Thermodynamic behaviour of second phases precipitation in vanadium-bearing high-speed steel for railway wheel
-
摘要: 利用热力学软件Thermo-calc计算了含钒高速铁路车轮钢中第二相的析出行为,详细分析了低碳车轮钢中平衡相的组成以及温度和钒含量对第二相析出的影响。结果表明,钢中钒含量的变化对车轮钢中第二相析出量有较大影响,对第二相析出的温度几乎无影响;温度变化对钢中稳定存在的第二相析出产物影响较小,对瞬态析出相的影响较大。Abstract: A thermodynamic Thermo-calc software was used to calculate the precipitation behavior of second phase in vanadium-bearing high-speed railway wheel steel. The composition of equilibrium phase in low-carbon wheel steel and the influence of temperature and vanadium content on the precipitation of the second phase were analyzed in detail. The results show that variation of vanadium content in steel has a great influence on the second phase precipitation in wheel steel, and almost no effect has been observed on the precipitated temperature of the second phase. The temperature variation has small effect on the stable second phase precipitated products in steel, but has great effect on the transient precipitated phase.
-
表 1 高速车轮钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of high-speed wheel steel
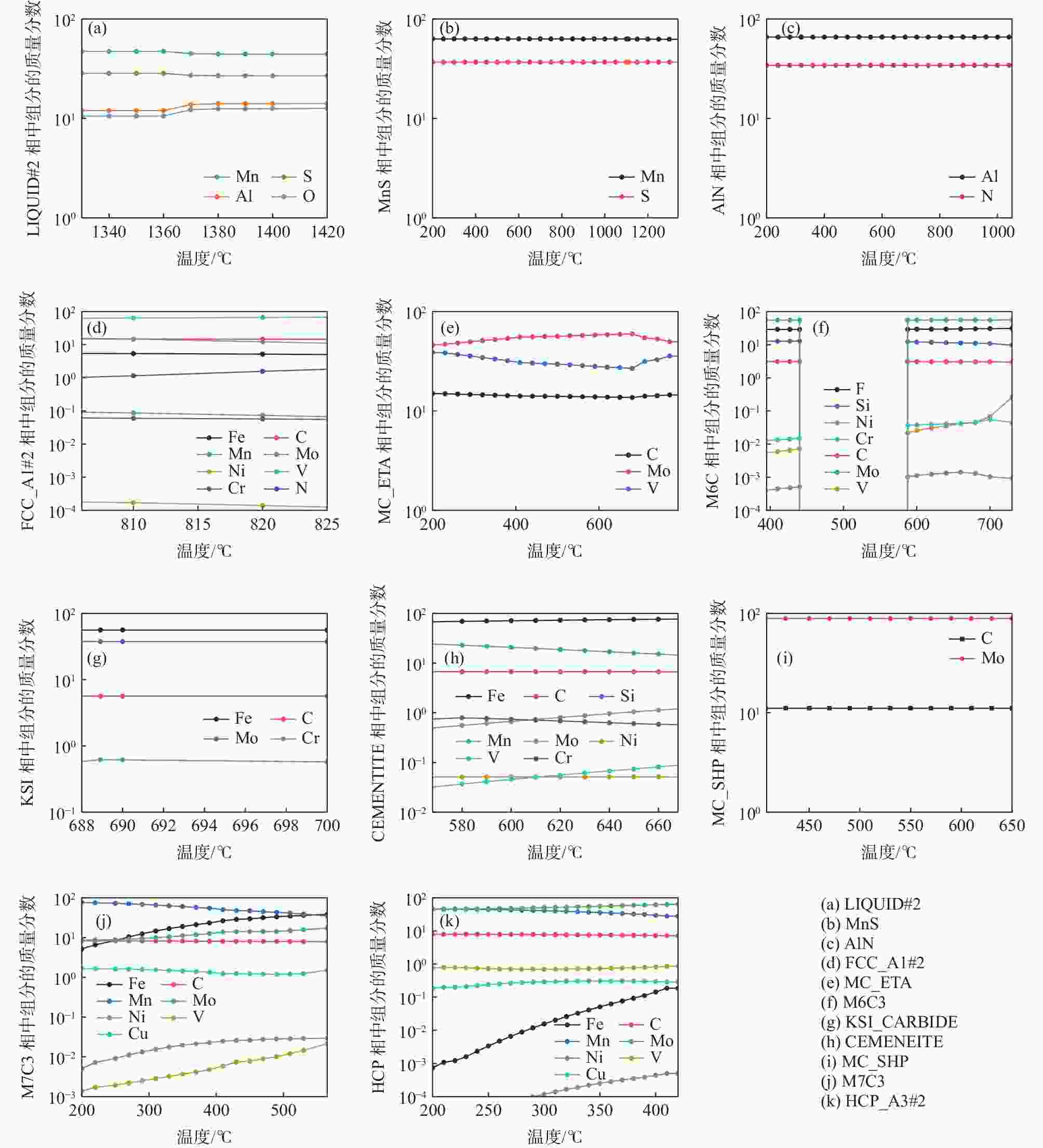
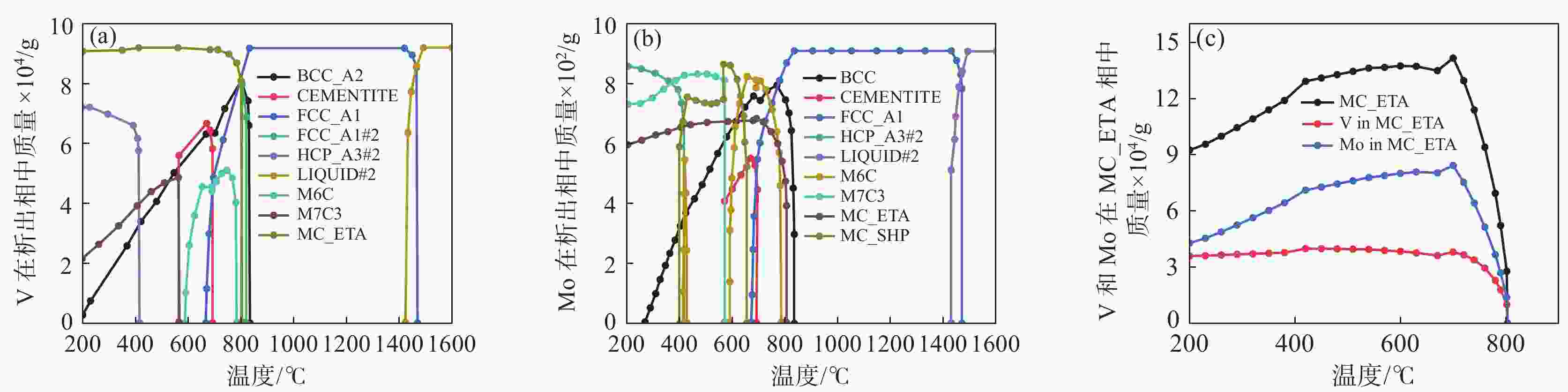
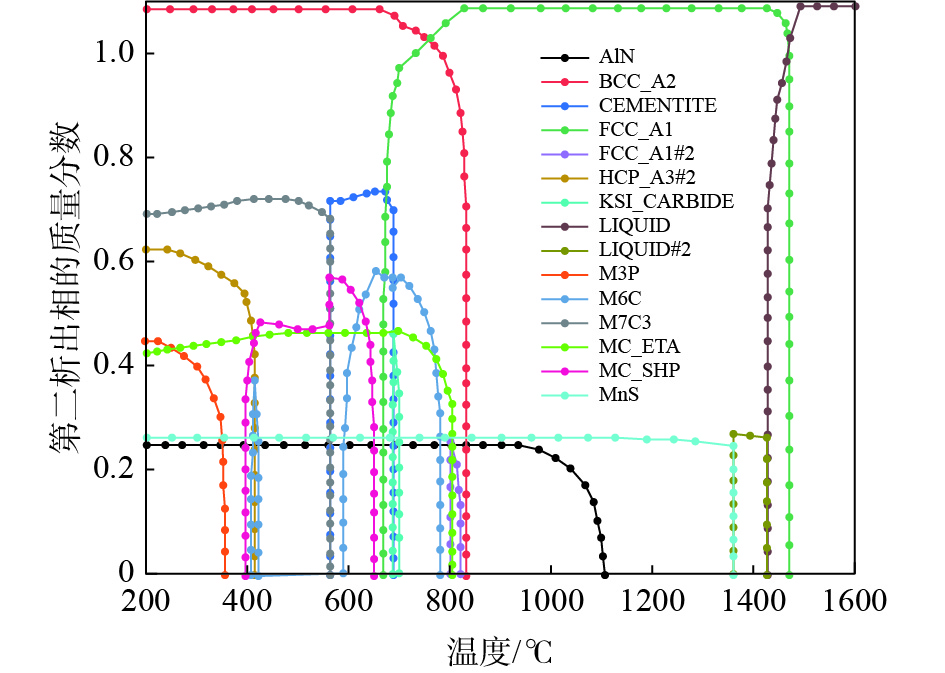
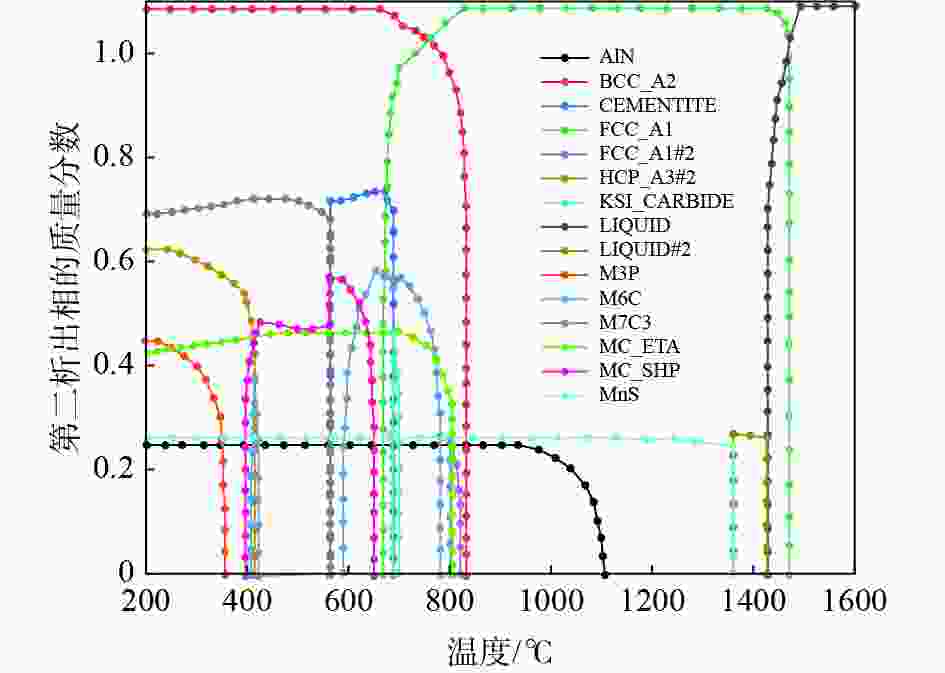
% C Si Mn Mo Ni V Cr S P Al O N 0.2 1.2 1.91 0.5 0.24 0.03~0.12 0.03 0.006 0.019 0.04 0.0001 0.004 表 2 试验钢中第二相粒子平衡析出结果
Table 2. The equilibrium precipitation of the second phases in high-speed wheel steel
第二析出相 最大质量分数 最大析出
温度/ ℃析出温
度/ ℃分解温
度/ ℃MnS 1.63×10−4 - 1362.52 - AlN 1.46×10−4 - 1184.86 - FCC_A1#2 1.55×10−4 803.02 826.79 801.63 MC_ETA 9.26×10−4 688.92 803.02 - M6C 4.71×10−3 653.13 780.00 400.00 KSI_CARBIDE 1.33×10−3 688.92 702.00 687.26 CEMENTITE 2.44×10−2 669.52 688.91 564.62 MC_SHP 4.11×10−3 565.44 653.13 392.26 M7C3 2.05×10−2 416.35 565.30 - HCP_A3#2 7.44×10−3 - 416.35 - M3P 1.15×10−3 - 359.95 注:二次相析出的计算温度范围为200~1600 ℃。“-”表示在计算温度范围内无法分解析出相或连续析出至200 ℃。 表 3 810 ℃时不同钒含量下FCC_A1#2相的含量和元素分布
Table 3. Content and element distribution of the FCC_A1#2 phase at 810 ℃ with different V contents
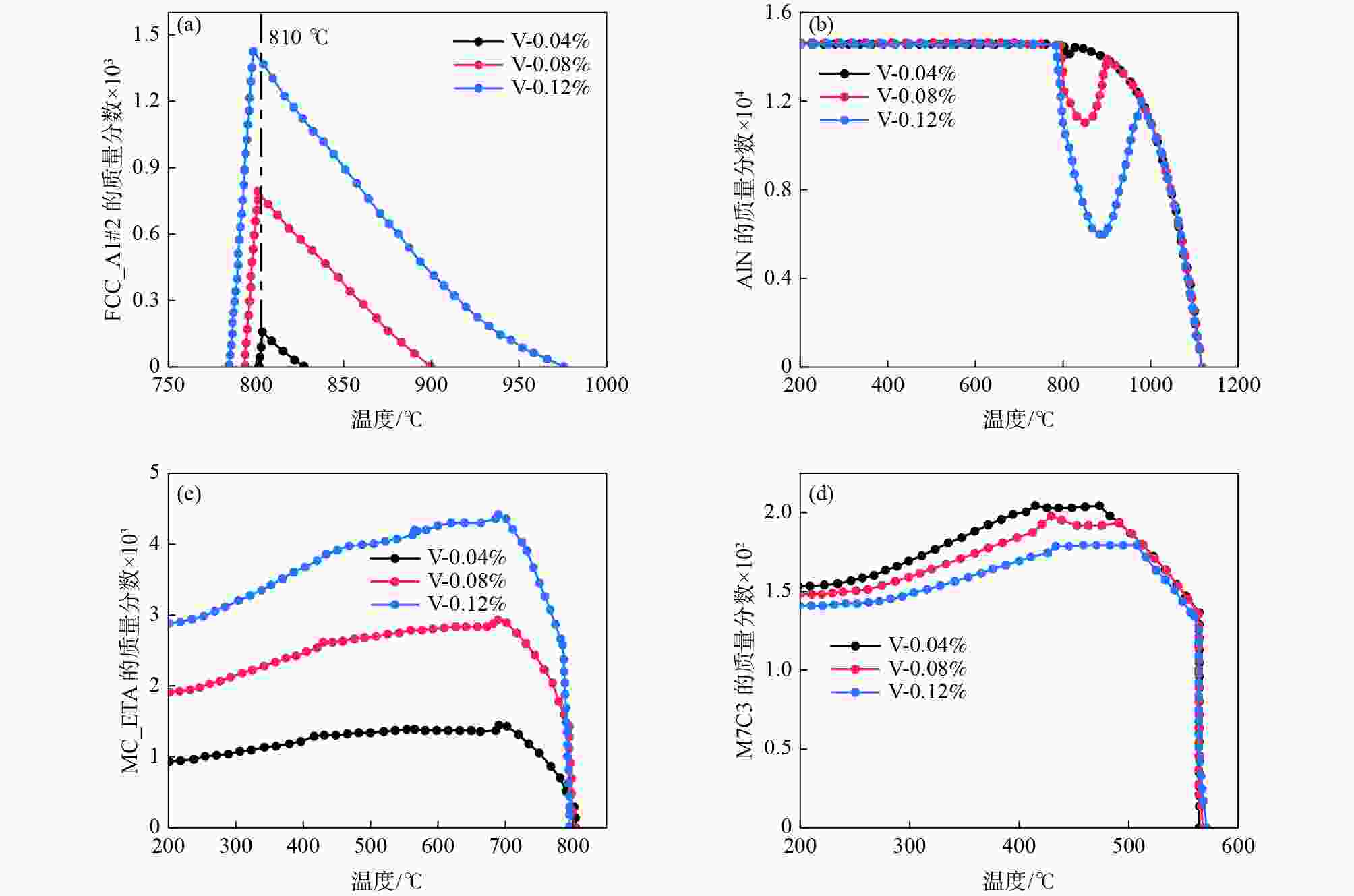
钢中V含量/% FCC_A1#2 Mo/% V/% C/% N/% 0.04 1.55×10−4 16.78 61.77 15.07 0.62 0.08 7.94×10−4 16.20 62.42 15.10 0.66 0.12 1.43×10−3 15.48 63.04 15.12 0.69 表 4 不同钒含量下相关相的析出温度
Table 4. The precipitation temperature of the related phase with different contents of V
钢中V含量/% 析出温度/℃ AlN MC_ETA FCC_A1#2 M7C3 0.04 1114.86 807.10 820.97 566.01 0.08 1113.90 804.01 883.87 569.05 0.12 1112.93 802.11 932.01 572.14 -
[1] Ekberg A, Åkesson B, Kabo E. Wheel/rail rolling contact fatigue–Probe, predict, prevent[J]. Wear, 2014,314(1-2):2−12. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2013.12.004 [2] Zeng D, Lu L, Zhang J, et al. Effect of micro-inclusions on subsurface-initiated rolling contact fatigue of a railway wheel[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016,230(2):544−553. doi: 10.1177/0954409714551808 [3] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 8.Yong Qilong. Secondary phase in steels[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 8. [4] 董瀚. 先进钢铁材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 103.Dong Han. Advanced steel materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 103. [5] Ollilainen V, Kasprzak W, Holappa L. The effect of silicon, vanadium and nitrogen on the microstructure and hardness of air cooled medium carbon low alloy steels[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003,134(3):405−412. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(02)01131-7 [6] Ma Yue, Pan Tao, Jiang Bo, et al. Study of the effect of sulfur contents on fracture toughness of railway wheel steels for high speed train[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2011,47(8):978−983. (马跃, 潘涛, 江波, 等. S含量对高速车轮钢断裂韧性影响的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2011,47(8):978−983.Ma Yue, Pan Tao, Jiang Bo, et al. Study of the effect of sulfur contents on fracture toughness of railway wheel steels for high speed train[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2011, 47(08): 978-983. [7] 文波. 碳化钒在Fe-C-V微合金钢中的析出行为研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011.Wen Bo. Precipitation behavior of vanadium carbide in the Fe-C-V micro-alloy steel[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011. [8] Batte A D, Honeycombe R W K. Strengthening of ferrite by vanadium carbide precipitation[J]. Metal Science Journal, 1973,7(1):160−168. doi: 10.1179/030634573790445370 [9] Wu D, Xiao F, Wang B, et al. Investigation on grain refinement and precipitation strengthening applied in high speed wire rod containing vanadium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2014,592:102−110. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.10.068 [10] Cui Chenshuo, Gao Cairu, Yang Xiongfei, et al. Dynamic precipitation behavior of V-N microalloyed steel in low temperature region[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(6):37−43. (崔辰硕, 高彩茹, 杨雄飞, 等. V-N微合金钢在低温区动态析出行为[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(6):37−43.Cui Chenshuo, Gao Cairu, Yang Xiongfei, et al. Dynamic precipitation behavior of V-N microalloyed steel in low temperature region[J]. Iron Steel V Anadium Ti Tanium, 2015, 36(06): 37-43. [11] Dunlop G L, Carlsson C J, Frimodig G. Precipitation of VC in ferrite and pearlite during direct transformation of a medium carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1978,9(2):261−266. doi: 10.1007/BF02646709 [12] Zhang J, Zhang K J. Strengthening mechanism and application of microalloying element vanadium in plate[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2009,31(2):15−18. [13] Di X, Li M, Yang Z, et al. Microstructural evolution, coarsening behavior of vanadium carbide and mechanical properties in the simulated heat-affected zone of modified medium manganese steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2016,96:232−240. [14] Sakamoto H, Toyama K, Hirakawa K. Fracture toughness of medium-high carbon steel for railroad wheel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2000,285(1-2):288−292. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00648-1 [15] Han Xiaoyong. Functions of Nb, V and Ti in micro-alloyed steel[J]. Wide and Heavy Plate, 2006,(1):39−41. (韩孝永. 铌、钒、钛在微合金钢中的作用[J]. 宽厚板, 2006,(1):39−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7864.2006.01.011Han Xiaoyong. Functions of Nb, V and Ti in micro-alloyed steel[J]. Wide and Heavy Plate, 2006, (1): 39-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7864.2006.01.011 [16] Faccoli M, Ghidini A, Mazzù A. Experimental and numerical investigation of the thermal effects on railway wheels for shoe-braked high-speed train applications[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2018,49(10):4544−4554. doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-4749-2 [17] Pan Tao, Cui Yinhui, Su Hang, et al. Effect of vanadium on strength and toughness of wheel steel normalized at different temperatures[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006,(3):71−76. (潘涛, 崔银会, 苏航, 等. 不同加热温度下钒对车轮钢强韧性的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2006,(3):71−76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.03.017Pan Tao, Cui Yinhui, Su Hang, et al. Effect of vanadium on strength and toughness of wheel steel normalized at different temperatures[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006, (03): 71-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.03.017 [18] Ekberg A, Sotkovszki P. Anisotropy and rolling contact fatigue of railway wheels[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2001,23(1):29−43. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(00)00070-0 [19] Zuo Yue, Zhou Shitong, Li Zhaodong, et al. Effect of V and Si on microstructure and mechanical properties of medium-carbon pearlitic steels for wheel[J]. Chinese Journal or of Materlals Research, 2016,30(6):401−408. (左越, 周世同, 李昭东, 等. V和Si对珠光体车轮钢显微组织和力学性能的影响规律[J]. 材料研究学报, 2016,30(6):401−408.Zuo Yue, Zhou Shitong, Li Zhaodong, et al. Effect of V and Si on microstructure and mechanical properties of medium-carbon pearlitic steels for wheel[J]. Chinese Journal or of Materlals Research, 2016, 30(06): 401-408. [20] Ning Jiapei, Zheng Kaihong, Zhou Hongming, et al. Microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of high carbon medium chromium wear resistant alloy steel after heat treatment[J]. Foundry, 2020,69(2):135−141. (宁嘉沛, 郑开宏, 周宏明, 等. 高碳中铬耐磨合金钢热处理后的组织及磨料磨损性能[J]. 铸造, 2020,69(2):135−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2020.02.004Ning Jiapei, Zheng Kaihong, Zhou Hongming, et al. Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Resistance of High Carbon Medium Chromium Wear Resistant Alloy Steel After Heat Treatment[J]. Foundry, 2020, 69(02): 135-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2020.02.004 [21] Yu Ting, Shimizu K, Kusumoto K. Effect of vanadium on the dry friction and wear properties of V-Cr-Mn alloy white cast iron[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2016,164(2):107−110, 119. (于婷, 清水一道, 楠本賢太. V含量对V-Cr-Mn合金白口铸铁干摩擦磨损性能的影响[J]. 大连交通大学学报, 2016,164(2):107−110, 119.Yu Ting, Shimizu K, Kusumoto K. Effect of Vanadium on the Dry Friction and Wear Properties of V-Cr-Mn Alloy White Cast Iron[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2016, 164(02): 107-110+119. [22] Ju J, Fu H G, Fu D M, et al. Effects of Cr and V additions on the microstructure and properties of high-vanadium wear-resistant alloy steel[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2018,45(2):176−186. [23] Kim C K, Lee S, Jung J Y. Effects of heat treatment on wear resistance and fracture toughness of duo-cast materials composed of high-chromium white cast iron and low-chromium steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006,37(3):633−643. doi: 10.1007/s11661-006-0035-9 [24] 高彩茹, 陈宇轩, 杜林秀, 等. Mo对钒微合金钢中碳化物在贝氏体区析出的影响[C]//第三届钒钛微合金化高强钢开发应用技术暨第四届钒产业先进技术交流会论文集. 重庆: 钒钛资源综合利用产业技术创新战略联盟, 2017: 14-22.Gao Cairu, Chen Yuxuan, Du Linxiu, et al. Effect of Mo on carbide precipitation from bainite in V-microalloyed steel[C]// The 3rd Vanadium Titanium Microalloyed High Strength Steel Development and Application Technology and the 4th Advanced Technology Exchange Conference of Vanadium Industry. Chongqing:The Strategic Alliance of the Vanadium and Titanium Resources Comprehensive Utilization and Industrial Technology Innovation, 2017: 14-22. [25] Miyamoto G, Hori R, Poorganji B, et al. Interphase precipitation of VC and resultant hardening in V-added medium carbon steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2011,51(10):1733−1739. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.51.1733 [26] Ioannidou C, Arechabaleta Z, Navarro-López A, et al. Interaction of precipitation with austenite-to-ferrite phase transformation in vanadium micro-alloyed steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019,181:10−24. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.09.046 [27] 肖寄光, 程慧静, 刘克明, 等. 钒对中铬白口铸铁组织和抗高温氧化性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2010, 31(12): 97−102.Xiao Jiguang, Chen Huijing, Liu Keming, et al. Effect of vanadium on microstructure and high temperature oxidation resistance of medium chromium white cast iron[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010, 31(12): 97−102. [28] Su Yinglong, Zhang Xuekun. Toughness improvement of high-chromium anti-wear cast iron[J]. Modern Cast Iron, 2000,(4):56−59. (苏应龙, 张学昆. 高铬抗磨铸铁韧性的提高[J]. 现代铸铁, 2000,(4):56−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8345.2000.04.018Su Yinglong, Zhang Xuekun. Toughness improvement of High-Chromium anti-wear cast iron[J]. Modern Cast Iron, 2000, (04): 56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8345.2000.04.018 -




 下载:
下载: