Study on the occurrence state of substances in sublimation sulfur from the tail gas of acid hydrolysis of titanium concentrate
-
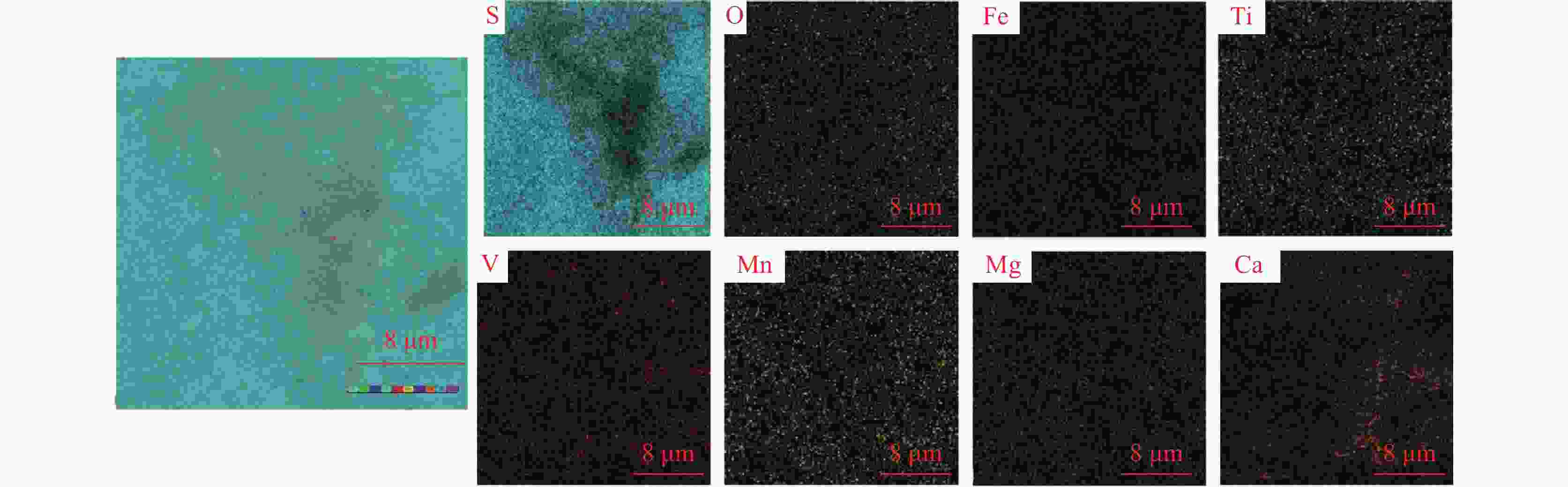
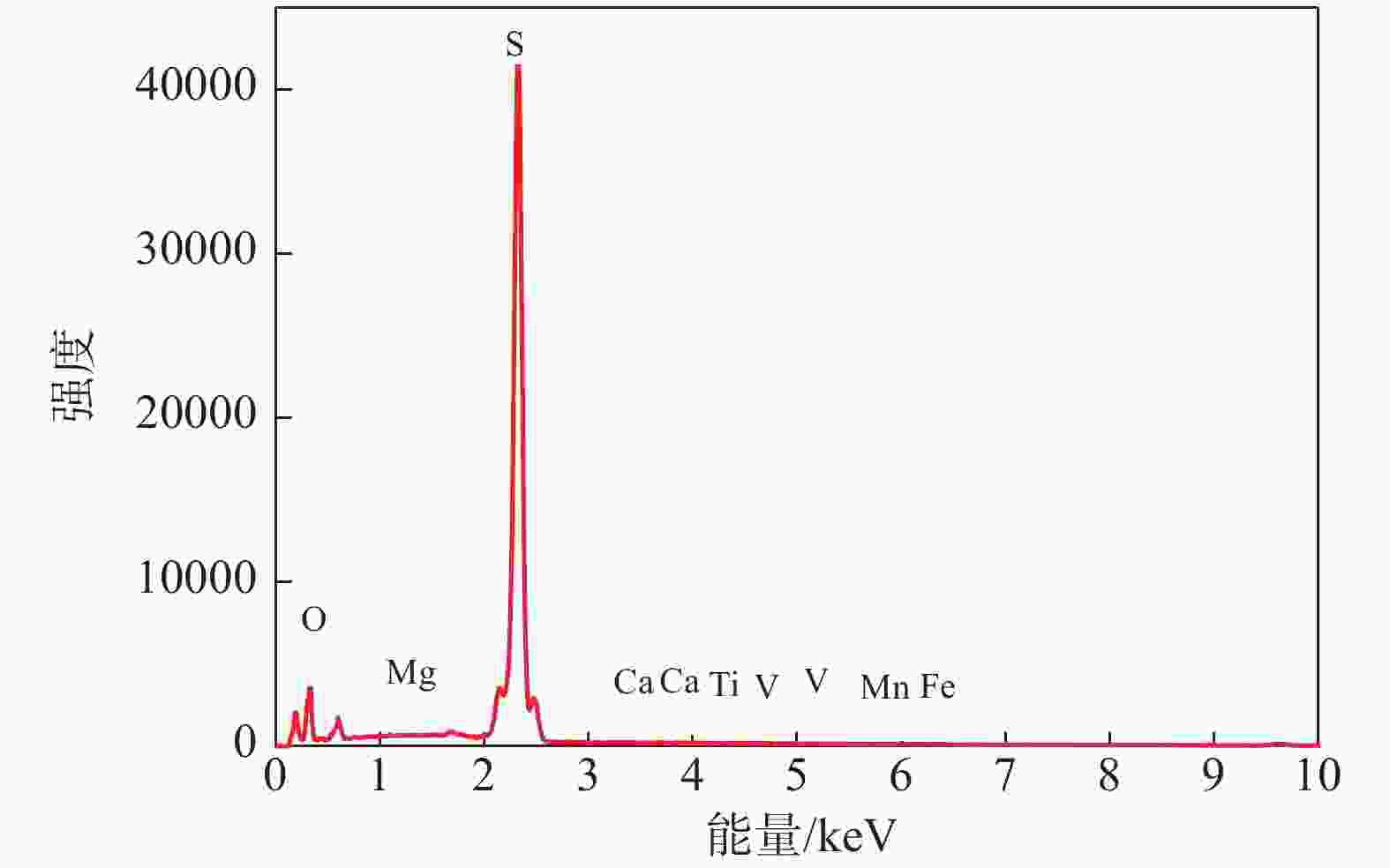
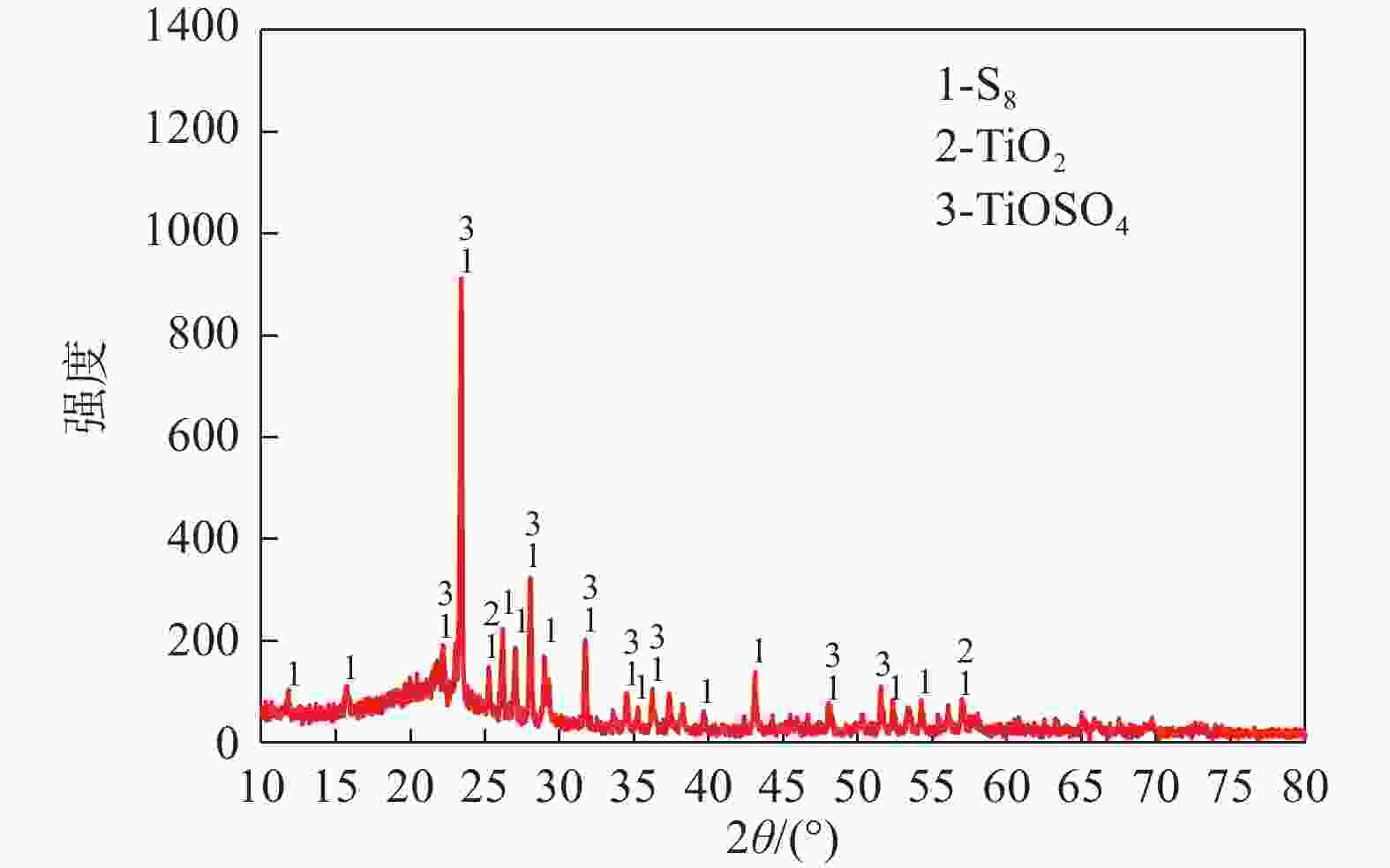
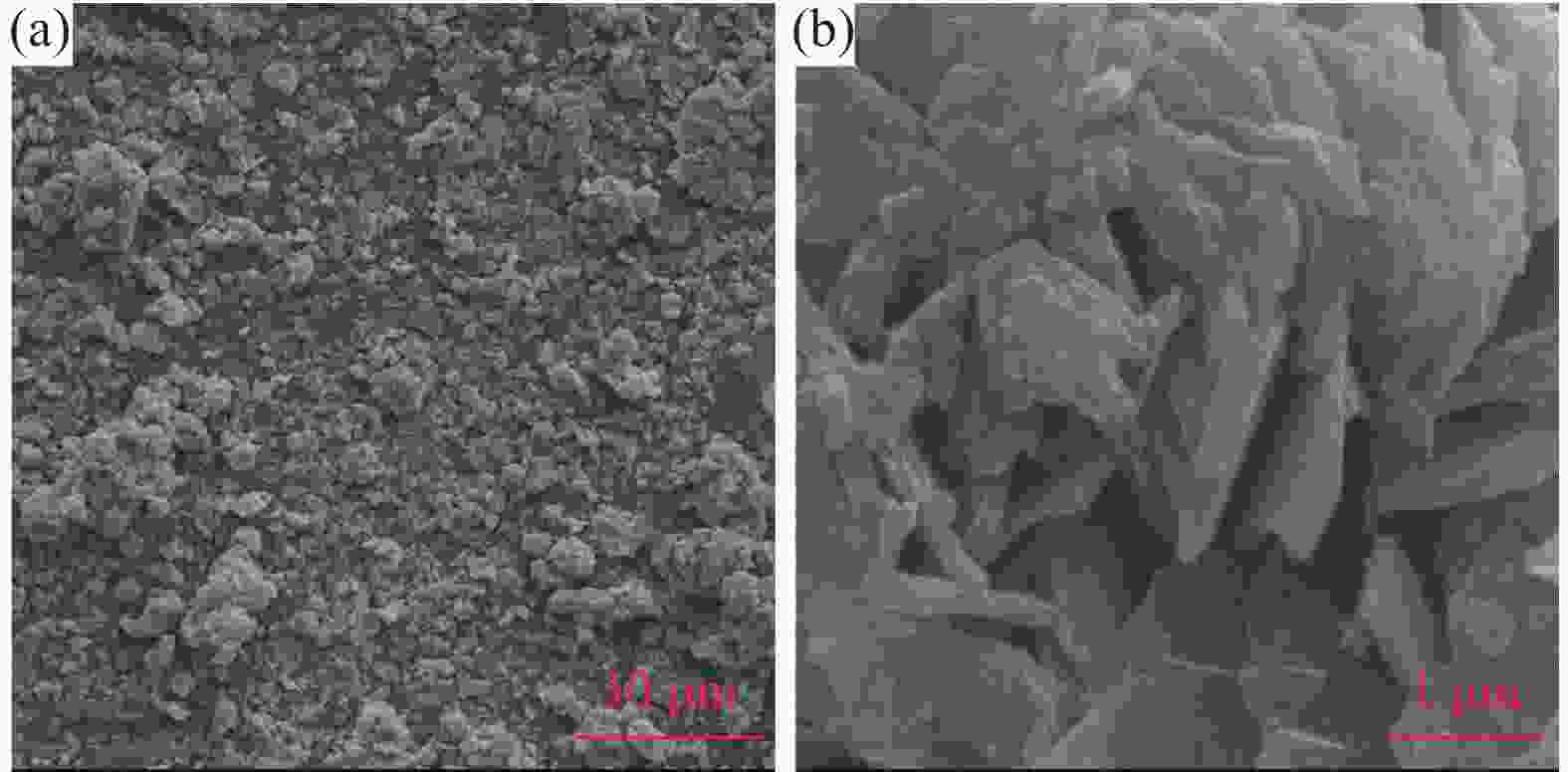
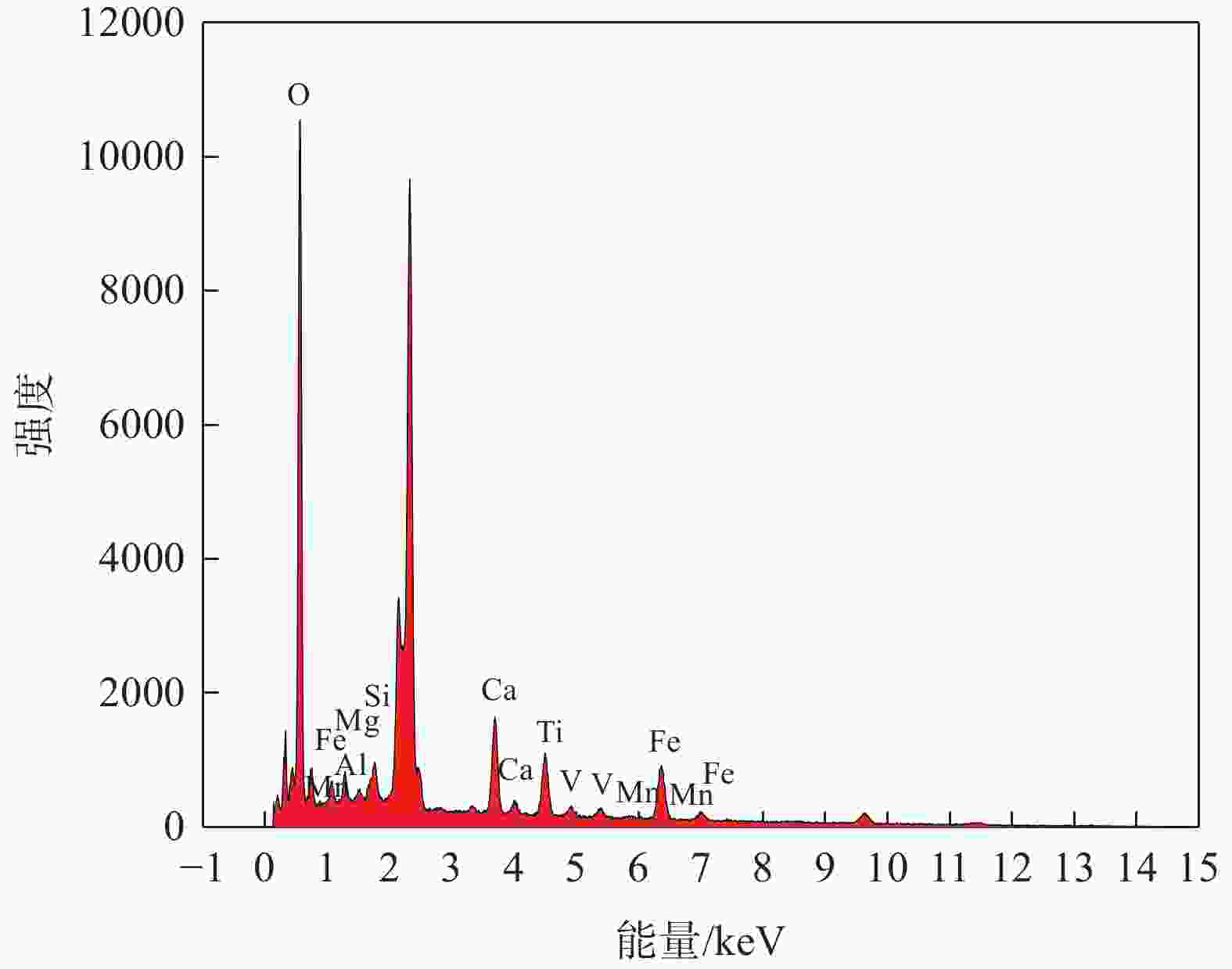
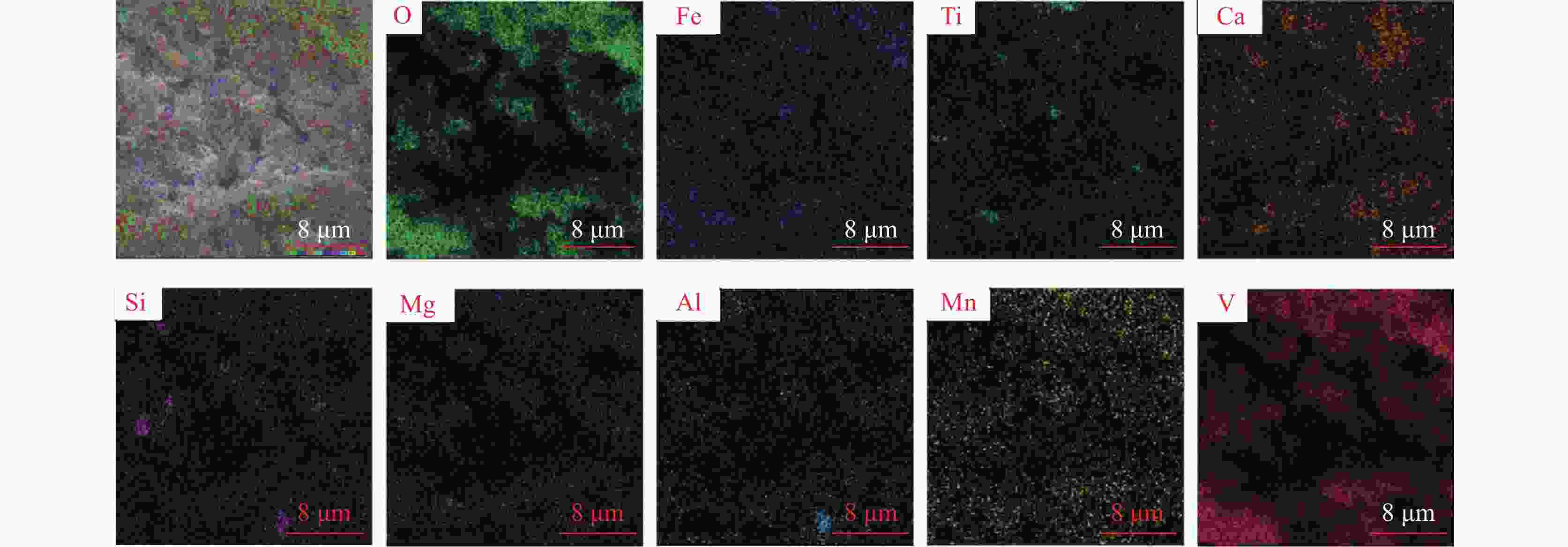
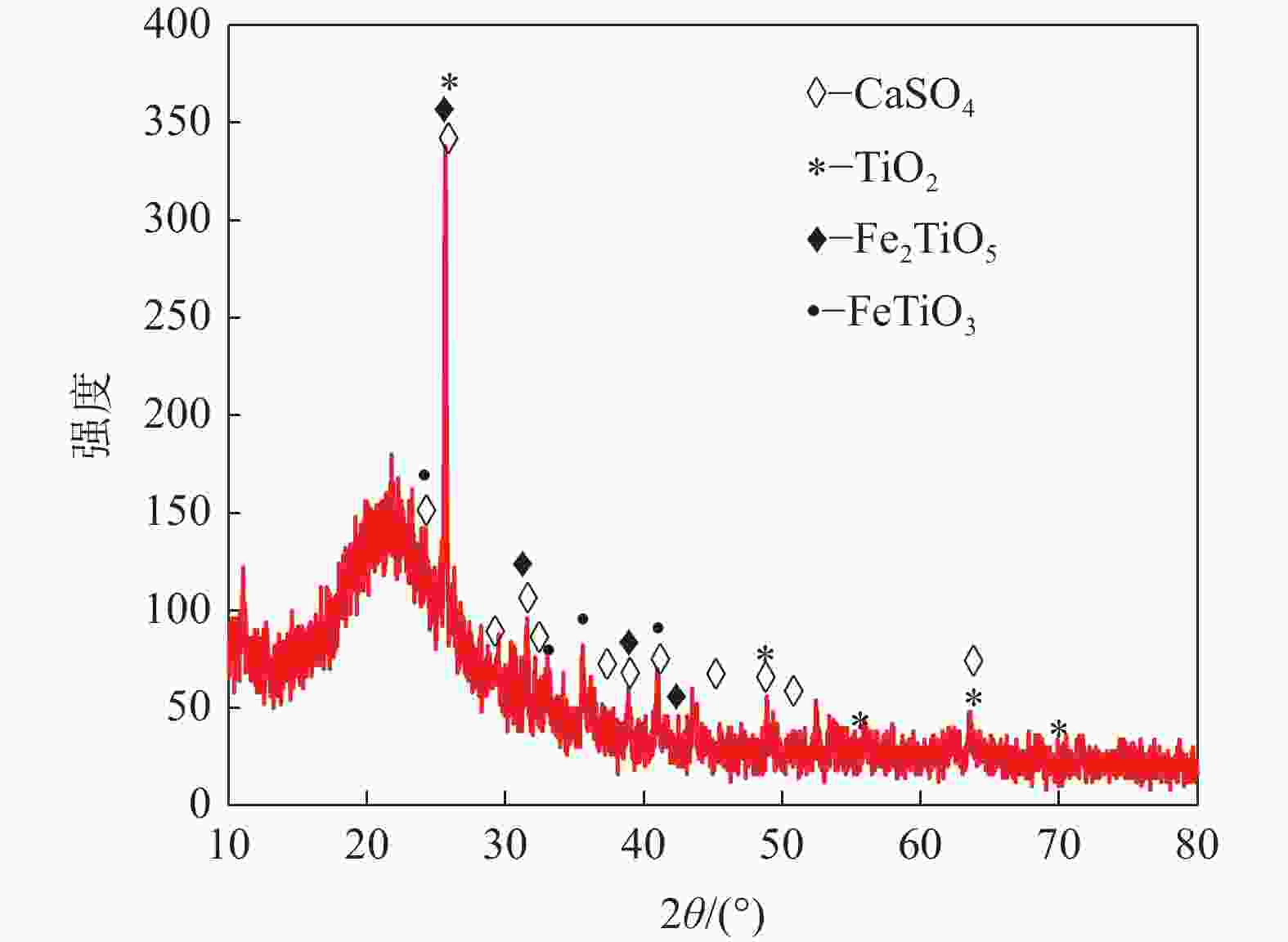
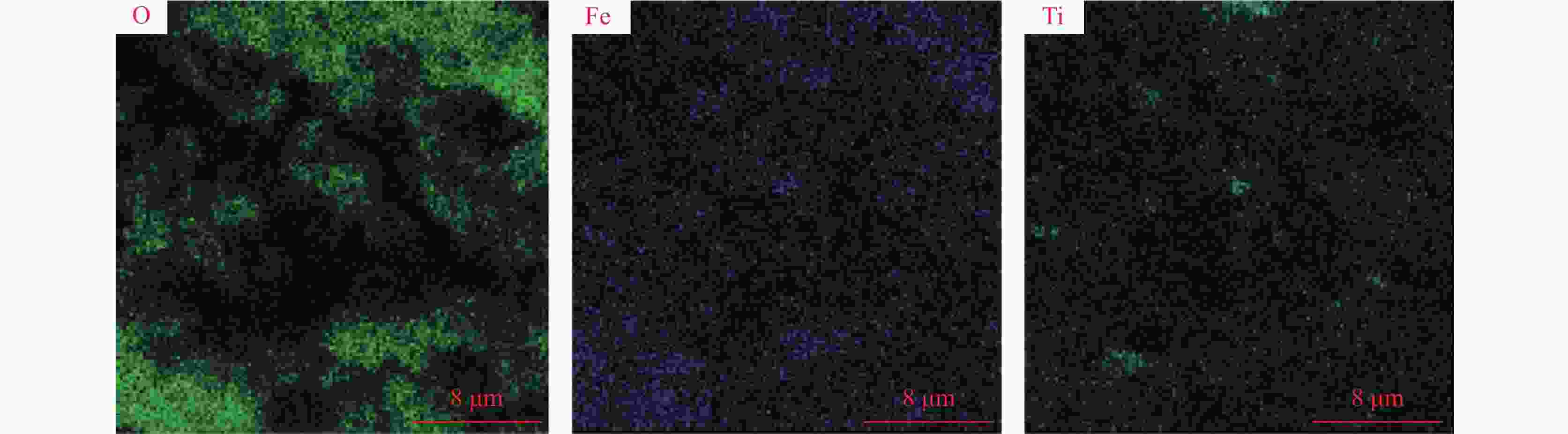
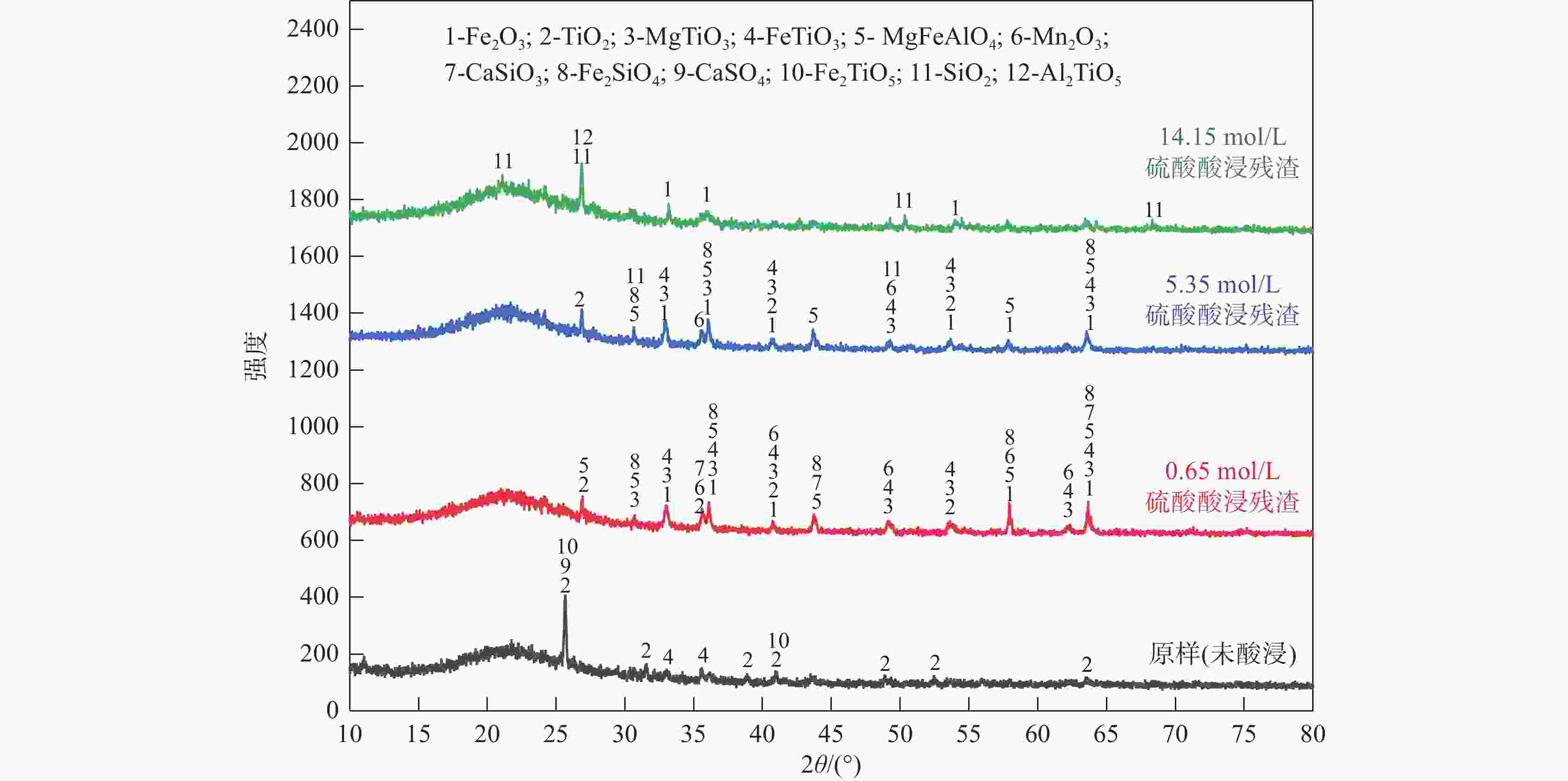
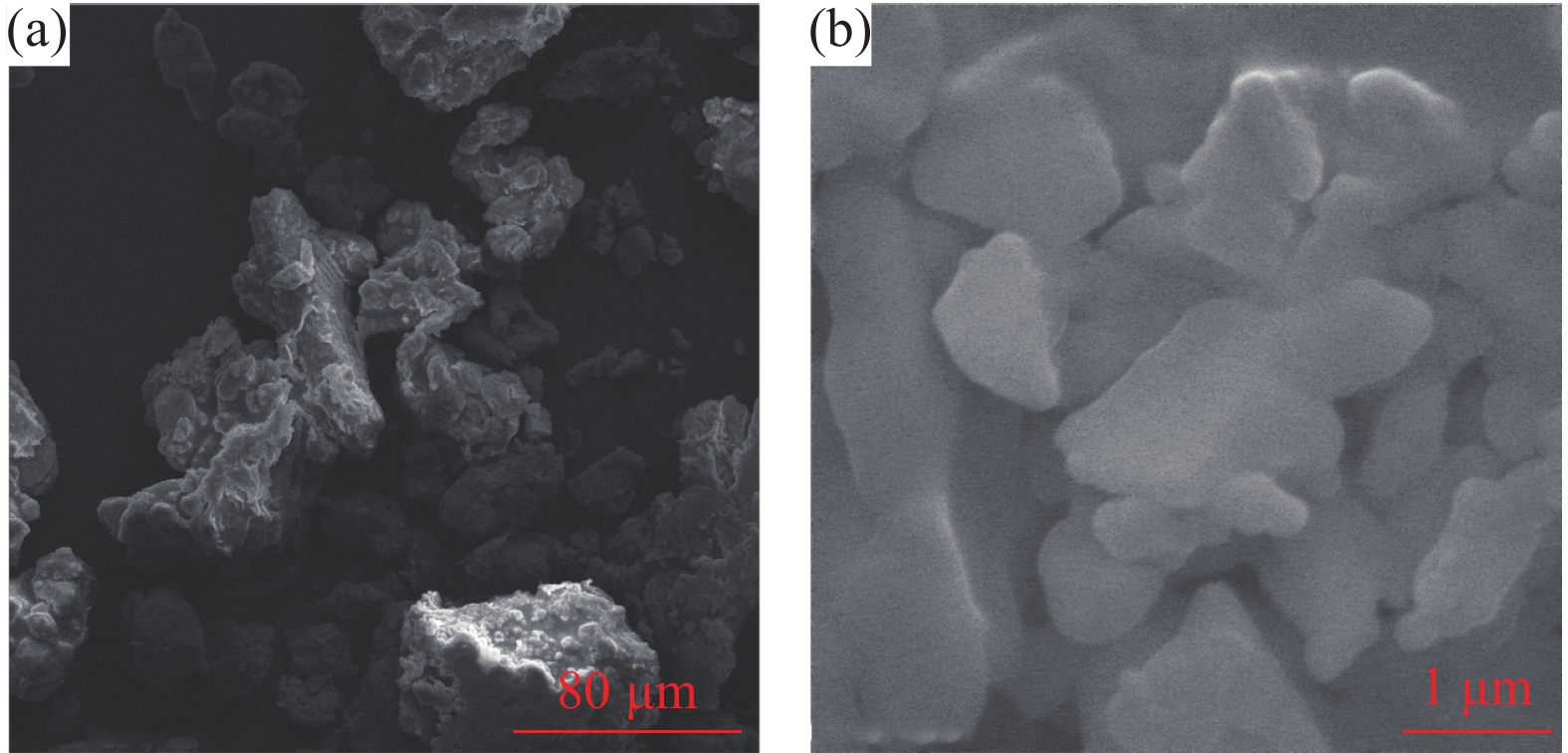
摘要: 目前使用硫酸法钛白工艺生产二氧化钛的厂家面临酸解尾气中升华硫堵塞管道问题,从而影响该工艺生产连续性,而目前对酸解尾气中升华硫的组成、结构、物质赋存状态以及升华硫冷凝行为缺乏认识。采用XRD、SEM和EDS对工厂升华硫粉及其中所含物质的结构、组成、主要元素分布及杂质元素的赋存状态进行了研究。结果表明,升华硫粉主要成分为S8,其中主要杂质元素有O、Fe、Ti、Si、Ca、Mg、Al、Mn和V等,且绝大部分钛和铁分布在钛铁矿和Fe2TiO5相中, 少部分铁分布在硅酸盐相中,以Fe2SiO4形式存在;钙分布在硫酸钙和硅酸盐相中,并以CaSiO3形式存在;硅主要以SiO2和硅酸盐形式存在;镁分布在MgTiO3和MgFeAlO4相中;铝以MgFeAlO4形式存在;锰以金属氧化物的形式分布在钛铁矿中。对硫酸法钛白酸解尾气中升华硫的赋存状态进行研究,可为后续酸解尾气中升华硫的冷凝行为研究提供基础。Abstract: At present, the manufacturers of titanium dioxide produced by sulfuric acid process titanium dioxide face the problem that sublimed sulfur in the acid hydrolysis tail gas clogs the pipeline, which affects the continuity of the production of titanium dioxide by this process. In this paper, XRD, SEM and EDS characterizations were used to study the structure, composition, distribution of main elements and occurrence of impurity elements in factory sublimed sulfur powder. The results show that the main component of sublimed sulfur powder is S8, in which the main impurity elements are O, Fe, Ti, Si, Ca, Mg, Al, Mn and V, and most of the titanium and iron are distributed in the ilmenite and Fe2TiO5 phase, and a small part of the iron is distributed in the silicate phase, in the form of Fe2SiO4. Calcium is distributed in calcium sulfate and silicate phases, and exists in the form of CaSiO3. Silicon mainly exists in the form of SiO2 and silicate. Magnesium is distributed in MgTiO3 and MgFeAlO4 phases. Aluminum exists in the form of MgFeAlO4. Manganese is distributed in ilmenite in the form of metal oxidation. The study of the occurrence state of sublimed sulfur in the exhaust gas of titanium dioxide acid-hydrolysis by sulfuric acid process can provide a basis for the study of condensation behavior of sublimed sulfur in the exhaust gas of post-sequence acid-hydrolysis.
-
表 1 钛精矿的主要化学成分[13]
Table 1. Main chemical components of titanium concentrate
% TiO2 TFe SiO2 MgO Al2O3 CaO V2O5 S MnO 46.14 19.65 0.79 1.277 0.06 0.84 0.08 0.14 0.26 表 2 升华硫粉中杂质的元素组成
Table 2. Elemental composition of impurities in plant sublimation sulfur powder
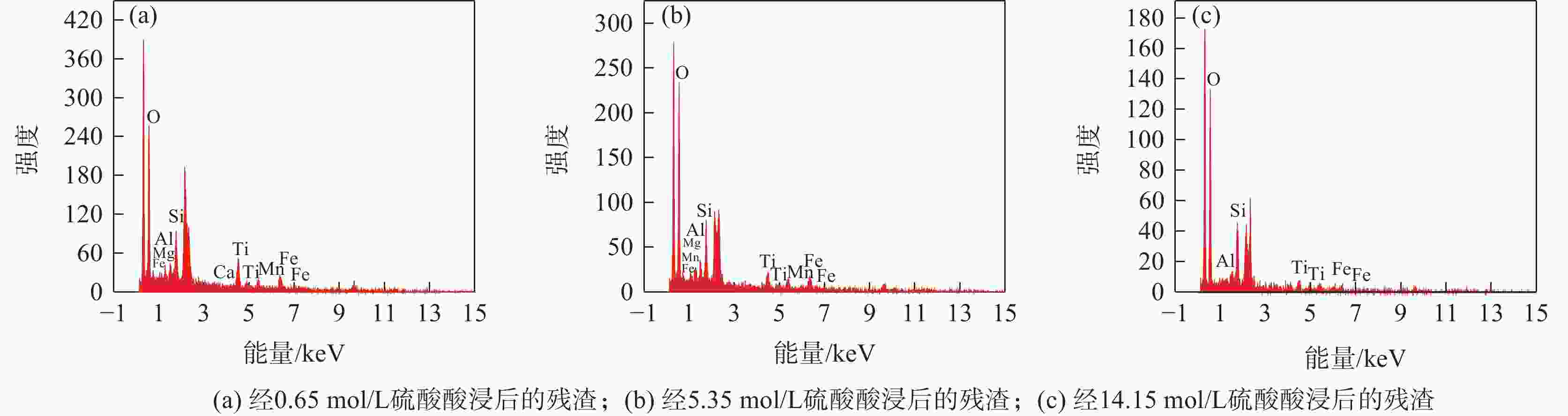
% O Fe Ti Ca Si Mg Al Mn V 61.16 17.48 8.56 8.04 1.84 1.70 0.63 0.47 0.11 表 3 杂质经不同浓度硫酸酸浸后残渣的元素组成
Table 3. The elemental composition of the residue leached with sulfuric acid
杂质酸浸条件 硫酸浓度/(mol·L−1) 残渣元素含量占比/% O Fe Ti Si Al Mn Mg Ca 硫酸酸浸 0.65 57.76 15.78 13.64 7.47 1.75 1.47 1.72 0.41 硫酸酸浸 5.35 58.65 15.80 8.70 8.93 4.02 2.80 1.10 0 硫酸酸浸 14.15 66.28 1.99 5.37 24.11 2.25 0 0 0 -
[1] Xu Xueli, Song Wei. Progress in the structural design of a titanium dioxide membrane and its photocatalytic degradation properties[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2022,17(9):220952. doi: 10.20964/2022.09.50 [2] Harrum W M W, Akhir R M, Afaah A N, et al. Comparative study of surface, elemental, structural and optical morphologies of titanium dioxide-zinc oxide (TiO2-ZnO) and titanium dioxide-zinc oxide/graphene (TiO2-ZnO/Gn)[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2023,75(1):147−150. [3] Virginia M V, Virginia A, Aida M, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in sunscreens and skin photo-damage development, synthesis and characterization of a novel biocompatible alternative based on their in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2023,15:100173. doi: 10.1016/j.jpap.2023.100173 [4] Prabhjot J S, Dapinder K, Ram P, et al. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Development and applications[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 2022,10:100361. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100361 [5] Liu Juan. Development of study on preparation of Ti-rich raw materials for boiling chlorinated from Panzhihua titanium resources[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2018,47(6):49−53. (刘娟. 攀枝花钛资源制备沸腾氯化用富钛原料研究进展[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2018,47(6):49−53. Liu Juan . Development of study on preparation of Ti-rich raw materials for boiling chlorinated from Panzhihua titanium resources[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy,2018 ,47 (6 ):49 −53 .[6] Wu You. Summary on characteristics of oxidation reactor for titanium dioxide production by chloride process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(2):92−96. (吴优. 国外氯化法钛白氧化反应器特点及分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(2):92−96. Wu You . Summary on characteristics of oxidation reactor for titanium dioxide production by chloride process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium,2016 ,37 (2 ):92 −96 .[7] Wang Liping, Wang Hao, Gao Qi, et al. Distribution and production status of titanium resources in China[J]. Rare Metals, 2004(1):265−267. (王立平, 王镐, 高颀, 等. 我国钛资源分布和生产现状[J]. 稀有金属, 2004(1):265−267. Wang Liping, Wang Hao, Gao Qi, et al . Distribution and production status of titanium resources in China[J]. Rare Metals,2004 (1 ):265 −267 .[8] Chen Hua, Tian Congxue. Current situation and existing problems in the production of titanium dioxide by sulfuric acid method in China[J]. Journal of Panzhihua University, 2014,31(1):99−102. (陈华, 田从学. 国内硫酸法钛白生产现状及存在问题[J]. 攀枝花学院学报, 2014,31(1):99−102. Chen Hua, Tian Congxue . Current situation and existing problems in the production of titanium dioxide by sulfuric acid method in China[J]. Journal of Panzhihua University,2014 ,31 (1 ):99 −102 .[9] Sun Liang. Treatment of waste acid and wastewater in the production of titanium dioxide by sulfuric acid method[J]. Chemical Management, 2022,635(20):34−36. (孙亮. 硫酸法钛白粉生产中废酸、废水的治理[J]. 化工管理, 2022,635(20):34−36. Sun Liang . Treatment of waste acid and wastewater in the production of titanium dioxide by sulfuric acid method[J]. Chemical Management,2022 ,635 (20 ):34 −36 .[10] Tang Wenqian, Liu Li. Comparison and review of continuous and intermittent acid hydrolysis in titanium dioxide production[J]. Chemical Design, 2015,25(5):8−10. (唐文骞, 刘丽. 钛白生产中连续与间歇酸解比较及评述[J]. 化工设计, 2015,25(5):8−10. Tang Wenqian, Liu Li . Comparison and review of continuous and intermittent acid hydrolysis in titanium dioxide production[J]. Chemical Design,2015 ,25 (5 ):8 −10 .[11] Wang Haibo, Luo Zhiqiang, Wu Xiaoping, et al. Study on the S content of titanium slag acid hydrolysis tail gas[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(4):92−96. (王海波, 罗志强, 吴小平, 等. 钛渣酸解尾气S含量研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(4):92−96. Wang Haibo, Luo Zhiqiang, Wu Xiaoping, et al . Study on the S content of titanium slag acid hydrolysis tail gas[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium,2020 ,41 (4 ):92 −96 .[12] Fan Y , Liu Y , Niu L , et al. Separation and purification of elemental sulfur from sphalerite concentrate direct leaching residue by liquid paraffin[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 186: 162-169. [13] Xiang Quanjin, Quan Yuanxia, Quan Xuejun, et al. Mechanism analysis of sublimation sulfur production in acid hydrolysis tail gas of titanium concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(3):100−104. (向泉锦, 全远霞, 全学军, 等. 钛精矿酸解尾气中升华硫产生的机理分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(3):100−104. Xiang Quanjin, Quan Yuanxia, Quan Xuejun, et al . Mechanism analysis of sublimation sulfur production in acid hydrolysis tail gas of titanium concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium,2023 ,44 (3 ):100 −104 .[14] Ye Endong, Wu Xuan. Study on occurrence state of main impurity elements in Panxi titanium concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(4):63−68. (叶恩东, 吴轩. 攀西钛精矿主要杂质元素赋存状态研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(4):63−68. Ye Endong, Wu Xuan . Study on occurrence state of main impurity elements in Panxi titanium concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium,2017 ,38 (4 ):63 −68 .[15] Wang Haibo, Wu Xiaoping, Ma Xin, et al. Study on the leaching behavior and kinetics of titanium in the solid phase of acid hydrolysis of titanium concentrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Non ferrous Metals, 2021,31(12):3655−3663. (王海波, 吴小平, 马鑫, 等. 钛精矿酸解固相物中钛的浸出行为及动力学研究[J]. 中国有色金属报, 2021,31(12):3655−3663. Wang Haibo, Wu Xiaoping, Ma Xin, et al . Study on the leaching behavior and kinetics of titanium in the solid phase of acid hydrolysis of titanium concentrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Non ferrous Metals,2021 ,31 (12 ):3655 −3663 . -





 下载:
下载: