Effect of micro-content tellurium on cutting performance of 38MnVS non-quenched and tempered steel
-
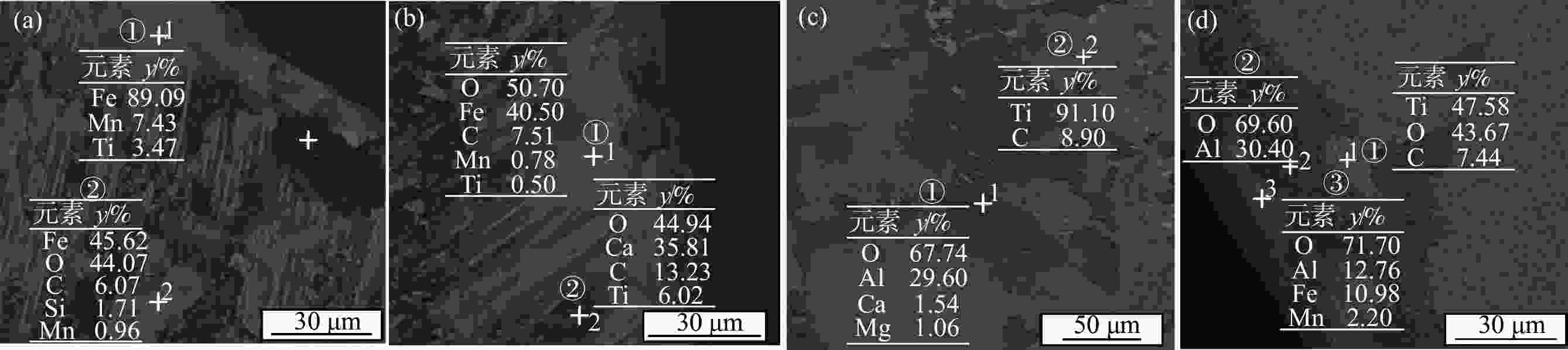
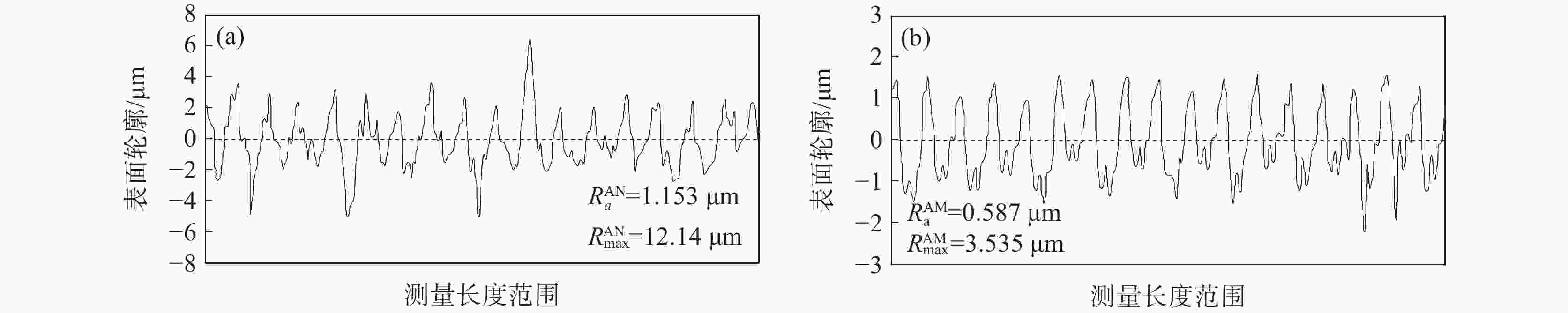
摘要: 为探讨碲改质对非调质钢切削性能的影响机制,对38MnVS非调质钢进行了加碲的硫化物改质试验,并对比加碲对钢中硫化物形态及切削性能的影响。结果表明,加入微量碲(0.0020%)后钢中硫化物形态显著改善,硫化物长宽比降低;由于加碲后硫化物形态的改善,降低了切削过程中的切削力,减小了刀具的磨损,阻止了积屑瘤的产生,同时改善了工件表面粗糙度,从而改善非调质钢的切削性能。Abstract: In order to explore the mechanism of effect of tellurium modification on the machinability of non-quenched and tempered steel (NQTS), a sulfide modification test of 38MnVS NQTS with tellurium was carried out, and effect of tellurium modification on morphology of sulfide and machinability of steel was compared. The results show that with tellurium addition, the morphology of sulfide in steel is significantly improved, and the aspect ratio of sulfide decreases. Due to the improvement of sulfide morphology after tellurium modification, the cutting force during cutting process is reduced, therefore tool wear is reduced and the generation of chip buildup is prevented as well. Consequently, the workpiece surface roughness is improved, thus improving the cutting performance of NQTS.
-
Key words:
- non-quenched and tempered steel /
- machinability /
- tellurium /
- sulfide
-
表 1 38MnVS钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 38MnVS6 steel
% 试样 C Si Mn P S Cr V Ni Ti Te AN 0.39 0.56 1.40 0.010 0.054 0.17 0.13 0.03 0.012 — AM 0.39 0.57 1.42 0.010 0.054 0.17 0.13 0.03 0.013 0.0023 表 2 非调质钢中硫化物评级情况
Table 2. Ratings for sulfide inclusion in NQTS
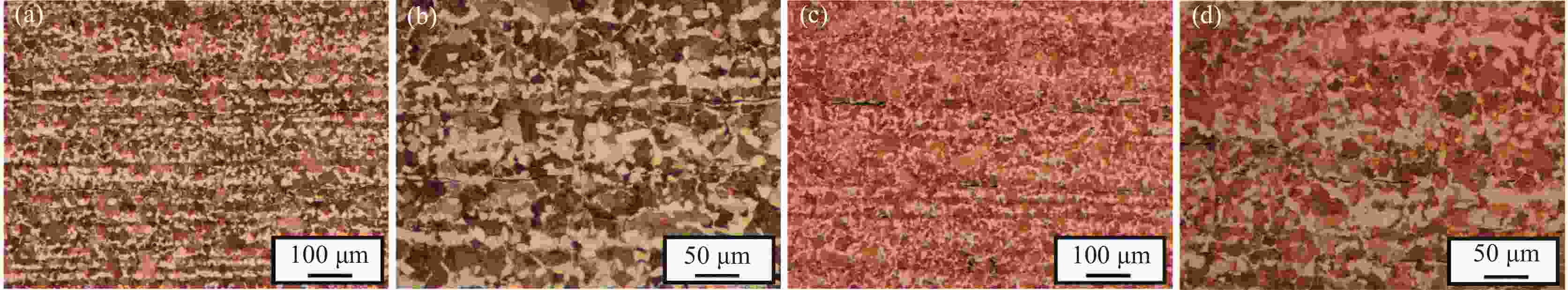
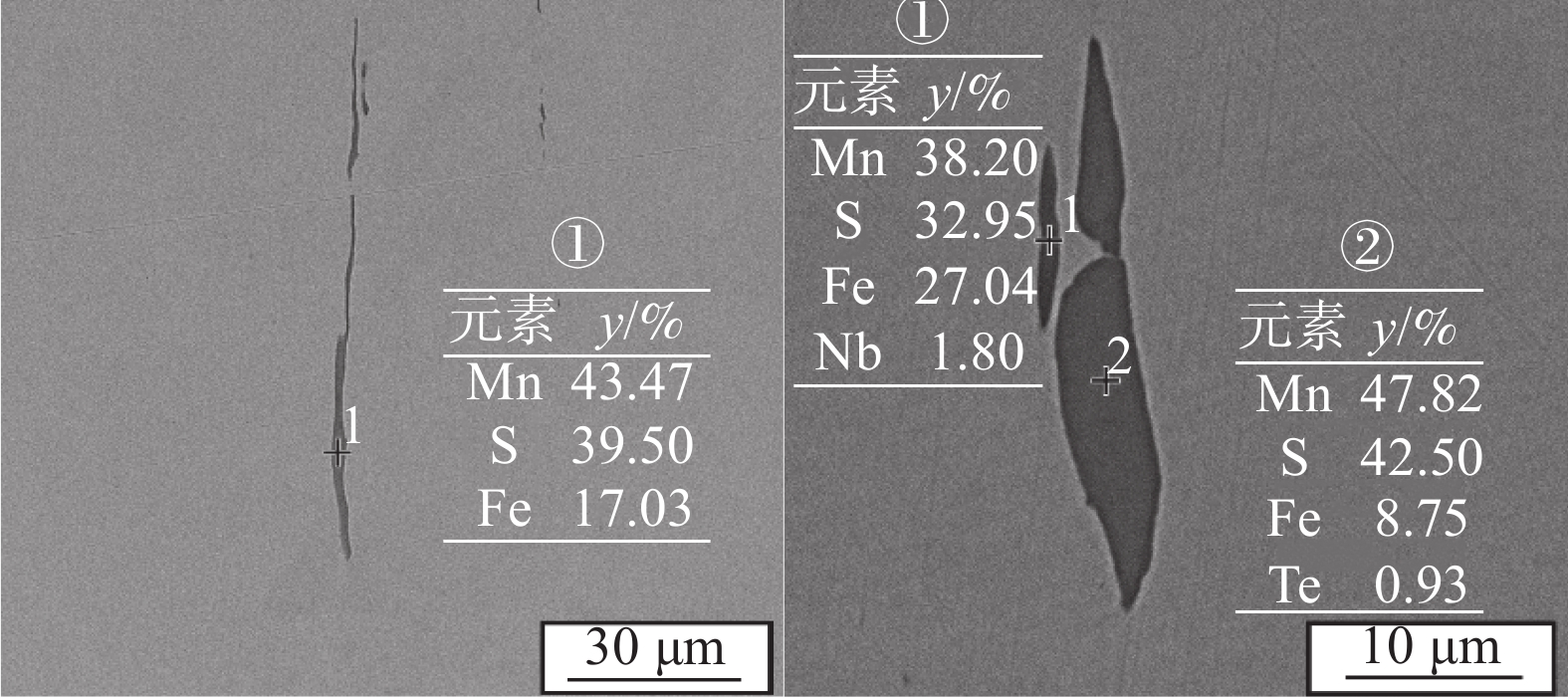
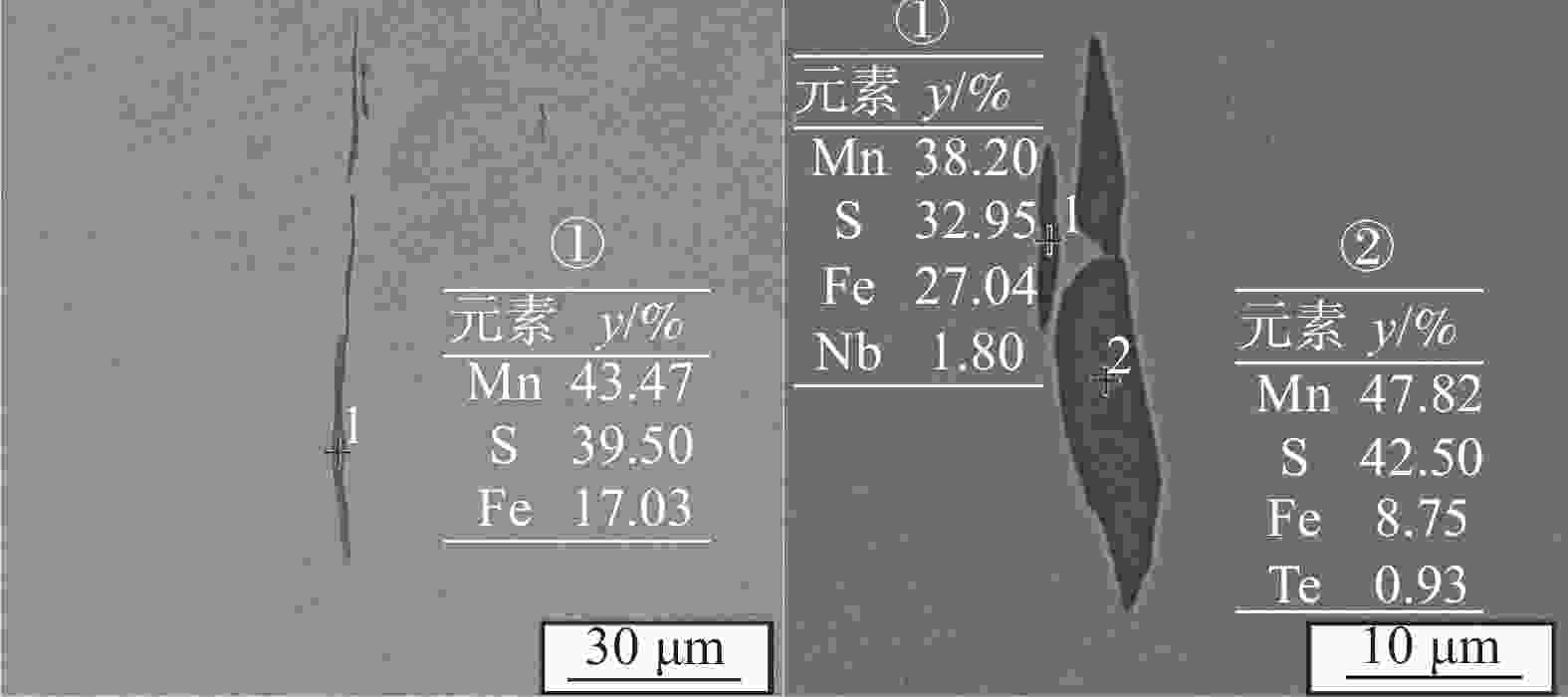
试样 硫化物级别 平均面积/μm2 等效直径/μm 平均长宽比 细系 粗系 AN 3.0 2.0 14.03 4.01 4.92 AM 2.5 1.5 12.89 3.61 2.91 表 3 两种材料铁素体含量及显微硬度测量结果
Table 3. Measurement results of ferrite fraction and microhardness of the two steels
试样 铁素体含量/% 硬度(HV) AN 26 268.4 AM 28 270.2 表 4 不同材料切削力的平均值
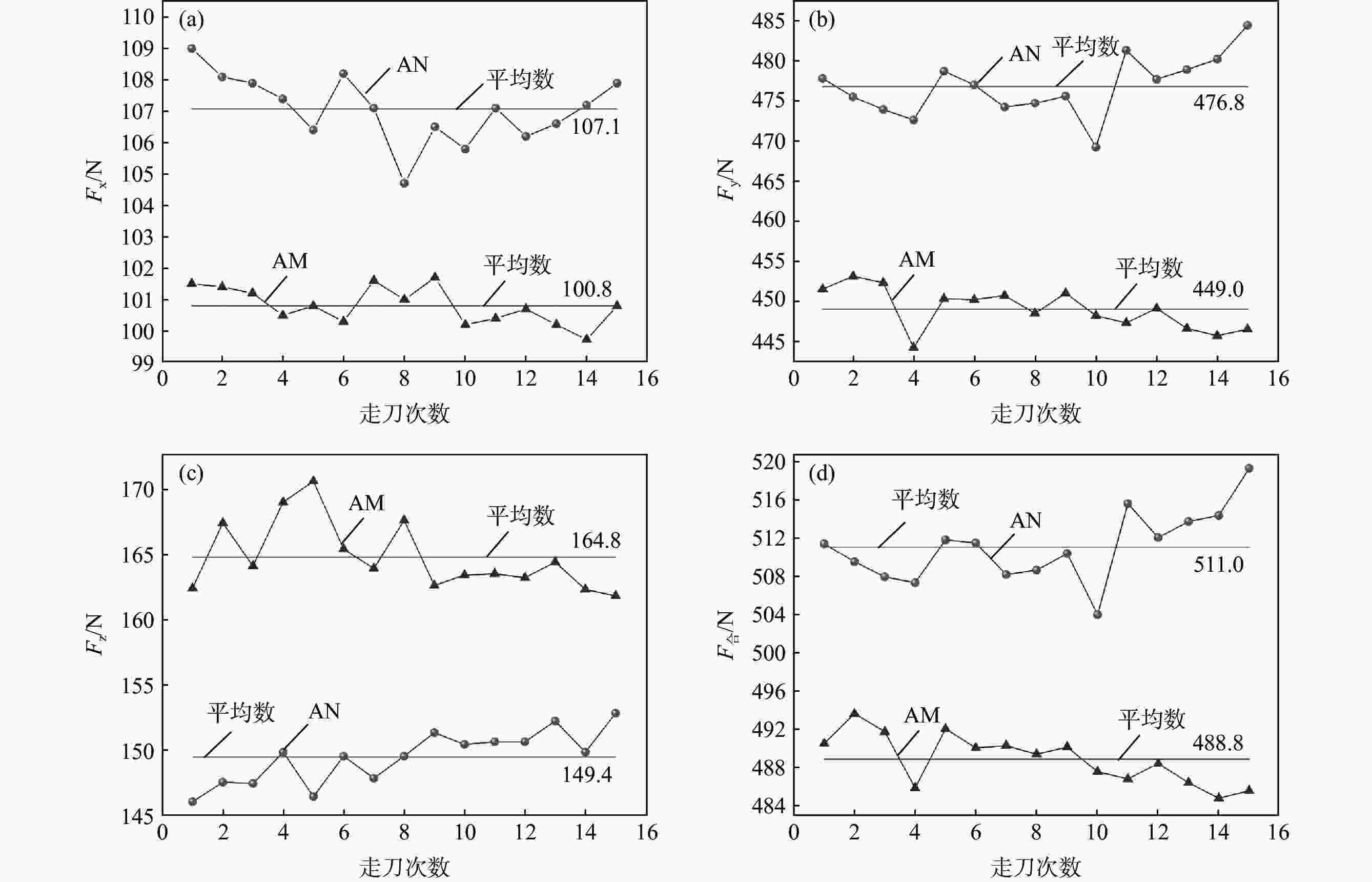
Table 4. Average value of cutting force for AN and AM steels
N 材料 Fx/N Fy/N Fz/N F合/N AN 107.1 476.8 149.4 511.0 AM 100.8 449.0 164.8 488.8 表 5 两种材料的车削刀片磨损情况
Table 5. Wear of turning inserts for AN and AM steels
材料 刀片磨损长度/mm 改善比值/% AN 3.75 - AM 1.73 53.87 -
[1] Koplev A, Lystrup A, Vorm T. The cutting process, chips, and cutting forces in machining CFRP[J]. Composites, 1983,14(4):371−376. doi: 10.1016/0010-4361(83)90157-X [2] Zheng Guangming, Cheng Xiang, Li Li, et al. Experimental investigation of cutting force, surface roughness and tool wear in high-speed dry milling of AISI 4340 steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2019,33(1):341−349. doi: 10.1007/s12206-018-1236-z [3] 李毅. 合金钢切削加工性能的实验研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳理工大学, 2020.Li Yi. Experimental study on the cutting performance of alloy steel [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Ligong University, 2020. [4] Sonawane G D, Sargade V G. Machinability study of duplex stainless steel 2205 during dry turning[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2020,21(5):969−981. doi: 10.1007/s12541-019-00305-8 [5] Anmark N, Karasev A, Jonsson P G. The effect of different non-metallic inclusions on the machinability of steels[J]. Materials (Basel), 2015,8(2):751−783. doi: 10.3390/ma8020751 [6] Shen Jingxia, Zheng Yan, Zhang Haixia, et al. Influence of sulfide on cutting properties in sulfur-containing gear steel 20CrMnTiH[J]. Special Steel, 2012,33(3):47−49. (申景霞, 郑艳, 张海霞, 等. 含硫齿轮钢20CrMnTiH中硫化物对切削性能的影响[J]. 特殊钢, 2012,33(3):47−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2012.03.014Shen Jingxia, Zheng Yan, Zhang Haixia, et al. Influence of sulfide on cutting properties in sulfur-containing gear steel 20 CrMnTiH[J]. Special Steel, 2012, 33(3): 47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2012.03.014 [7] Yaguchi H. Effect of MnS inclusion size on machinabilty of low-carbon, leaded, resulfurized free-machining steel[J]. Journal of Applied Metalworking, 1986,4(3):214−225. doi: 10.1007/BF02833929 [8] Qiu Bingli, Sui Hui, Che Dehui, et al. Effect of oxygen content and forging ratio on sulfide morphology and cutting performance in free-cutting stainless steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021,33(5):418−425. (仇兵利, 随晖, 车德会, 等. 易切削不锈钢中氧含量和锻造比对硫化物形态及切削性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2021,33(5):418−425. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20200097Qiu Binli, Sui Hui, Che Dehui, et al. Effect of oxygen content and forging ratio on sulfide morphology and cutting performance in free-cutting stainless steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021, 33(5): 418-425. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20200097 [9] Dogra M, Sharma V S, Sachdeva A, et al. Tool wear, chip formation and workpiece surface issues in CBN hard turning: a review[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2010,11(2):341−358. doi: 10.1007/s12541-010-0040-1 [10] 宁贵春. 机床切削颤振的检测研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2019.Ning Guichun. Research on the detection of cutting chatter in machine tools[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2019. [11] 张宗阳. 基于最小表面磨损率的刀具磨损及加工表面层特性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2012.Zhang Zongyang. Research on the characteristics of tool wear and machined surface layer based on minimum surface wear rate [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2012. [12] Kuntoğlu M, Sağlam H. Investigation of progressive tool wear for determining of optimized machining parameters in turning[J]. Measurement, 2019,140:427−436. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.04.022 [13] Lalwani D I, Mehta N K, Jain P K. Experimental investigations of cutting parameters influence on cutting forces and surface roughness in finish hard turning of MDN250 steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008,206(1-3):167−179. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.018 [14] Xu T D. A kinetic model of non-equilibrium segregation[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1987,22(2):337−339. [15] Jiang L Z, Cui K. Fractal geometry study of correlation between impact toughness of steel and parameters of free cutting phase[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 1992,(4):250−255. [16] Atwal K S, Reeder A, Pike T J. The product characteristics and machinability of bloom cast free-cutting steels[J]. Revue De Metallurgie-Cahiers D Informations Techniques, 1989,86(6):531−542. [17] Zaslavskii A Y, Gol'dshtein Y E, Shenk R I. Metallography of steel with selenium, tellurium, and lead[J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1967,9(9):694−696. doi: 10.1007/BF00649055 -




 下载:
下载: