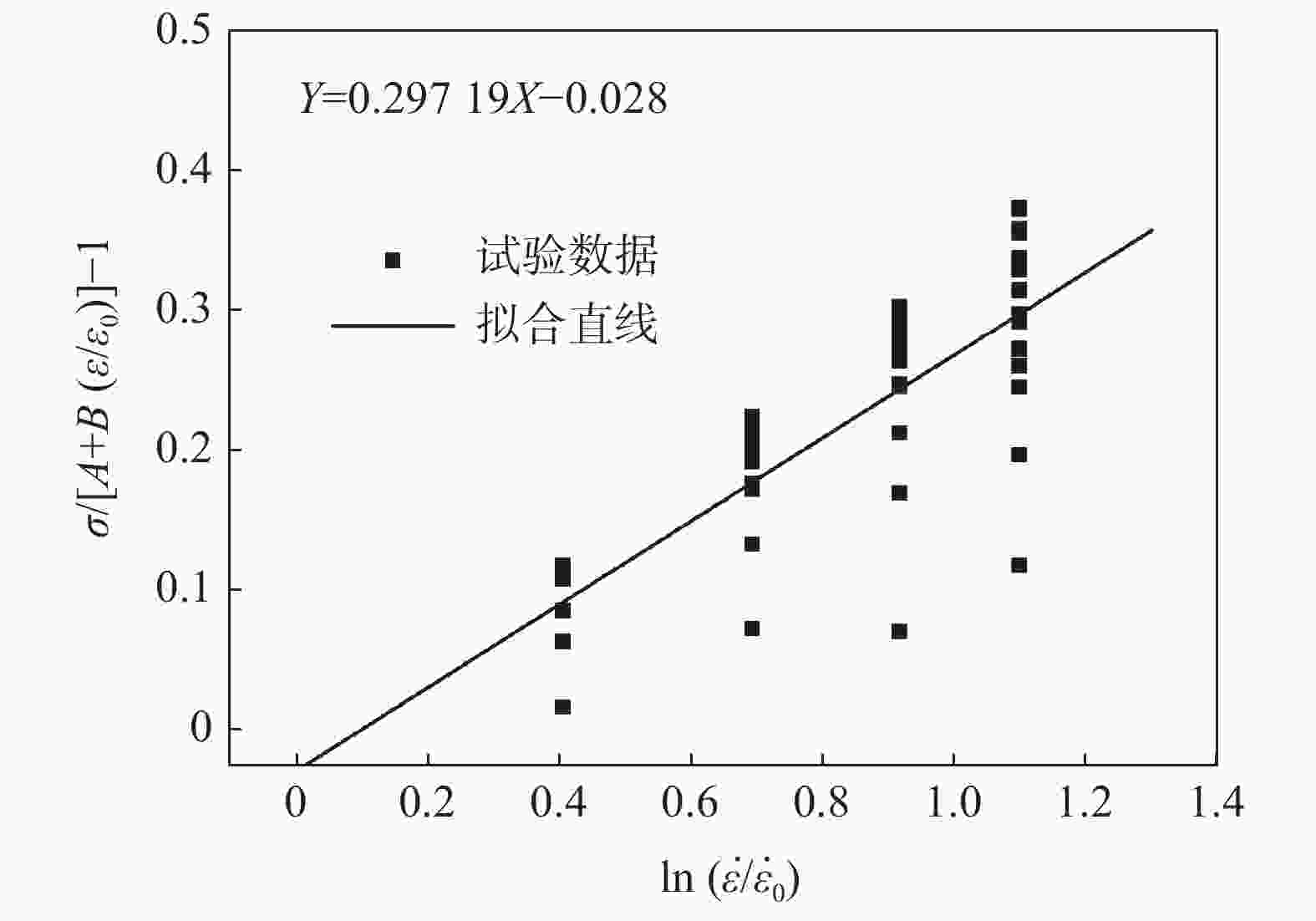
A/MPa B/MPa n C m 511.071 1629.9751 0.88228 0.29719 0.71712 表 3 修正Johnson-Cook模型参数
Table 3. Modified Johnson-Cook model parameters
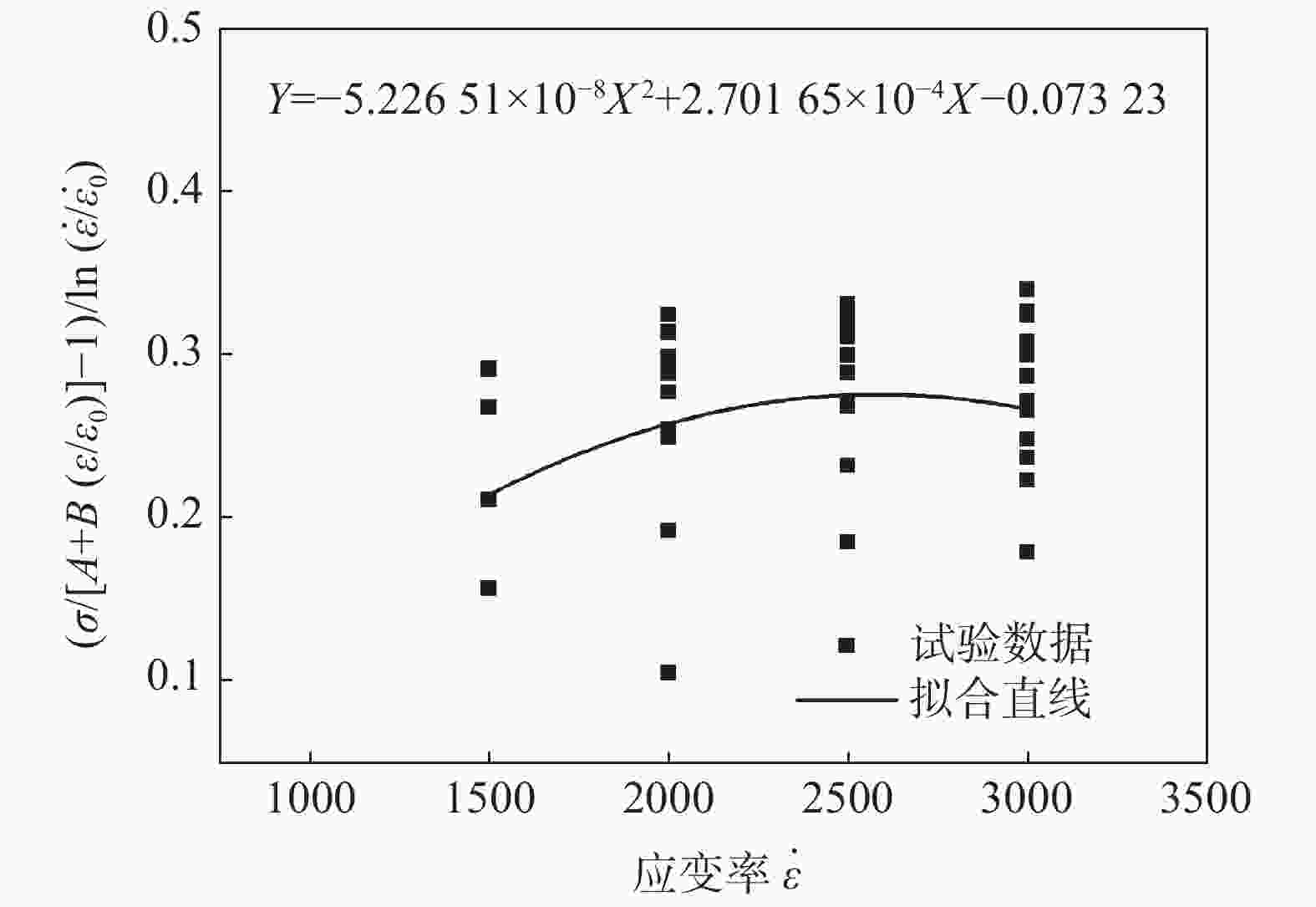
A/MPa B/MPa C0 C1 C2 m D 511.071 1629.9751 −5.22651×10−8 2.70165×10−4 −0.07323 0.82144 1.33643 -
[1] 周芳娟. 304不锈钢切削加工表面特性的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014.Zhou Fangjuan. Research on machined surface characteristics of 304 stainless steel[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2014. [2] 李星星. 304不锈钢本构模型参数识别研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012.Li Xingxing. Research on the constitutive model parameters identification of 304 stainless steel[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012. [3] Mei Rong, Ren Zhijun, Qiu Wei. Hot deformation behavior of 06Cr18Ni11Ti austenitic stainless steell[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2019,42(6):88−92. (梅荣, 任志俊, 仇伟. 06Cr18Ni11Ti奥氏体不锈钢热变形行为研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2019,42(6):88−92.Mei Rong, Ren Zhijun, Chou Wei. Hot deformation behavior of 06 Cr18 Ni11 Ti austenitic stainless steell[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2019, 42(6): 88-92. [4] Li Kai, Xue He, Cui Yinghao, et al. Establishment and validation of stress-strain constitutive equation during cold working of 304 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2019,26(2):225−232. (李凯, 薛河, 崔英浩, 等. 304不锈钢冷加工过程中应力-应变本构方程的建立与验证[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2019,26(2):225−232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2019.02.030Li Kai, Xue He, Cui Yinghao, et al. Establishment and validation of stress-strain constitutive equation during cold working of 304 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2019, 26(2): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2019.02.030 [5] Ma Yonglin, Li Zhifeng, Xing Shuqing, et al. Effect of annealing tension on mechanical properties and residual stress of cold rolled SUS304 stainless steel strips[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2014,21(5):116−120. (麻永林, 李志峰, 邢淑清, 等. 退火张力对冷轧 SUS304 不锈钢带力学性能和残余应力的影响[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2014,21(5):116−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2014.05.022Ma Yonglin, Li Zhifeng, Xing Shuqing, et al. Effect of annealing tension on mechanical properties and residual stress of cold rolled SUS304 stainless steel strips[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2014, 21(5): 116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2014.05.022 [6] Zheng Baofeng, Shu Ganping, Shen Xiaoming. Experimental study on mechanical properties of stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Steel Structure, 2011,26(5):1−6. (郑宝锋, 舒赣平, 沈晓明. 不锈钢材料常温力学性能实验研究[J]. 钢结构, 2011,26(5):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2011.05.001Zheng Baofeng, Shu Ganping, Shen Xiaoming. Experimental study on mechanical properties of stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Steel Structure, 2011, 26(5): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2011.05.001 [7] Ma Bin, Li Ping, Liang Qiang. Comparison on high-temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021,45(1):92−99. (马斌, 李平, 梁强. 基于修正JC模型和BP-ANN算法预测HNi55-7-4-2合金高温流变行为的对比[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021,45(1):92−99. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202101015Ma Bing, Li Ping, Liang Qiang. Comparison on high-temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 45(1): 92-99. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202101015 [8] Peng Xiaona, Guo Hongzhen, Shi Zhifeng, et al. Constitutive quations for high temperature flow stress of TC4-DT alloy incorporating strain, strain rate and temperature[J]. Materials and Design, 2013,50:198−206. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.009 [9] Khan A S, Huang S. Experimental and theoretical study of mechanical behavior of 1100 aluminum in the strain rate range 10-5-104 s-1[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1992,8:397−424. doi: 10.1016/0749-6419(92)90057-J [10] Lin Y C, Chen X M. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working[J]. Materials & Design, 2011,32(4):1733−1759. [11] Wu Liang, Hu Yisen, Song Kun, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive model of FV520B martensitic precipitation-hardening steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2018,40(3):584−588. (吴亮, 胡毅森, 宋鹍, 等. 马氏体沉淀硬化不锈钢 FV520B 动态力学性能及本构模型的研究[J]. 机械强度, 2018,40(3):584−588.Wu Liang, Hu Yiseng, Song Kun, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive model of FV520 B martensitic precipitation-hardening steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2018, 40(3): 584-588. [12] Shang Bing, Sheng Jing, Wang Baozhen, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of stainless steel materials[J]. Explosion and Shock, 2008,28(6):527−531. (尚兵, 盛精, 王宝珍, 等. 不锈钢材料的动态力学性能及本构模型[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008,28(6):527−531. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.06.008Shang Bing, Sheng Jing, Wang Baozhen, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of stainless steel materials [J]. Explosion and Shock, 2008, 28(6): 527-531. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.06.008 [13] Yan Qiushi, Sun Bowen, Yang Lu. Study on dynamic mechanical behavior of structural stainless steel at elevated temperature and high strain rate[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019,47(5):128−132. (闫秋实, 孙博文, 杨璐. 高温高应变率下建筑不锈钢动态力学性能研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,47(5):128−132. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.190524Yan Qiushi, Sun Bowen, Yang Lu. Study on dynamic mechanical behavior of structural stainless steel at elevated temperature and high strain rate[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(5): 128-132. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.190524 [14] Bao Zhiqiang, Zhang Yong, Zhang Zhuzhu, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and J-C constitutive model for 38CrMoAl high strength steel[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021,45(5):76−83. (包志强, 张勇, 张柱柱, 等. 38CrMoAl高强度钢动态力学性能及其J-C本构模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021,45(5):76−83. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202105014Bao Zhiqiang, Zhang Yong, Zhang Zhuzhu, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and J-C constitutive model for 38 CrMoAl high strength steel[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 45(5): 76-83. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202105014 [15] Wang Jiabin, Ding Jun, Song Kun, et al. Studied on dynamic stress response of 20CrMnTi steel under impact load and considered for adiabatic temperatuer rise modification of the J-C constitutive model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2019,41(5):1066−1070. (王佳斌, 丁军, 宋鹍, 等. 冲击载荷下20CrMnTi钢动态应力响应与考虑绝热温升修正J-C本构模型研究[J]. 机械强度, 2019,41(5):1066−1070.Wang Jiabin, Ding Jun, Song Kun, et al. Studied on dynamic stress response of 20 CrMnTi steel under impact load and considered for adiabatic temperatuer rise modification of the J-C constitutive model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2019, 41(5): 1066-1070. [16] Bao Weiping, Ren Xueping, Zhang Yi. The characteristics of flow stress and dynamic constitutive model at high strain rates for pure iron[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2009,16(5):125−129. (包卫平, 任学平, 张毅. 纯铁在高应变率下的流动应力特征及其动态塑性本构关系[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2009,16(5):125−129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2009.05.024Bao Weiping, Ren Xueping, Zhang Yi. The characteristics of flow stress and dynamic constitutive model at high strain rates for pure iron[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2009, 16(5): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2009.05.024 [17] Zhu Jinhua, Xue Jinxue, Ling Yuanfei, et al. The dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 1020 steel[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University(Natural Science), 2016,35(6):841−847. (朱金华, 薛进学, 凌远非, 等. 20钢动态力学性能及本构模型的建立[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016,35(6):841−847. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2016.06.015Zhu Jinhua, Xue Jinxue, Ling Yuanfei, et al. The dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 1020 steel[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University(Natural Science), 2016, 35(6): 841-847. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2016.06.015 [18] Zhang Changqing, Xie Lansheng, Chen Minghe, et al. Dynamic mechanical property and plastic constitutive relation of TC4-DT Ti alloy under high strain rate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015,25(2):323−329. (张长清, 谢兰生, 陈明和, 等. 高应变率下TC4-DT钛合金的动态力学性能及塑性本构关系[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015,25(2):323−329. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.02.007Zhang Changqing, Xie Lanshen, Chen Minghe, et al. Dynamic mechanical property and plastic constitutive relation relation of TC4-DT Ti alloy under high strain rate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 323-329. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.02.007 [19] Bao Weiping, Zhao Yuzhen, Li Chunming, et al. Experimental research on the dynamic constitutive relation of pure iron at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010,46(4):74−79. (包卫平, 赵昱臻, 李春明, 等. 纯铁高温高应变率下的动态本构关系试验研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010,46(4):74−79. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.04.074Bao Weiping, Zhao Yuzhen, Li Chunming, et al. Experimental research on the dynamic constitutive relation of pure iron at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46 (4): 74-79. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.04.074 [20] Chen Gang, Wang Qingquan, Du Hongjun. Experimental study of dynamic mechanical property on S500MC steel[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2019,47(5):27−30. (陈刚, 王青权, 杜洪军. S500MC钢动态力学性能试验研究[J]. 铁道技术监督, 2019,47(5):27−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2019.05.008Chen Gang, Wang Qingquan, Du Hongjun. Experimental study of dynamic mechanical property on S500 MC steel[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2019, 47(5): 27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2019.05.008 [21] Hui Xulong, Bai Chunyu, Ge Yujing, et al. Dynamic properties of 2A16 aluminum alloy under intermediate strain rate[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017,36(19):66−70. (惠旭龙, 白春玉, 葛宇静, 等. 2A16铝合金中应变率力学性能研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017,36(19):66−70.Hui Xulong, Bai Chunyu, Ge Yujing, et al. Dynamic properties of 2 A16 aluminum alloy under intermediate strain rate[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(19): 66-70. [22] Guo Pengchen, Li Jian, Cao Shufen, et al. Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of an AM80 magnesium alloy at large strain rate range[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018,38(3):586−595. (郭鹏程, 李健, 曹淑芬, 等. 大应变率范围内AM80镁合金的变形行为及组织演变[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018,38(3):586−595.Guo Pengchen, Li Jian, Cao Shufen, et al. Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of an AM80 magnesium alloy at large strain rate range[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 38(3): 586-595. [23] Qian Xinyuan, Peng Xuebing, Song Yuntao, et al. Dynamic constitutive relationship of CuCrZr alloy based on Johnson-Cook model[J]. Nuclear Materials and Energy, 2020,24(8):100768−100774. -




 下载:
下载: