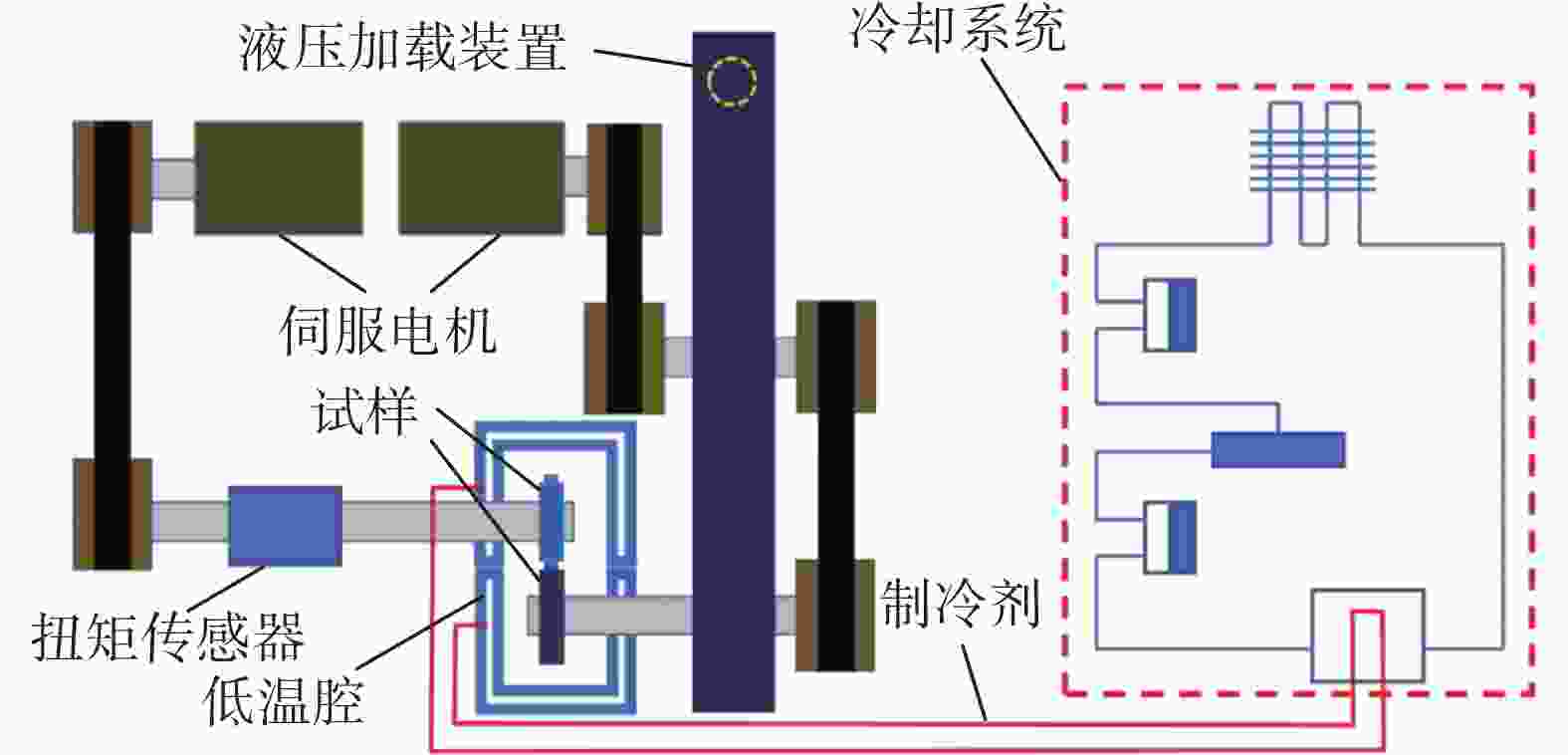
Study on rolling wear and rolling contact fatigue behavior of pearlite/bainite rail steels at the low temperature of −35 ℃
-
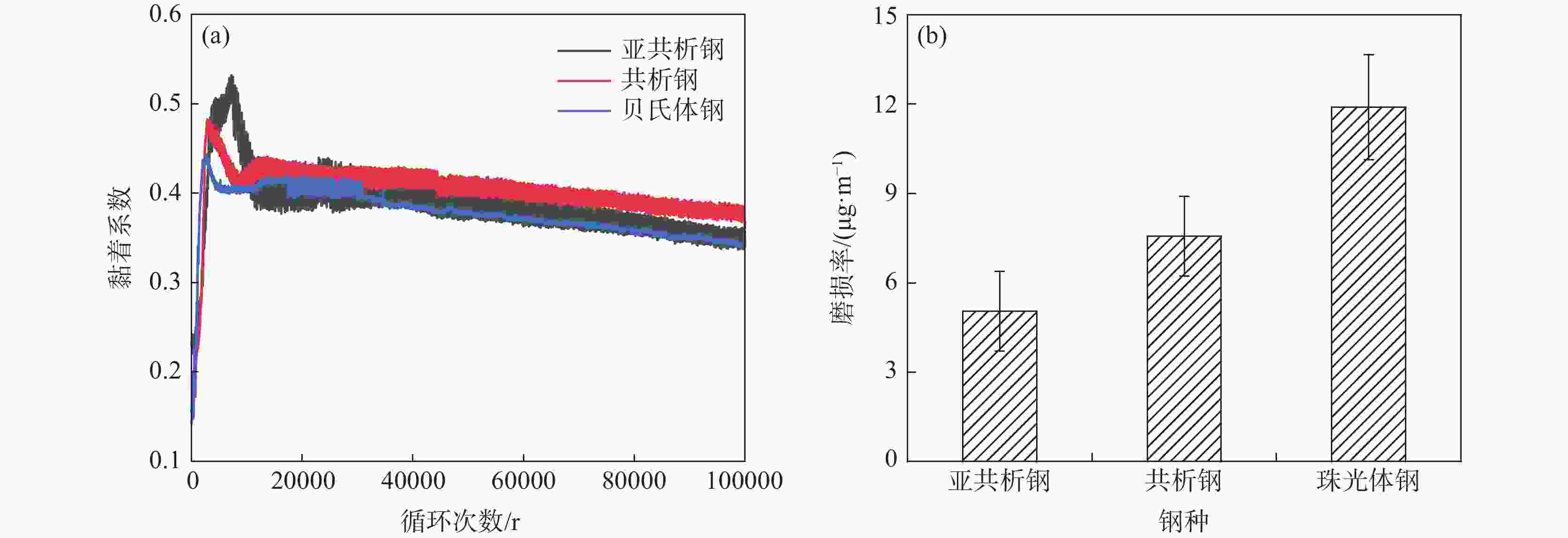
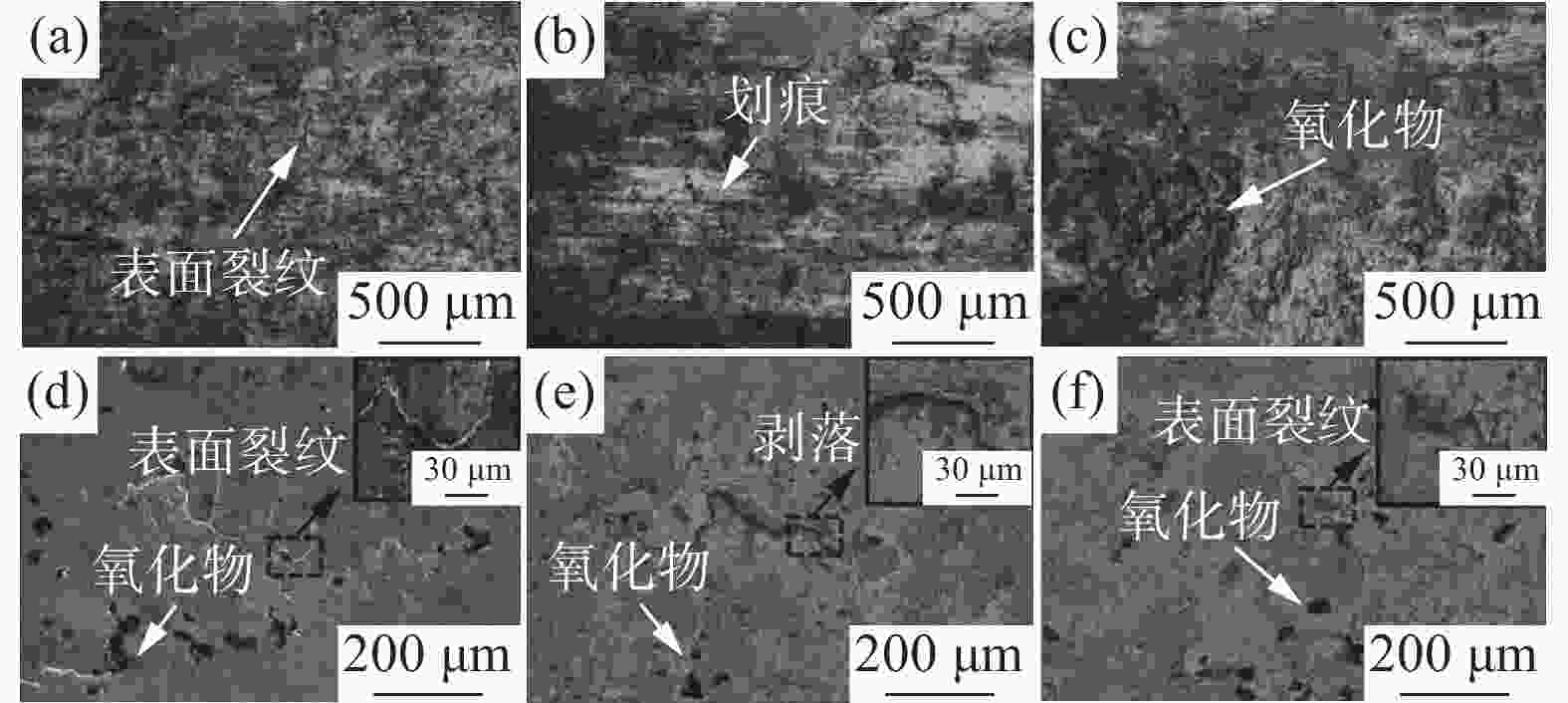
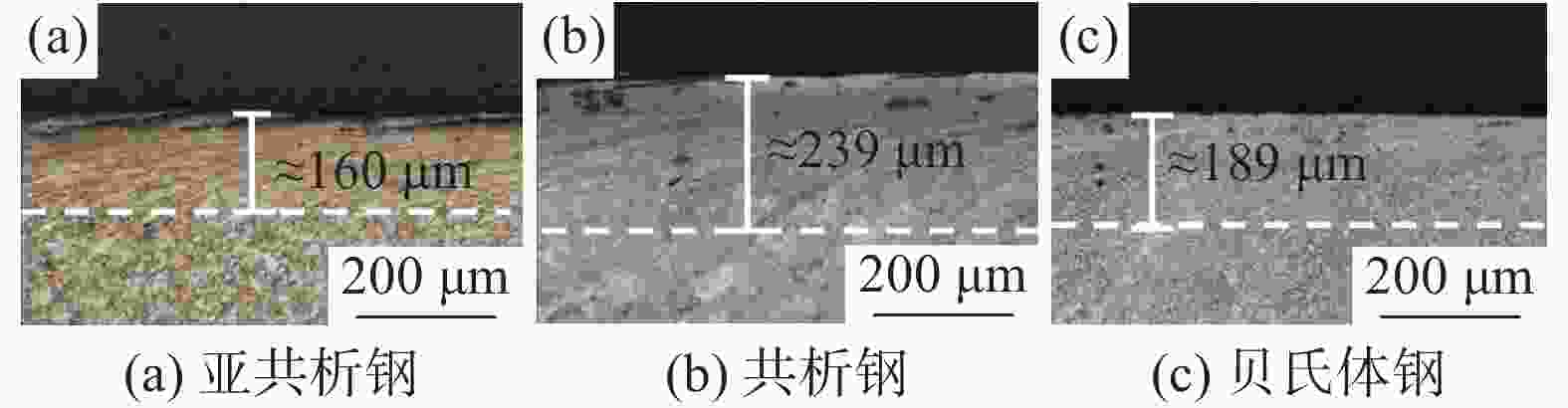
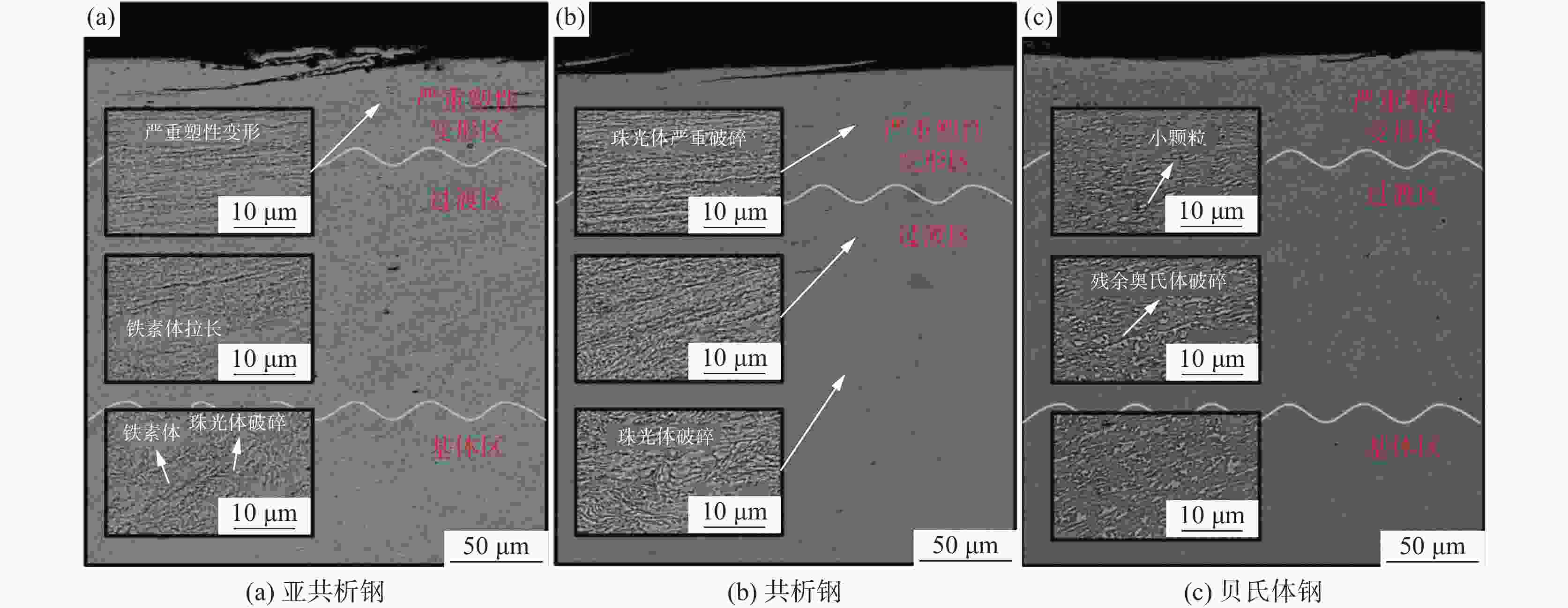
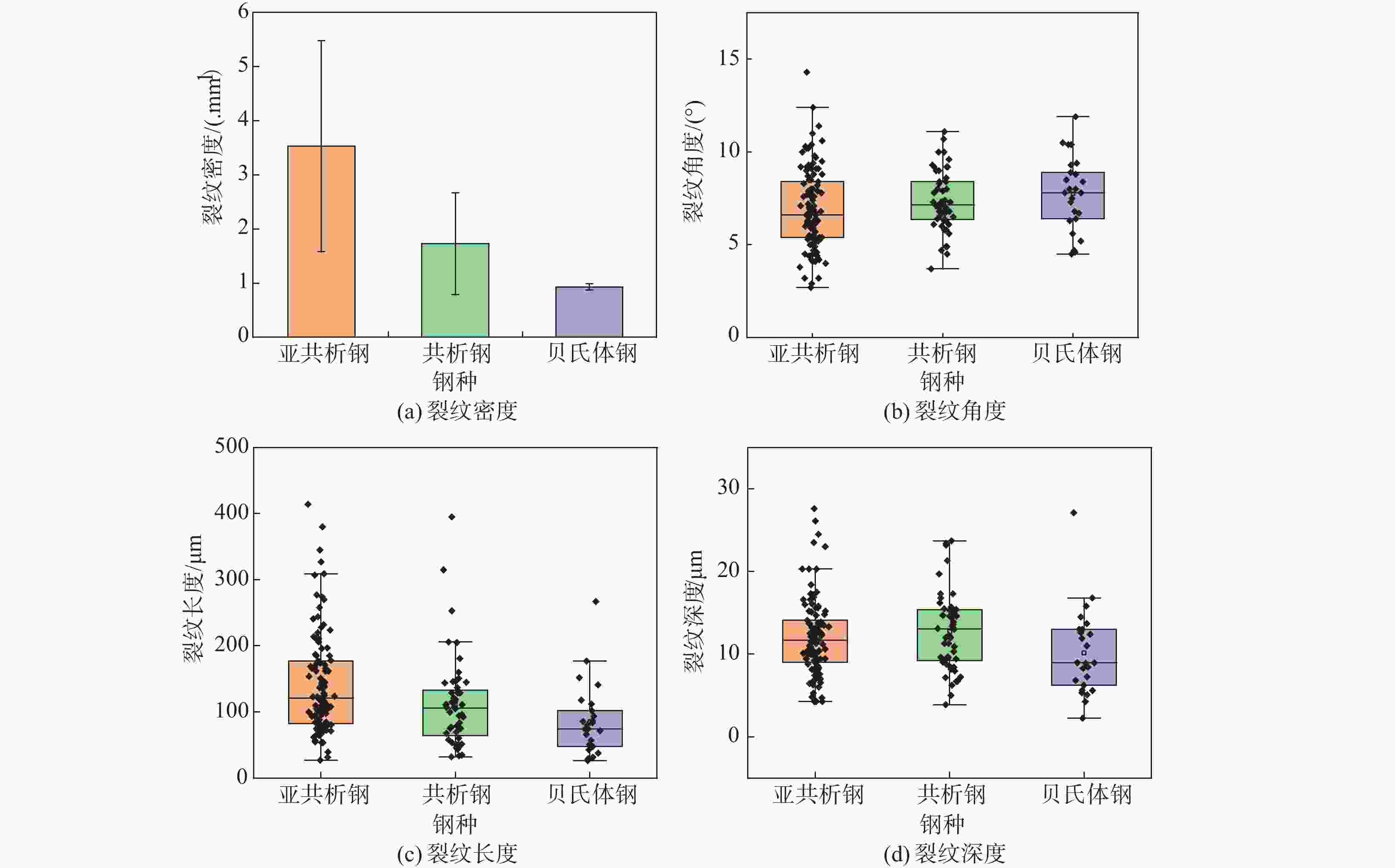
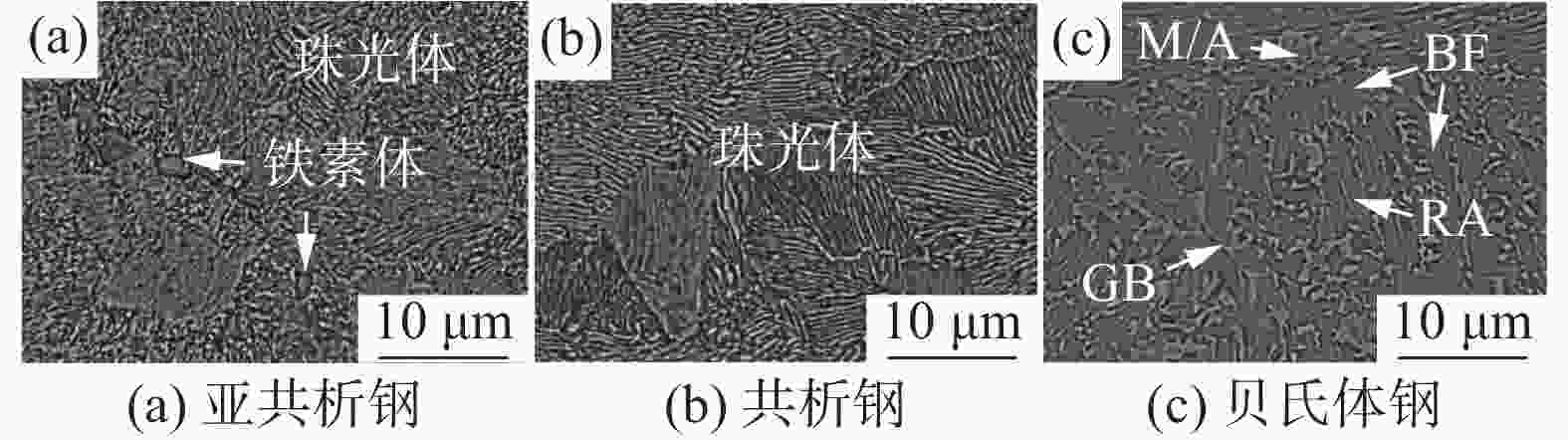
摘要: 高寒地区铁路钢轨面临着低温服役环境,低温下钢轨的滚动磨损与损伤行为是影响其服役安全的重要因素。通过轮轨滚动接触模拟试验研究了−35 ℃温度下珠光体(亚共析钢和共析钢)和贝氏体钢轨磨损与滚动接触疲劳(RCF)损伤行为。结果表明,贝氏体钢轨在−35 ℃试验温度下硬化程度较低,导致磨损程度高于珠光体钢轨,珠光体钢轨中亚共析钢轨磨损程度低于共析钢轨;三种钢轨存在不同程度的RCF损伤,疲劳裂纹主要以小角度(<10°)扩展。磨损和RCF存在竞争关系,磨损较小的亚共析钢轨RCF损伤严重,共析钢轨次之,磨损最严重的贝氏体钢轨RCF损伤最轻微。Abstract: The rail in the high altitude and high latitude regions faces the low temperature service environment. The rolling wear and damage behaviors under low temperature are the significant factors influencing the rail service safety. The wear and rolling contact fatigue (RCF) damage laws of pearlite rail steels (hypoeutectoid and eutectoid) and bainite rail steel were explored at the low temperature of −35℃ using wheel/rail rolling contact simulation experiments. The results showed that the hardening degree of bainite rail was lower at −35℃, and the wear degree was higher than those of pearlite rails. The wear degree of hypoeutectoid rail steel was lower than that of eutectoid rail steel. Different RCF damage levels occurred on the explored three kinds of rail steels. Cracks mainly propagated with small angles (< 10°). There was a competitive relationship between the wear and RCF. The RCF damage of hypoeutectoid rail steel with less wear was serious, followed by eutectoid rail, and the RCF damage of bainite rail steel with the most severe wear was the mildest.
-
Key words:
- pearlite rail steel /
- bainite rail steel /
- low temperature environment /
- wear /
- RCF
-
表 1 钢轨材料性能
Table 1. Properties of rail steels
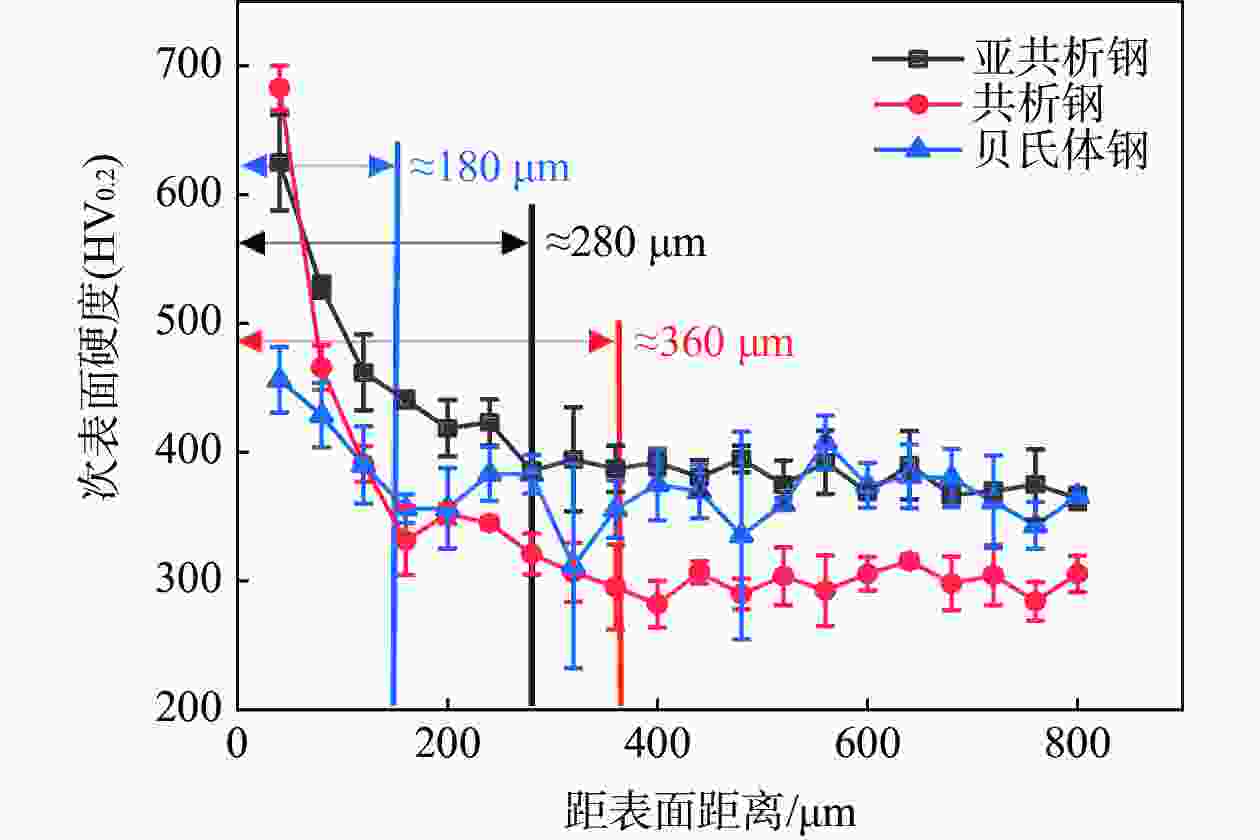
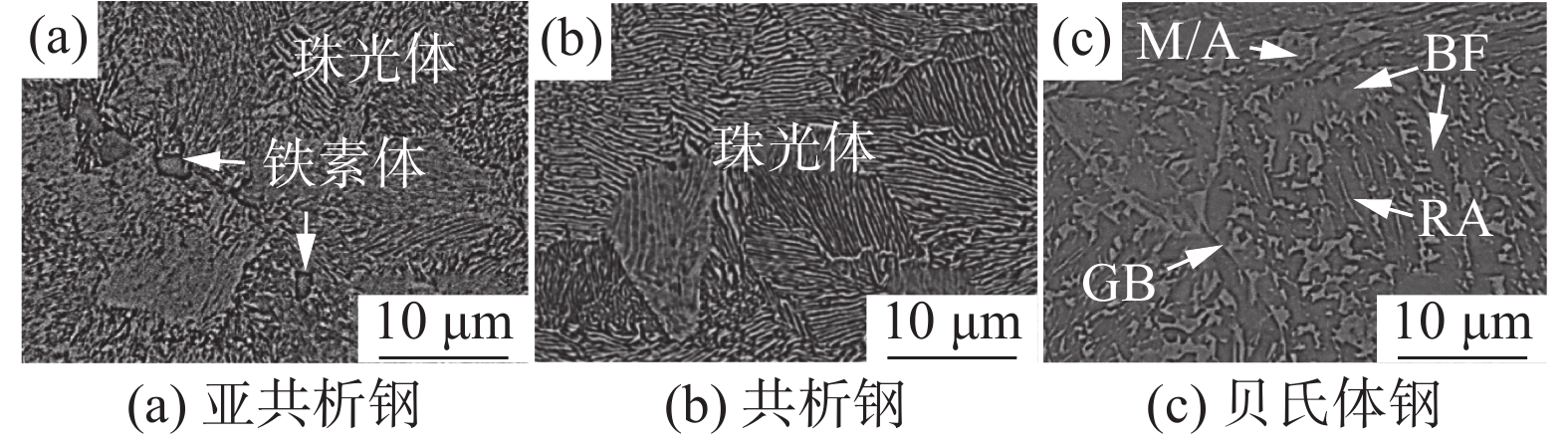
钢轨材料 微观组织 含碳量/% 硬度(HV0.2) 亚共析钢 珠光体+先共析铁素体 0.64~0.7 377±11 共析钢 珠光体钢 0.65~0.77 300±9 贝氏体钢 贝氏体铁素体+残余奥氏体+
马氏体/奥氏体岛0.20~0.50 368±20 表 2 钢轨近表层硬度
Table 2. The hardness at near surface of rail steel
钢轨材料 40 μm深度处硬度(HV0.2) 硬化率 亚共析钢 624 1.66 共析钢 682 2.27 贝氏体钢 456 1.24 -
[1] Stock R, Pippan R. Rail grade dependent damage behaviour - Characteristics and damage formation hypothesis[J]. Wear, 2014, 314: 44-50. [2] Zerbst U, Beretta S, Köhler G, et al. Safe life and damage tolerance aspects of railway axles – A review[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013,98:214−271. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2012.09.029 [3] Wang W J, Guo H M, Du X, et al. Investigation on the damage mechanism and prevention of heavy-haul railway rail[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013,35:206−218. [4] Wang Y P, Ding H H, Zou Q, et al. Research progress on rolling contact fatigue of railway wheel treads[J]. Surface Technology, 2020,49:120−128. [5] Ding H H, Fu Z K, Wang W J, et al. Investigation on the effect of rotational speed on rolling wear and damage behaviors of wheel/rail materials[J]. Wear, 2015,330:563−570. [6] Ding H H, He C G, Ma L, et al. Wear mapping and transitions in wheel and rail materials under different contact pressure and sliding velocity conditions[J]. Wear, 2016,352-353:1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2016.01.017 [7] Wang W J, Jiang W J, Wang H Y, et al. Experimental study on the wear and damage behavior of different wheel/rail materials[J]. Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016,230:3−14. doi: 10.1177/0954409714524566 [8] Zhang S Y, Spiryagin M, Ding H H, et al. Rail rolling contact fatigue formation and evolution with surface defects[J]. International Journal Fatigue, 2022,158:106762. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106762 [9] Zhang S Y, Spiryagin M, Lin Q, et al. Study on wear and rolling contact fatigue behaviours of defective rail under different slip ratio and contact stress conditions[J]. Tribology International, 2022,169:107491. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107491 [10] Feng Baorui, Wang Yuanqing, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis on CTOD and J integral of rail steel under low temperature[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2007,3(3):29−32. (冯宝锐, 王元清, 石永久. 低温下铁路钢轨钢材的断口与弹塑性断裂韧性分析[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2007,3(3):29−32.Feng Baorui, Wang Yuanqing, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis on CTOD and J integral of rail steel under low temperature[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2007, 03: 29-32 [11] Feng Baorui, Wang Yuanqing, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis and discussion on the design method for rail fracture-resisting under low temperature[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2009,26(3):15−19. (冯宝锐, 王元清, 石永久. 低温下铁路钢轨抗脆断设计方法分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2009,26(3):15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2009.03.004Feng Baorui, Wang Yuanqing, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis and discussion on the design method for rail fracture-resisting under low temperature[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2009, 26(03): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2009.03.004 [12] Wang Yuanqing, Feng Baorui, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis of fracture toughness properties of rails steel under low temperature conditions[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2007,4(4):1−5. (王元清, 冯宝锐, 石永久. 低温下铁路钢轨断裂韧性分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2007,4(4):1−5.Wang Yuanqing, Feng Baorui, Shi Yongjiu. Analysis of fracture toughness properties of rails steel under low temperature conditions[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2007, 4(04): 1–5 [13] Valtonen K, Ratia V, Ramakrishnan K R, et al. Impact wear and mechanical behavior of steels at subzero temperatures[J]. Tribology International, 2019,129:476−493. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2018.08.016 [14] Ma Lei, He Chenggang, Zhao Xiangji, et al. Simulation experiment for rolling wear of wheel/rail materials under low temperature environment[J]. Tribology, 2016,36(1):92−97. (马蕾, 何成刚, 赵相吉, 等. 低温环境下轮轨材料滚动磨损模拟试验研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2016,36(1):92−97.Ma Lei, He Chenggang, Zhao Xiangji, et al. Simulation experiment for rolling wear of wheel/rail materials under low temperature environment[J]. Tribology, 2016, 36(1): 92–97 [15] Ma L, Guo J, Liu Q Y, et al. Fatigue crack growth and damage characteristics of high-speed rail at low ambient temperature[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2017,82:802−815. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.07.026 [16] Ma L, Shi L B, Guo J, et al. On the wear and damage characteristics of rail material under low temperature environment condition[J]. Wear, 2018,394-395:149−158. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.10.011 [17] Mo Wenfeng. Thermodynamic control of pearlite lamellar sheet spacing and its effect on mechanical properties of steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(5):175−179. (莫文锋. 珠光体片间距的热力学控制及其对钢力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(5):175−179.Mo Wenfeng. Thermodynamic control of pearlite lamellar sheet spacing and its effect on mechanical properties of steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(05): 175-179. [18] Tang Jianwei. Effect of bainite isothermal time on microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-high strength cold-rolled transformation induced plasticity steel.[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(6):133−136. (唐建伟. 贝氏体等温时间对超高强冷轧相变诱导塑性钢组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(6):133−136. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.06.024Tang Jianwei. Effect of bainite isothermal time on microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-high strength cold-rolled transformation induced plasticity steel. [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(06): 133-136. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.06.024 [19] Steele R, Reiff R. Rail: it’s behaviour and relationship to total system wear [C]//Pro 2nd Conf on Heavy Haul. Colorado Springs, USA, 1982. [20] Shi L B, Ma L, Guo J, et al. Influence of low temperature environment on the adhesion characteristics of wheel-rail contact[J]. Tribology International, 2018,127:59−68. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2018.05.037 [21] Zhou Liang, Guo Lichang, Ding Haohao, et al. Wear and damage evolution behaviours of railway wheel steel in the low temperature environment[J]. Tribology, 2022,42(4):844−853. (周亮, 郭立昌, 丁昊昊, 等. 低温环境下列车车轮材料磨损与损伤演变行为研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2022,42(4):844−853.Zhou Liang, Guo Lichang, Wang Wenjian, et al. Wear and Damage Evolution Behaviours of Railway Wheel Steel in the Low Temperature Environment[J]. Tribology, 2022, 42(04): 844-853. [22] Hu Y, Zhou L, Ding H H, et al. Microstructure evolution of railway pearlitic wheel steels under rolling-sliding contact loading[J]. Tribology International, 2021,154:106685. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106685 [23] Hu Y, Zhou L, Ding H H, et al. Investigation on wear and rolling contact fatigue of wheel-rail materials under various wheel/rail hardness ratio and creepage conditions[J]. Tribology International, 2020,143:106091. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2019.106091 [24] Suh N P. The delamination theory of wear[J]. Wear, 1973,25(1):111−124. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(73)90125-7 -




 下载:
下载: